OCR GCSE Economics (9-1) Paper 1
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
What are the three economic groups?
Consumers, Producers, Government
What is a consumer?
People that use goods or services. They are the end users of a product.
What is consumption?
spending on goods or services by households. Consumption is the largest proportion of aggregate demand in the economy.
What is a producer?
individuals, groups of individuals or governments that supply goods or services.
What is the government?
looks to meet the needs of society
What is meant by a good?
A good is a tangible product - it can be seen or touched.
What is meant by a service?
A service is an intangible product - it cannot be seen or touched.
Explain the interdependence of the economics groups.
Consumers buy off producers, allowing them to make a profit. Consumers pay taxes to government, helping it to provide goods and especially services to benefit society. Producers supply goods and services to consumers, other producers and government. To do this, they pay and employ people, who will become their customers. Government looks to meet the needs of society. To do this, it will spend on goods and services that it deems appropriate. Many of these will be bought from producers and supplied to consumers.
What are factors of production?
economic resources used in the production process to add value to factor inputs by creating factor outputs.
What are the factors of production?
Land, Labour, Capital and Enterprise
What is land?
natural resources from the earth sea and sky e.g. oil, coal, trees, the sea or farmland.
What is labour?
The available skill of all of the workforce in an economy.
What is capital?
the man aids to the production process. Machinery, tools, offices, factories.
What is enterprise?
the risk taken by an entrepreneur by combining the other factors of production to produce products that will be profitable.
How are the factors of production combined?
An entrepreneur will decide on the quantities of the other factors of production to combine and organizes them to create factor outputs.
What is meant by scarce resources?
when there isn't enough of something to satisfy all wants and needs.
What is meant by unlimited wants?
Unlimited wants are the infinite desire for something.
What is a need?
A need is something a consumer has to have to survive e.g. water, shelter and food.
What is a want?
A want is something a consumer would like to have, but which isn't needed for survival e.g. a new phone, a laptop, makeup, a car.
What is meant by the basic economic problem?
when there are finite resources available to satisfy unlimited wats and needs.
What are the three economic choices(about how to use scarce resources?)
What should be produced? How should it be produced? Whom should it be produced for?
What are economic choices?
Those made due to the scarcity of resources. an option for the use of scarce resources
What is the purpose of economic activity?
the production of goods and services to satisfy the wants and needs of society.
What do economic groups make choices based on?
the satisfaction or utility gained. For consumers, this will also take into account disposable income.
What is opportunity cost?
the cost of the next best alternative given up
What is meant by economic sustainability?
the best use of resources in order to create responsible development or growth, now and into the future e.g. Employment, growth, government spending, taxation, costs of production, price
What is social sustainability?
the impact of development or growth that promotes an improvement in quality of life for all, now and into the future.
What is environmental sustainability?
Environmental sustainability is the impact of development or growth where the effect on the environment is small and possible to manage, now and into the future-(non) renewable, pollution ,climate change, the availability of future resources.
What is the role of producers?
make and supply goods and services by combining the factors of production. They influence market prices. Often producers aim to sell goods and services to make profit. Help to influence market prices. Important in economic system as they employ workers and pay their wages.
What is the role of individuals as producers?
Individuals can be producers of non-market goods and services e.g. child-minding, cooking and cleaning. These producers may only work part time. Others are self-employed and work directly for themselves. These individuals produce goods and services that enter the market. They work for themselves and thus keep all the profits e.g. market traders, joiners, plumbers
What is the role of firms as producers?
Supply goods and services to consumers to make profit.
How is the government a producer?
Governments are producers of a range of services. They mainly supply services to society
What is production?
Production refers to the total output of goods and services produced by a firm or industry in a period of time.
What is productivity?
Productivity is one measure of the degree of efficiency in the use of the factors of production in the production process..
Evaluate the importance of production for an economy.
higher production may lead to an increase in employment, unless greater productivity causes it - increase in profits for firms and the industry- larger economies of scale- increase in market share if production of one firm increases as against that of other firms.- economic growth for economy- rise in standard of living as consumers have more goods and services to buy. However, Diseconomies of scale could also arise which results in average cost of production increasing as the firm grows in size.
How is productivity measured?
Productivity is measured as Total output/total input.
In the case of individuals, what is higher productivity likely to be rewarded by?
Higher wages. Increase in standard of living.
Evaluate the importance of productivity for an economy
lower average costs and increasing economies of scale (makes firm more competitive so that it can decrease prices and/or compete more effectively on a world scale. Will benefit the economy by increasing gross domestic product (GDP) through greater consumption and more exports. This then also improves the balance of payments. greater profits, allowing firms to pay higher wages to attract the best workers, and reinvest in new equipment and research. Investment will increase competitiveness and GDP. Higher wages will benefit the economy by encouraging people to get better qualifications and to improve their skills. However, if a firm increases productivity by using capital equipment in place of labour, this may increase unemployment. Will have immediate effect of causing the government to have to support the worker and their family through benefits - increased productivity leads to greater international competitiveness, which may lead to other countries retaliating, leading to a fall in GDP.- productivity increases total output of economy and is likely to lead to greater employment and higher wages, which then leads to greater government revenue through taxes. more competitive firms will lead to greater exports and thus further economic growth
What are total costs?
Total costs (TC) consists of the variable (VC) and fixed costs (FC) of production. all the costs of a firm
How are total costs calculated?
Total Costs (TC) = Total Fixed Costs (TFC) + Total Variable Costs (TVC).
What is average cost?
Average cost is the cost of producing a unit (unit cost of production).
How is average cost calculated?
Average cost (AC) = Total cost (TC) / Quantity (Q)
What is total revenue?
Total revenue (TR) is the total income of a firm from the sale of its goods or services.
How is total revenue calculated?
Total revenue (TR) = Price (P) x Quantity (Q)
What is average revenue?
Average revenue (AR) is the revenue per unit sold(same as the price of the product)
How is average revenue calculated?
Average revenue (AR) = total revenue (TR) / Quantity (Q)
What is profit?
Profit is when a firm gains more revenue than it pays out in costs.
How do you calculate profit?
Profit = total revenue (TR) - total cost (TC).
What is a loss?
when a company pays out more in costs than it gains in revenue.
Evaluate the importance of revenue for firms.
Without revenue, a producer cannot earn a profit and remain in business in the long run. Low revenue levels, therefore, may lead to a loss and the producer going out of business. An increase in revenue will encourage investors to invest money into the firm, allowing for companies to expand. Steady levels of revenue allow producers to secure loans and favourable interest rates on overdrafts etc. This means that they do not have to worry in the short run whether they can pay workers and suppliers. It also creates confidence in the firm. Workers ae more likely to remain in firms and people are more likely to invest in and supply to firms and allow them to pay later
Evaluate the importance of costs for a firm
A fall in average costs shows that a firm is becoming more efficient (gaining greater economies of scale) and vice versa.If the cost of production falls, then firms can supply more at every price. if costs increase, firms can supply less at every price.Firms try to keep costs under control in order to gain a profit.
Evaluate the importance of loss for a firm
Loss results in a firm closing in the long term as they will run out of money or the people who have lent money will demand repayment. This fulfills the opposite role to profit. If an industry is making a loss, it factors of production will leave it to find an industry that is making a profit. However, it may not matter to a firm depending on whether it has reserves (saved profits) to enable it to continue.
Evaluate the importance of profit for firms.
Profit signals scarce resources to move to firms making large profits. It is a measure of success of investment in a firm by people. It is also an important source of finance, allowing businesses to invest and grow. It allows a producer to attract resources to the firm/industry.
What are economies of scale?
advantages a firm gains by increasing the scale of production, leading to a fall in average costs.
What are internal economies of scale?
Internal economies of scale result from growth within the firm.
What are external economies of scale?
External economies of scale result from growth of the industry or its location. factors outside firm's control. available to all firms, regardless of size
Internal economies of scale: Technical economies
The use of more efficient machines to reduce unit costs.
Internal economies of scale: Purchasing economies
Buying in bulk reduces the cost per item.
Internal economies of scale: Financial economies.
Borrowing from banks at a lower rate of interest. They can also sell assets to raise finance cheaply.
Internal economies of scale: Managerial economies.
Larger firms can afford specialist staff to help increase revenue/reduce costs
Internal economies of scale: Risk-bearing economies.
ability to spread risks and make losses in one market because they make profits in others.
External economies of scale: Infrastructure
Better road and rail makes transportation quicker.
External economies of scale: Education.
A local university could provide a firm with a local skilled workforce.
External economies of scale: Concentration of firms
suppliers may be close to firms, reducing transport costs
External economies of scale: Location.
An area with a good reputation in a certain industry will attract others more companies
What is meant by competition?
Competition is where different firms are trying to sell a similar product to a consumer.
Why does competition take place between producers?
Competition between producers takes place because they are trying to achieve objectives such as profit maximisation or increased market share and customers etc. It can also lead to greater efficiency, as they do whatever is necessary to lower their costs of production. Reduced costs of production can in turn lead to lower prices.
What is price competition?
where firms lower their prices to attract customers and thus gain market share. Any firm that cannot achieve this will lose customers and potentially go out of business.
What is non-price competition?
competition on specialist products, better and more personalised consumer service. conveniently located, quality of the product. marketing also creates consumer loyalty. Buyers are often prepared to pay higher prices for a brand they now, and which has been heavily advertised, rather than an unknown brand or a shop's own make
What does non-price competition often lead to?
Non-price competition often leads to consumer loyalty.
Why do producers compete?
- to enter a market- to survive in a market- to make a profit
Why do producers compete - Market Entry
If a producer wants to enter a market, it has not previously been in, the business must devise ways of persuading consumers to buy the product at a low price. This will then force existing producers to respond = competition.
Why do producers compete?- Survival
To survive in a market, firms often find it necessary to compete for consumers and market share. Existing customers need to be persuaded to return, while new consumers should be enticed to try the product. Firms often extend the range of products they offer as to persuade their customers to buy more goods
Why do producers compete?- Profit
Firms need to make a profit to survive and to grow. Profits provide the means for investment, in order for the firm to expand the business and innovate. Producers that are able to innovate successfully are ten able to compete strongly in the market.
Analyse how competition affects price
If competition increases, supply increases. This increases quantity bought and sold and leads to a fall in price and vice versa.
Evaluate the impact of competition on producers?
greater efficiency, lower costs of production. greater demand for goods/services, leading to greater profits for more efficient producers, which will then expand output to meet demand).Competition will affect price, promotional activities, location decisions and market share. It will also increase the need to innovate in order to differentiate products and increase productivity from developing technology. However, new technology may lead to unemployment as firms no longer need workers. Those who are slow to innovate will go out of business. It will increase productivity, leading to economic growth, increased demand and profit
Evaluate the economic impact of competition on consumers
lower prices and better quality products. Competition will increase consumer sovereignty as they will have a range of products to choose from due to invention and innovation, leading to lower prices. Rise in standard of living as they have to spend less on goods and services. However, producers may introduce goods such as pesticides that are harmful to consumers. advertising can be a method of persuasion-consumers may be encouraged to buy products they do not need. in cases such as cigarettes, producers may offer low prices to tempt consumers to buy, but then rise the price once they are 'hooked' on it. customer exploitation
What is a monopoly?
A monopoly is a sole producer or seller of a good or service. (they set either the price or quantity of products in the market)
Give some examples of barriers to entry.
legal barriers: e.g. only Royal Mail can deliver letters to your home. greater efficiency than potential rivals due to very large economies of scale, which reduce costs for larger producers. location: even small firms can be monopolies, e.g. village post office may be the only place to buy milk until you can get to a town. copyrights and patents that prevent copying while they exist
Legally, what percentage of the market share does a monopoly have to cover?
25%
What is meant by oligopoly?
Oligopoly is where a small number of firms control the large majority of market share e.g. supermarkets
When is an oligopoly said to exist?
Technically, an oligopoly is said to exist if the five largest firms have 50% or more of the market share.
What is a competitive market
a market with many buyers and sellers trading identical products so that each buyer and seller is a price taker
Compare competitive markets and monopolies/oligopolies
(picture)
What is price?
Price is the sum of money you have to pay for a good or service. It is determined by the interaction of supply and demand.
Explain price as a reflection of worth
Price reflects the value/worth people are willing to put on a good or service. This will depend on the utility gained from the product. It is determined from the interaction of demand and supply.
Explain price's role in determining an effect use of resources
Price gives a signal to producers as to what they should produce and how they should distribute their products due to the price consumers are willing to pay. This also helps to ration scarce resources as if resources are scarce, price rises. Firms will supply what consumers want to buy, so the price mechanism is efficient.
What is efficiency?
Efficiency is the optimal production and distribution of scarce resources.
What is meant by equilibrium price and quantity?
Equilibrium price and quantity is where the quantity supplied exactly matches the quantity demanded.
Draw and analyse the interaction of supply and demand.
An increase in demand will cause price and quantity to increase. We now have a new market equilibrium. A decrease in demand will cause price and quantity to decrease. We now have a new market equilibrium. A decrease in supply will cause price to increase and quantity to decrease. An increase in supply will cause price to decrease and quantity to increase.
What is the determination of price?
the interaction of the free market forces of demand and supply to establish the general level of price for a good or a service.
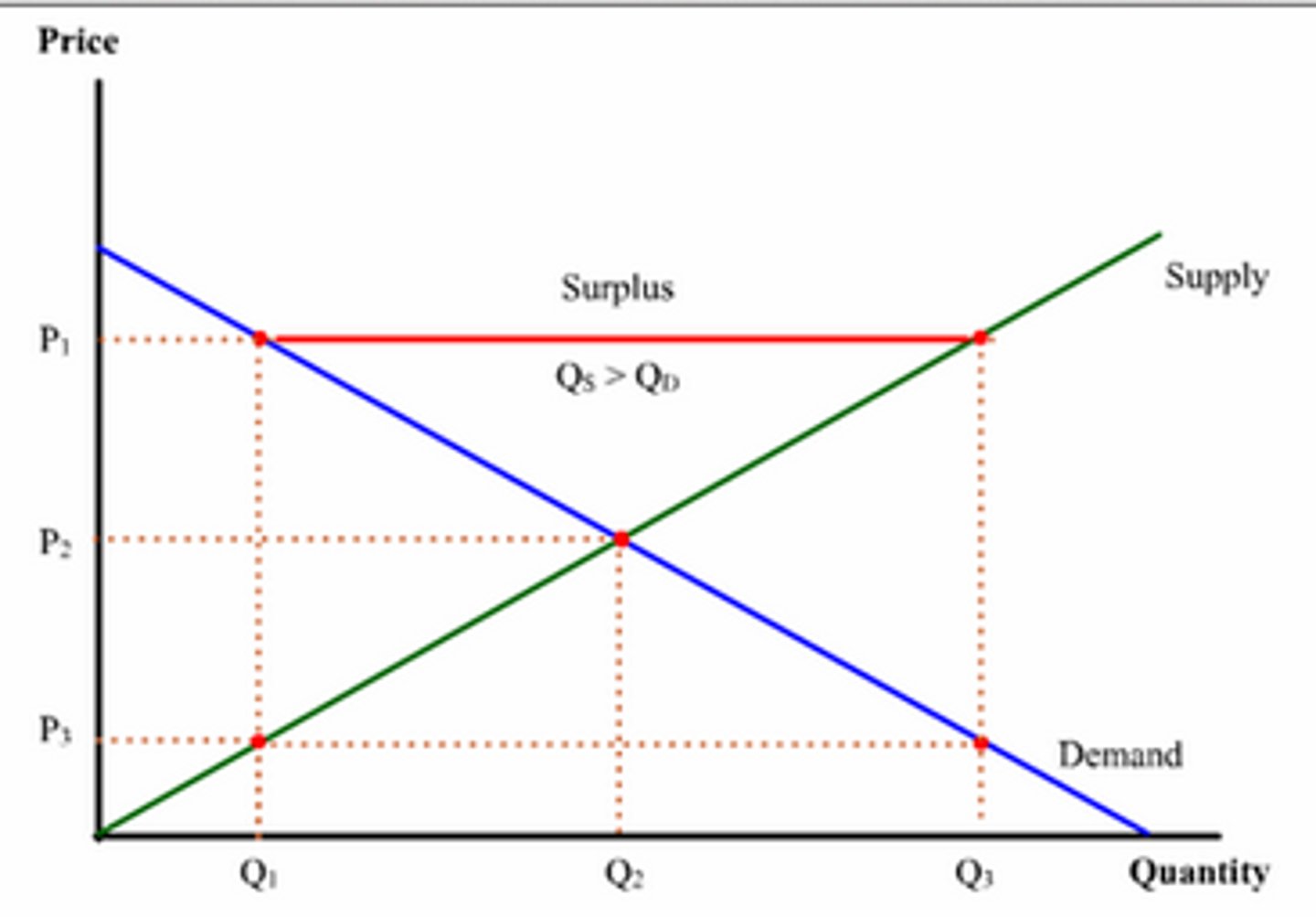
What is excess supply?
Excess supply occurs when quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
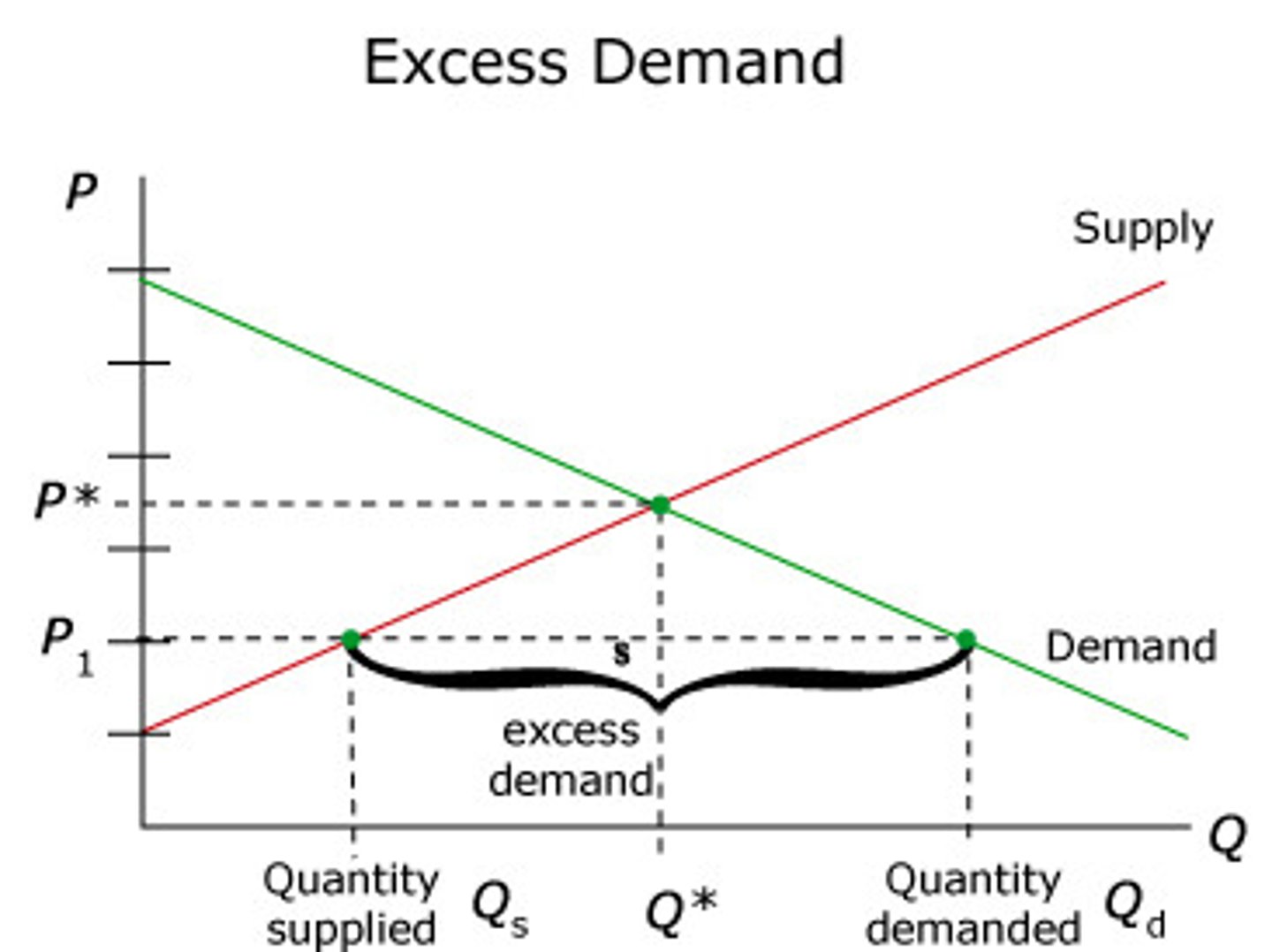
What is excess demand?
Excess demand occurs when quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
What is the role of markets in determining prices?
Markets bring together buyers and sellers, allowing them to set a price. The market forces of supply and demand are combined to interact and determine price. As producers charge high prices (excess supply), and low prices (excess demand), markets signal to the producers to adjust the price back to the price equilibrium. If there is excess demand, this signals to producers to increase price, if there is excess supply, this signals to producers to decrease price
What is allocation of resources?
how scarce resources are distributed among producers, and how scarce goods and services are allocated among consumers.
What is the role of markets in the allocation of resources?
producers are given signals and incentives. These can be of excess demand / supply, consumer spending signals to producers where to allocate resources- what goods to produce and how much of these goods. if there is excess demand, this signals to move scarce resources to the production of that good and vice versa. this power of consumers to influence how the market allocates resources is called consumer sovereignty.
What are market forces?
factors that determine price levels and the availability of goods and services in an economy without government intervention(supply and demand)
Analyze how the market forces of demand and supply affect equilibrium price and quantity
An increase in demand will cause price and quantity to increase. We now have a new market equilibrium. A decrease in demand will cause price and quantity to decrease. We now have a new market equilibrium. A decrease in supply will cause price to increase and quantity to decrease. An increase in supply will cause price to decrease and quantity to increase.
What is supply?
the amount of a good or service producers are willing and able to sell at a specific price point at a specific point in time.
Supply curve
is the aggregate of individual supply curves (market supply). It follows the law of supply.(picture)