Chapter 8: Competitive Firms & Markets
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Market structure is a function of:
# of firms in the market
# of buyers
Ease of entry/exit
Ability of firms to differentiate their products
Perfectly competitive firms are
price takers
because of this, the demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic (horizontal line)
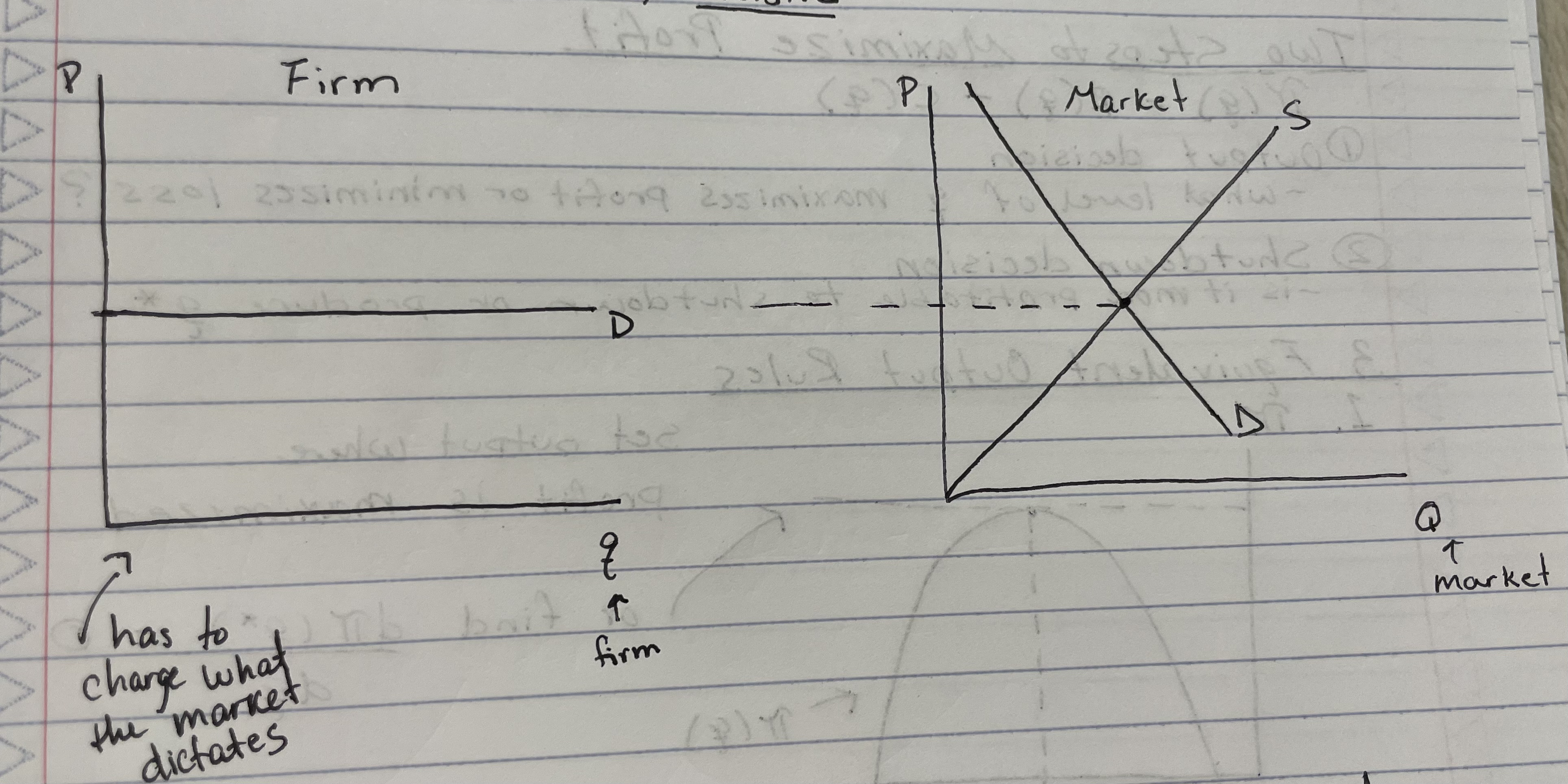
5 key characteristics that force perfectly competitive markets to be price takers
Many small buyers and sellers
Firms sell identical products
Buyers and sellers have full information about price and product
Low transaction costs
Firms can freely enter/exit the market
What is economic profit?
Profit = R - C
What is the firm’s profit function? π
π(q) = R(q) - C(q)
To maximize its profit, any firm must answer two questions
Output decision - what output level, q*
maximizes its profit or minimizes its loss?Shutdown decision - is it more profitable to produce q* or shutdown?
1st output decision rule:
The firm sets its output where its profit is
maximized.
2nd output decision rule:π
The firm sets marginal profit equal to zero.
(necessary condition) marginal profit = dπ(q*)/dq = 0
(second order condition) if second derivative of marginal profit is negative
3rd output decision rule:
Set output where MR = MC
What are the shutdown rules in the SR?
Assume profit < 0
In SR, C = F + VC
if VC = 0, R = 0 → shutdown
if R > VC or P > AVC → stay open
What are the shutdown rules in the LR?
In the long-run, all costs are avoidable, therefore a firm should shutdown if making a loss
In perfect competition, MR is equal to
MR = D = P
In perfect competition, to maximize profit P =
P = MC(q^*)
What does a positive profit in the SR look like for perfect competition
P > AC
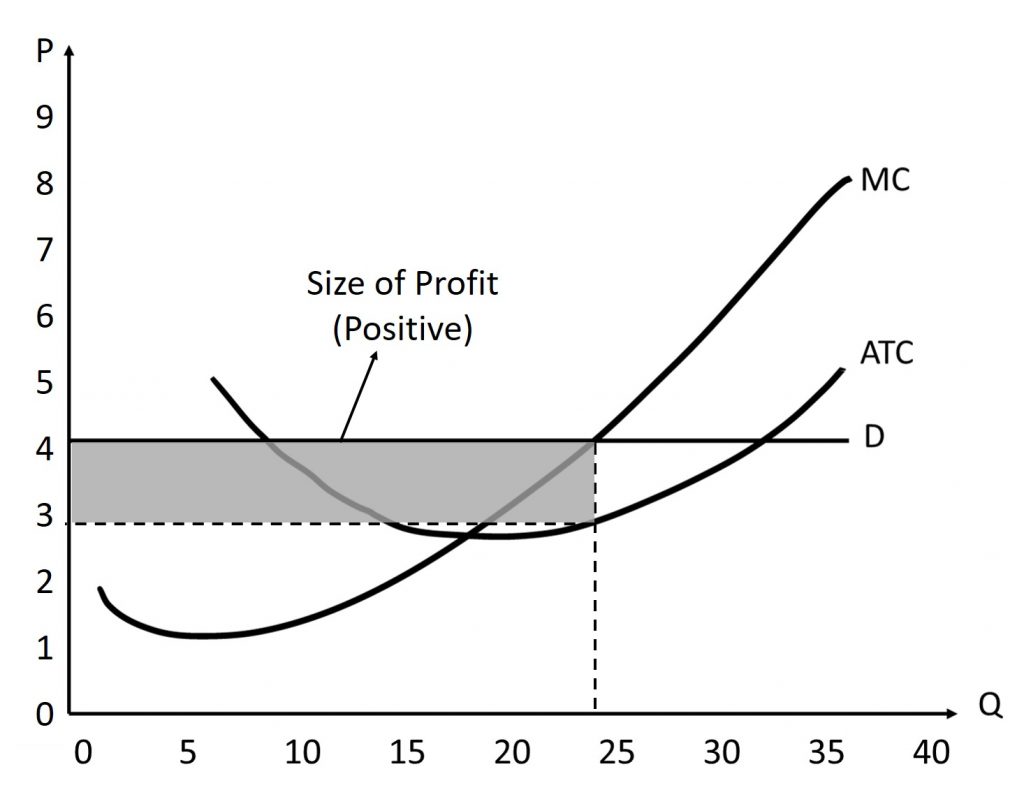
What is the formula to calculate profit given a cost function? π
π(q) = (P - [AC(q)])q
When do you have negative profit in the short run?
if P < AC
What does a negative profit in the SR look like for perfect competition
P < AC
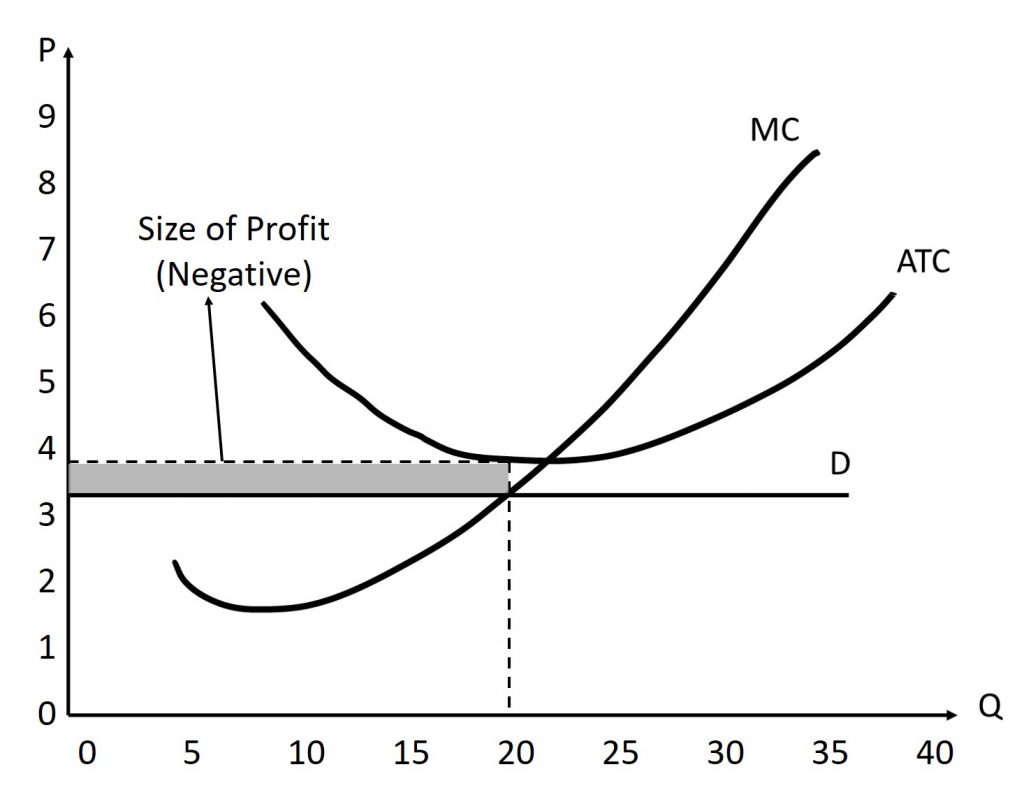
Another way to calculate FC
(*Think graphically)
FC = (AC - AVC)q
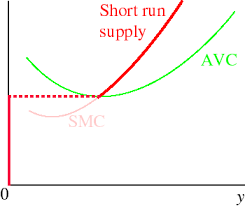
As long as P is above ____, stay open
AVC
Whenever P is below AVC,
shut down
When is a firm breaking even?
When P = AC
(or MC = AC)
In the SR: the competitive firm’s short-run supply curve is its
MC curve above minimum AVC curve

In the SR, number of firms __
does not change
(so no entry or exit)
the more identical firms producing at a given price, the _____ the short-run market supply curve at that price
flatter (more elastic)
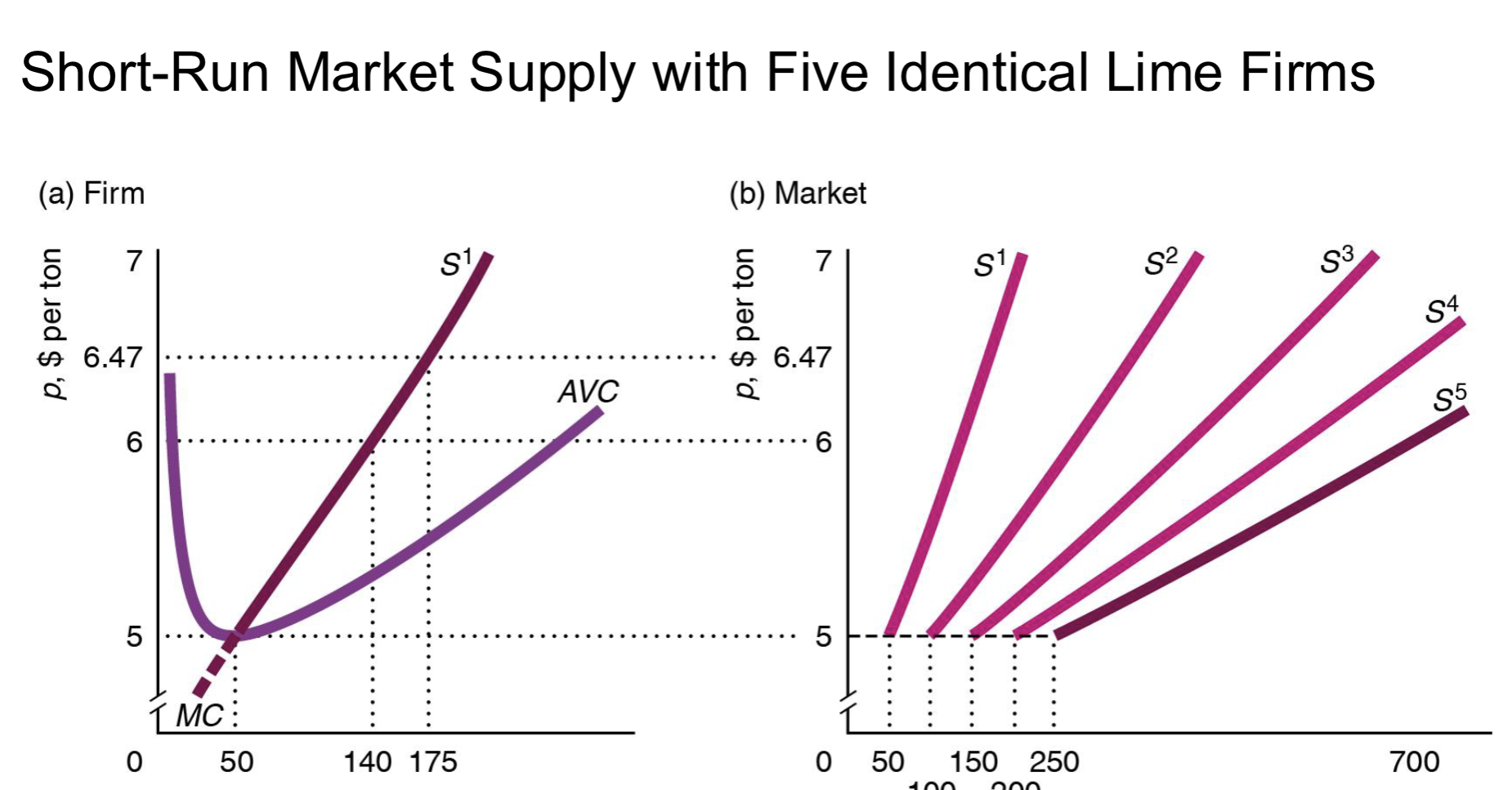
How to find the total amount the market produces with identical costs in the SR?
You have n (number of firms), cost function, market demand
Find:
MC
Set MC = P (to find q, firm’s SR supply curve)
Given that Q = nq find market supply Q(P)
Find equilibrium P and Q (set market demand = market supply)

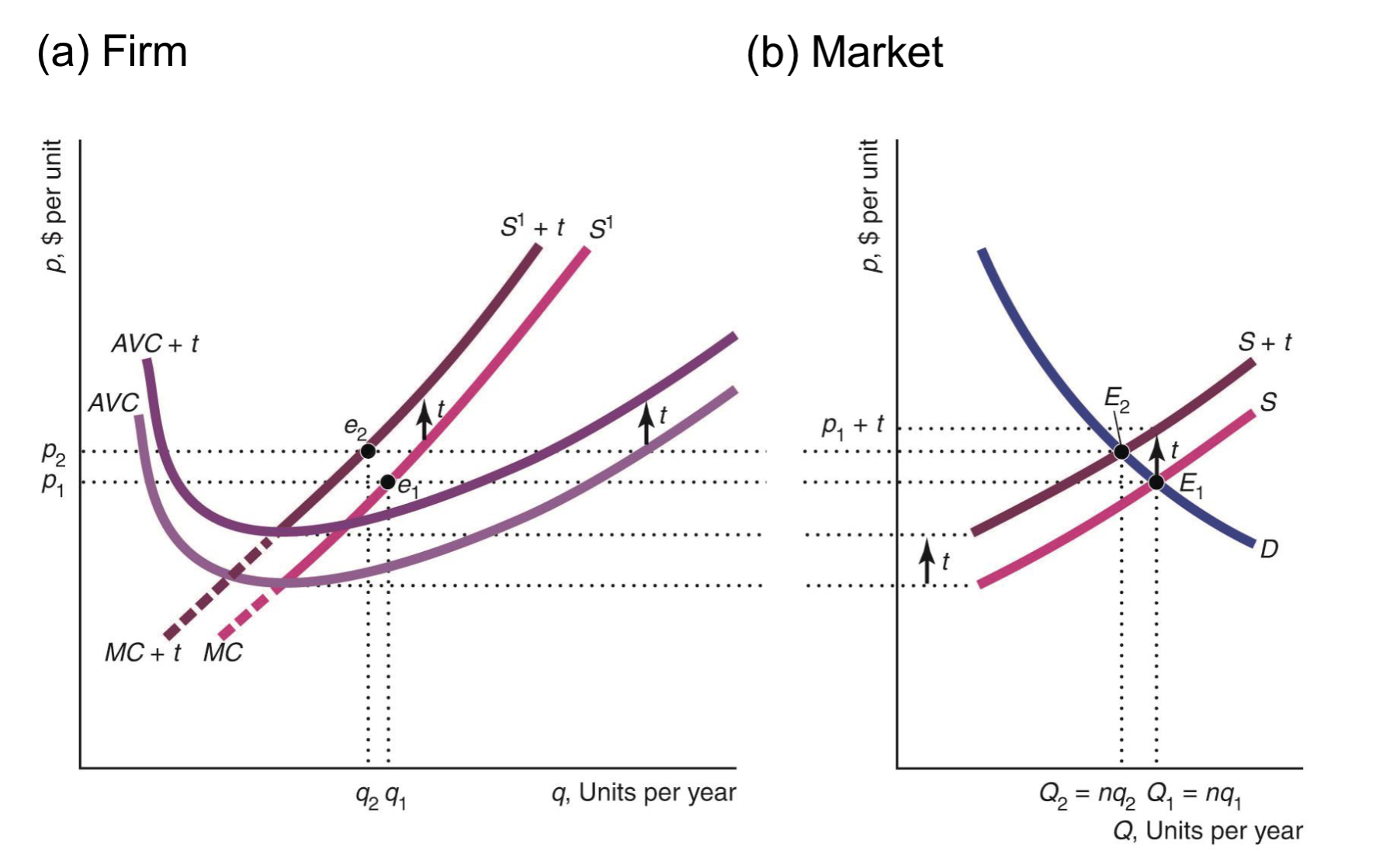
In the short-run, what is the effect on the supply curve when there is a specific per unit tax? (4)
The AVC shifts by the tax
Supply shifts left by size of tax
Q decreases, P increases
Incidence of tax is paid shared by consumers and producers (more so depending on which side is more inelastic)
When do firms enter and exit the market in the long-run?
If profits > 0 → firms enter
If profits < 0 → firms exit
(firms indifferent if profit = 0)
In the LR, firms make ____ economic profit
0
Where do LR competitive firms operate?
marginal profit = 0 & where MR = MC
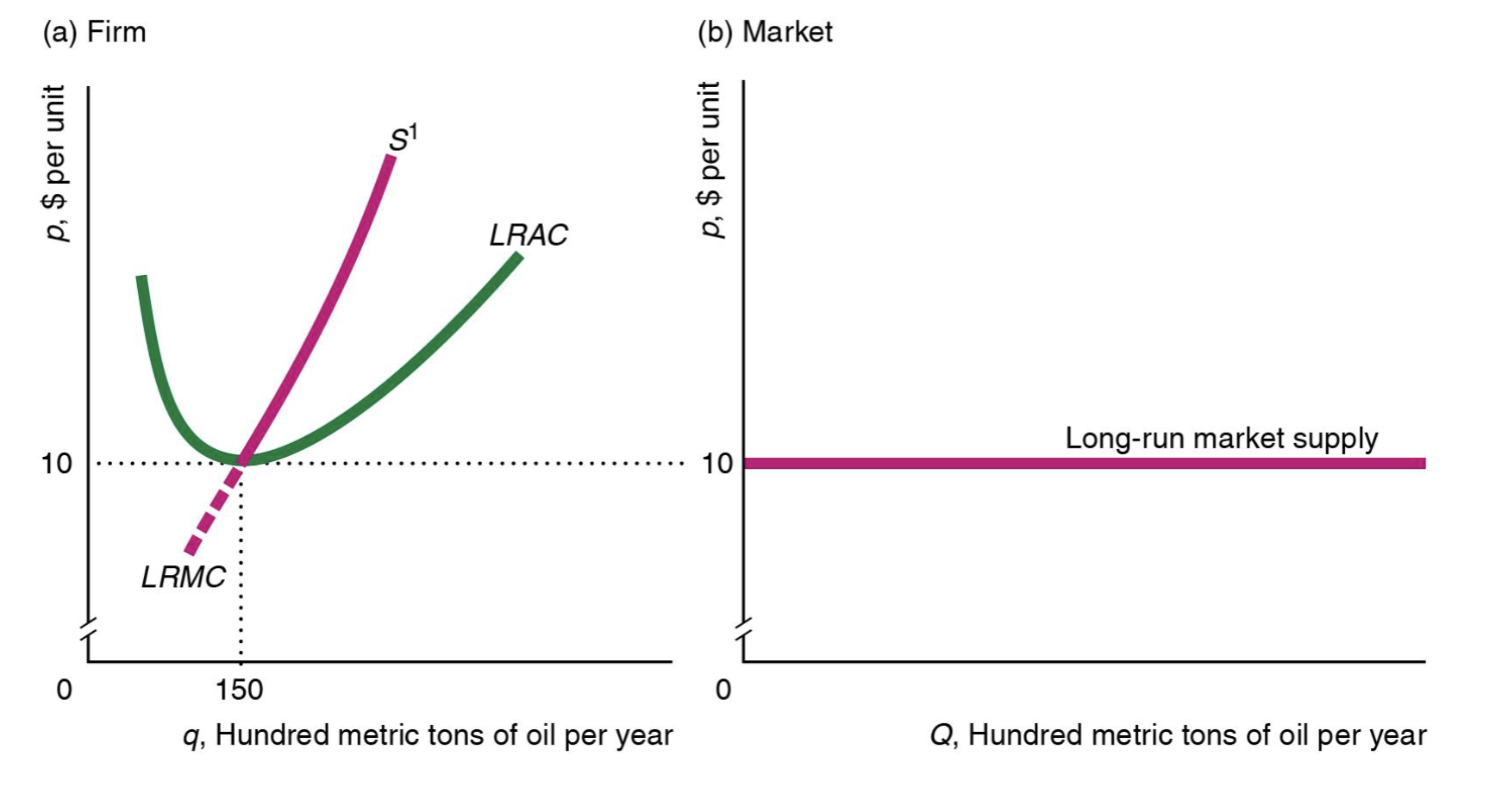
If firms can freely enter and exit the market (and input prices are constant and firms have identical costs), what does the LR market supply curve look like?
No matter what happens, profit always leads to 0, which leads to the flat LR market supply curve
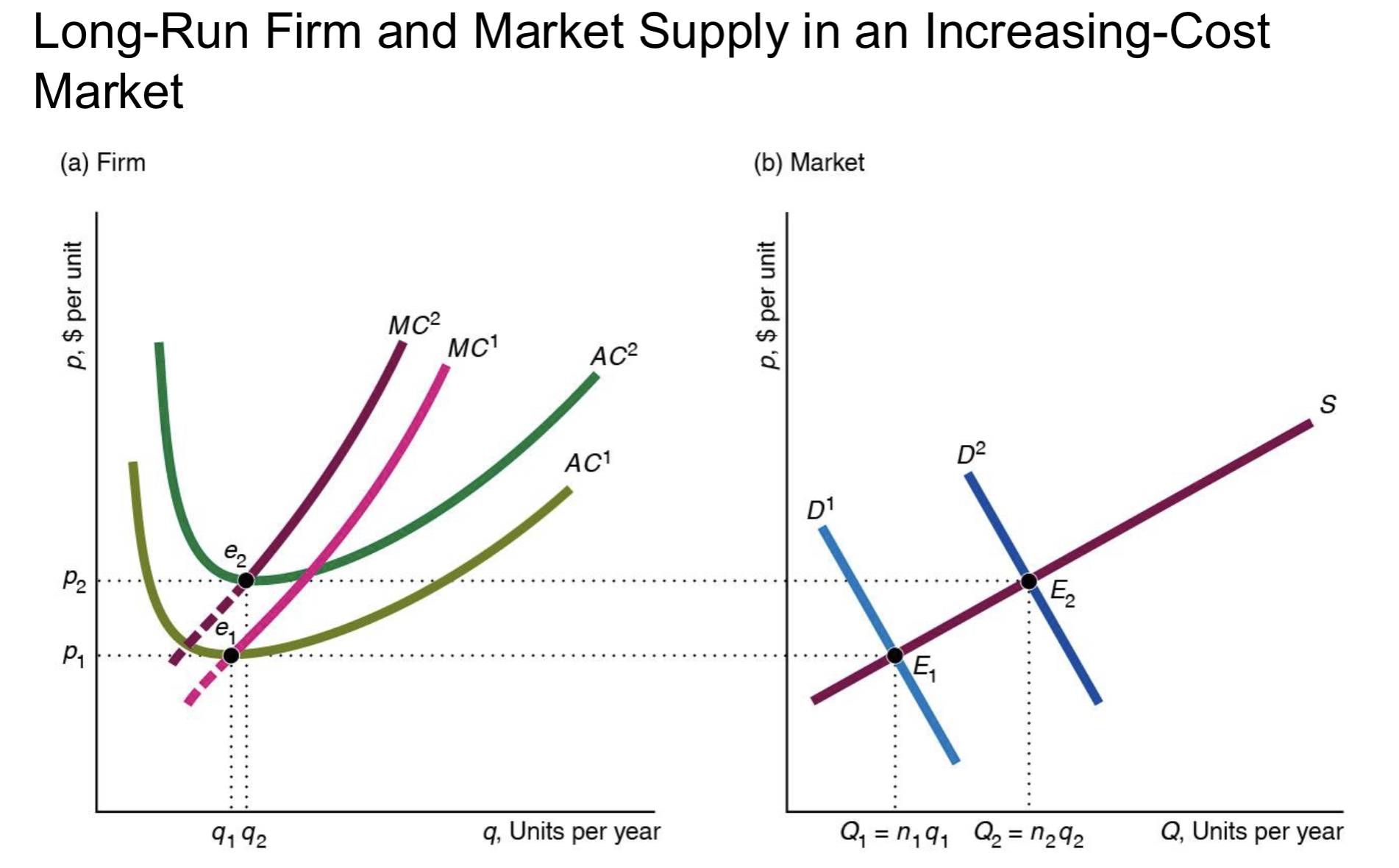
What does the LR market supply curve look like when entry is limited?
it is upward sloping
(The number of firms is limited if the government restricts the number, if firms need a scarce resource, or if entry is costly.)
Can there be downward sloping LR market supply curves?
Yes, it may be a decreasing cost industry as it grows
Method to minimize AC
Take the derivative of AC function and set it equal to 0
(dAC/dq = 0)
(or set MC = AC)