PP4: Wetlands
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
How did people used to view wetlands
During settlement of the U.S., wetlands were considered “bug-infected, disease ridden wastelands that impeded settlement and economic development”
Policies/regulations
Have changed over time dramatically. We view wetlands in a more positive light now
Most of our land has tiles underground to help to flow of water and to prevent flooding of farmland

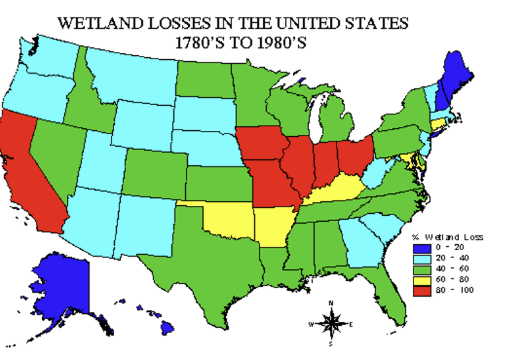
Wetland losses in the 80’s
Not much data on wetland loss now, but there hasn’t been a net gain of wetlands, if anything its a net loss
estimated rate of wetland loss
The rate of wetland loss was higher in the 50-70s
In the 80s we see the rate really decline
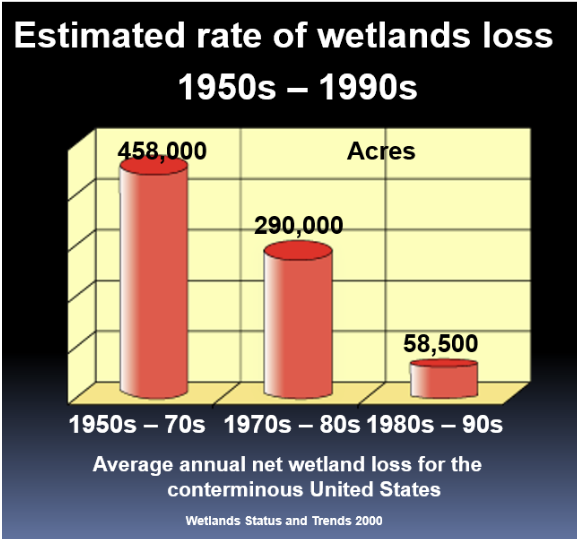
To a federal policy of “no net loss” of wetlands, including subsidy and technical assistance to restore and create wetlands
pic

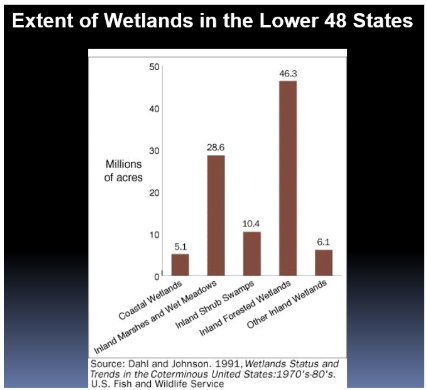
Acres of wetlands
pic
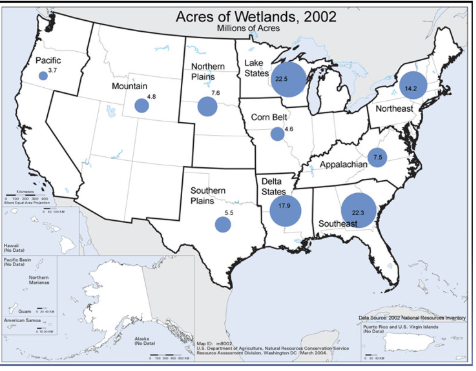
Extent of wetlands in the lower 48 dtates
There are many different types of wetlands
Costal wetlands have experienced the least amount of loss, inland forested wetlands have experienced the most
People now view wetlands in a more positive light
The public, especially user groups, began to recognize the resource values of wetlands
Concern began to grow in the 1950’s and 1960’s over an alarming rate of wetland loss in the U.S.
Consequently, appreciation of wetlands increased
More recent programs and legislation provide indirect protection and incentives to conserve and restore wetlands:
Section 404 of the Clean Water Act
No net loss policies (executive orders)
Conservation provisions of the Farm Bills (Food Security Acts)
Costal Zone Management Act
N. American Wetlands Conservation Act
Wetlands: Kashian definition
periodically or permeated flooded by surface or ground water. They have to support some kind of vegetation that has adapted to saturated soil
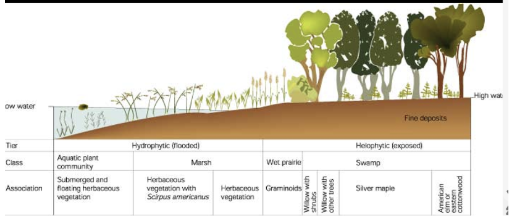
Wetlands: general definition
-wetlands include emergent macrophyte (if it comes out of the water its a macrophyte)-dominated portions of lake fringing communities (including small lakes and protected embayments of large lakes), as well as marshy areas associated with streams, and marshes, bogs, swamps, fens, and flooded woodlands
Difficult to define
Hydric soils= soils saturated with water
Typically anaerobic activity (low oxygen)
If you’re saturated, you’re normally low oxygen
Wetlands: technical definition
National classification system (USFWS 1977): “land where the water table is at, near, or above the land surface long enough to promote formation of hydric soils or to support the growth of hydrophytes”
Gosselink and Turner: “areas flooded frequently enough so that roots of emergent vegetation exist in an anaerobic environment”
-They used to be seen as a transition state. Now we know they’re their own thing
History: wetland science emerged as a subdiscipline of ecology in the late 1970s
Conservation groups became concerned over wetlands losses
Public began to appreciate the unique ecological functions and social values that wetlands provide
Driven by policy debate, managers needed a scientifically-based definition and criteria to delineate and classify wetlands
The issues of wetlands definition and delineation illustrates the interplay of science, public policy, and values
Liberal, strictly scientifically-based definition provides maximal protection of wetlands, but with social, economic, and political costs
USFWS definition describes the unique conditions under which wetlands preform ecological functions that humans value
More restrictive definition preserves individual property rights, allows more flexibility to accommodate social and economic pressures, but at the cost of certain ecological services and resource values that are not accounted for in our economic system
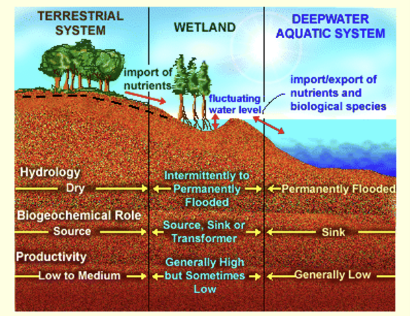
Connection of wetlands to other systems
pic
How do we define (delineate) wetlands?
-Wetland scientists provide the answer (3 legged stool)
Hydrology
Hydric soils
Hydrophytes
Plants that can handle the low oxygen of the soil because the soil is always saturated
Hydrology criterion
Lands that are inundated or saturated to within 18’’ of the soil surface for > 7 consecutive days during the growing season

Hydric soil criterion
Soils, recognizable by their color, physical structure, and chemical characteristics, that have developed under anoxic conditions associated with saturation or inundation by water
Hydrophytic vegetation criterion
Lands that support a preponderance (more plants than not) of plants that are adapted to growing under conditions of substrate inundation or saturation
The devil is in the details: specific criteria to satisfy different purposes
-Scientific definition (USFWS)
Serves an heuristic purpose
Objectively broad
One or more criteria must be present
Generally liberal
Parameters tied to function (e.g. 7 days inundation)
-Regulatory definition (USACE)
Serves social, political, or economic purposes
Subjectively narrowed
All three criteria must be present
More restrictive parameters (e.g. 21 days inundation)
target/meijer ponds
People will put ponds in target or meijer parking lots if they destroy a natural wetland because then TECHINICALLY there is no net loss
what happens when a soil is saturated or inundated
Water acts as a barrier to diffusion of O2 into pore space from atmosphere
Aerobic respiration by soil organisms depletes O2 within 7 days when the temperature is above biological zero
Respiration continues via alternative pathways in which soil microbes oxidize organic matter by using a sequence of different molecules as electron acceptors
pic
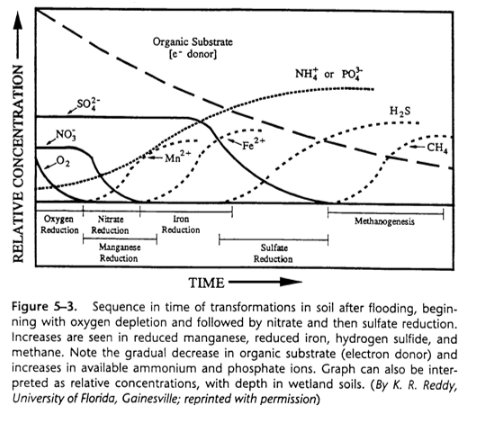
What happens to terrestrial plants and animals?
Macrophytes and metazoan animals respire aerobically (O2 is final e- acceptor in respiration)
Reduced compounds are generally more toxic than oxidized compounds
So lack of O2 is a stressor that wetland-dependent species must be adapted to
Some adaptions of wetlands-dependent species: plants
Rigid, highly vascularized stems
Active diffusion of O2 to roots
Carbohydrate storage
Alternative metabolic pathways
Reproductive strategies- seed dispersal, germination, and growth requirements
Some adaptions of wetlands-dependent species: animals
Morphology-locomotion in water
Morphology-feeding in water
Anaerobic respiration (driving reflex)
Seasonal movement and/or aestivation strategies
Reproductive strategies- oviposition and development and care of young
Wetlands dogma
-Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems in the world
Some types of wetlands are NOT very productive
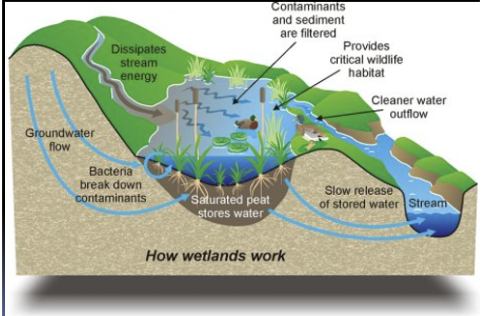
-Wetlands act as “sponges” on the landscape
Can hold rainwater and help prevent flooding
-Wetlands are the “kidneys” of the landscape
Chemical contaminants will some into the wetlands, and the carbon there will hold onto the toxicity, and the water will come out clean
-Wetlands are hotspots of biodiversity
Wetland functions depend on the location of the wetland within a watershed
Isolated wetlands are the “sponges” and “kidneys”
Lake margin wetlands are kinda a transition region
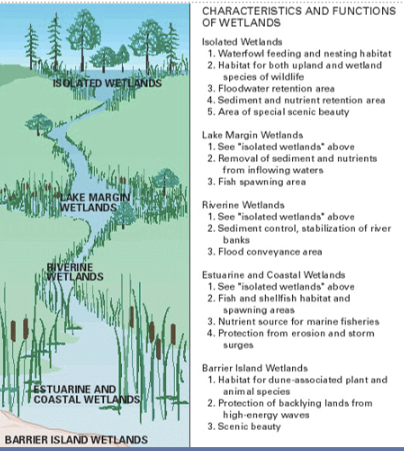
Purported ecological functions and values of wetlands: hydrology
discharge and recharge groundwater, regulate surface water flows and sedimentation
Purported ecological functions and values of wetlands: nutrient cycling
transform or sequester nutrients and chemical contaminants
Purported ecological functions and values of wetlands: habitat
support biological diversity, recreation
Purported ecological functions and values of wetlands: habitat: trophic support
provide food and fiber products
wetland values/functions
pic
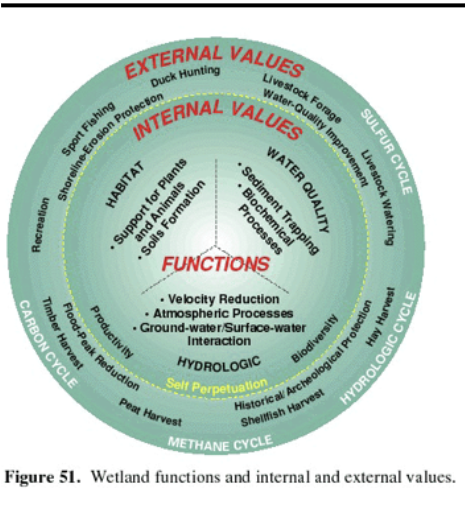
Hydrology functions: regulation of surface water flow and sedimentation
pic
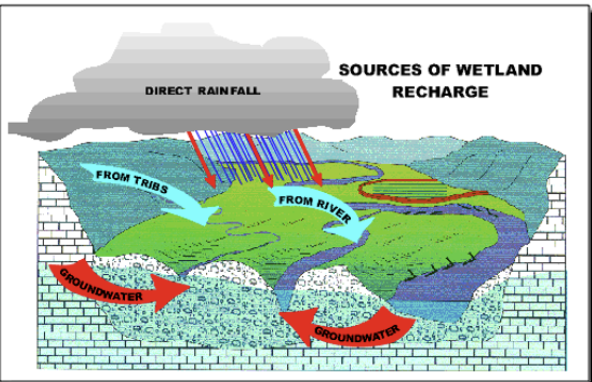
Water Quality Functions: biogeochemical cycling
pic
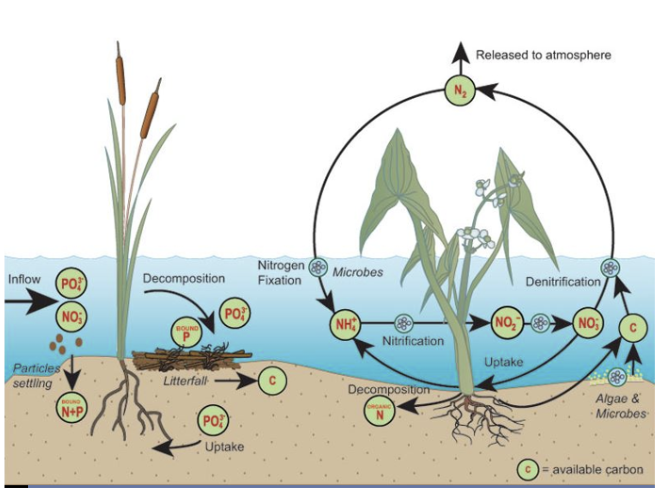
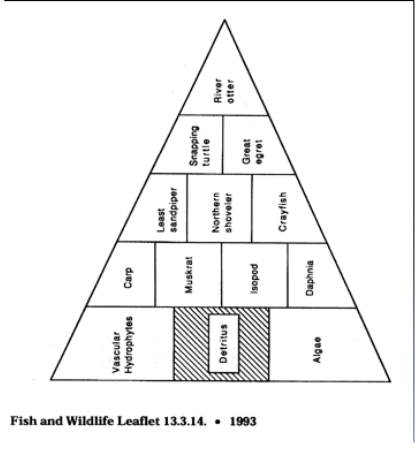
Habitat and trophic support functions
Wetlands are detrital-based systems
! Know this
Decaying plant matter supports invertebrates that are utilized by consumers

biodiversity scores
Center of a lake/ocean, biodiversity is very low, fish are the obvious exception for this, not a lot of fish by the dirt
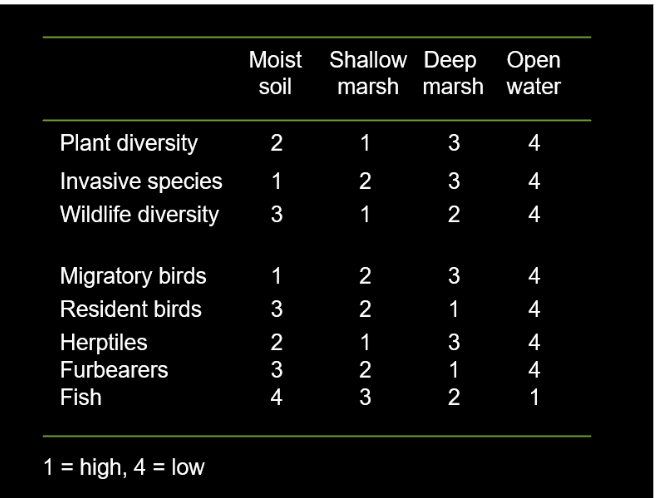
Total economic value of wetlands
helpful since most people are driven by money
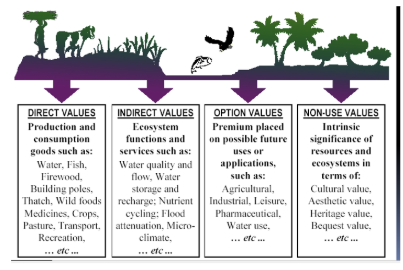
wetland functions
Habitat: nesting, spawning, rearing and resting sites for aquatic and land species, food chain production
Hydrology: protection of other areas from wave action and erosion, storage areas for storm water and flood water, ground and surface water aquifer recharge
Water quality: water quality protection, water filtration and purification, treatment of nonpoint source runoff
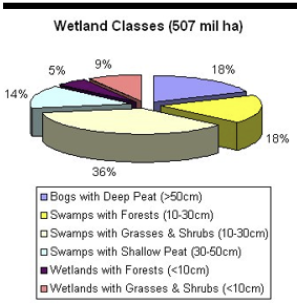
Types of Aquatic systems: Wetlands
Water table is at surface or within 1m of surface
Vegetation and soils similar to submersed, littoral areas
Can be lentic, lotic, fresh, or saline
Swamps (contain shrubs and trees, woody plants), marshes (contain grasses, no trees), bogs (dominated by mosses)
! Know these differences
Are among the most productive biological systems on earth
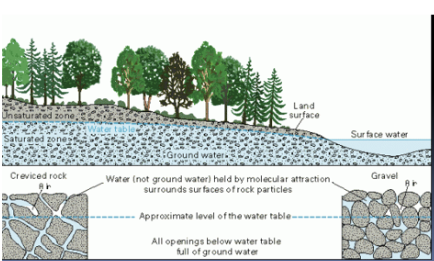
Wetlands: controlled by soil type, climate, source and rate of water input
Open, high energy systems: with significant flow-through of surface water (usually contiguous with lake or stream)
Closed, low energy systems with little or no surface flow

Major freshwater wetland types: northern wetlands
Bogs and peatlands (organic-filled kettle lakes), permanent
Major freshwater wetland types: deepwater swamp
Continually filled, SE United States
Major freshwater wetland types: riparian (means river)
Adjacent to rivers (floodplain areas), high water table, seasonal
Major freshwater wetland types: swamps
(hardwood and shrub swamps), unlike marshes, are dominated by woody shrubs and trees
Major freshwater wetland types: bogs
peatlands, usually lacking an overlying layer of mineral soils
Major freshwater wetland types: vernal pools
Are, literally, spring pools that tend to fill up in spring and dry up in summer. Biological activity peaks in spring
Major freshwater wetland types: forested floodplain wetlands
Develop along larger rivers
Major freshwater wetland types: prairie potholes
Are shallow depressions scattered across the upper Midwest and the Dakotas that were carved out by retreating glaciers some 10,000 years ago
wetland designation
Both scientific and legal definitions vary greatly
Of concern because of high value of drained wetlands to agriculture and urban development (S)
When you drain a wetland, that soil is very nice
Still unclear

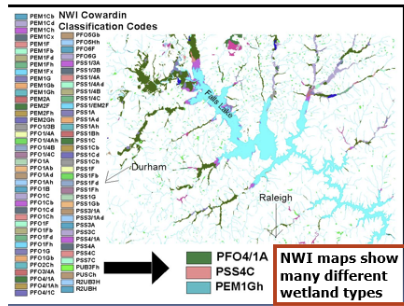
Example of National Wetland inventory (NWI) Map
the U.S. Fish and Wildlife service’s national wetland inventory (NWI) uses what is called the Cowardin classification to classify wetlands. This classification system is used by scientists and resource managers nationwide. This complex system can be difficult for the average user to interpret
Wetland values
maintain biodiversity
Provide habitat for animals
Maintain water quality
Support commercial fishing, forestry
Nutrient uptake from watershed
Nitrogen compounds converted to N gas
Play a huge role in the matinance of our atmosphere
Reduce flood damage
Hiking, fishing, hunting, bird watching, boating
Aesthetic value
Carbon sequestered into plants
support hydrophytes (plants that are adapted to living in wet, saturated, low-oxygen soils)
General importance
-A wetland is an “ecotone” between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, which functions in
Habitat for organisms from both primary ecosystems
Alteration of material transport to the water, often including a nutrient sink by uptake in the vegetation (although there are limits to this that can be overwhelmed by excessive inputs)
Water regulation- as in a sponge, the wetland soil and vegetation matrix holds large quantities of water and retards rapid surface flow-through
Why are they threatened?
-Wet soil is not perceived as readily useful to humans
-Drained for agriculture- then its super useful
-Fluvial wetlands (river floodplains)
-Drained for urban development (part of Boston was a wetland area; Netherlands was diked)
-Loss varies by region
Iraq (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers)- drained in 1990s as punishment to indigenous people
US (drained “black swamp” coastal wetlands of great lakes of indiana and ohio 1800s)
Illinois- 85% of wetlands drained
Indiana- 87% lost
Ohio- 90% lost
Mitigation techniques: replacement
If you get rid of a wetland, you can just replace it
Obviously not the same as the original wetland

Mitigation techniques: reclamation
Trying to bring an established wetland back
Has greater success than replacement

How wetlands work pic
pic