CH14 alcohols
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What are the volatility and boiling points of alcohols like compared to alkanes?
BP: higher than alkanes as they have polar bonds O-H bond making the whole molecule polar. There will be strong hydrogen bonds between the O-H bonds.
V: because of stronger bonds in alcohols, it takes more energy to to overcome them than the weaker London forces in alkanes so it is harder for the liquid alcohol to change into a gas making them less volatile.
What is solubility like for alcohols?
Very soluble as hydrogen bonds form between polar OH groups. However solubility slightly decreases down the carbon chain as influence of OH groups becomes smaller.
How do you classify primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols?
Primary - OH group is attached to the carbon with 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 alkyl group
Secondary - OH group is attached to one hydrogen atom and 2 alkyl groups
Tertiary - OH group is attached to no hydrogen atoms and 3 alkyl groups.
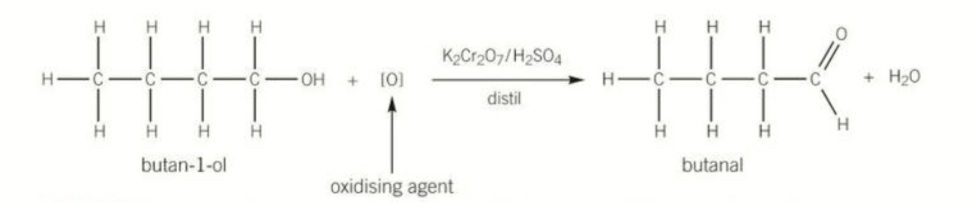
Equation for oxidation of primary alcohols Using distillation and the states needed
K2CrO7 OR H2SO4 catalyst
Produces an aldehyde
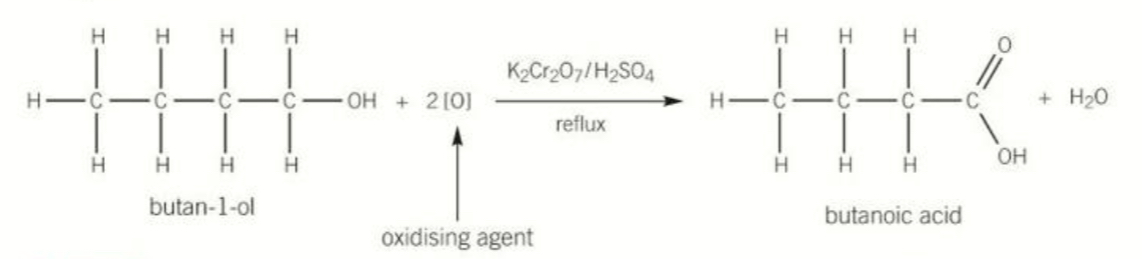
Equation for oxidation of primary alcohols by reflux and states required
K2Cr2O7 OR H2SO4 catalyst
Produces a carboxylic acid
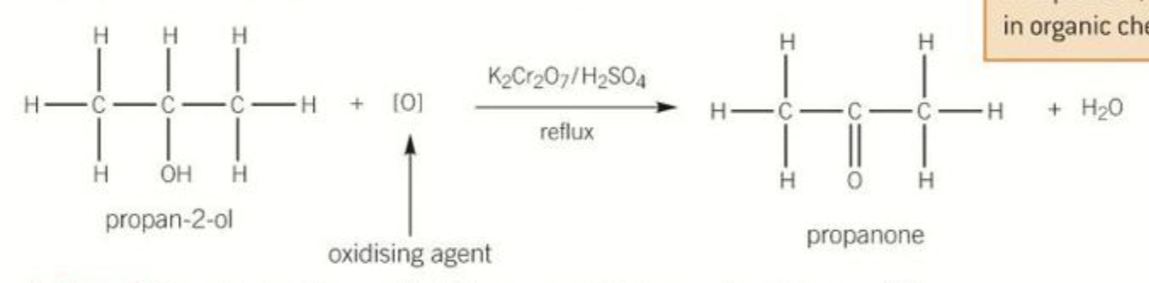
Equation for oxidation of secondary alcohols by reflux and states required
K2Cr2O7 OR H2SO4 catalyst
Produces a ketone
Equation for dehydration of alcohols and conditions required
C3H8O > C3H6 + H2O
Requires HPO4 catalyst
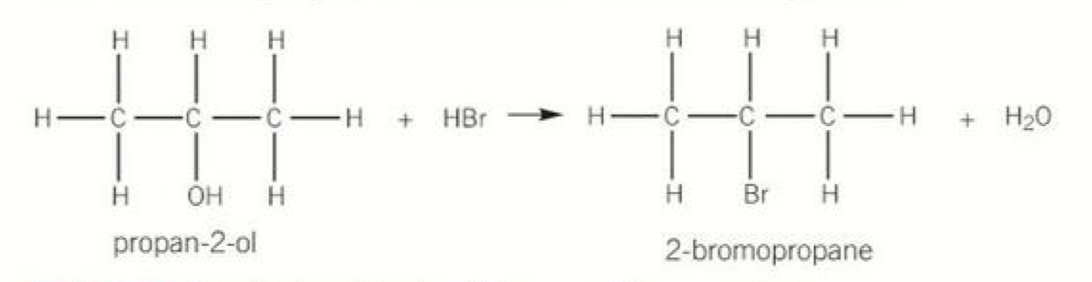
Equation for substitution reaction of alcohols