The Meat We Eat Exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What factors affect dressing percentage in lambs?
Fill, finish, fleece, sex, and muscling
what is the normal range for dressing percentage for sheep
44-56
Extensive Management Systems
Southwestern Range Operations• Utilize fine wool Rambouillet ewes and Hampshire orSuffolk Rams with very little supplementation
Majority of operations
Hands off
Extensive Management Systems
Northwestern Range Operations• Very similar to Southwest only more availability offeed• Often graze federal lands managed by the ForestService and the Bureau of Land Management
Intensive Management Systems
Farm Flock Operations• Common in the Midwest• Smaller in size and represents very small part of U.S. sheep production• Breeding stock and show lambs are produced
show operations
a lot of management
Intensive Management Systems
Lamb Feedlot Industry• Intensively managed system where lambs are fed high concentratediets• All of the consumed feed is harvested and brought to the lamb• Colorado and Texas are the leading lamb feeding states.
Katahdin
Developed in the 1950's on thePiel farm in Maine
• Crossing of hair sheep from theCaribbean with various Britishbreeds, especially the Suffolk
• Blends the best qualities ofCaribbean hair sheep with thesuperior growth and carcassquality of wooled sheep
• Excel in maternal and fitnesstraits, including parasiteresistance
• Most numerous registeredbreed of sheep in the US
which sheep breed is popular in research?
Katahdin
live weight- sheep
Most lambs are marketed between 105 and 130 pounds
• Avg = 125lbs
What is the normal range of dressing percentage for shorn lambs?
an average of 54
What is the normal range of dressing percentage for unshorn lambs?
an average of 52
Fat thickness
Measured at the 12th rib, it is the single factor used in yield grading ribbed lambcarcasses
fat thickness
The normal range is 0.05-.5 inches with an average of .25
Body wall thickness
The measurement taken approximately 4.5 inches form the midline of the ribbed lambcarcass. A lot of variation exists for this measurement based mostly off of age, breed andweight.
body wall thickness
The normal range is between 0.6 and 1.25 inches
rib eye area
The cross-section of the longissimus dorsi muscle between the 12th and 13th rib
what is the Normal range for rib eye area
The normal range is 1.5-3.5 square inches with an average of 2.3
rib eye area
highly correlated to weight
A 125-pound lamb has around a 2.5 square inch rib eye.
Break joints,
rib shape- mod narrow
lean color-slightly pink,
lean texture- fine
lamb
break or 1 spool,
rib shape- mod wide; flat,
lean color-slightly dark red,
lean texture- slightly coarse
yearling mutton
2 spool joints
rib shape- wide and flat
lean color-dark red
lean texture-course
mutton
what do lamb quality grades predict?
palpability
A preliminary grade is determined based on
maturity, flank streakings, and flank firmness
The preliminary grade and conformation score are then used to determine
the final quality grade
4 factors of quality grade
• Maturity
• Flank streakings
• Flank firmness
• Confirmation
what does lamb yield grades predict?
cut-ability
yield grade equation
0.4 + (10 X fat thickness,in)
what is one factor that impacts yield grade for lambs?
fat thickness
95-98 percent of lamb is
prime or choice
what are the three sectors of goat production
hair, meat, and dairy
what is produced by the Angora and is a long, lustrous fiber that is noted for durability and briliant color when dyed
mohair
goat pro facts
There is no grading system for meat goats, so there is agreater inconsistency in palatability and quality of theproduct.
goat pro facts
Boer Goat has played a vital role in improving goatproductivity and carcass characteristics
SouthAfrican Boer Goat
A hardy, fast growingmeat-type goat
• Medium size withprominent horns andbroad, drooping ears
• Generally brown head and neck with white body and legs, having short to medium hair
• Good meat type conformation with superior spring of rib,body length, and muscling
within 24 hrs after death
glycogen--> lactic acid
via anaerobic glyolosis
what is the muscle ph within 24 hrs after death
7.4 --> 5.6
Lactic acid build up
• Rate of lactic acid build up in impacted by the glycogen levels in the muscle at death and postmortem temperature
what is the muscle color during postmortem changes
purple --> bright red or pink
What is the ideal Postmortem pH decline?
gradual decrease from 7.4 to 5.6 or 5.7
What is the high Postmortem pH decline?
pH slowly declines and remains stable around 6.0 to 6.5
what is the outcome of a high pH decline
- Dark cutters or Dark, Firm and Dry
What is the low Postmortem pH decline?
pH drops rapidly to 5.4 or5.5 and then ultimately drops to 5.1 or 5.3
what is the outcome of a low ph decline
- pale soft and exudative
postmortem
The drop in postmortem pH also affects thewater holding capacity (WHC) of meat.
What is Water Holding capacity? (WHC)
WHC is the ability of a muscle to retain water duringcutting, heating, grinding, etc.
pH Impact on Water Holding Capacity
Water-holding capacity is the lowest is the isoelectric point (pH ~ 5.1)
• The number of positively and negatively charged groups of the myofibrillar proteins is equal
• The charges cancel out and no charge is available to hold the bound and immobilized water
Long Term Stress
Long-term glycogen depletion or glycogen deficiency at the time of slaughter
• High pH
• Dark color
• High water holding capacity
• Firm lean texture
Long Term Stress
Physiological response to stress
What are the types of stress?
Temperature
• Sound
• Space
• Handling
• Transportation
• Sickness
• Exhaustion
DFD beef (Dark Cutters
caused by long term glycogen depletion as a response to "alarm"
a) Glycogen is converted to lactic acid and pyruvic acid inorder to generate more ATP; initiated by adrenaline
factors for DFD beef
exhaustion, exposure to cold, excitement,feed withdrawal, sickness
how to prevent DFD
Stress prevention and proper handling are best solutions
short term stress
High levels of lactic acid in muscle at time of slaughter• Rapid decline in pH
short term stress
Low pH
• Pale color
• Loss of water holding capacity
• Decreased processing yield
• Increase cook loss
• Decreased juiciness
Short Term Stress
Less than 6 hours prior toharvest
short term stress
Typically in pork
• Short-term glycogen depletion -hereditary
• Porcine Stress Syndrome
• Extreme muscularity
• Anxious behavior
• Muscle tremors
• Redding of skin
Pale, Soft, and Exudative (PSE) Pork
Results from short-term glycogen depletion
Pale, Soft, and Exudative (PSE) Pork
Caused by swine susceptibility to PSS and toexcitementa) Antemortem: rapid glycolysis due to excitementb) Postmortem: too long on kill floor accelerates glycolysiswhile carcass temperature is high
Pale, Soft, and Exudative (PSE) Pork
pH of muscle reaches 5.2 within 2 h4. Solution: decrease emphasis on heavy muscle;• rest prior to slaughter and handle properl
ph impact- normal
Muscle color- normal
Glycogen at death- 1.0%
Glycogen at 24 hr- 0.1%
Lactate production- high
Ultimate muscle pH-5.6
ph impact-dark
Muscle color-dark
Glycogen at death- 0.3%
Glycogen at 24 hr-0.1%
Lactate production- low
Ultimate muscle pH- 6.0 to 6.5
ph impact- pale
Muscle color-pale
Glycogen at death- 0.6
Glycogen at 24 hr-0.1
Lactate production- very high
Ultimate muscle pH- 5.1- 5.3
what is rigor mortis
stiffness of death
what stage is rigor mortis complete?
stage 3
100% rigor
what are the phases of rigor mortis
1. Delay phase
2. Onset phase
3. Completion phase
4. Resolution
taste and eating satisfaction
Tenderness
Juiciness
Flavor
Appearance
Aroma
Freshness
what is the goal for taste and eating satisfaction
Best possible eating experience each time a consumer chooses meat
why is tenderness the most studied?
Accounts for ~ 80% of consumer's overall acceptability
• Varies far more than flavor and juiciness
• Flavor and juiciness can be influenced by cooking method and seasonings
Warner-Bratzler Shear Force (objective)
Pounds of force to shear one-half-inch cores, removed parallel to the muscled fibers of cooked muscles from steaks and roasts
Slice Shear Force (objective)
Pounds of force to shear the lateral end of each steak a 1-cm-thick, 5-cm-long slice that is parallel to the muscle fibers
SENSORY TESTING (subjective )
Sensory Testing Environment
• Trained vs Consumer Panel setting
reasons for cooking meat
Food Safety
• Improve Palatability
•Aroma• Flavor
what does cooking meat impact?
tenderness and juiciness
dry heat
Roasting
• Broiling
• Grilling
• Pan Broiling
• Griddle
• Deep-fat frying
• Stir-frying
• Air frying
moist heat
Braising
• Cooking in liquid
• Boiling
• Simmering
• Stewing
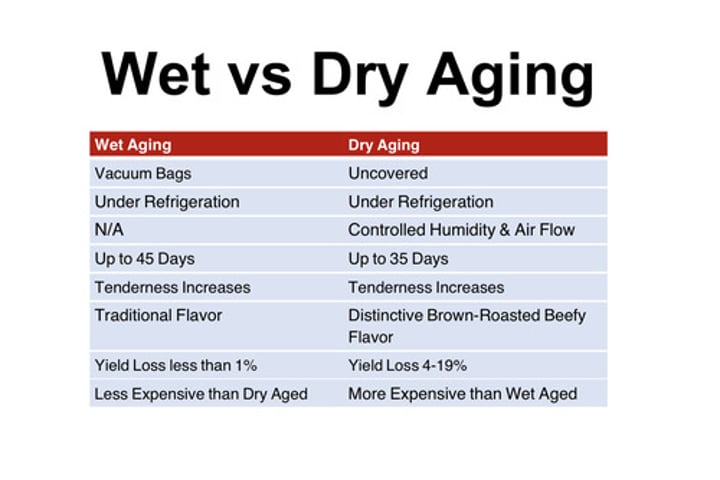
what is the most popular in the meat industry wet or dry aging?
wet
what are the two types of cut for tenderness
High collagen
• Low collagen
tenderness
Increase Degree of Doneness
• Reduce muscle fiber tenderness
• Gelatinize collagen
what impacts juiciness
marbling
juiciness
Ultimate pH impacts water holding capacity• Dry Heat• Less Juicy when cooked for extended time• Moist Heat
in terms of flavor what is impacted by animals
marbling
finishing ration
in terms of flavor what is impacted by the industry
Chill time
• Tenderization
in terms of flavor what is impacted by the chief
Salt
• Pepper
Marinades
beef flavor development
Rich beef flavor moves front to back (follows fat)
• Chuck & Rib = very rich beef flavor
• Loin and Sirloin = moderate beef flavor
• Round = mild beef flavor
what are the odds of a bad eating experience for Prime
3% (1 in 33)
what are the odds of a bad eating experience for upper 2/3 choice
10 % ( 1 in 10)
what are the odds of a bad eating experience for choice
16% (1 in 6)
what are the odds of a bad eating experience for select
27% (1 in 4)
what are the odds of a bad eating experience for standard
50% (1 in 2)
what is the oldest method of tenderizing
grinding
What meat quality issue results from short-term glycogen depletion?
pse
What factor does not impact Palatability?
hot carcass weight
What is the ideal fat thickness of a market lamb?
0.25
Which of the following species has the fastest onset of rigor?
pork
What is the ideal pH of meat?
5.6
What type of meat quality issue results form short-term glycogen depletion and causes meat to have the lowest water holding capacity?
pse
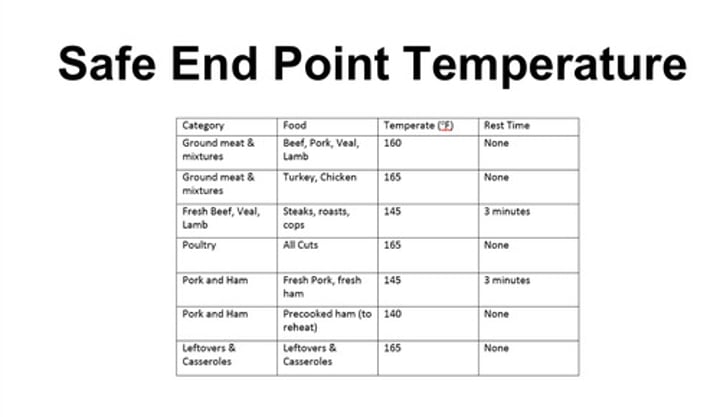
What is the safe end point cooking temperature for ground beef?
160
wet vs dry
safe end point