IGCSE Biology
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
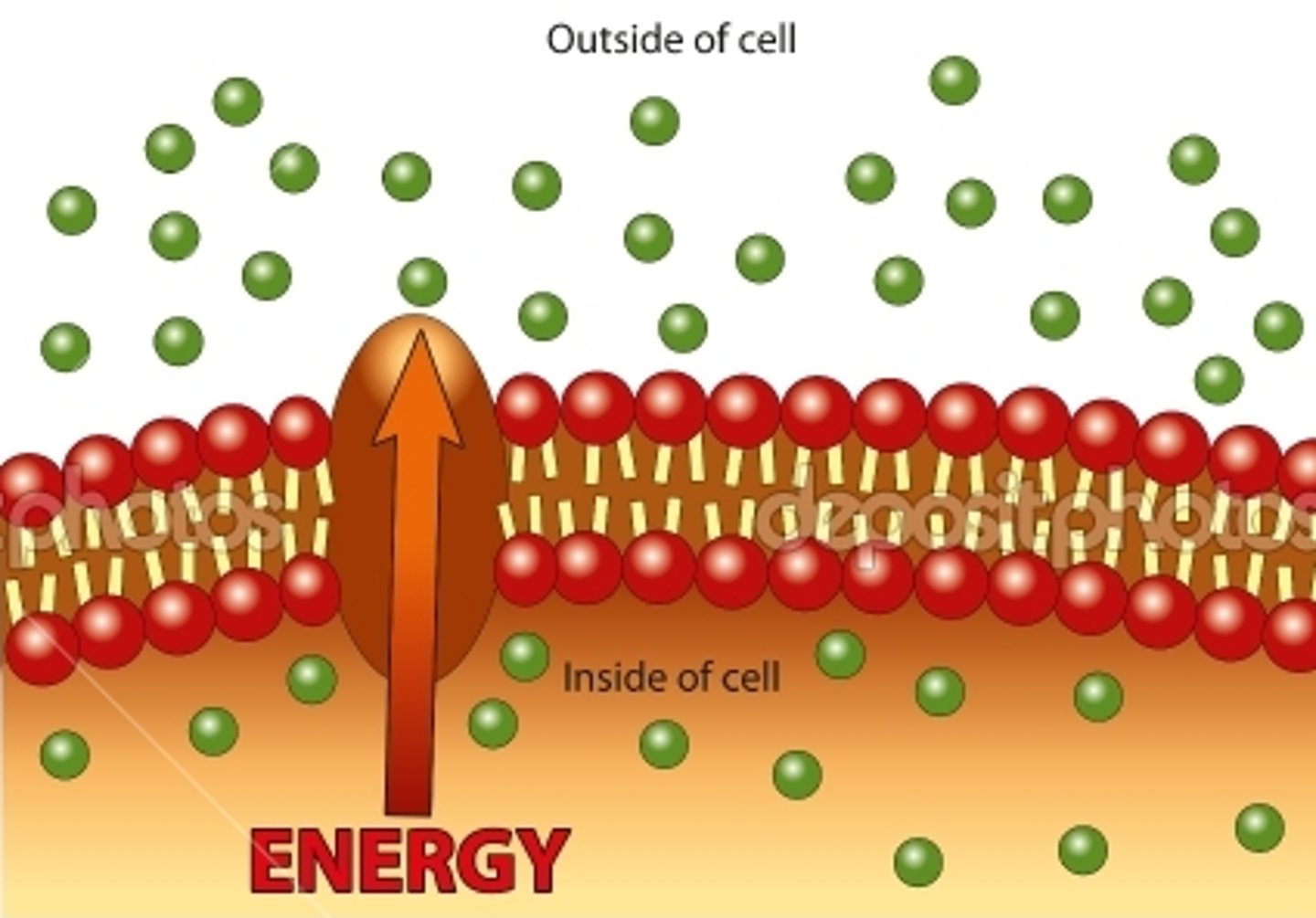
Active transport
The process in which energy is used to move the particles of a substance against a concentration gradient, that is, from a region where they are of lower concentration to a region where they are of higher concentration.
Adaptation
Any characteristic of an organism that improves its chances of surviving in its environment.
Aerobic respiration
Respiration with oxygen. It's the oxidation of food substances in the presence of oxygen with the release of a large amount of energy. Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products.

AIDS
An abbreviation for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene which occupy the same relative positions on a pair of homologous chromosomes.
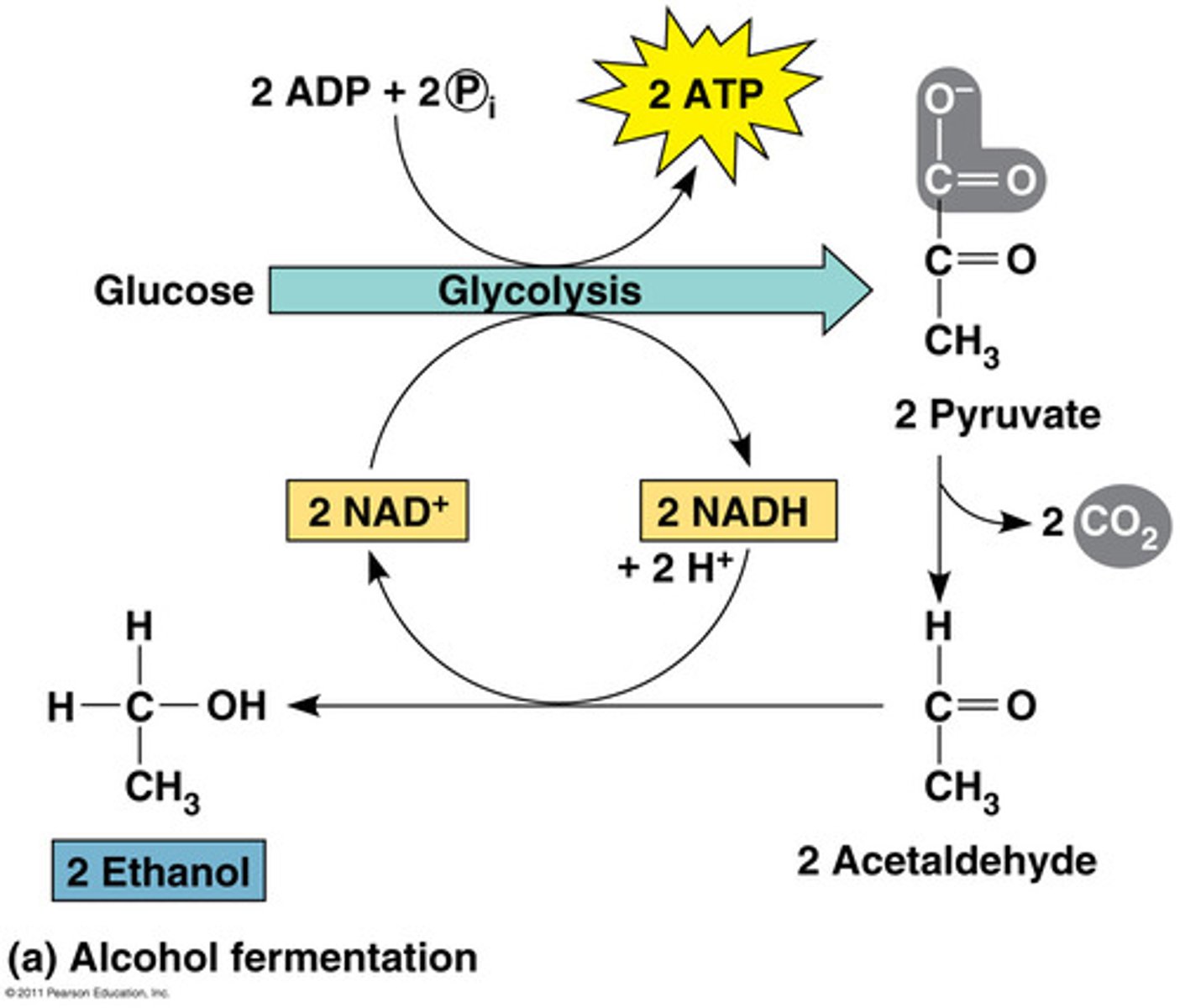
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration without oxygen. It's the oxidation of food substances in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration.
Anaesthetics
Drugs that make the body unable to feel pain
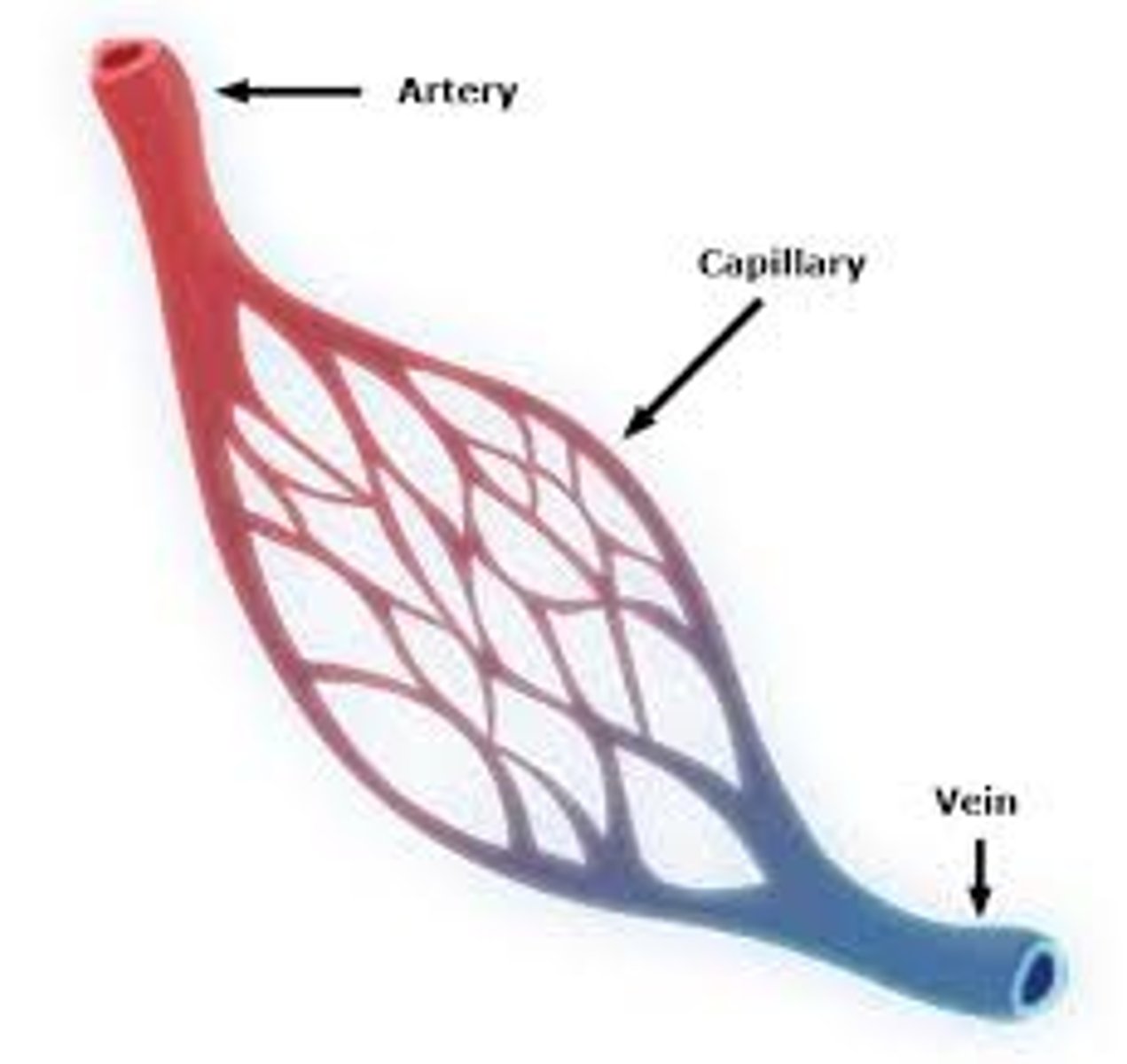
Arteries
Blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart.
Artificial selection
A method used by human beings to produce plants and animals with desired qualities.
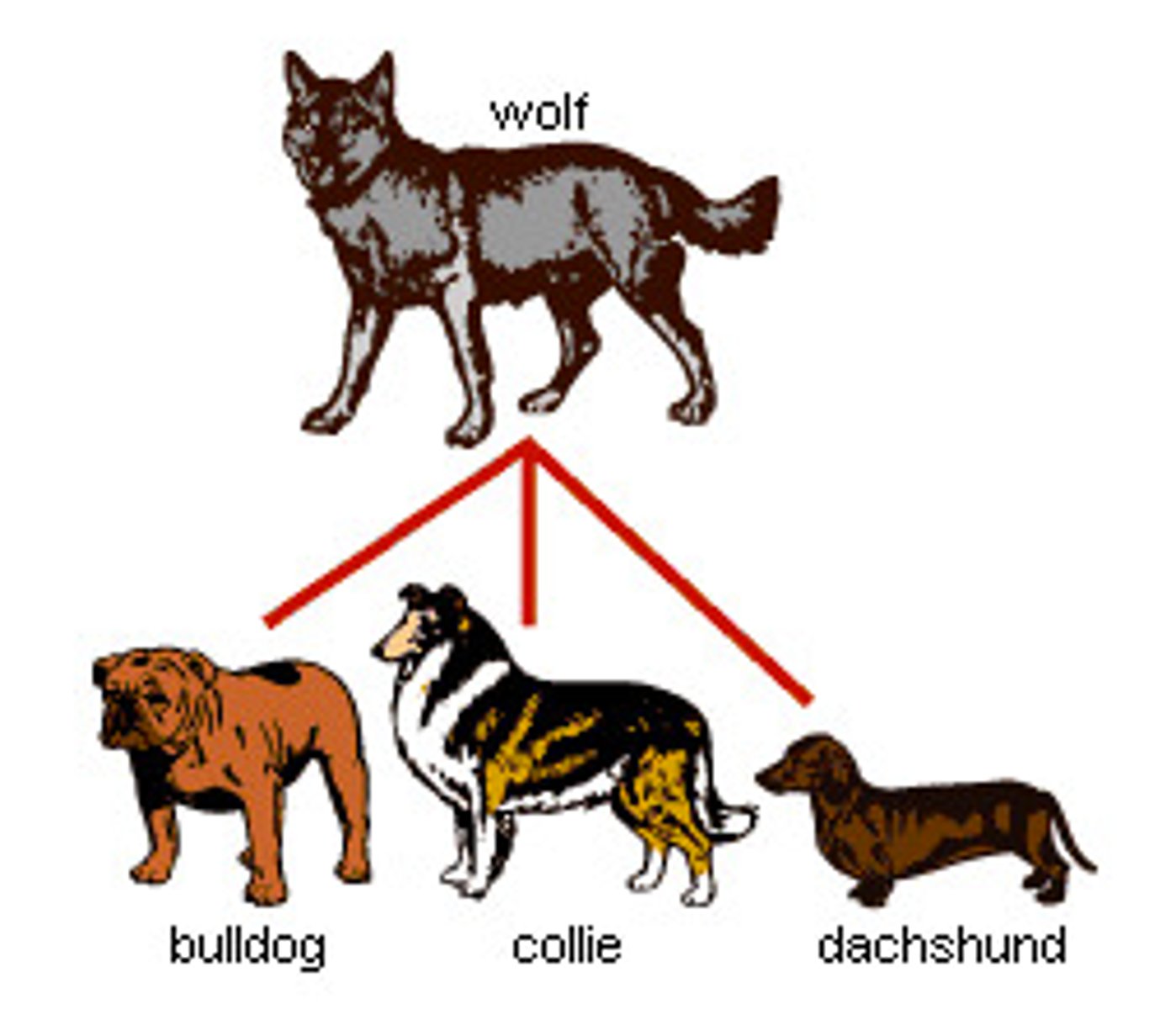
Asexual reproduction
The process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent, without the fusion of gametes.
Assimilation
The process whereby some of the absorbed food materials are converted into new protoplasm or used to provide energy.
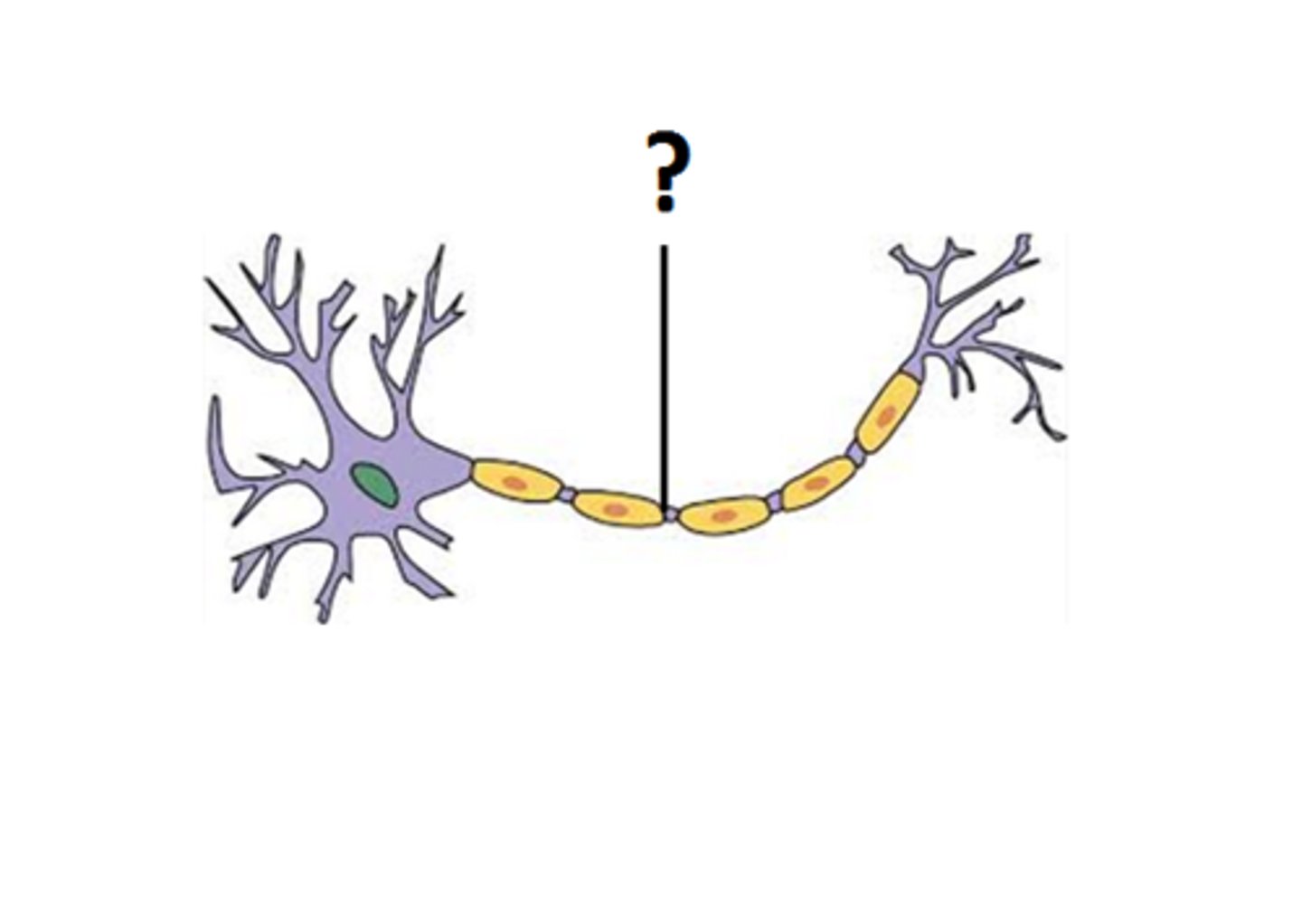
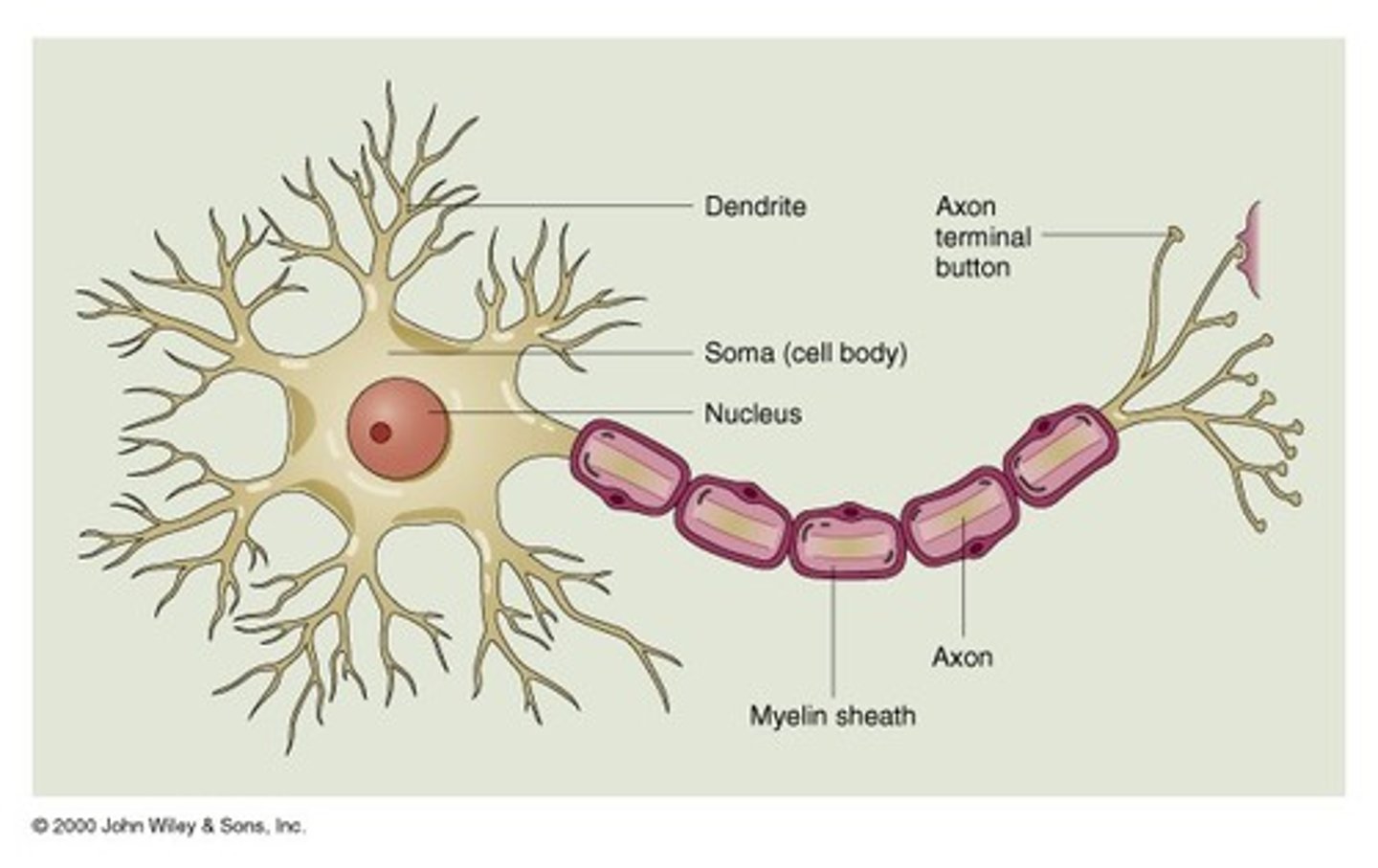
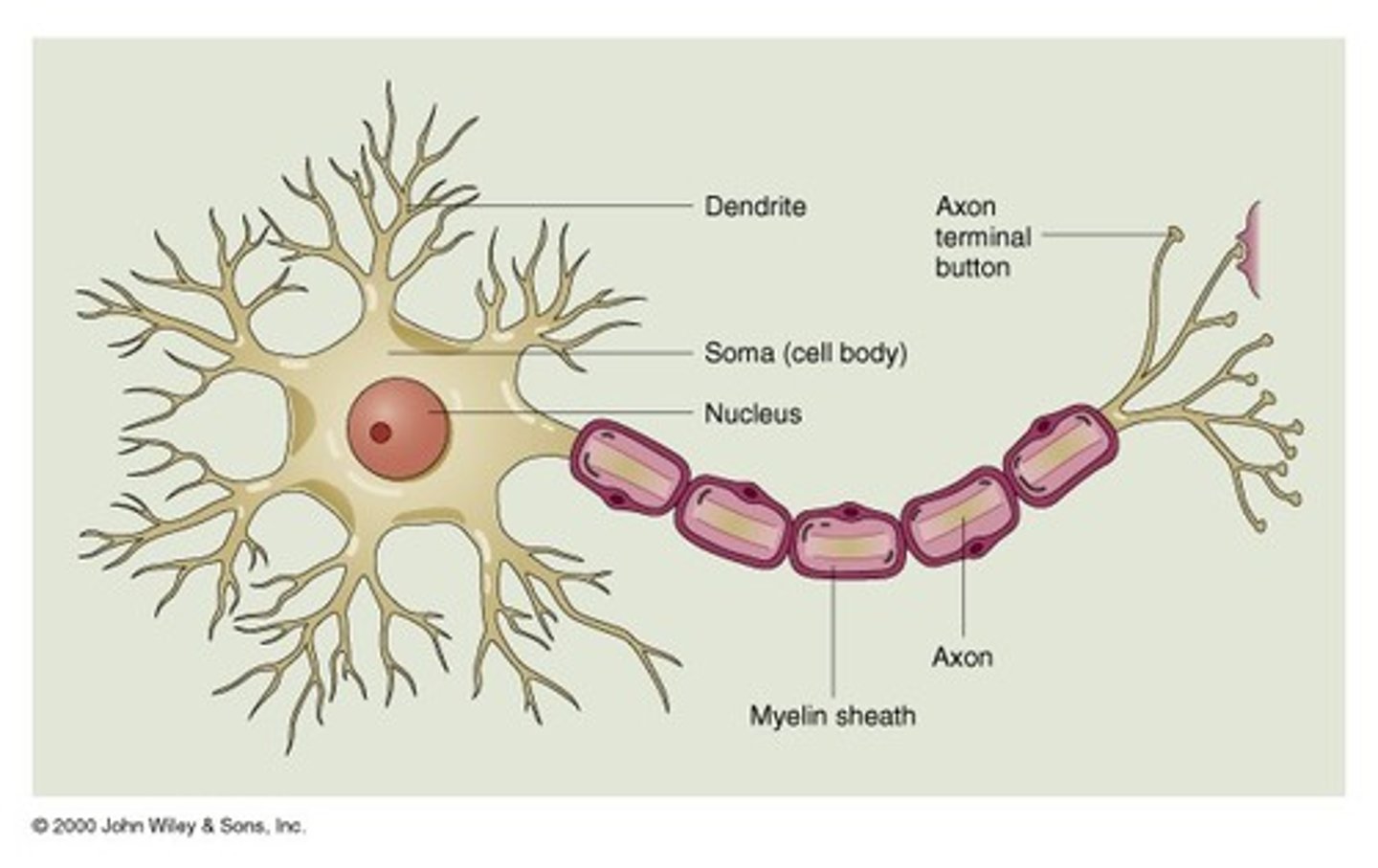
Axon
A nerve fibre that transmits impulses away from the cell body of a neurone.
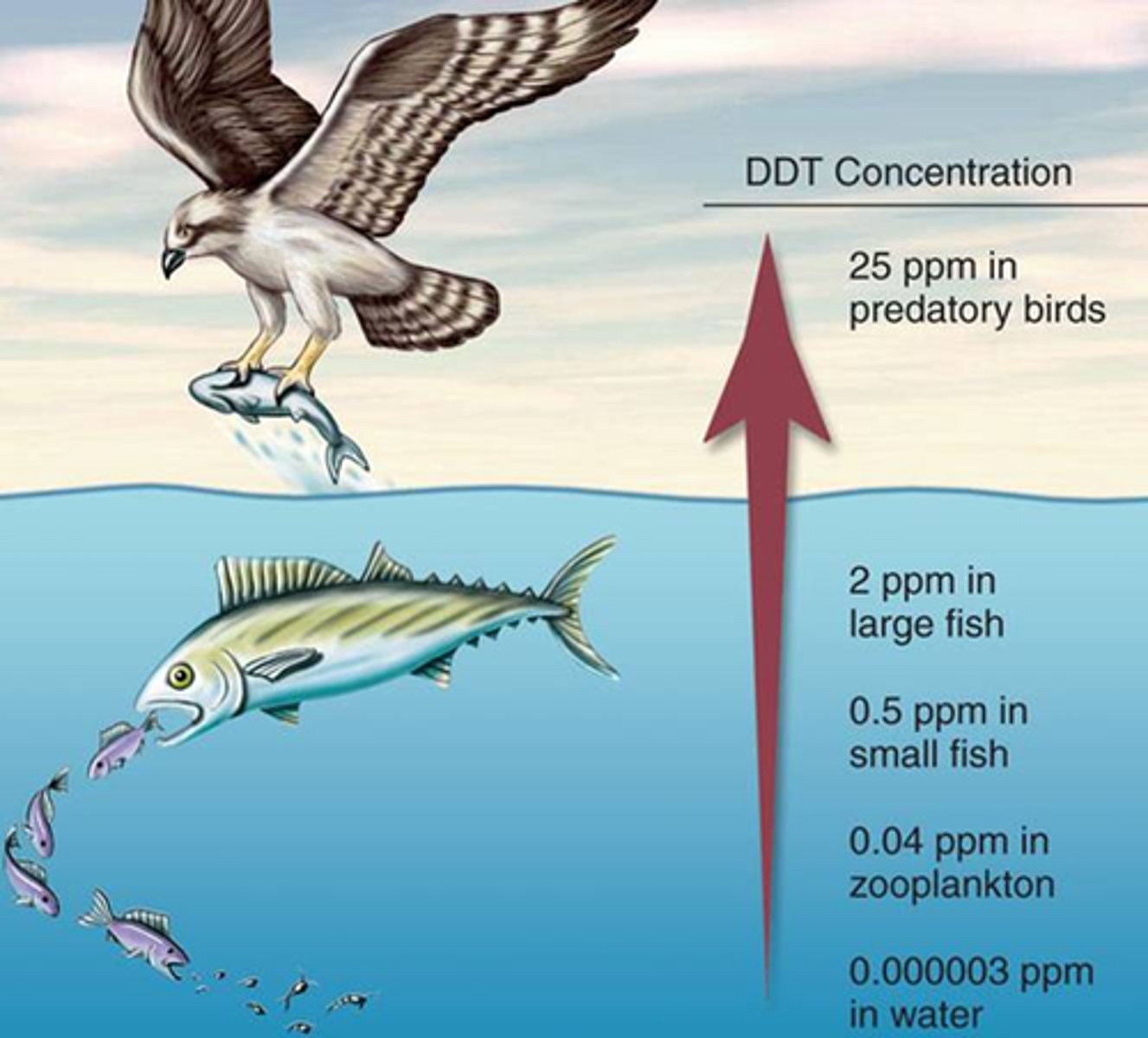
Bioaccumulation
The process by which substances collect in all parts or part of a living organism.
Breathing
The process that brings about an exchange of gases between an organism and its environment.

Capillaries
Microscopic thin-walled (one cell thick) blood vessels which carry blood from a small artery (arteriole) to a small vein (venule).
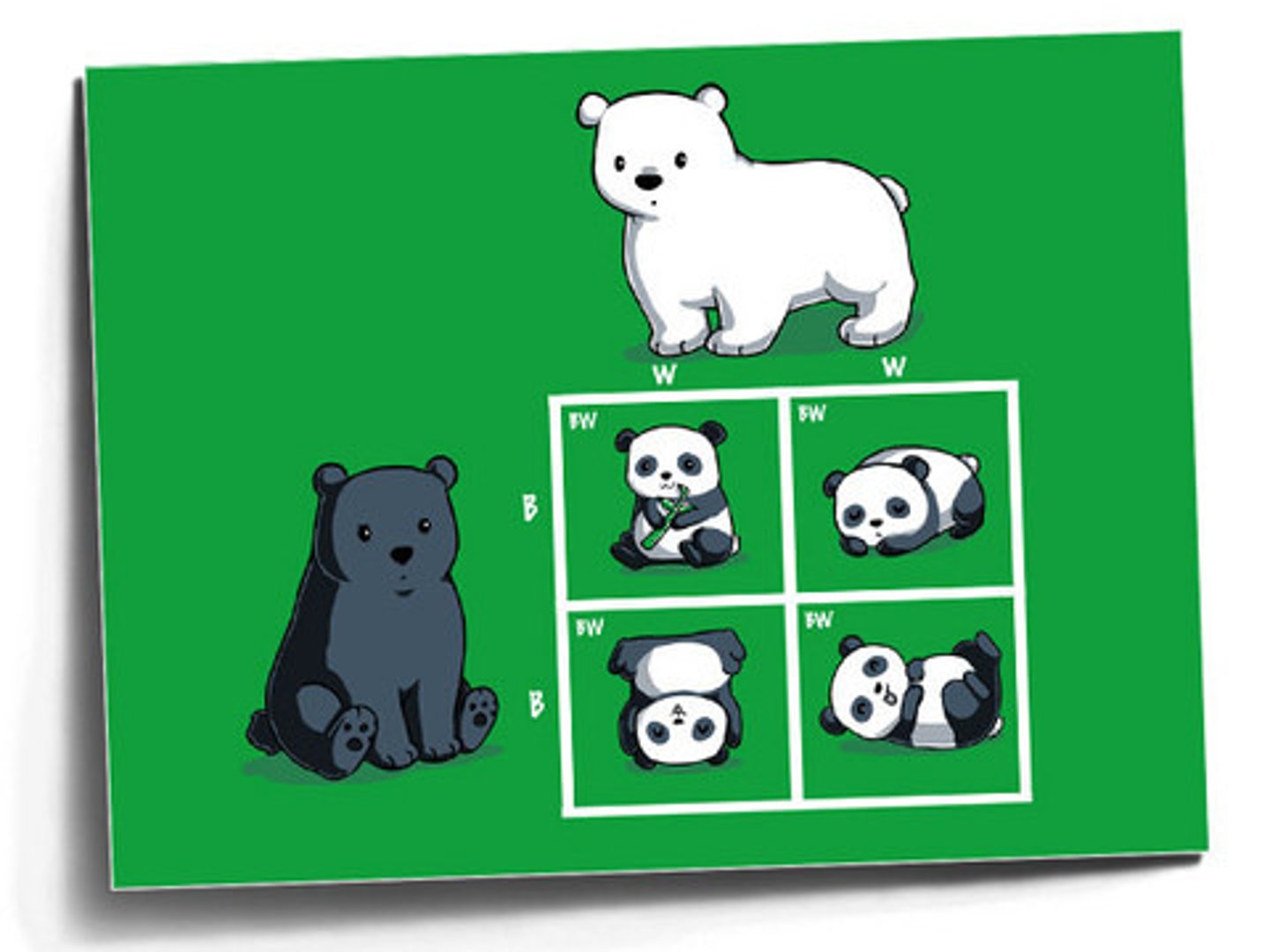
Codominance
A condition where both alleles express themselves in a hybrid, as they are both either dominant or recessive to one another. (Roughly equal expression.)
Community
Populations of organisms living together and interacting with one another under the same environmental conditions.

Conservation
The protection and preservation of natural resources of the environment.

Consumers
Organisms which obtain their energy by feeding on other organisms.

Continuous variation
Traits with phenotypes ranging from one extreme to the other. It is brought about by combined (or additive) effects of many genes. It is affected by environmental conditions, e.g. intelligence, height and skin colour in human beings.

Cross-pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from one plant to the stigma of a flower in another plant of the same species.

Decomposers
Saprotrophs and detritivores. Organisms which obtain energy by breaking down dead organisms, faeces and excretory products.

Dendron
A nerve fibre that transmits impulses towards the cell body of a neurone.
Desertification
The destruction of land leading to desert-like conditions.

Detoxification
The process of converting harmful substances into harmless ones in the body.

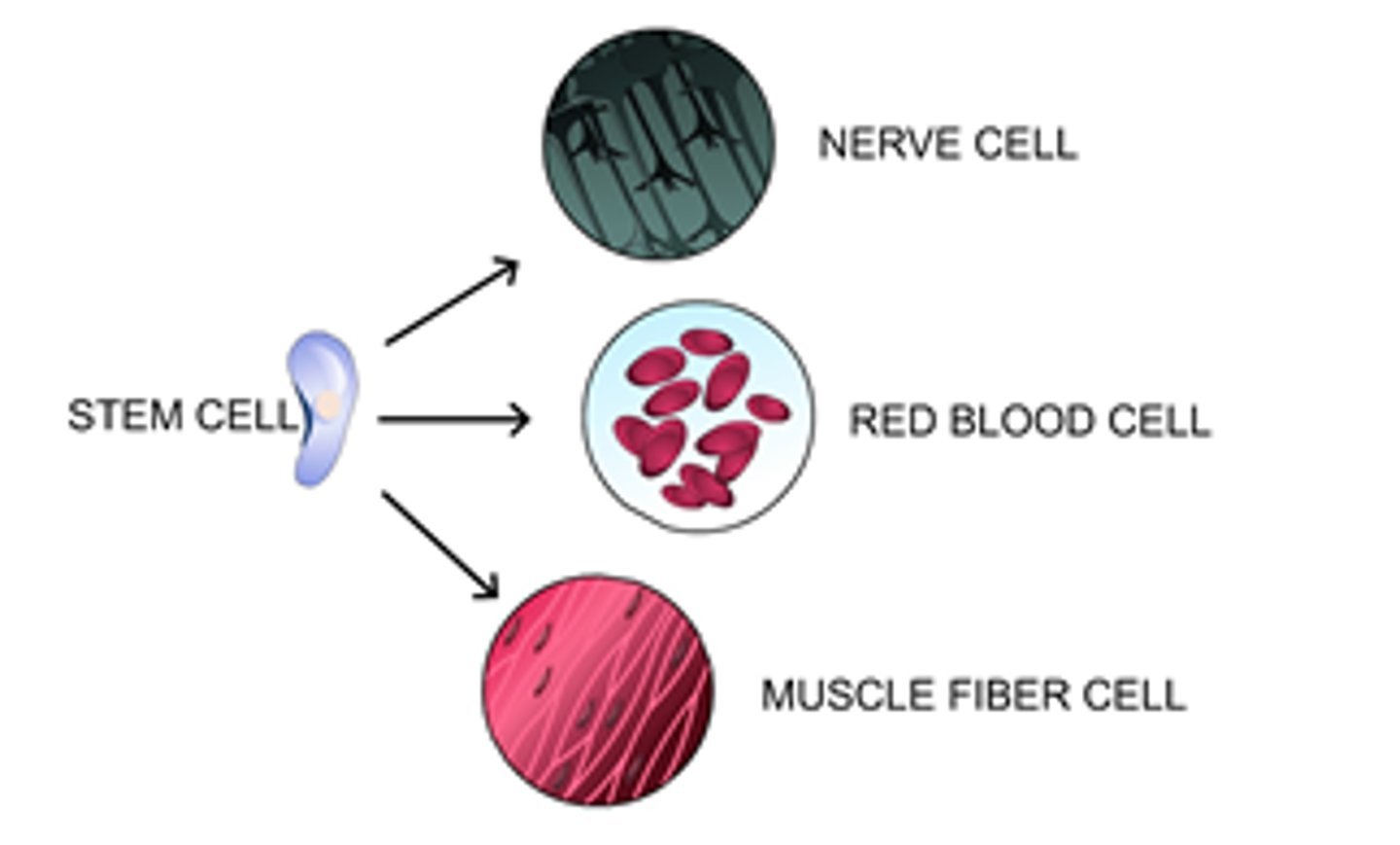
Differentiation
The process by which a cell becomes specialized for a specific function.
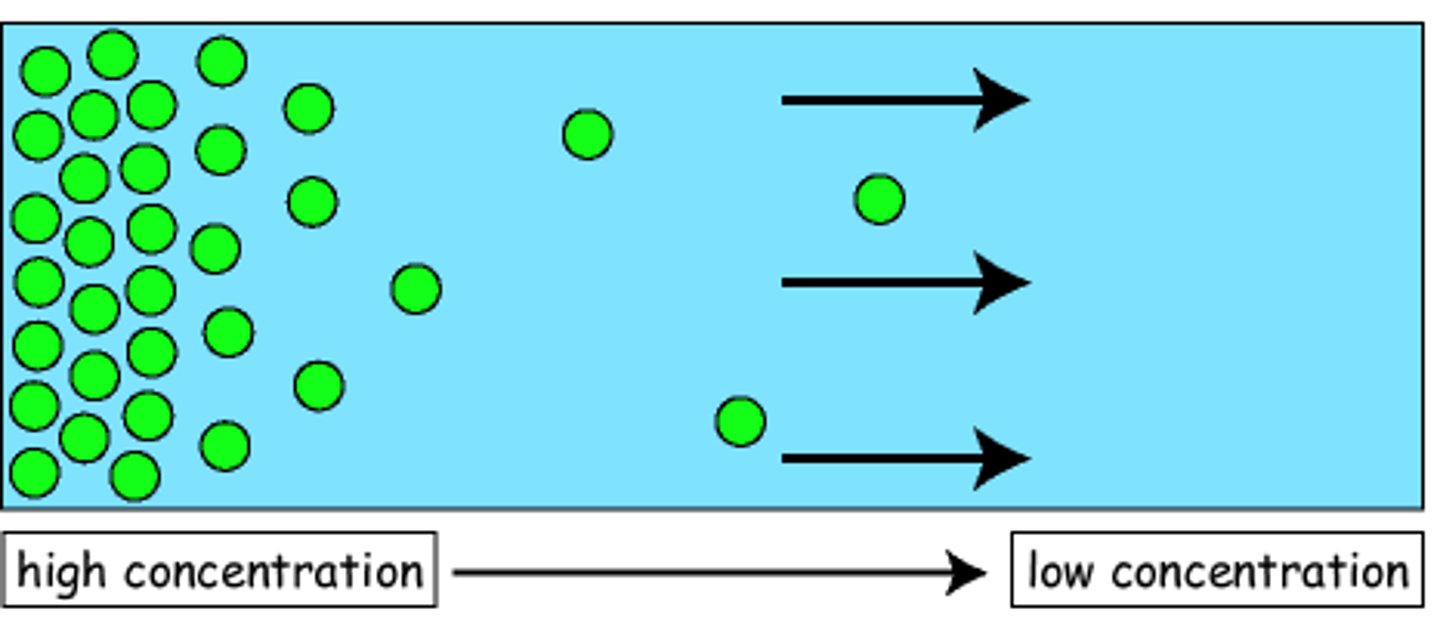
Diffusion
The net movement of particles (atoms, ions or molecules) from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, that is, down a concentration gradient.
Digestion
The process by which large food molecules are broken down into small, soluble and diffusible molecules that can be absorbed by the body cells.
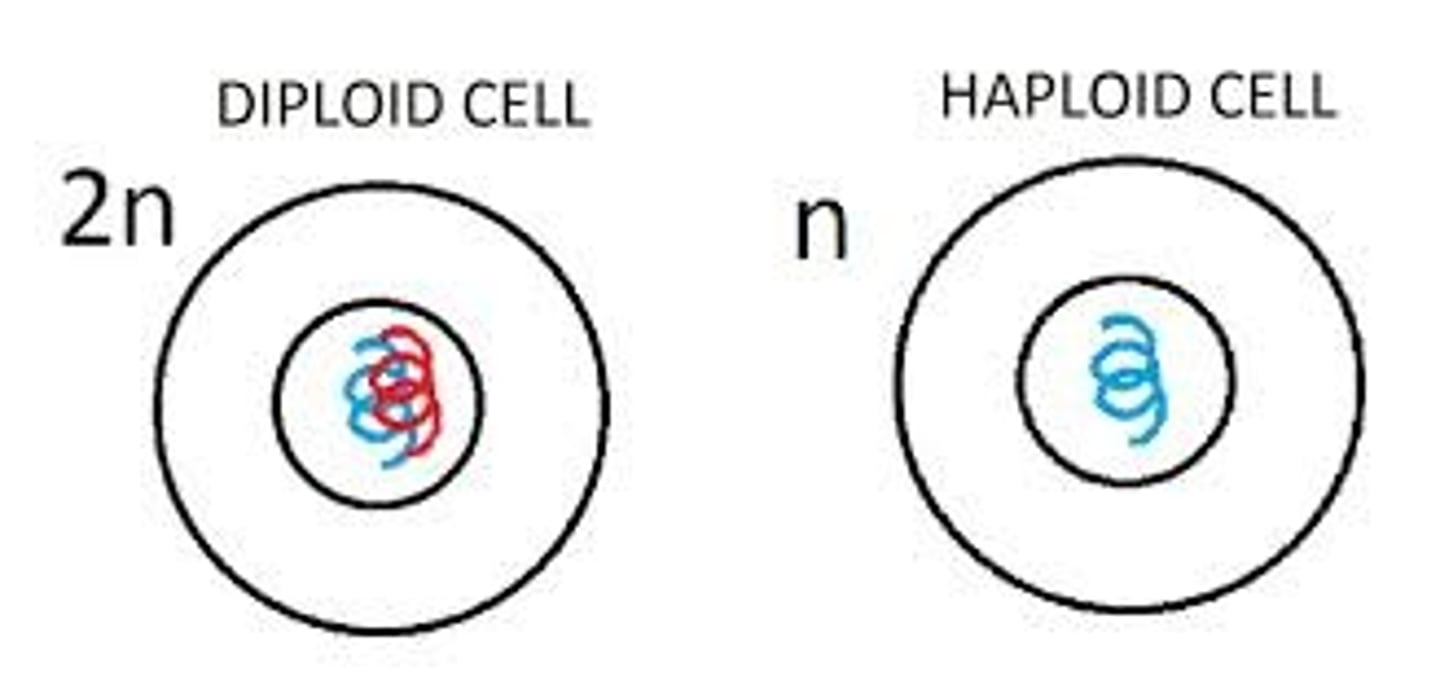
Diploid
Cells that contain the full number of chromosomes.
Discontinuous variation
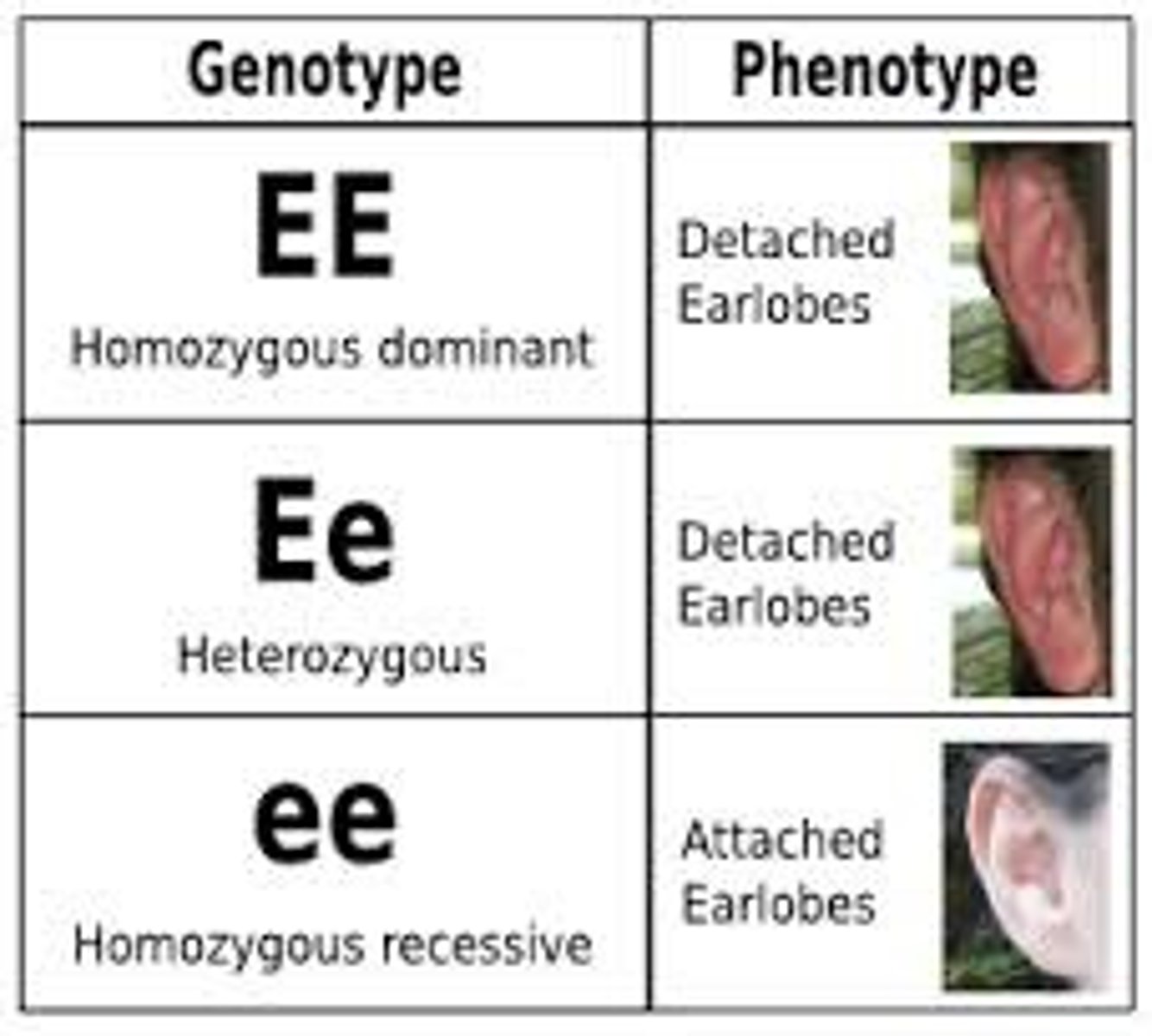
Traits that show limited variation in their phenotypes which are easily distinguishable. It is usually controlled by only one or a few genes. It is not affected by the environment. E.g. detached earlobes-it's either yes or no.
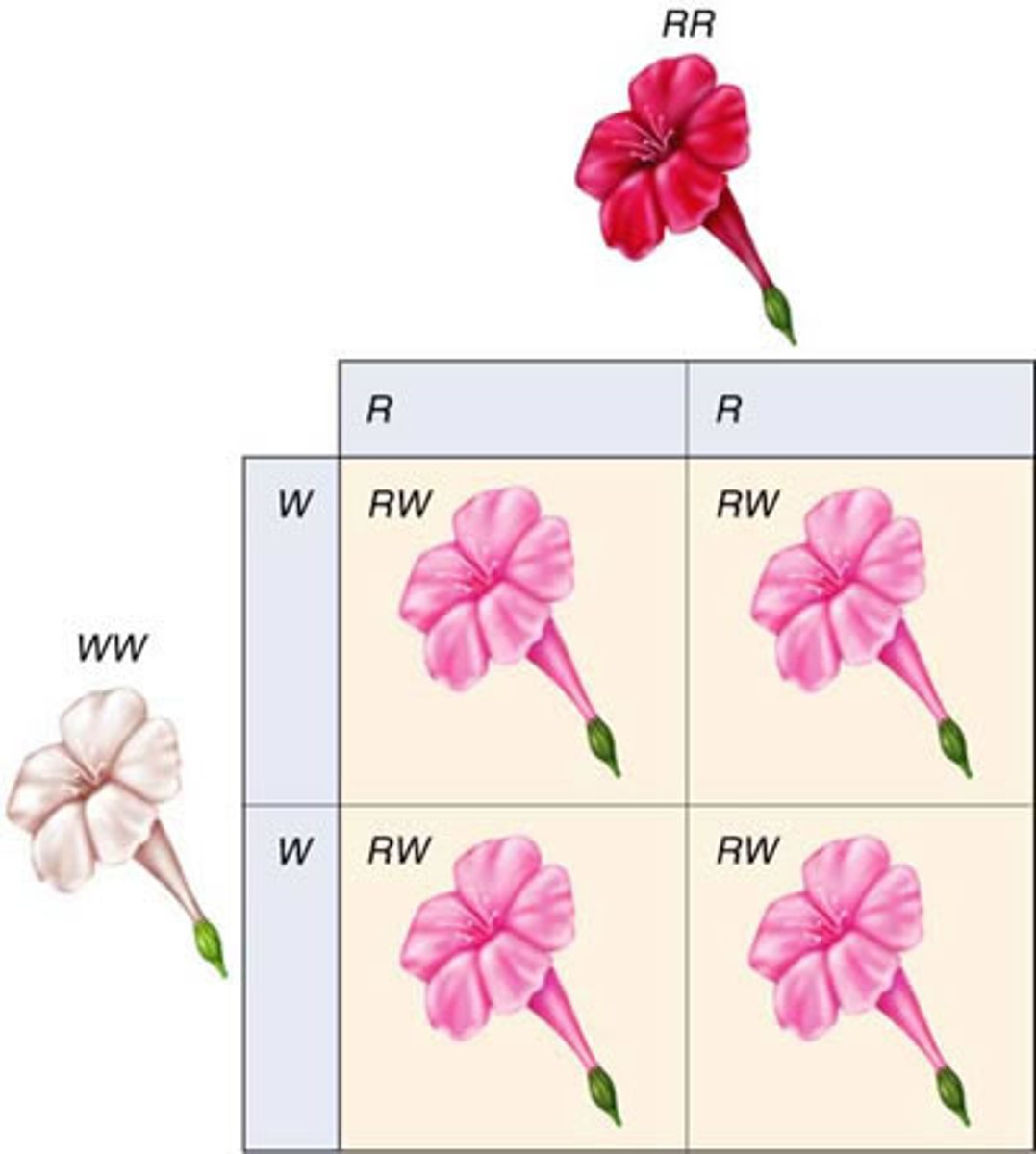
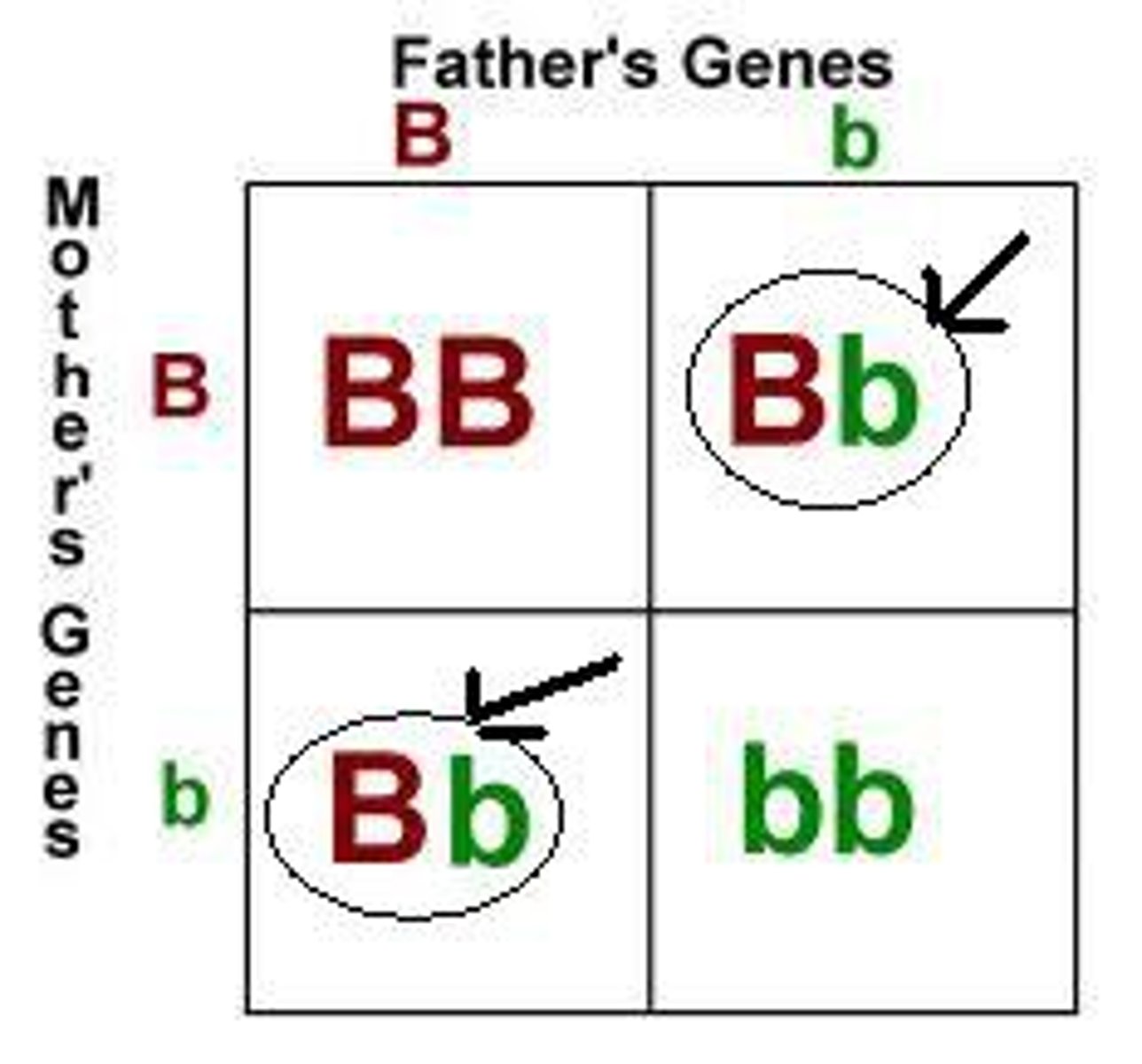
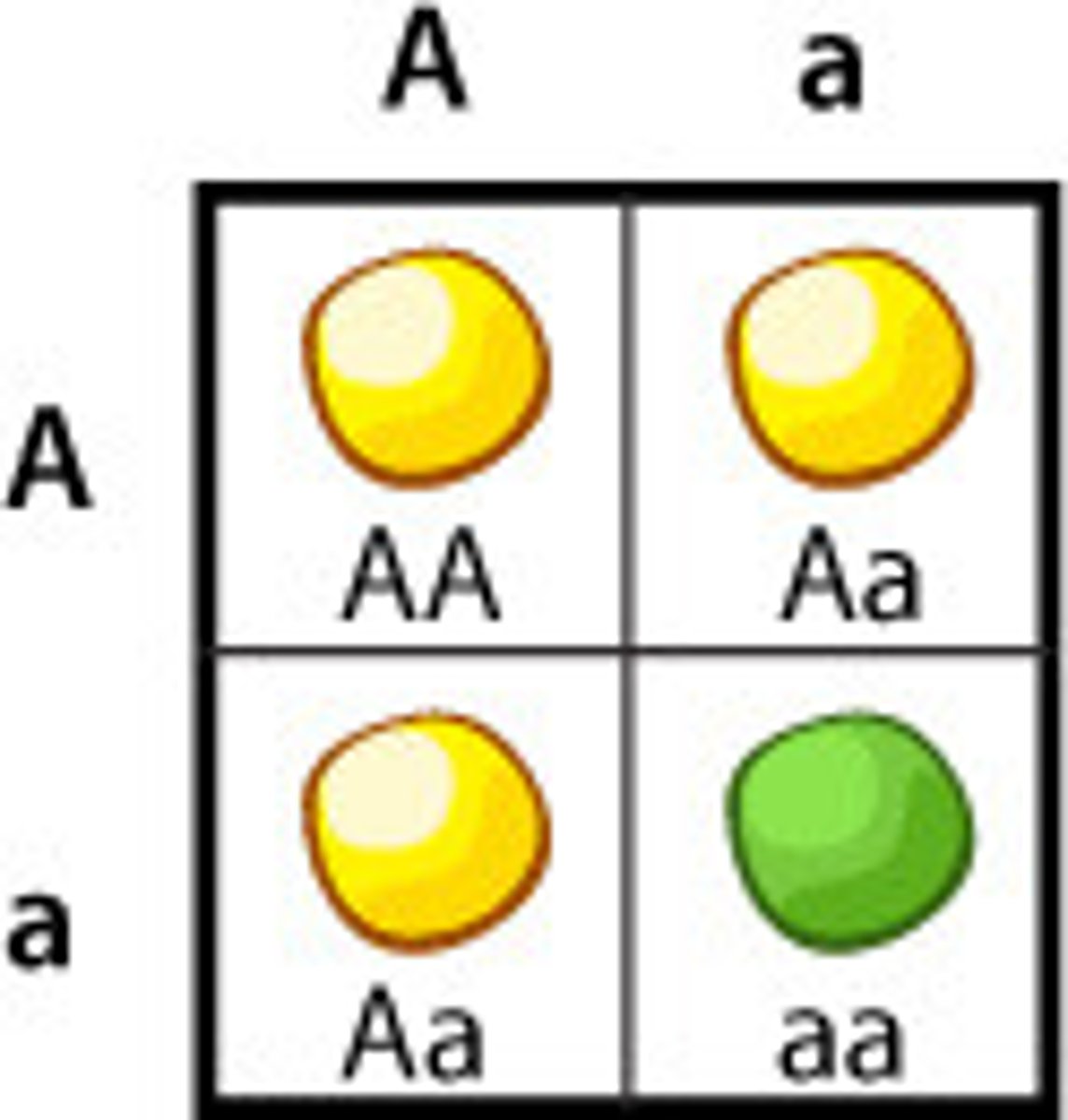
Dominant
A form of a gene that is expressed and masks the recessive gene. It gives the same phenotype in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions as it expresses itself.
Ecology
The study of the relationships between living organisms and the natural environment.

Ecosystem
An ecological system formed by the interaction of living organisms (biotic) and their non-living (abiotic) environments.

Egestion
The removal of undigested matter from the body. Egestion would be like pooing-you're egesting faeces which are basically undigested food.

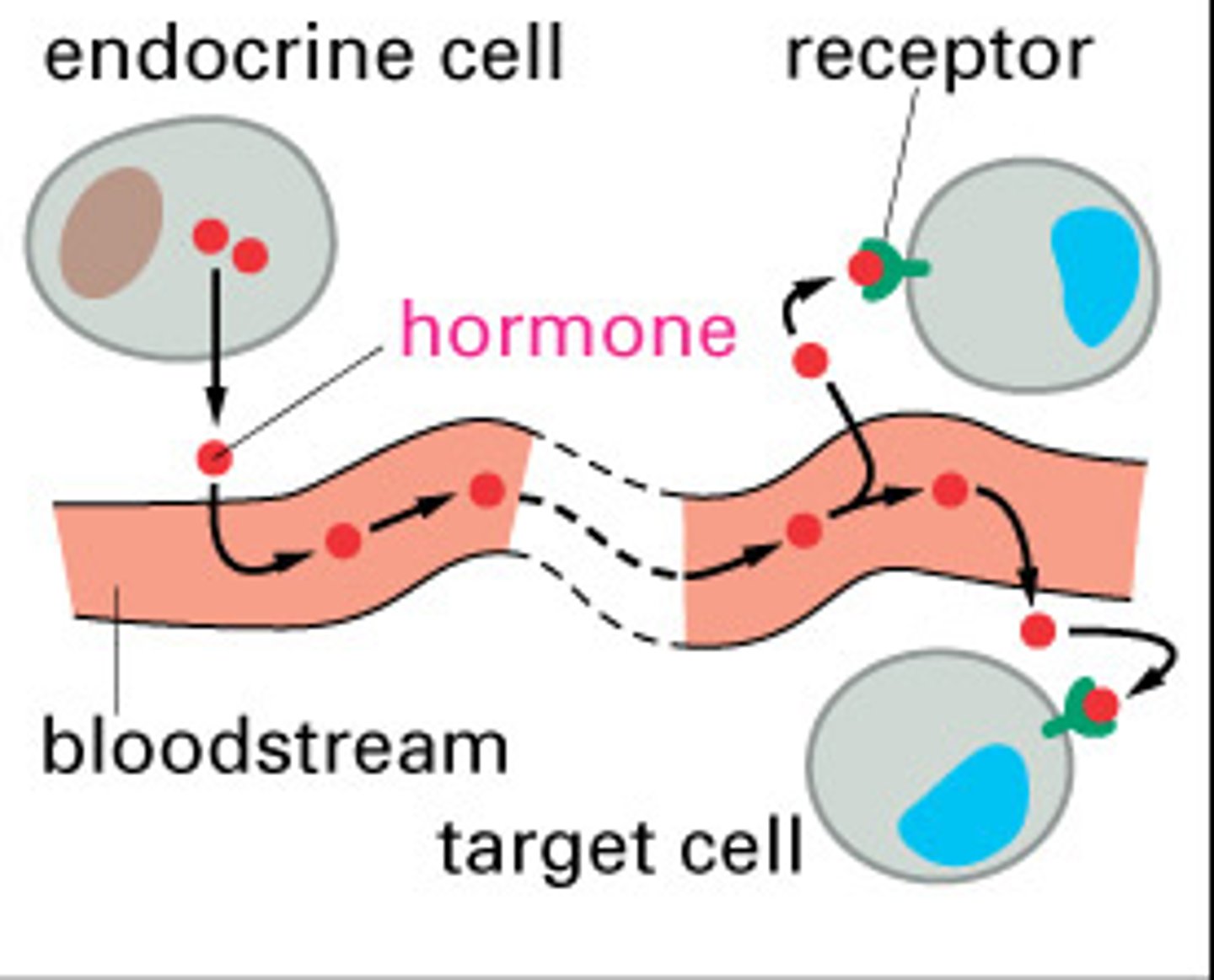
Endocrine glands
Ductless glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
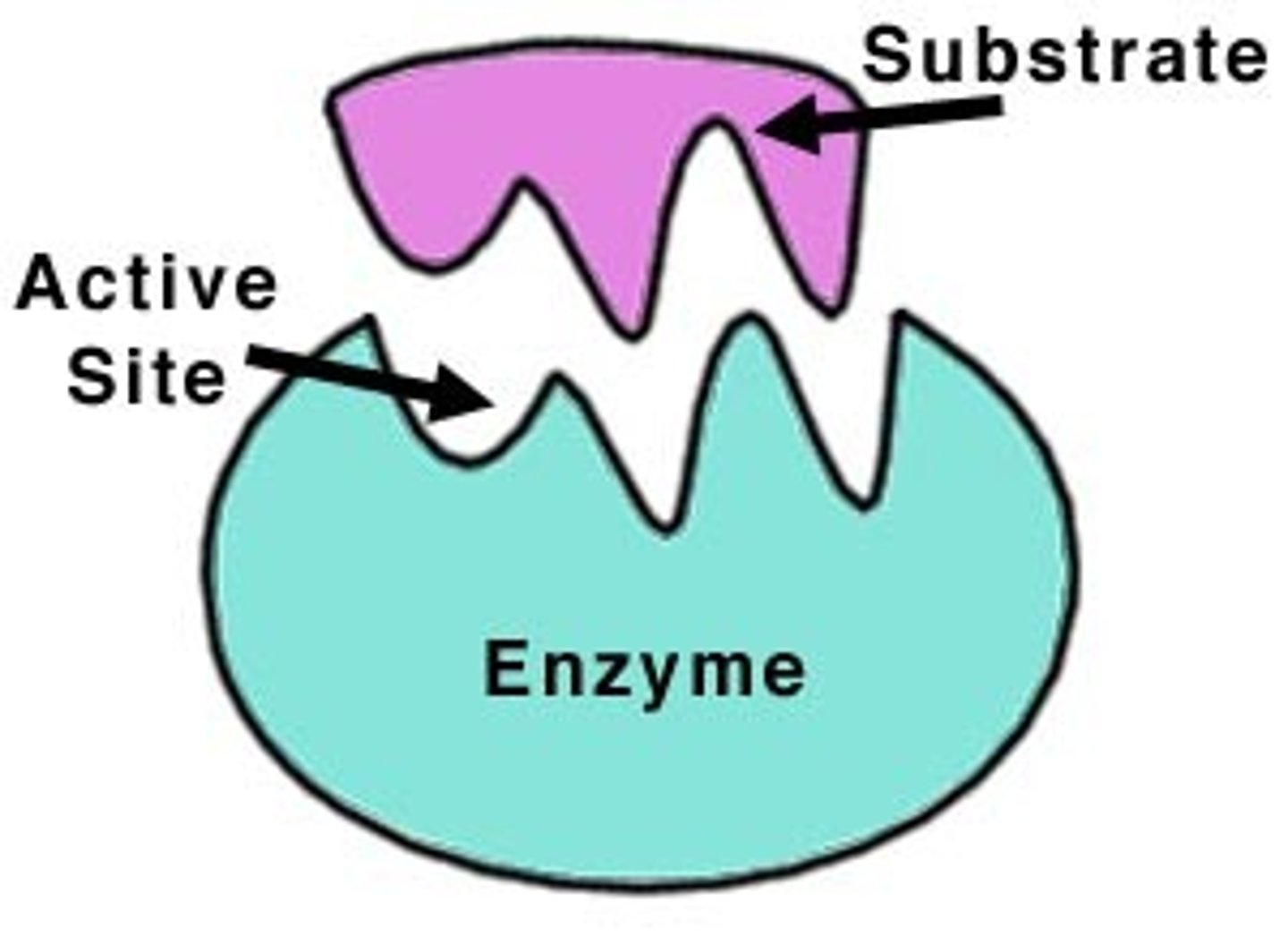
Enzymes
Biological catalysts made of protein. They alter the rate of (mostly catalyse) chemical reactions without themselves being chemically changed at the end of the reactions.
Eutrophication
The profuse growth and multiplication of algae and green plants as a result of the enrichment of nutrients in the water. Often leads to depletion of oxygen levels.

Excretion
The process by which metabolic waste products and toxic materials are removed from the body of an organism. E.g. sweating, sweat is a metabolic waste product.

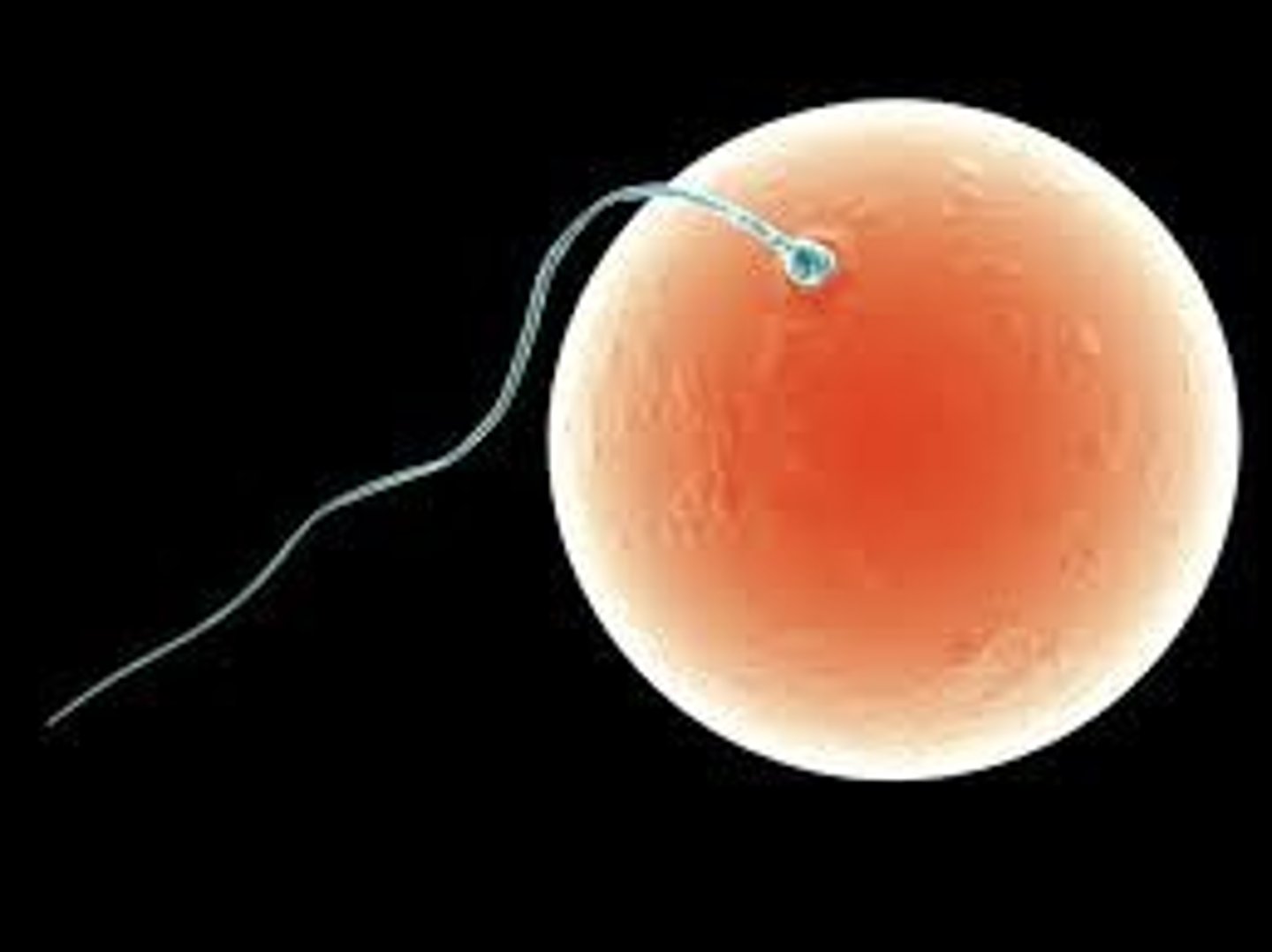
Fertilisation
The process by which the male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote.
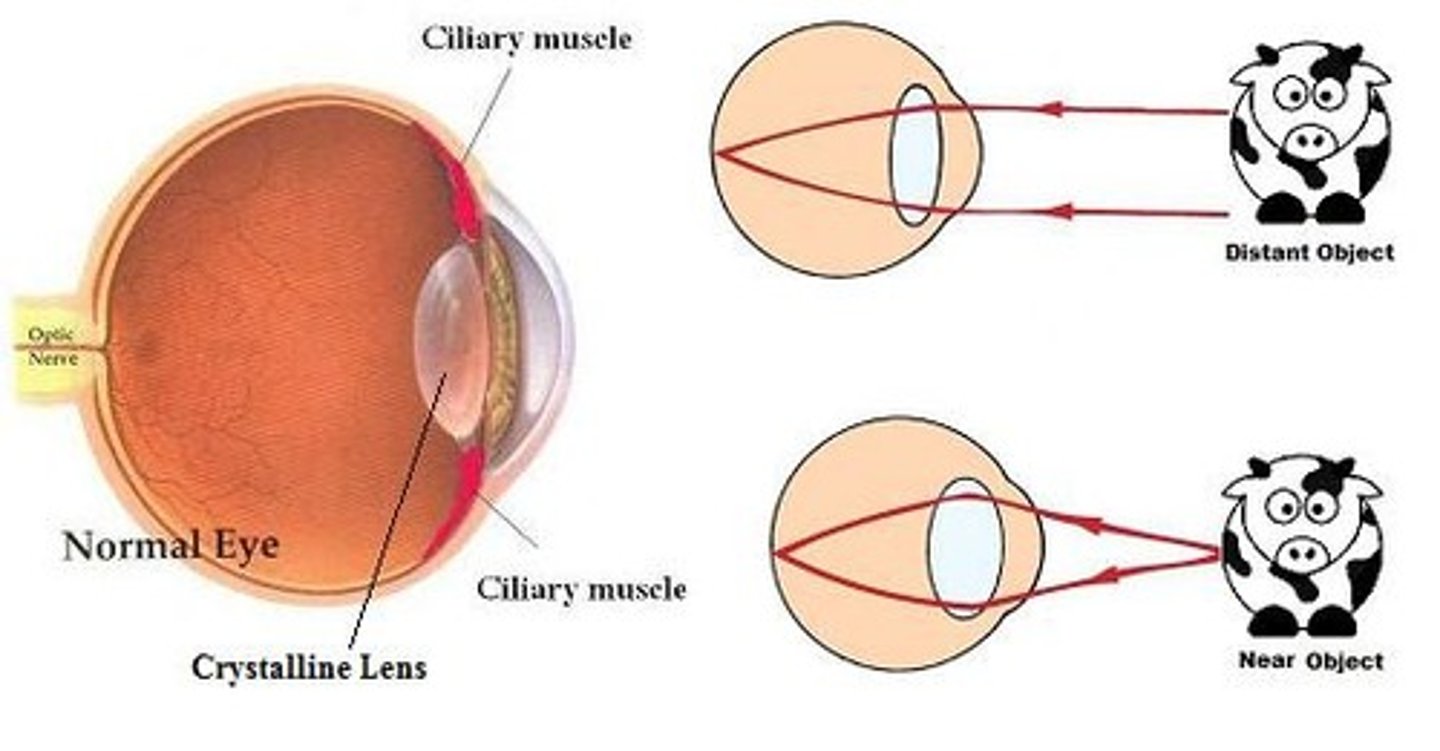
Focusing/accommodation
The adjustment of the lens of the eye so that clear images of objects at different distances are formed on the retina.
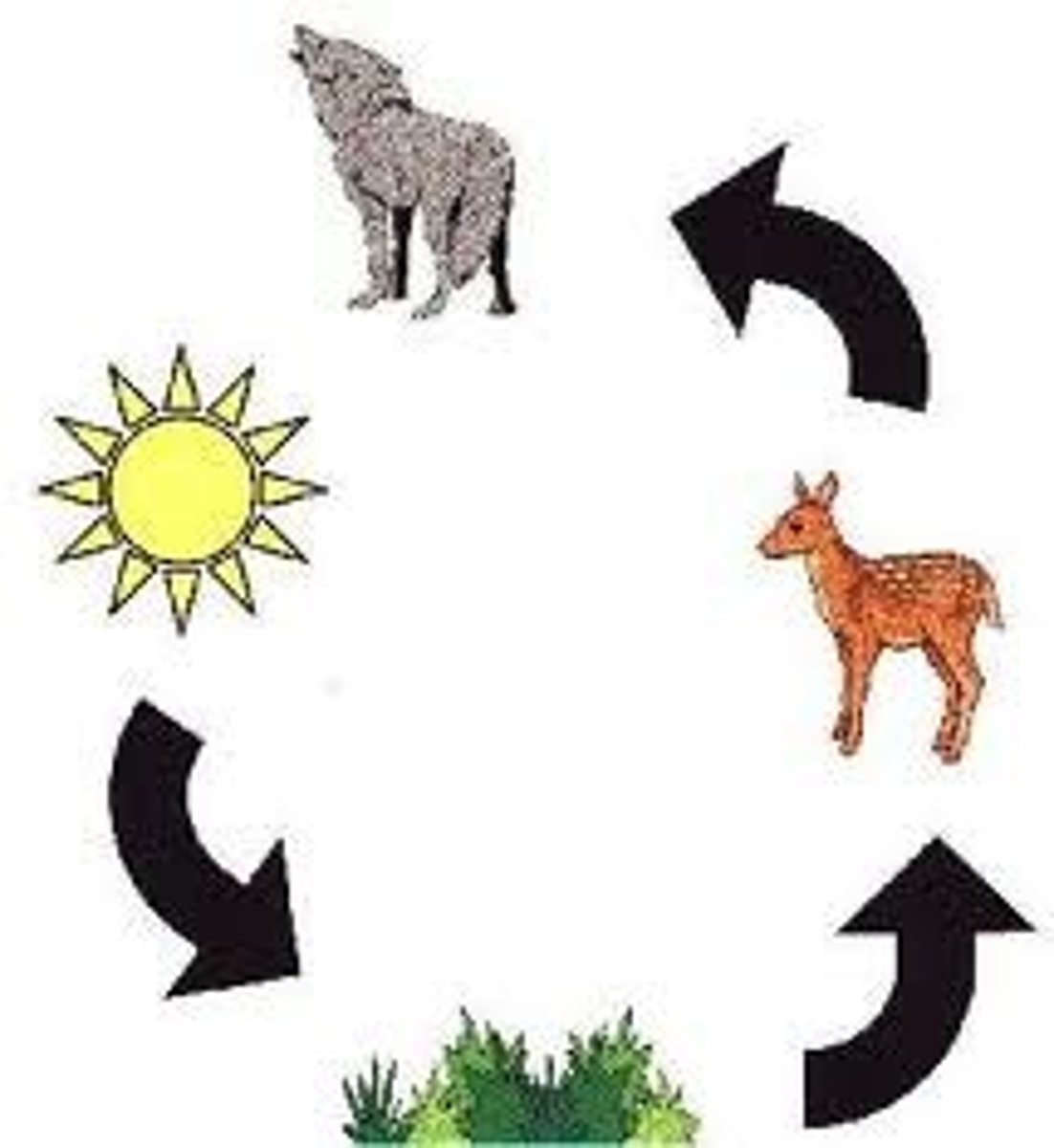
Food chain
A series of organisms through which energy is transferred in the form of food.
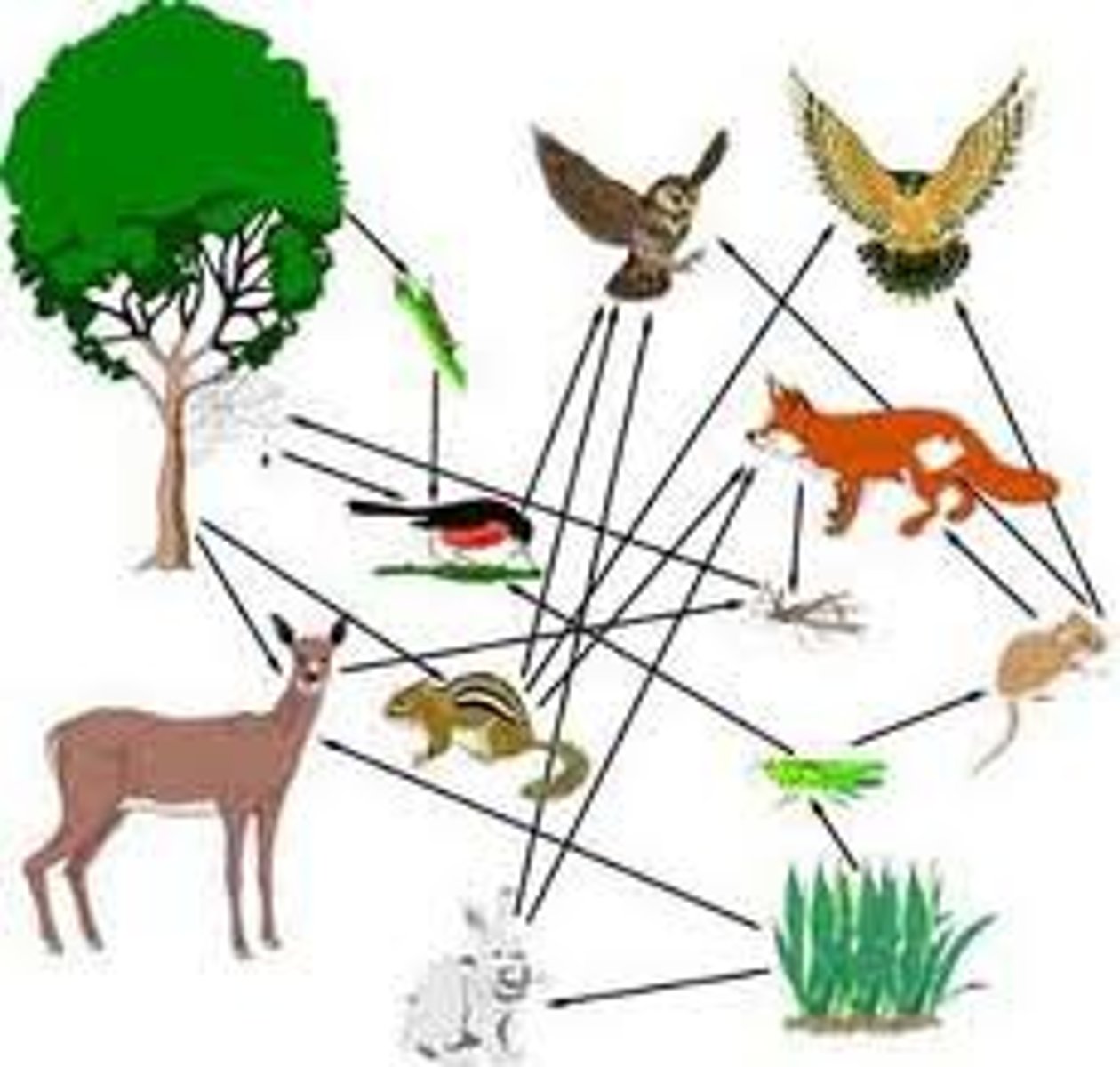
Food web
Two or more food chains interlinked together.
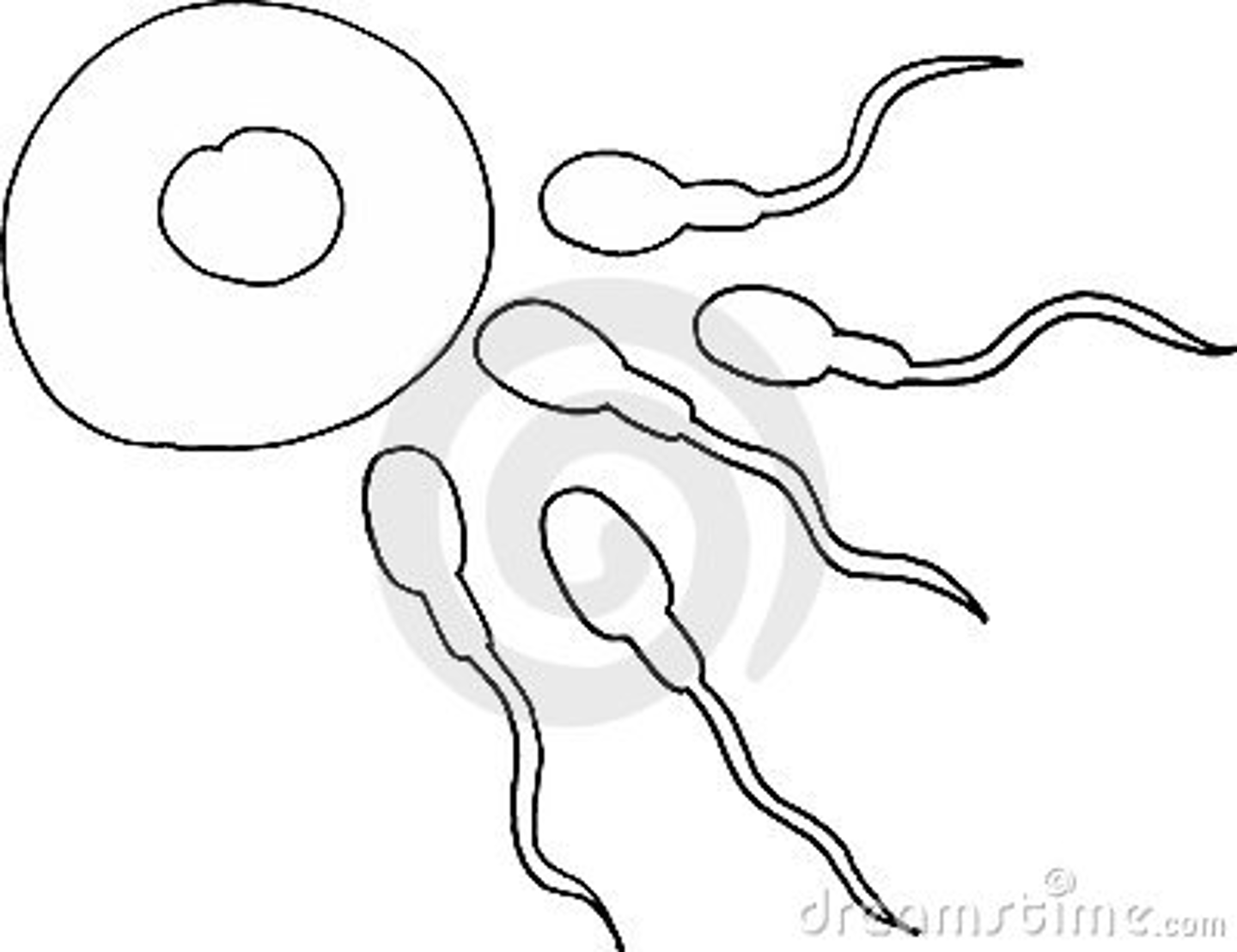
Gamete
A reproductive cell containing the haploid number of chromosomes.
Gene
A hereditary factor found on a particular locus in a chromosome. It controls a particular characteristic and codes for a specific protein.
Genetic engineering
A technique used to transfer genes from one organism to another.

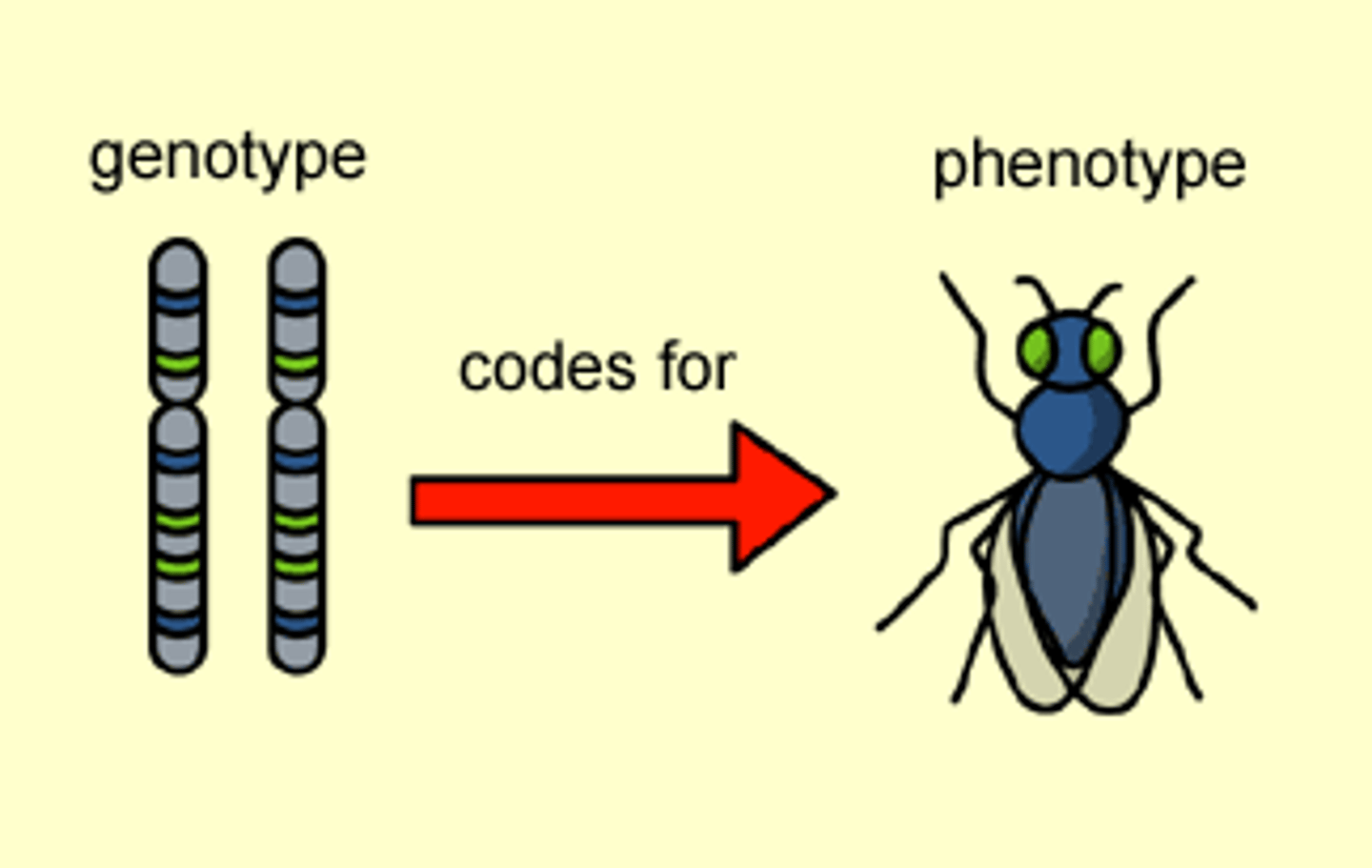
Genotype
The combination of genes in an individual.
Gland
A cell, tissue or an organ that secretes chemical substances.
Habitat
The place where an organism lives.
Haploid
Cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells which produced them.
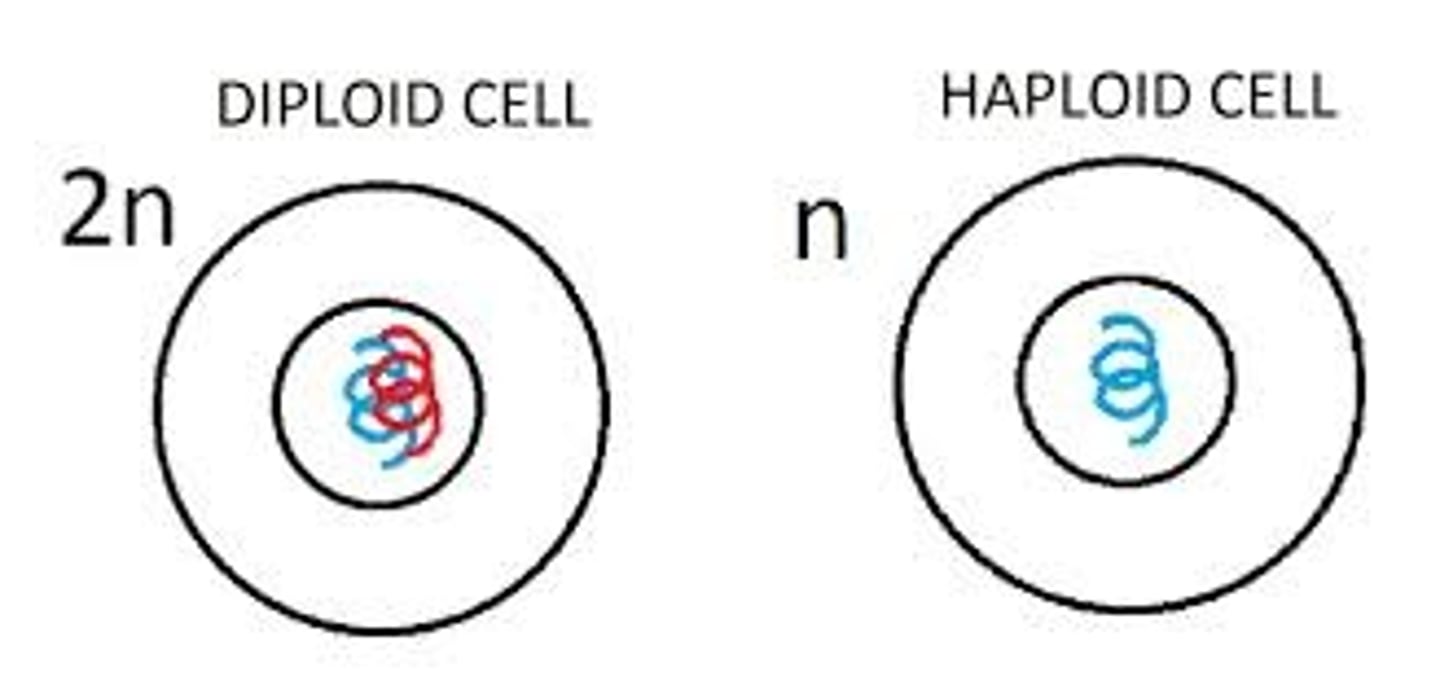
Heterozygous
A condition where you have different alleles for a particular trait. E.g. if B codes for brown eyes (dominant allele is always upper case) and the recessive allele is b (always the lower case of the dominant alleles' letter), then a person with a Bb genotype for eye colour is heterozygous dominant, so will have brown eyes.
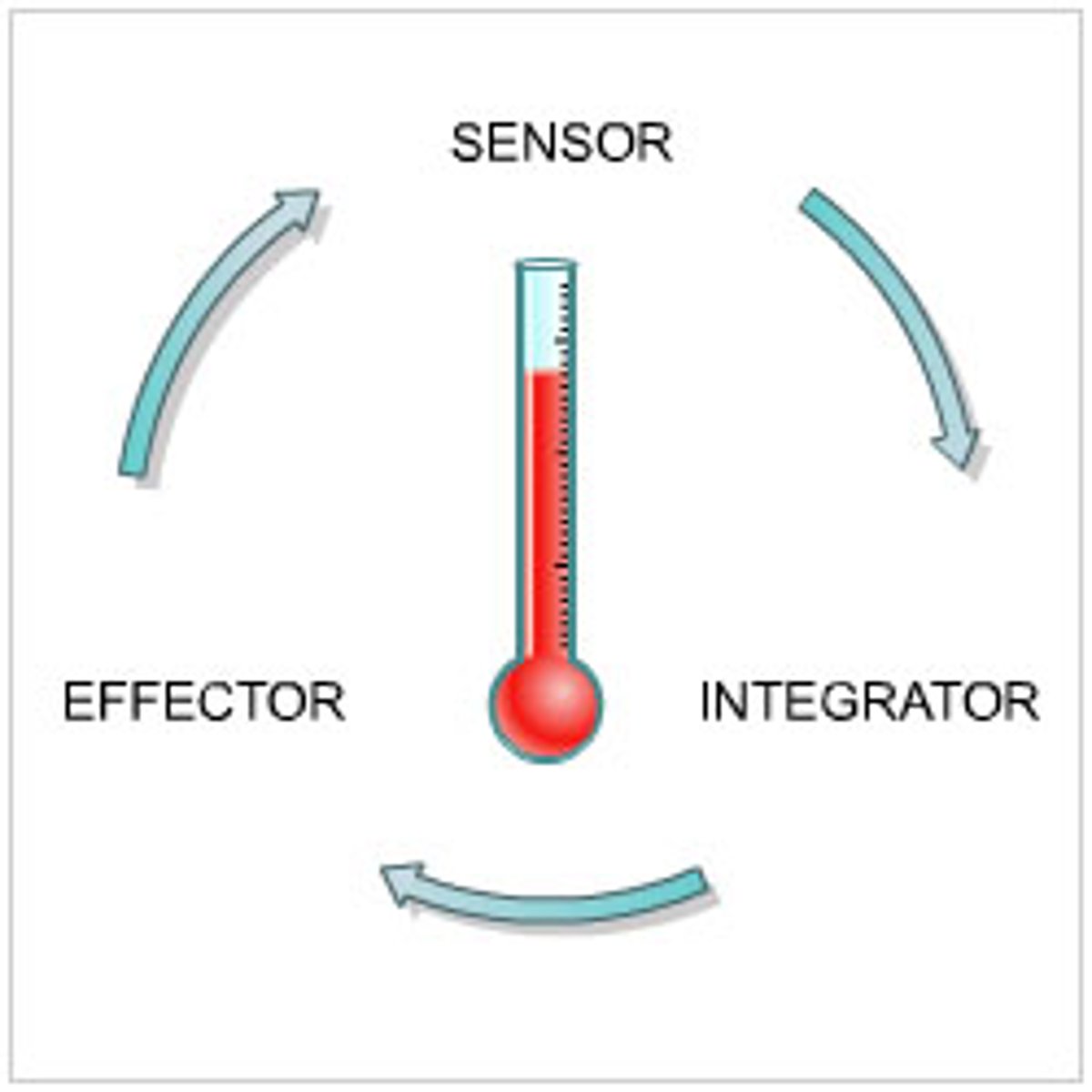
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment.
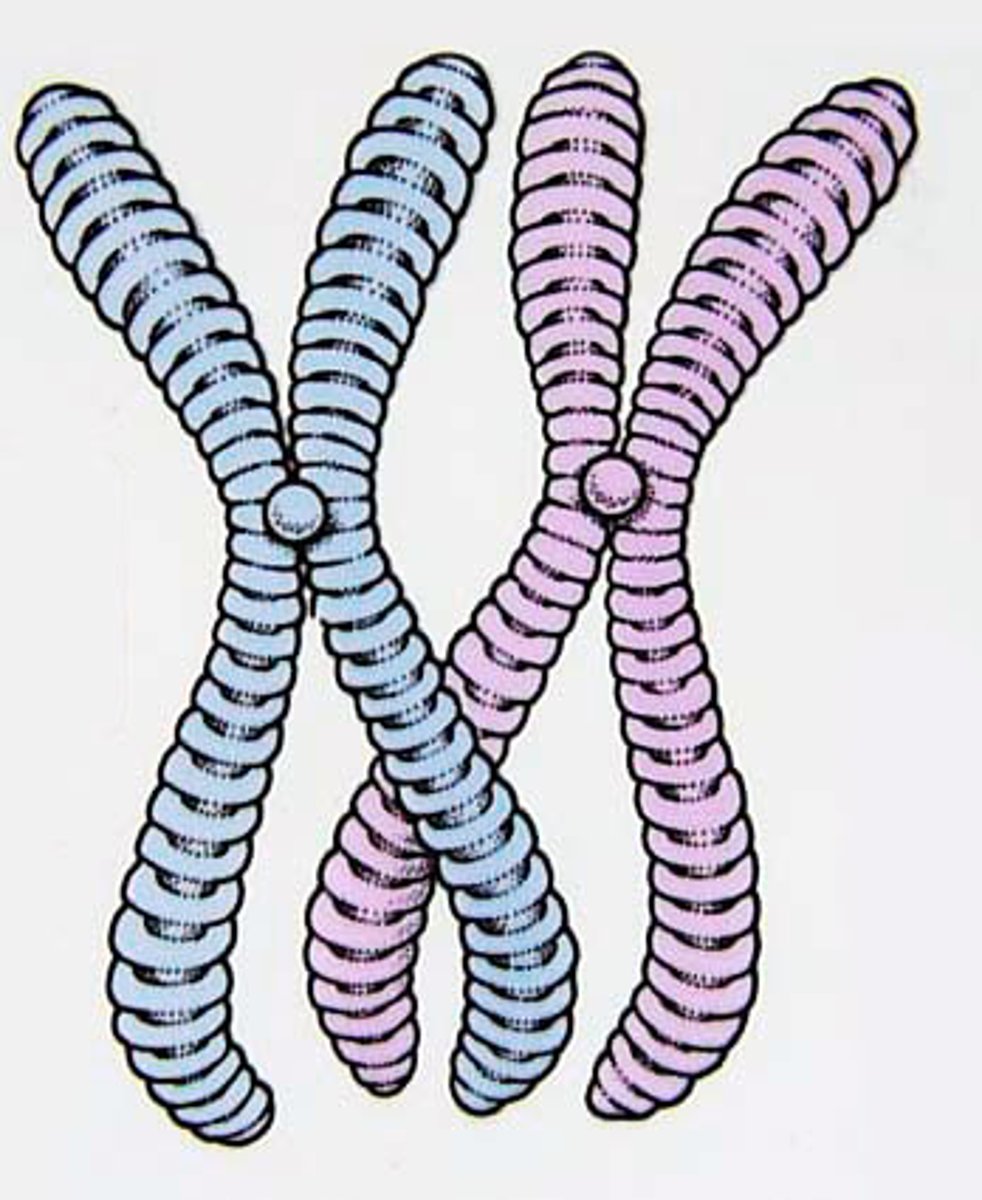
Homologous pairs
Chromosomes which have the same genes, shape and length.
Homozygous
Having identical alleles for a particular trait. E.g. BB-homozygous dominant, or bb-homozygous recessive.

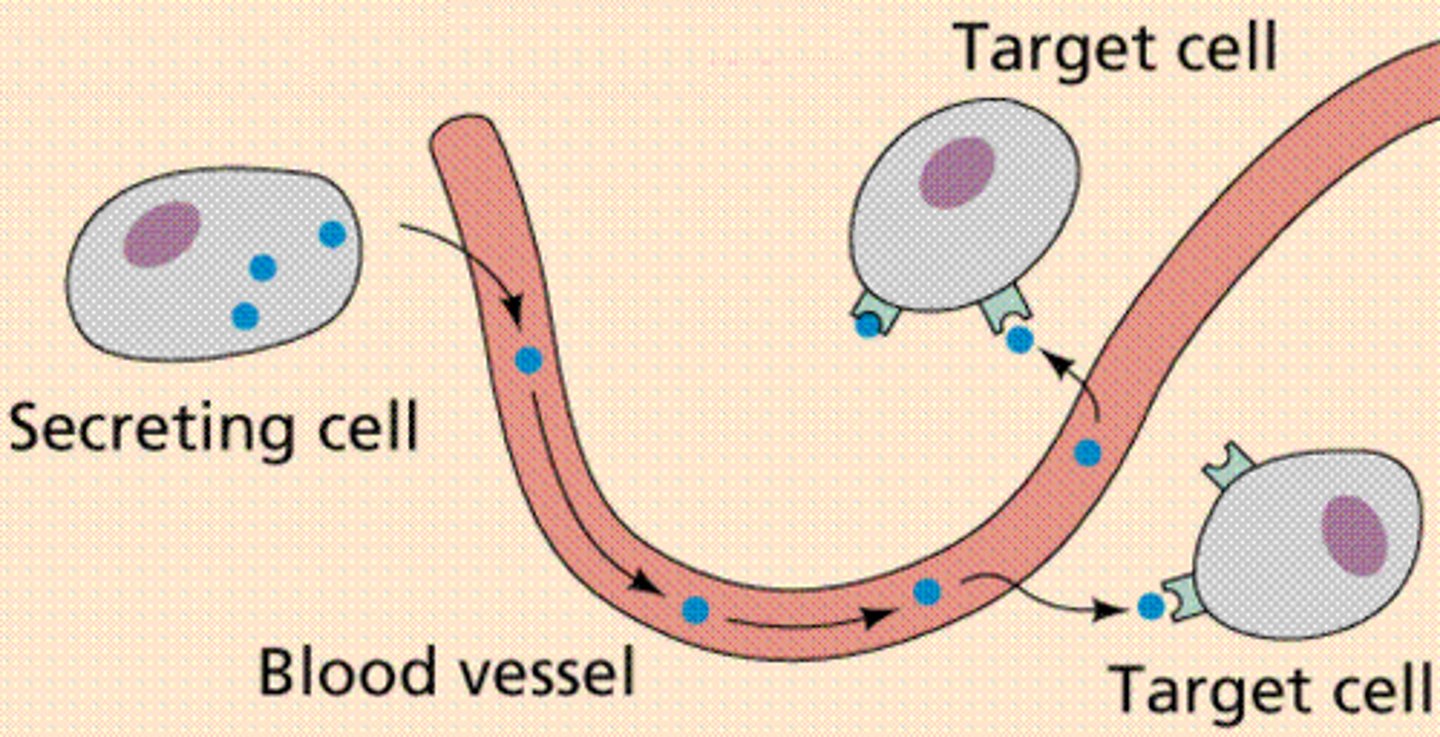
Hormone
A chemical substance produced in minute quantities by an endocrine gland. It is transported in the bloodstream to target organ(s) where it exerts its effects
Irritability/sensitivity
The ability of an organism to respond to a stimulus.

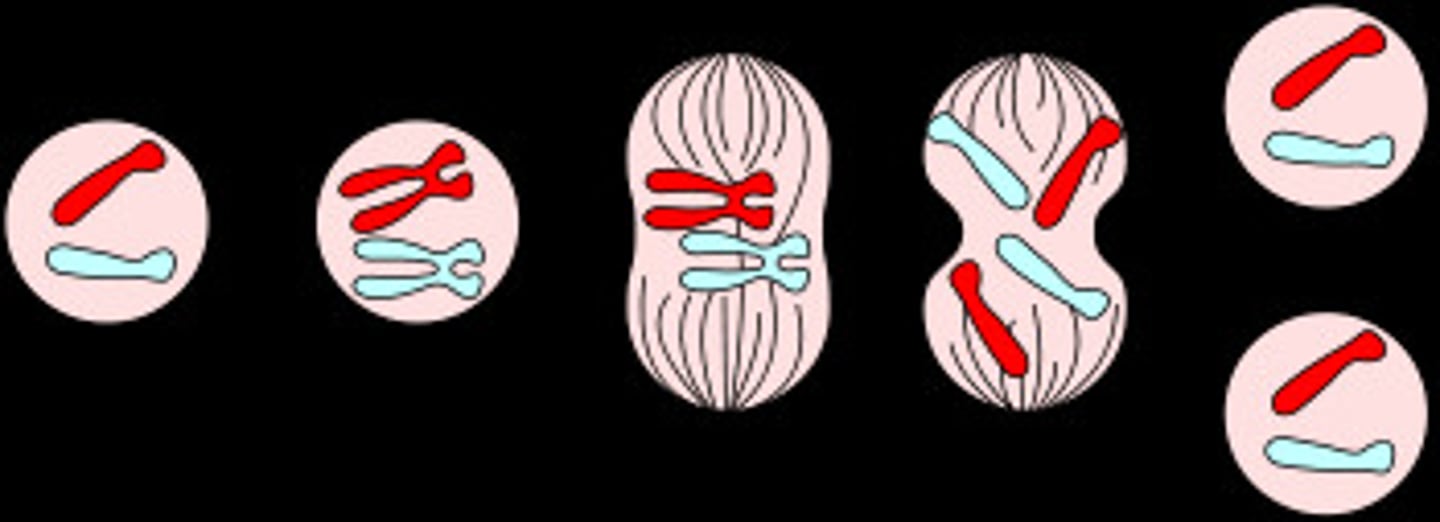
Meiosis
A form of cell division such that the daughter cells contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. -will be haploid, e.g. to form sex cells/gametes (Chromosomes are in the nucleus.)
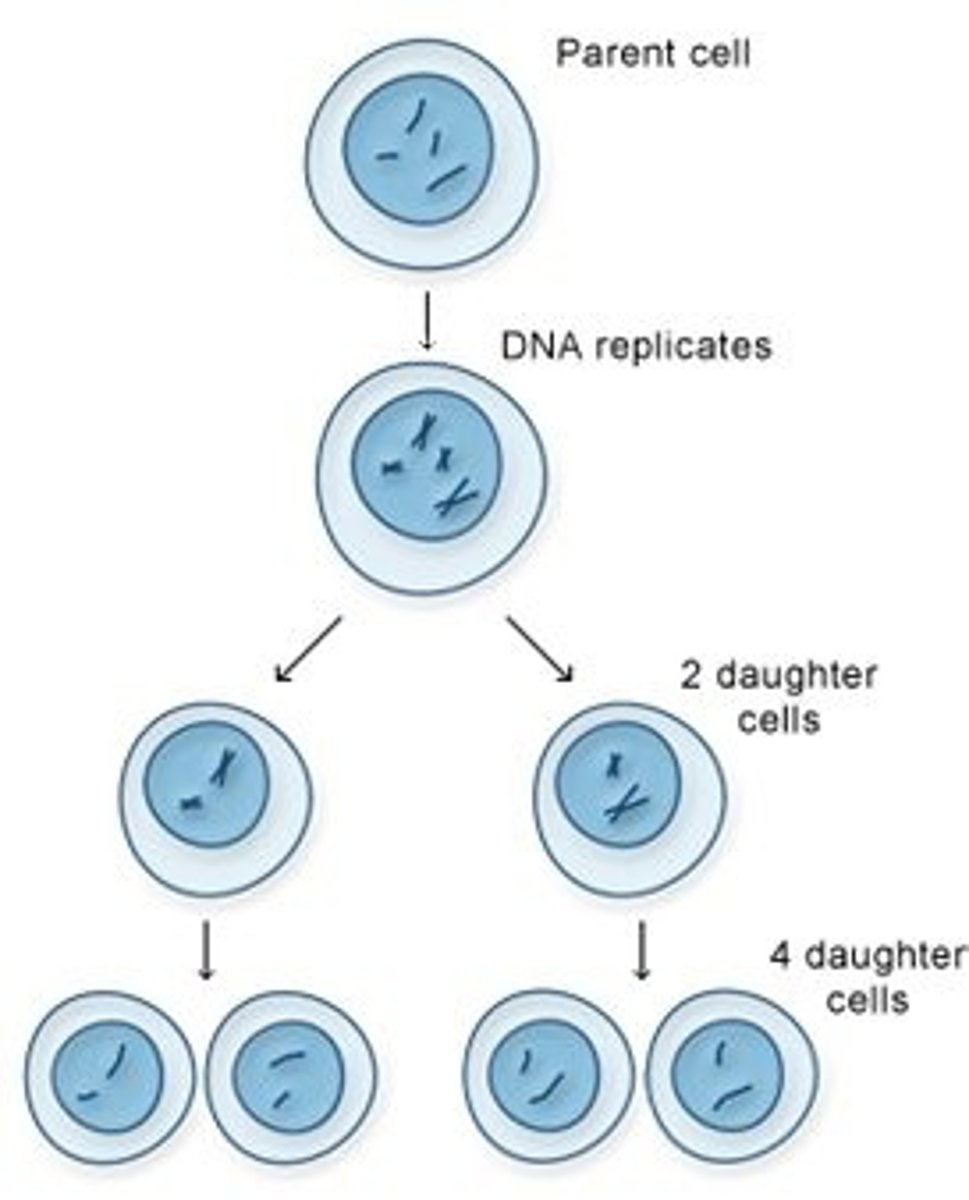
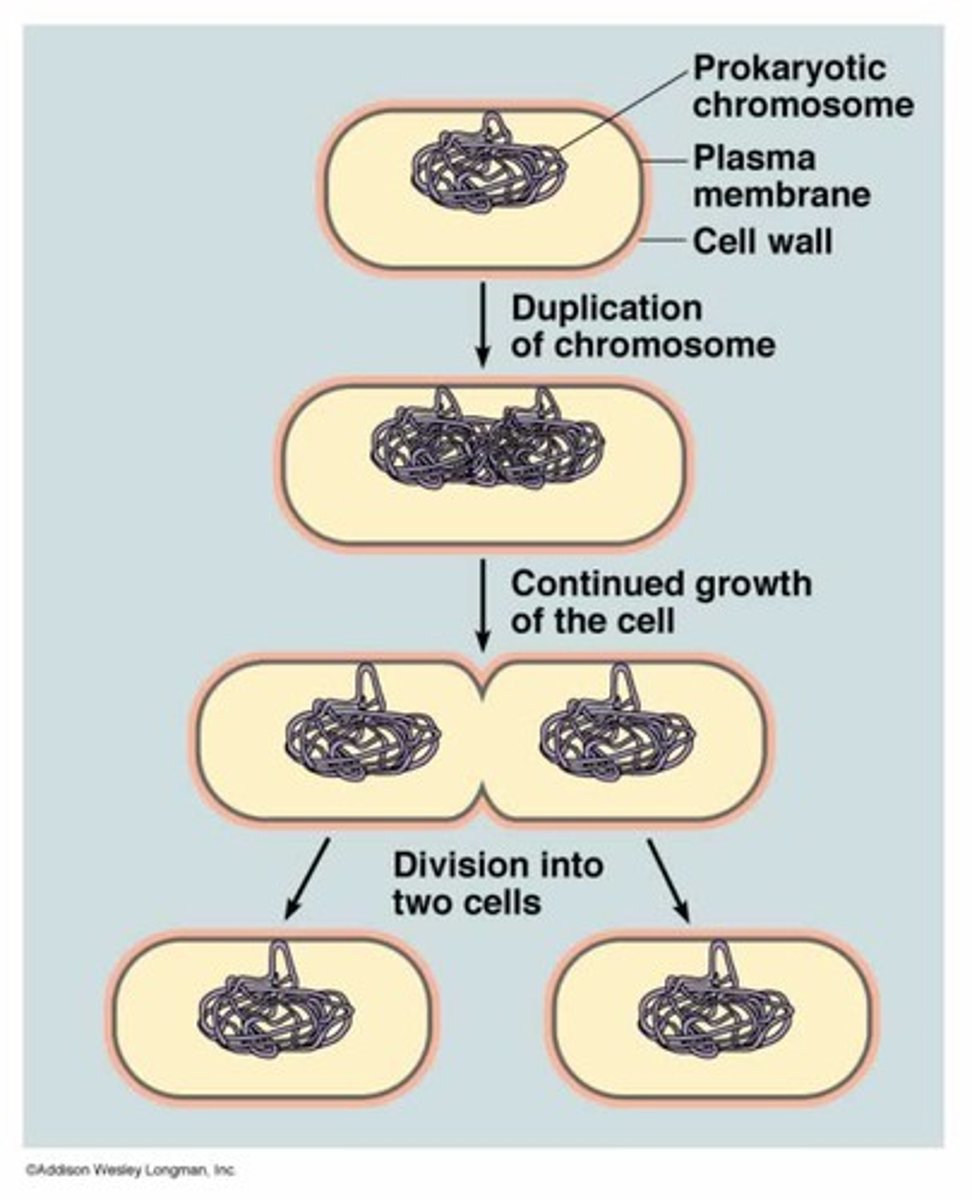
Mitosis
Cell division such that the daughter cell produced contains the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. -will be diploid, e.g. to form somatic (body) cells
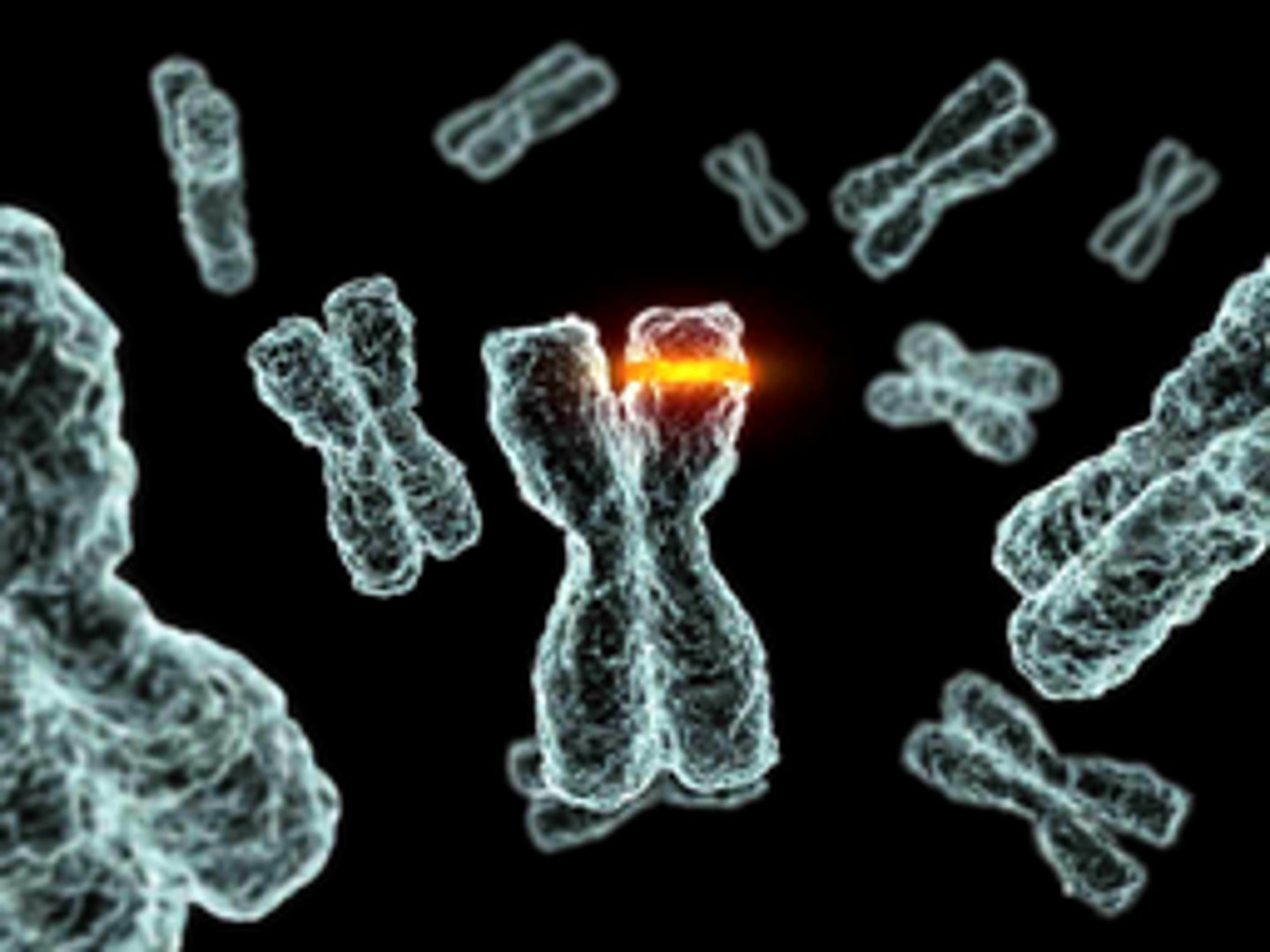
Mutation
The sudden or spontaneous change in gene structure or a chromosome, or even the chromosome number, and may be inheritable.
Nerve
A collection of nerve fibres.
Nerve fibre
A long cytoplasmic extension of the cell body of a neurone. It serves to transmit impulses.

Neurone
A nerve cell.
Nutrition
The intake of food and the processes that convert food substances into living matter.

Osmoregulation
The control of water and solute levels in the blood to maintain a constant water potential in the body. Basically to maintain blood water levels.
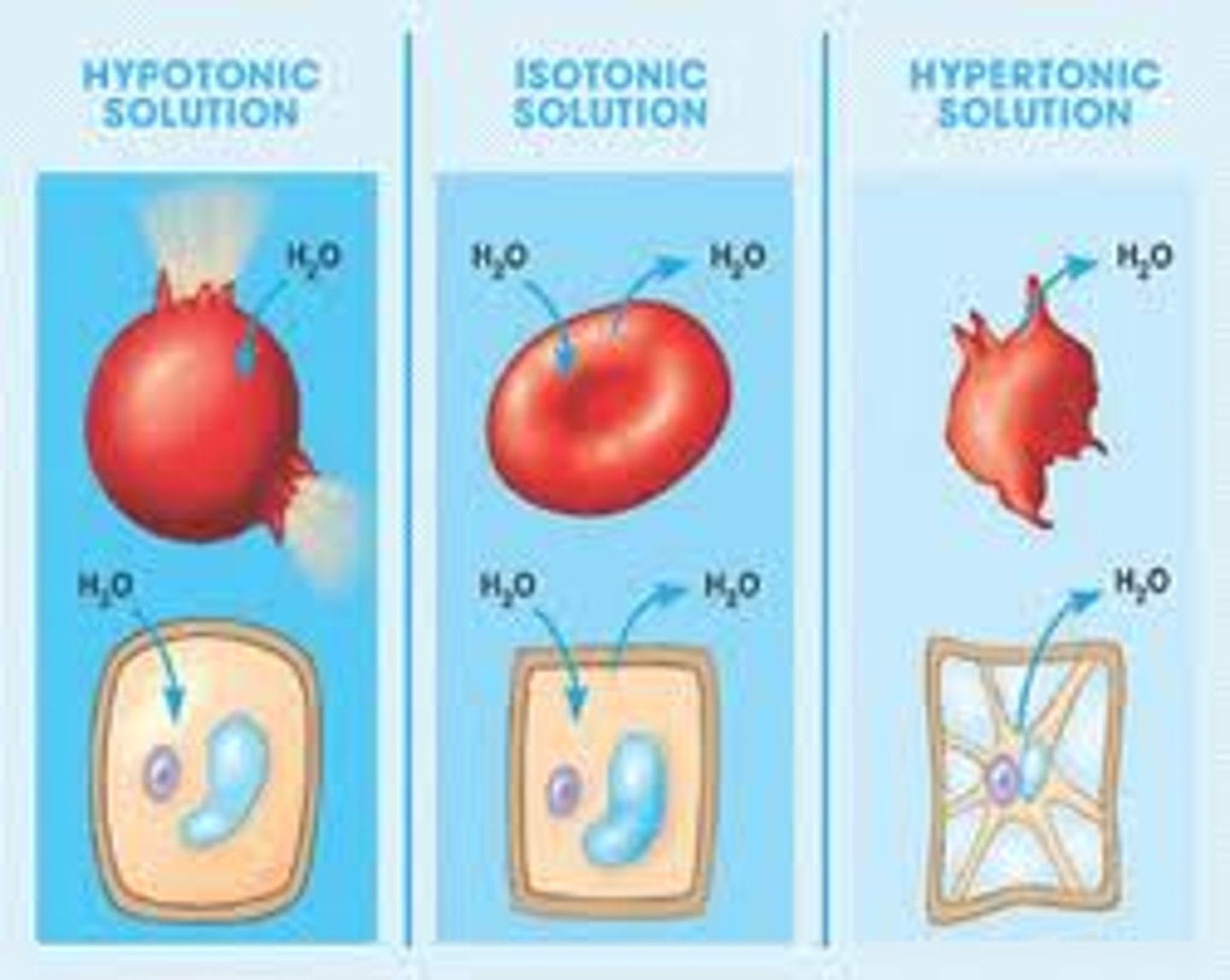
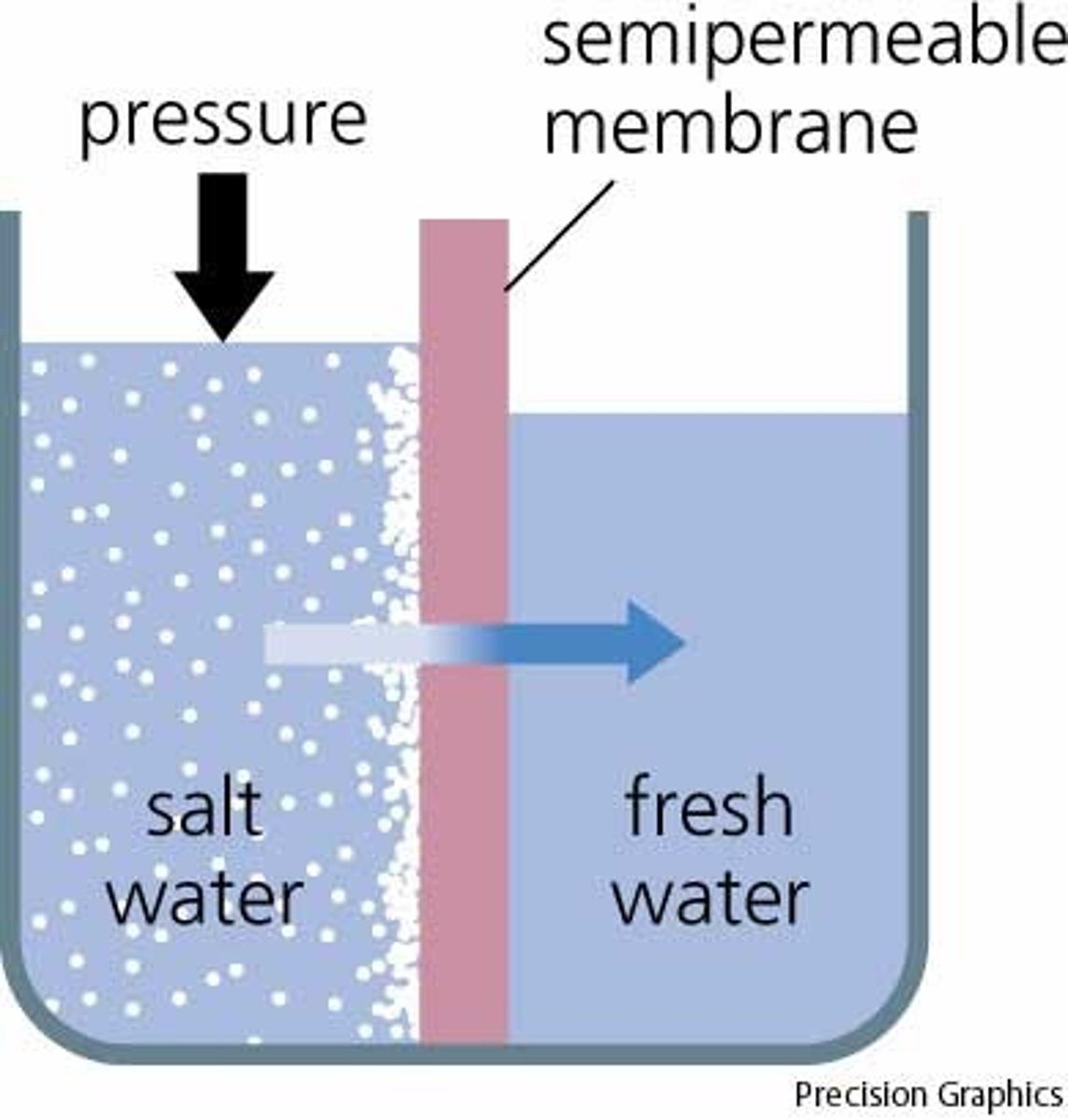
Osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a solution of higher water potential to a solution of lower water potential, through a partially permeable membrane, i.e. down a water potential gradient. Or, from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration, through a partially permeable membrane, i.e. down a concentration gradient.
Oxygen debt
The amount of oxygen required to oxidize the lactic acid produced in muscles during anaerobic respiration and convert it into harmless substances.
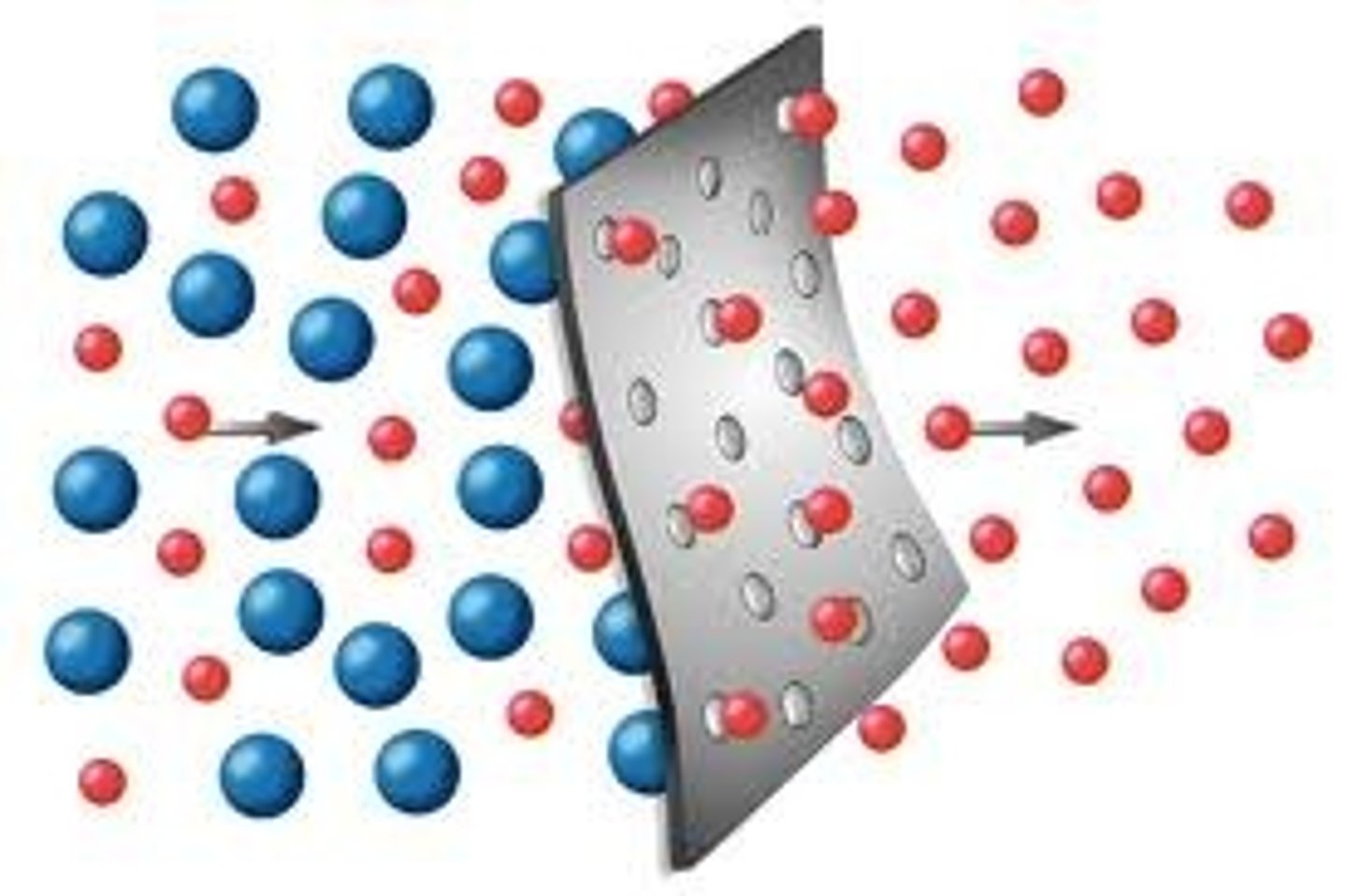
Partially/selectively permeable membrane
A membrane that allows selected substances to pass through.
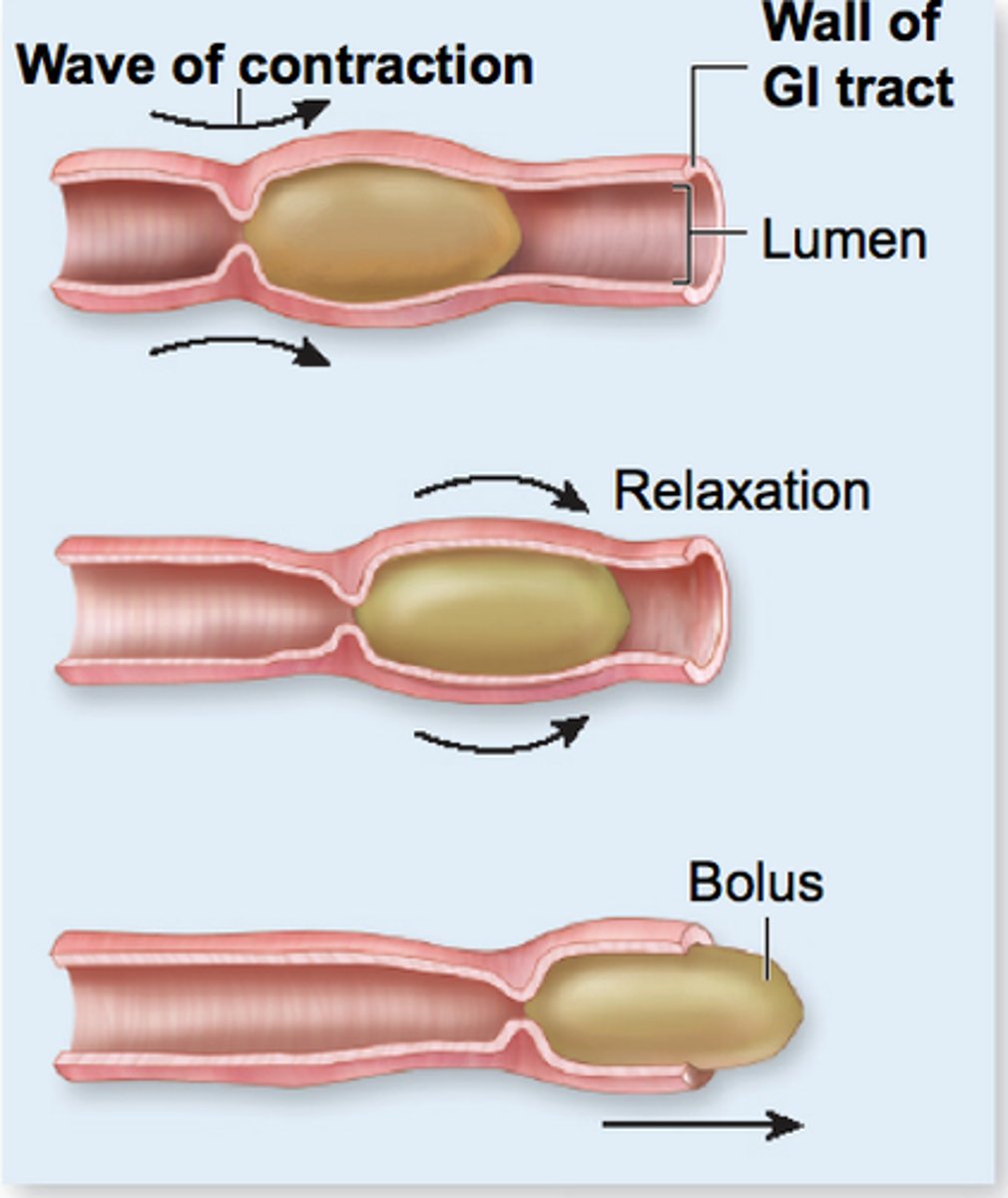
Peristalsis
The rhythmic wave-like contractions of the walls of the gut.
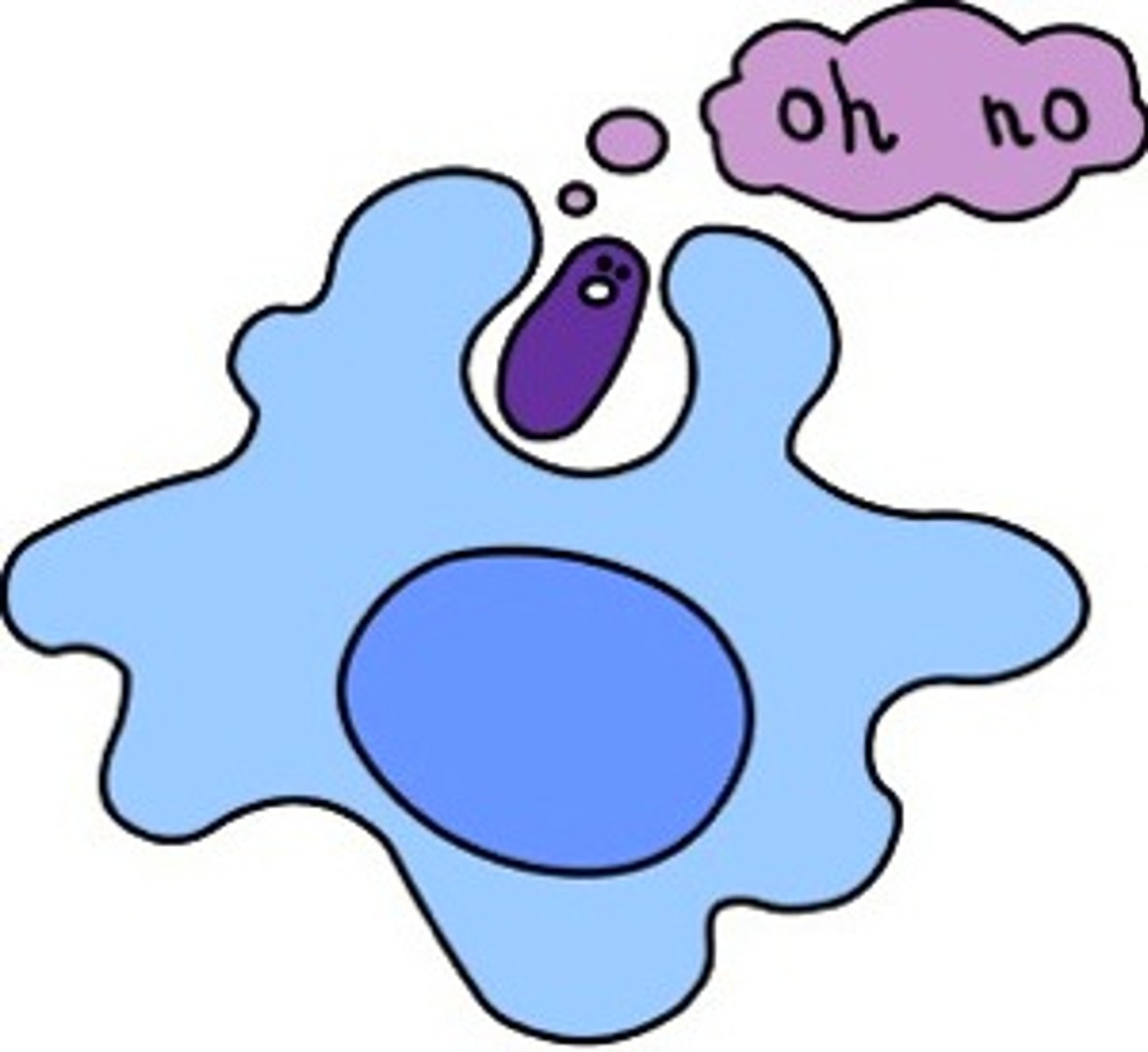
Phagocytosis
The process of engulfing and ingesting foreign particles, such as bacteria, by phagocytes such as the white blood cells
Phenotype
The physically expressed trait in an individual, e.g. outward appearances such as height and eye colour.
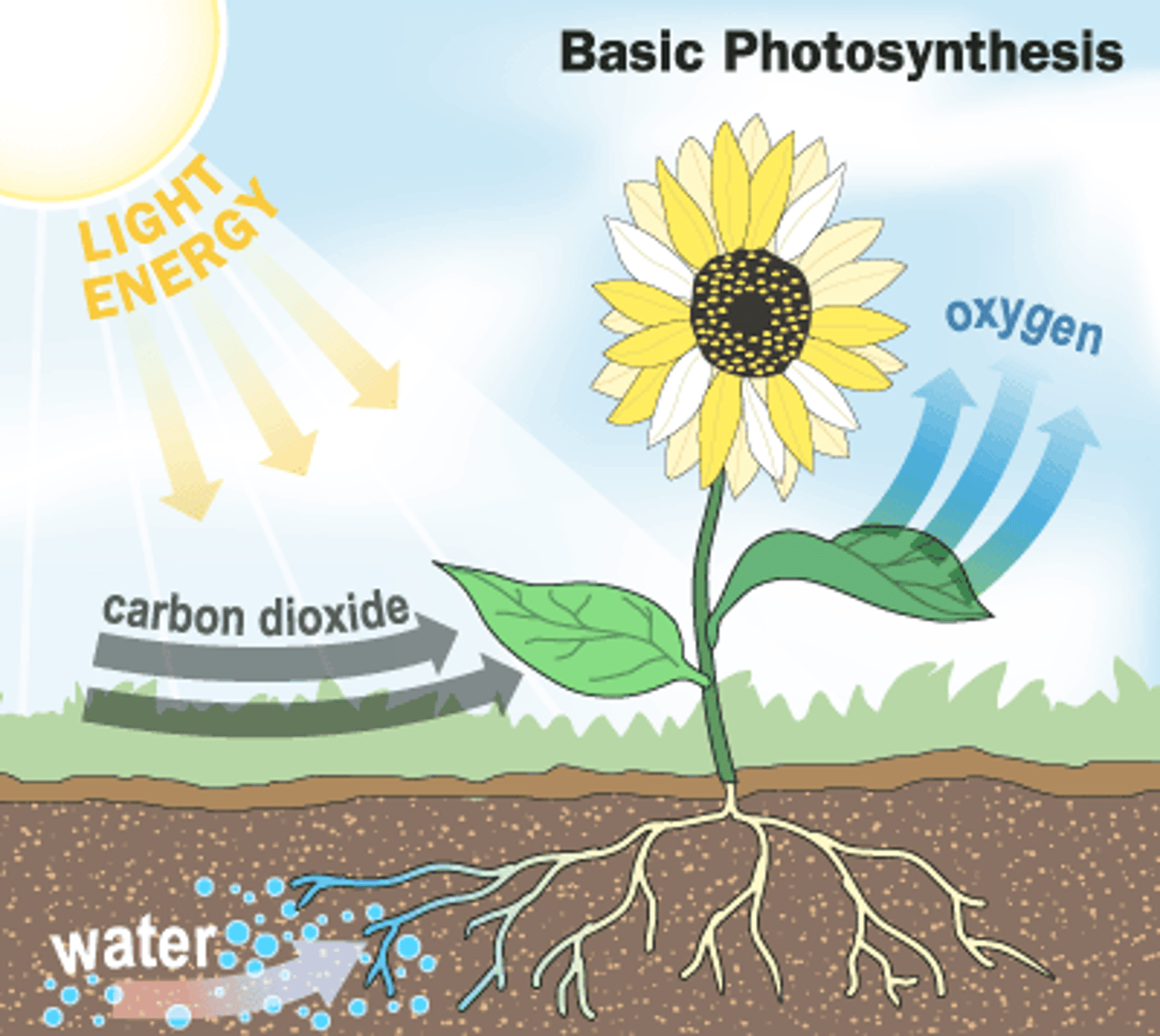
Photosynthesis
The process in which light energy absorbed by chlorophyll is transformed into chemical energy.
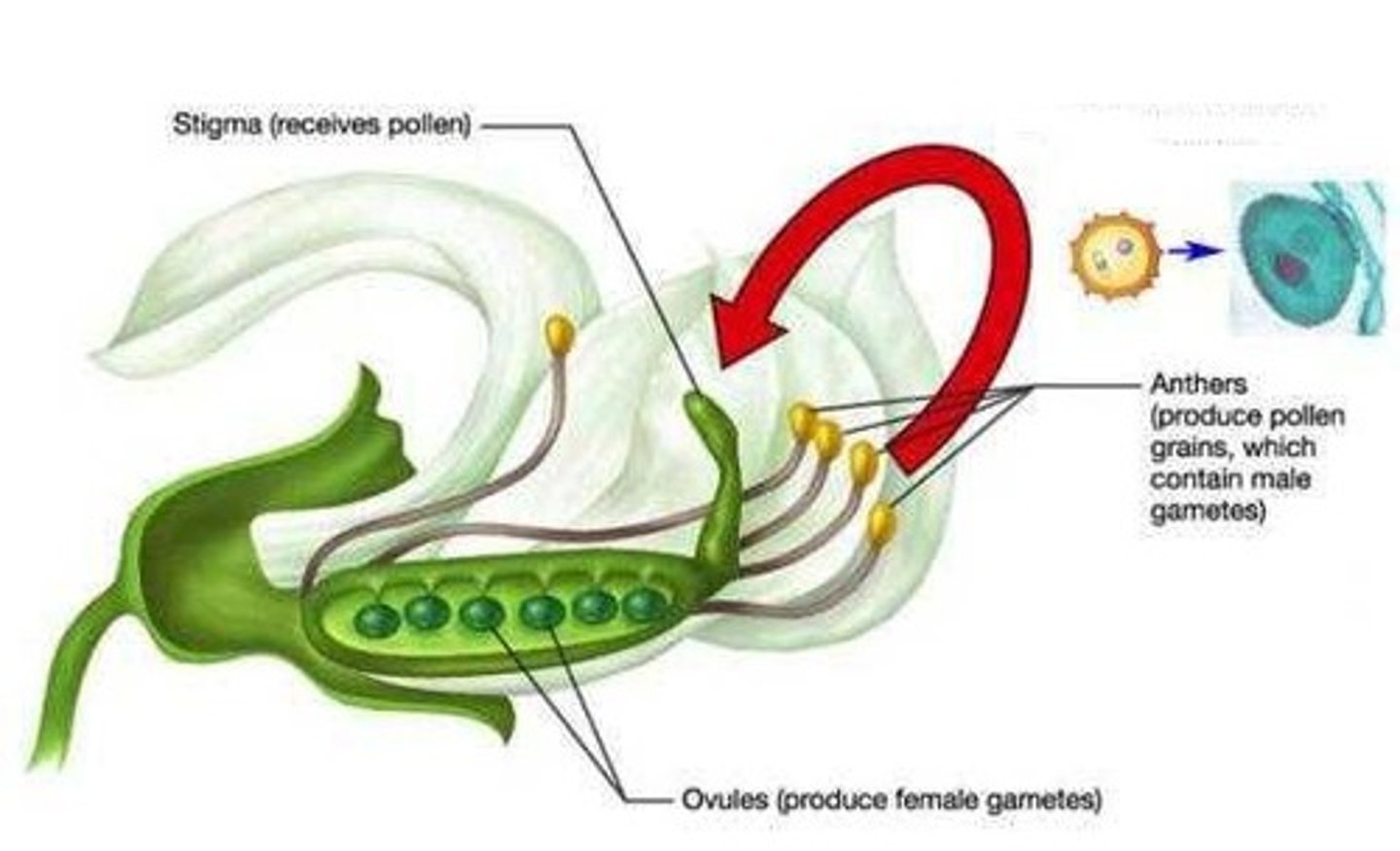
Pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma.

Pollution
The addition of substances to the environment that damage it, making it unfit for life.

Population
A group of organisms of the same species living together in the same habitat.

Producers
Organisms which convert energy from the sun, or light energy, into chemical energy and store it as food during photosynthesis. They are the start of the food chain.

Recessive
A form of a gene that expresses itself only in the homozygous condition. E.g. Bb, it won't be expressed because the dominant 'B' allele masks it and is expressed instead. But in 'bb', this is homozygous recessive, so it will be expressed.
Reducing sugars
Sugars that produce a red precipitate when boiled with Benedict's solution. E.g. glucose, maltose, fructose, lactose.

Reflex action
An immediate response to a specific stimulus without conscious control.
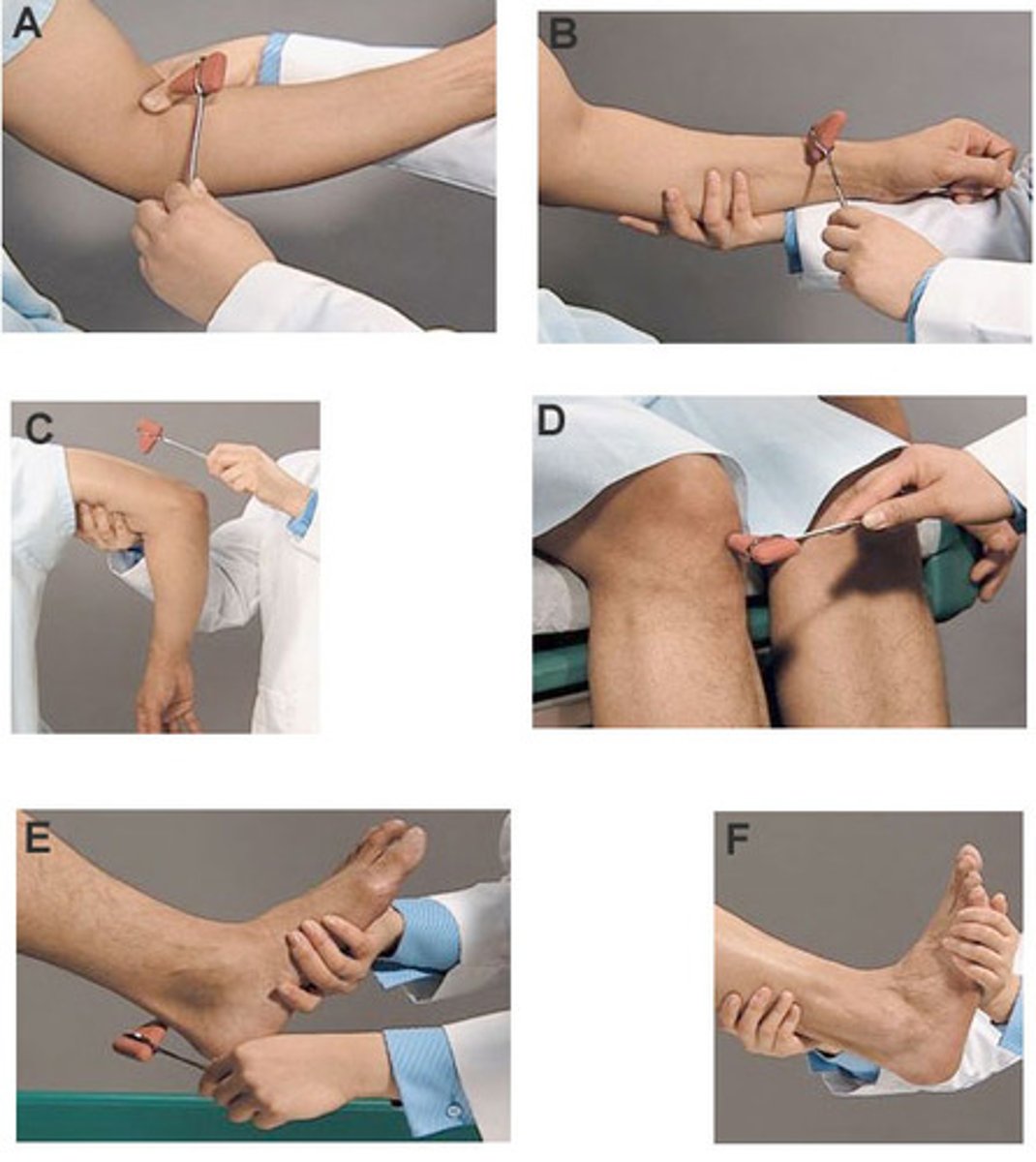
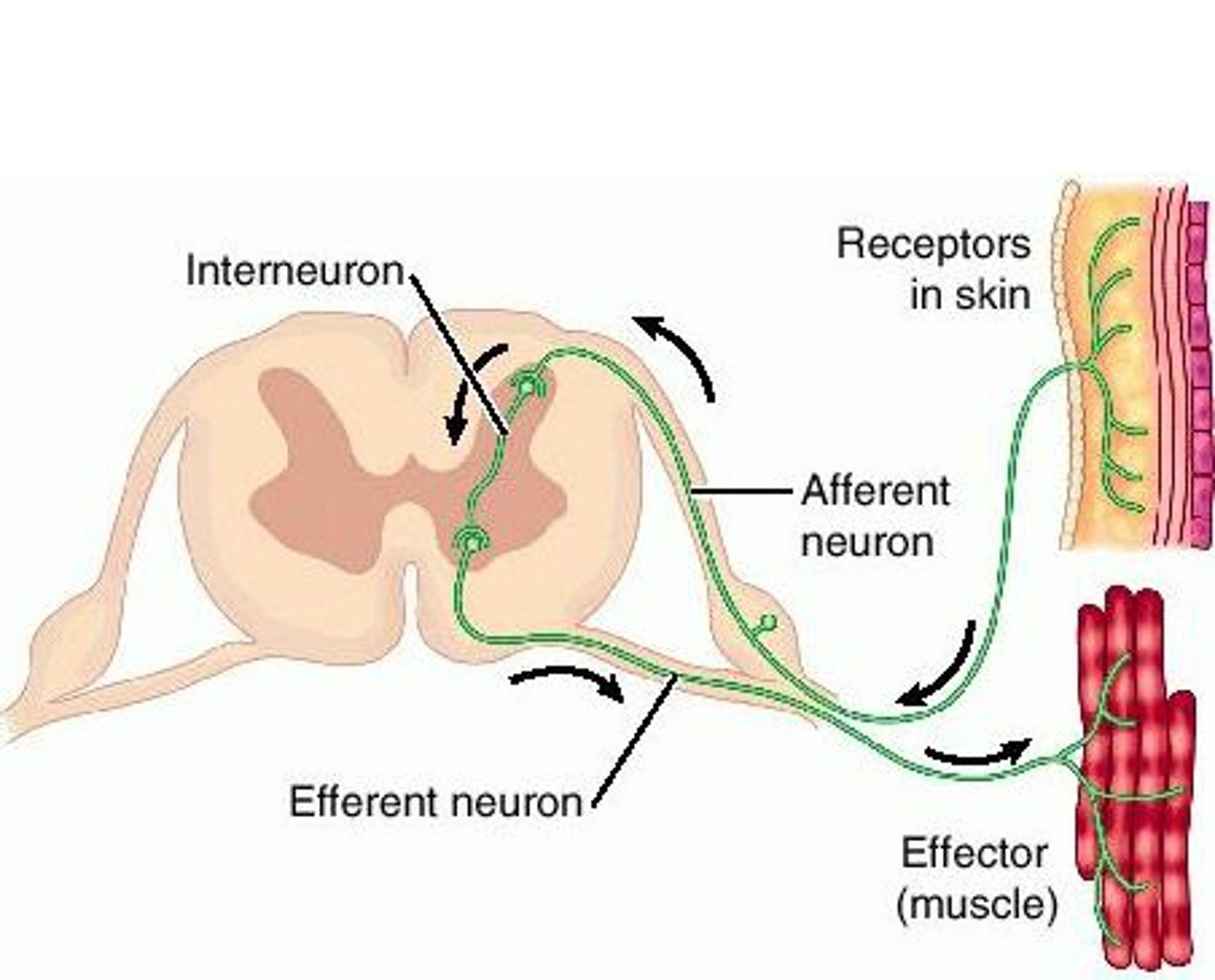
Reflex arc
The shortest pathway by which impulses travel from the receptor to the effector in a reflex action.
Respiration
The oxidation of food substances with the release of energy in living cells.
Self-pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther the stigma of the same flower or of a different flower on the same plant.
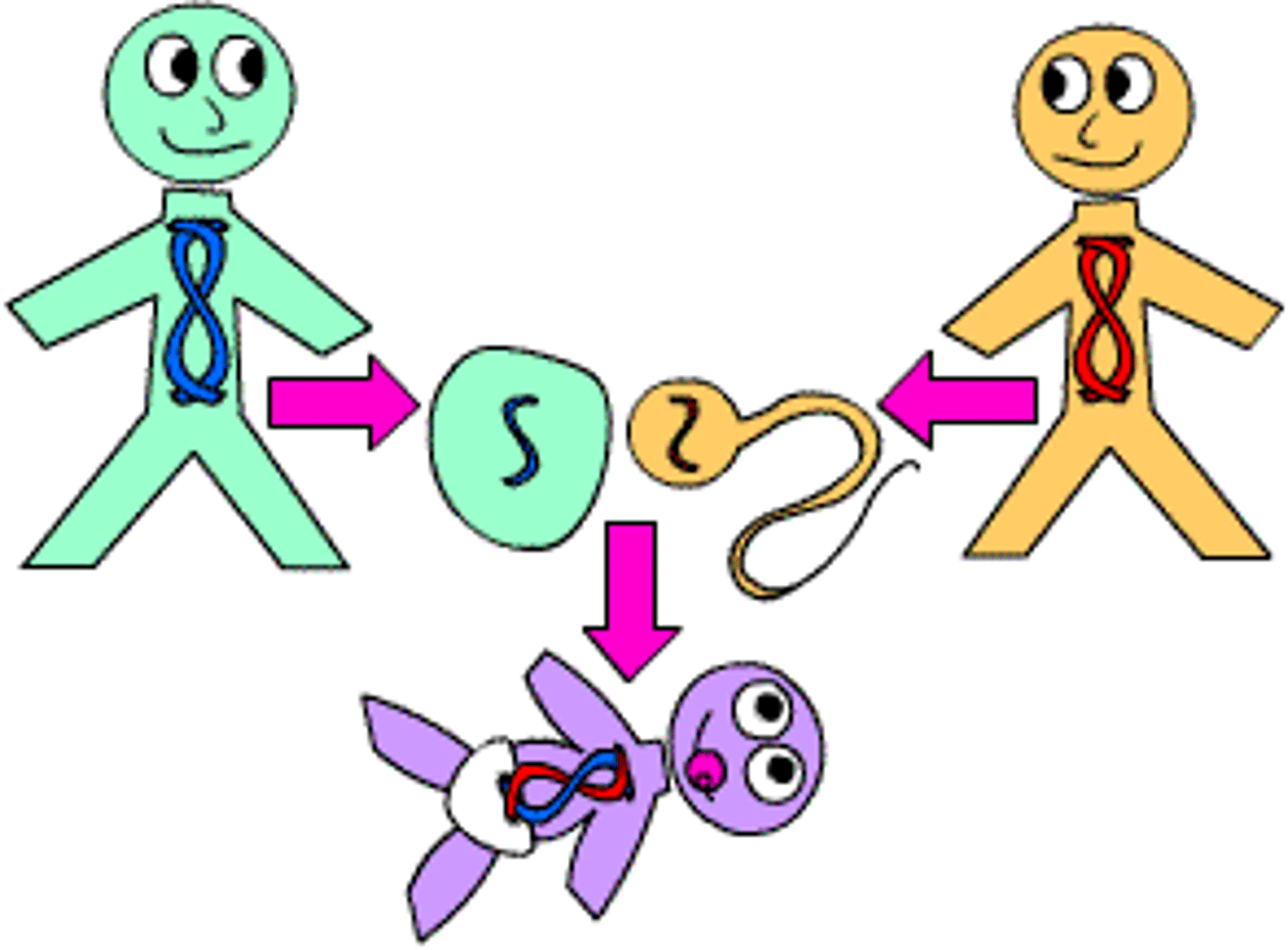
Sexual reproduction
The process involving the fusion of two gametes to form a zygote, resulting in the production of genetically dissimilar offspring-as in there will be variation.
Species
A group of similar organisms. Organisms within a species can breed. They produce healthy offspring that are able to grow, develop and reproduce normally.

Synapse
A junction between two neurones.
Tissue
A group of similar cells which work together to perform a specific function.
Tissue respiration
The process in living cells by which food substances are oxidized with energy released for the vital activities of the cells. Basically: C6H12O6 + 6O2 à 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP)

Translocation
The transport of manufactured food substances such as sugar and amino acids in plants (in phloem.)
Transpiration
The loss of water vapour from aerial parts of a plant, especially through the stomata of the leaves.
Transpirational pull
The suction force caused by transpiration that is the main factor causing water movement up the xylem.
Turgor pressure
The pressure exerted outwards on the cell wall due to the water in the cell-hence the cell becomes turgid.

Variation
The differences that can be observed within a species.

Veins
Blood vessels which carry blood towards the heart.
Voluntary action
An action that is under the control of the will, requires thinking so it's obviously slower than involuntary/reflex actions.