3.3b Macroeconomic Objectives - Unemployment
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Definition of workforce/labour force
those who are legal, capable, and willing to work
not the same as working-age population, as housewives/students are not actively seeking jobs => unwilling to work
calculated by
workforce = # of employment + # of unemployment
Factors affecting the size of workforce
school-leaving age
retirement age
number of net migration (# of immigration- # of emigration)
income tax rate
amount of unemployment benefits
definition of unemployment
those who are legal, capable, and willing to work but fail to find a job
unemployment rate = (# of unemployment ÷ workforce) x 100
Difficulties in measuring unemployment
Hidden unemployment
Discouraged workers - those who have been unemployed for a long time and are no longer finding a job —> excluded from calculation of unemployment (only those actively seeking a job in the past 4 weeks are included)
∴ there are people who are jobless, but not included in the unemployment figure
Underemployment
part timers: classified as employed as they have a job, but want to work as full time, so their income is not as high as they want
over-qualification: under-utilisation of an employed population. technically employed, but their skills and abilities are not fully utilised
Disparities
regional: rural areas have higher unemployment rates than urban areas (varies among regions in a country)
ethnic: ethnic minorities usually suffer from higher unemployment rates than the national average/locals (i.e. Southeast Asians in HK)
age: younger populations suffer from higher unemployment rates (2017, US - 9% youth unemployment rate, compared to national figure 4.2%
gender: female unemployment rate is usually higher in industrialised economies due to education levels and employer discrimination. (2017, India - 4.2% female unemployment rate, compared to national figure 3.5%). mainly for primary sector
types of unemployment
cyclical unemployment (related to business cycle)
natural unemployment (unrelated to business cycle)
structural unemployment (mis-matched skills)
frictional unemployment (between jobs)
seasonal unemployment (demand for job changes due to weather/climate)
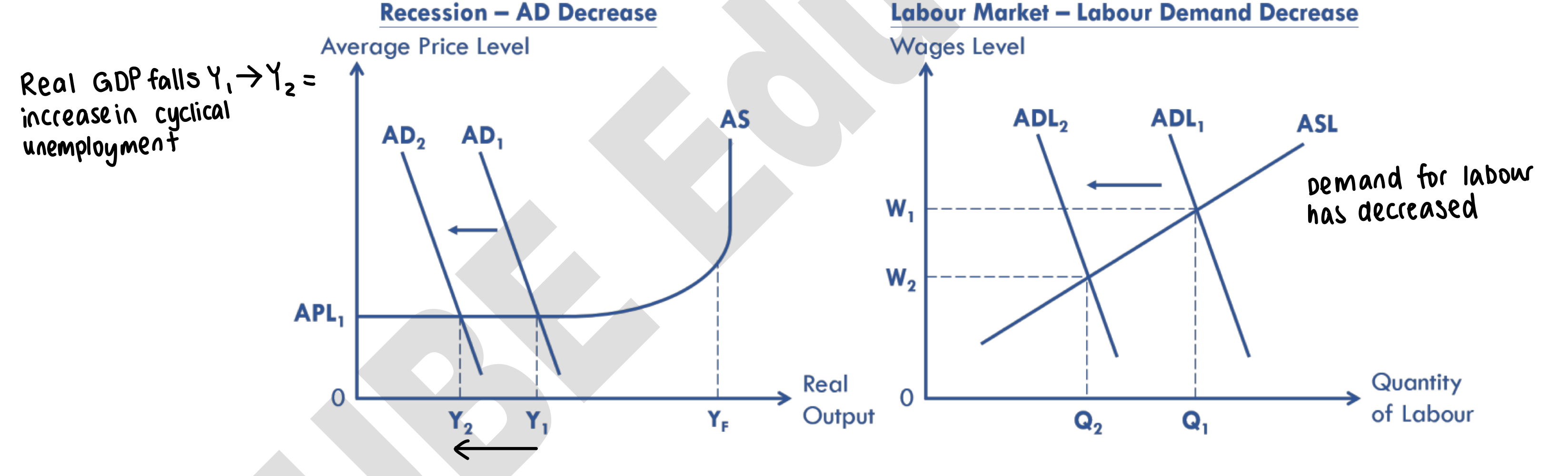
cyclical unemployment
occurs when there is economic recession (less economic growth)
in a recession, househols have lower disposable income + lower consumer confidence —> consumption decreases —> firms have less revenue and profit to hire labours
households’ demand for G&S fall —> fall in consumption —> fall in AD
firms’ demand for labours decrease —> rise in unemployment
natural unemployment
lowest level of unemployment an economy may reach (unemployment # when the economy is producing at the potential output level)
implies that even though the labour market is at equilibrium and there is a boom, and there is no cyclical unemployment, there are always still jobless people
structural unemployment
mismatches between skills and knowledge possessed by labours and the skills required by the job vacancies
caused by a change in the type of labour demanded
causes
occupational immobility of labours: labourers are unable to switch industries when there are industrial changes or technological advancement, caused by lacking skills & knowledge
industrial changes: the entire industry declines, causes a permanent fall in demand for these particular skills. E.g. de-industrilization of Hong Kong in the late 1980s - demand for manufacturing labours decreased
increasing use of technology: capitals goods and labourers may be substituted, labours may be replaced, and need to learn new skills
geographical immobility of labours: unable to move from one region to another to seek a job, caused by:
imperfect information on job vacancies
high money costs of moving to another region
high regional difference in living costs
social/family ties
wage rigidities/inflexibilities: real wage level is higher than the equilibrium wage level causing Qd<Qs of labour, caused by:
minimum wage set by government
power of labour union (can ask for higher wages)
unexpired employment contract

frictional unemployment
unemployment period of the original and new job.
always present as it takes time to find a job
professionals don’t really lose their jobs
lots of job opportunities for non-professionals
seasonal unemployment
caused by regular and periodical changes in demand for certain goods and services, usually due to weather or climate
same every year —> workers know how to survive —> not significant stress
e.g. life guards, skiing coaches
economic costs of unemployment
economic recession
worsens the government’s budget
reduction in tax revenue
increase in unemployment benefits expenditure
widen income inequality
personal costs of unemployment
lower standards of living
deskills of labour
increase in stress levels & family breakdown
social costs of unemployment
increase in criminal rates
social disintegration