BIO 2100 Exam 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
the study of ligaments and related joints
Syndesmology
True or false: more joints in childhood than adulthood
true
Classify these: Sutures, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis
Fibrous Joint
Classify: Primary & Secondary Cartilaginous Joints
Cartilaginous Joint
Ball & Socket, Saddle, Condylar, Ellipsoid, Hinge, Pivot, Plane joints
Synovial Joint
3 Functional classification of joints
Synarthrosis, Amphiarthrosis, Diarthrosis
Where bones are bound by tough, fibrous tisse
Fibrous Joint
True or false: Fibrous joints require strength and stability
true
Sutures are between flat bones in skull
true
sutures are immovable joints
ture
sututres have limited movement until age 20
true
Gomphoses are immovable joints
true
where are gomphoses found?
teeth sockets in the maxilla and mandible
Syndesmoses are slightly moveable
true
give examples of syndesmoses
radioulnar joint, middle tibiofibular joint
Synchondrosis are immovable
true
What unites the bones at a symphysis joint?
fibrocartilage
examples of symphysis
pubic symphysis, joints between vertebrae
Synovial joints are freely moveable
true
synovial are the least common joint in body
false, most common
example of a hinge joint
elbow joint, ankle joint, knee joint
what action do hinge joints do>
flexion and extension
how many planes do hinge joints permit?
one plane
examples of a condylar joint?
knee joint, temporomandibular joint,
Examples of an Ellipsoid Joint
wrist joint, atlanto occipital joint
example of a ball and socket joint?
hip and shoulder joint
example of synarthroses
sutures
what is the functions of synaarthroses?
fixed joints where there is no movement
example of Amphiarthrosis
intervertebral discs
function of Anphiarthrosis
joints where slight movement
example of Diathrosis
all synovial joints
function od diarthrosis
freely moveable joints
name the labeled parts
1: articular cartilage
2: synovial layer
3: fibrous layer
4: joint cavity
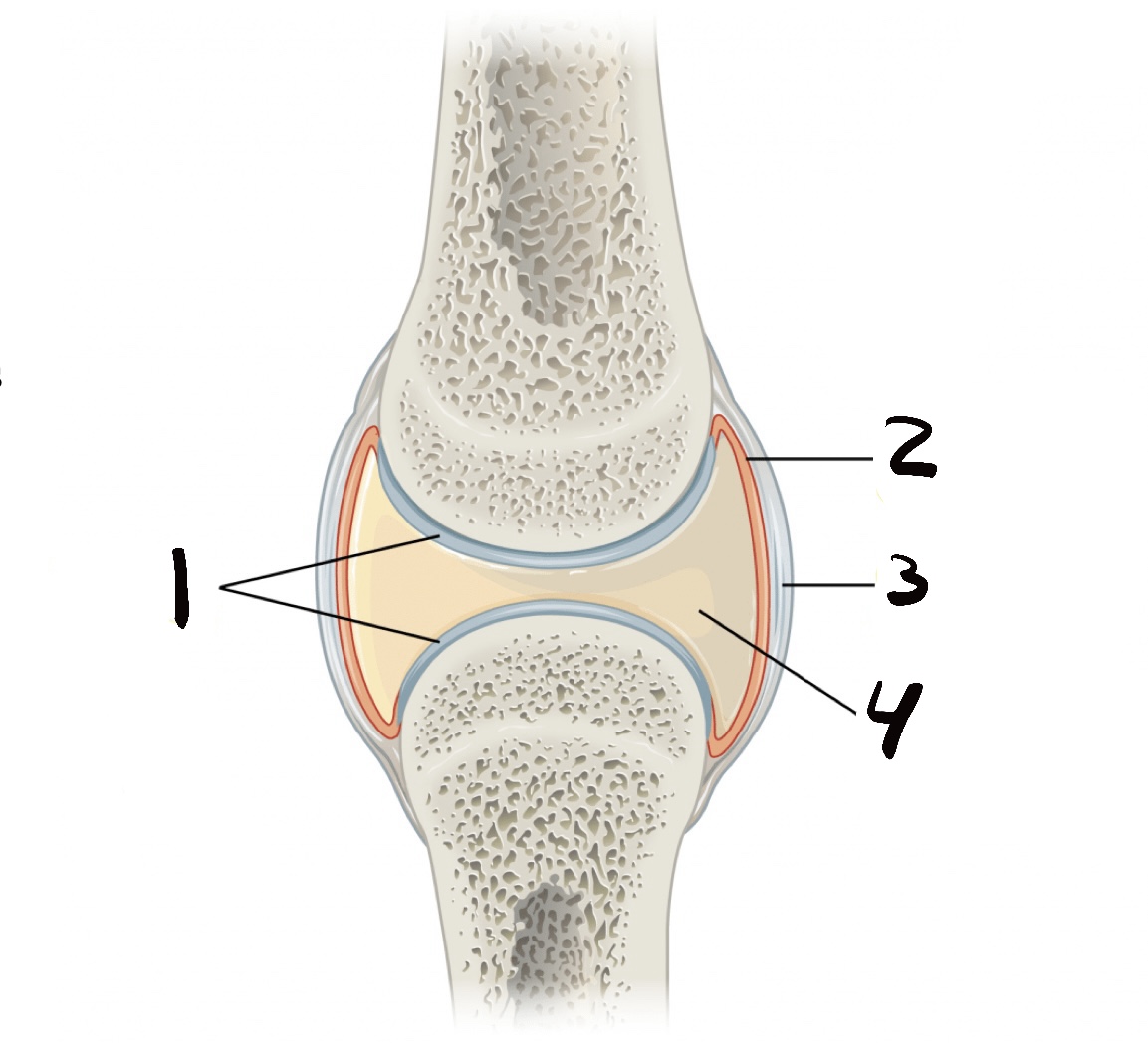
what is the fibrous layer called?
capsular ligament
What is hilton’s law?
nerves supplying joint must also supply the muscle and skin
connective tissue layer covering each muscle fiber
endomysium
layer covering bundles of muscle fiber
Perimysium
covering entire muscle
Epimysium
Light area
I Band
dark area
A band
thin dark line
Z Line
mid region of A band
H band
middle of H band
M line
all muscles of the face are innervated by the facial nerve
true
circular muscle around the eye
orbicularis oculi
outer orbital part function
forcefully shuts eye
Inner palpebral part
gently closes eye
buccinator action
moves mouth side to side
temporal fossa is where you find muscles of mastication
true