DNS Records - CompTIA Network+ N10-009 - 3.4
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
DNS Records
• Resource Records (RR) - The database records of domain name services
• Over 30 record types - IP addresses, certificates, host alias names, etc.
• These are important and critical configurations - Make sure to check your settings, backup, and test!
Start forward lookup file
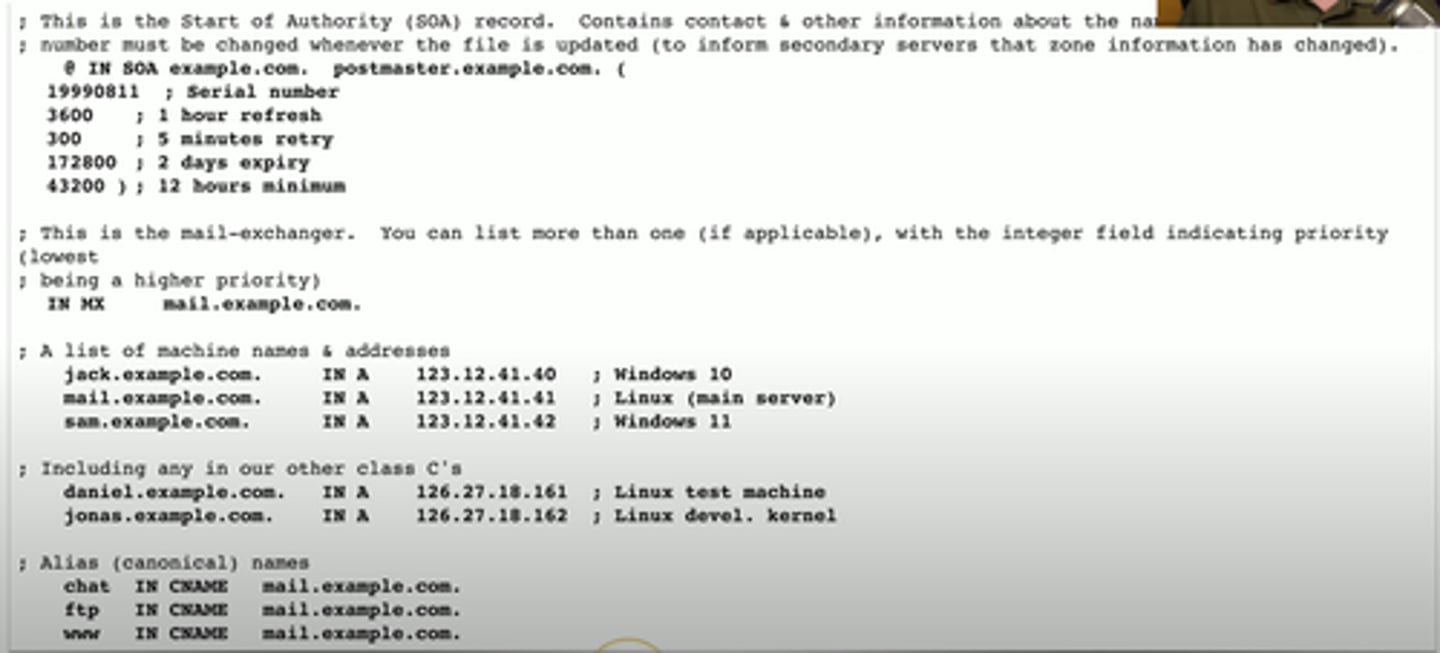
Start of Authority Record (SOA)
Describes the DNS zone details
Structure
- IN SOA (Internet Zone, Start of Authority) with name of zone
- Serial number
- Refresh, Retry, and expiry time frames
- Caching duration/TTL

Address Records (A) or (AAAA)
Defines the IP of a host
- Most popular query
A records are for IPv4
- Modify the A record to change the host name
AAAA records are for IPv6 addresses
- The same DNS server, different accounts

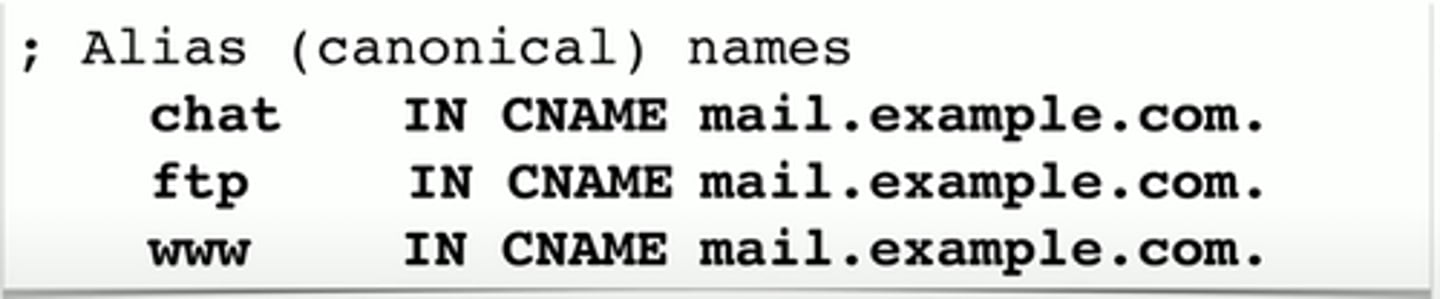
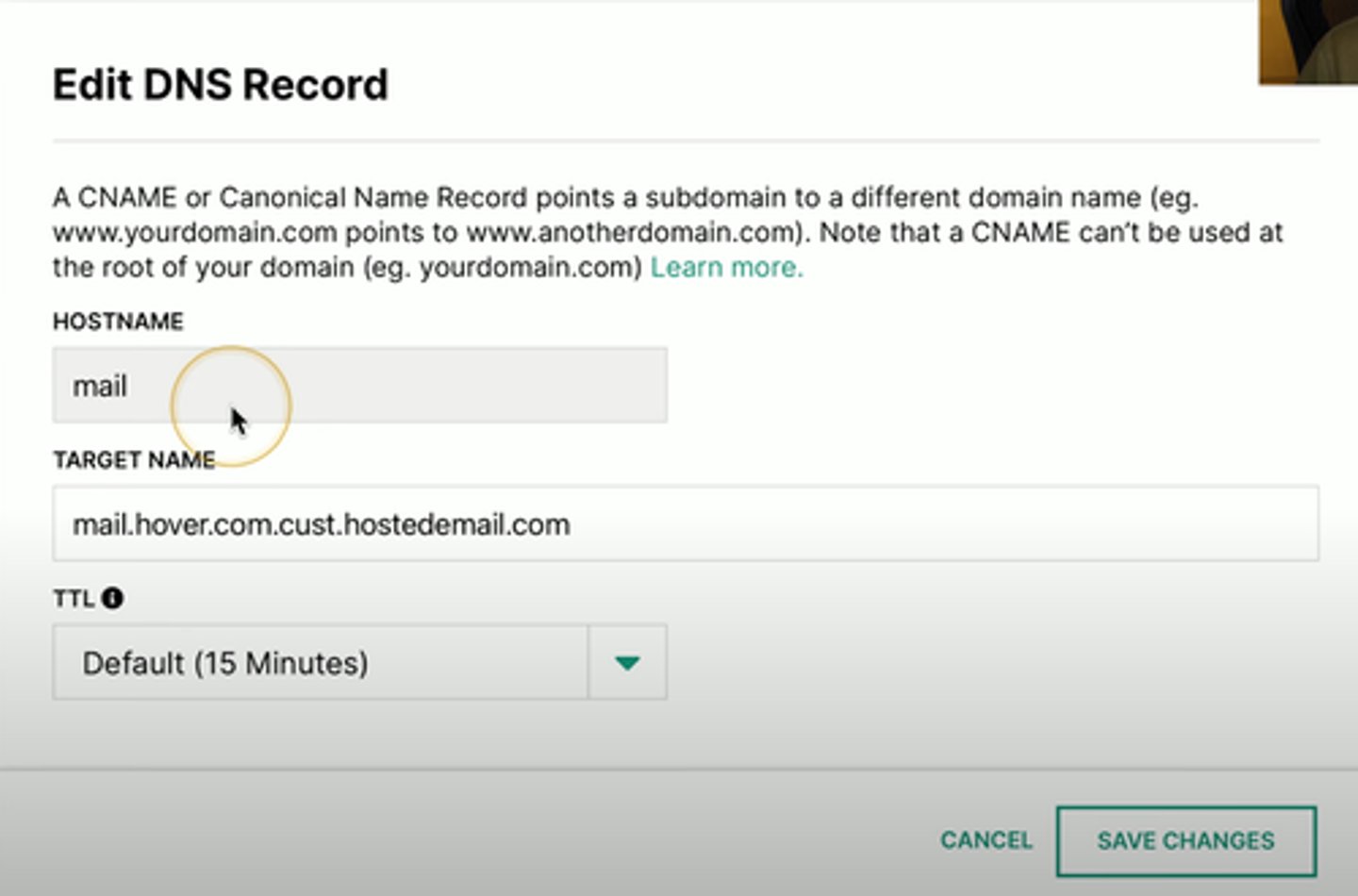
Canonical name records (CNAME)
A name is an alias of another, canonical name
- One physical, server multiple services
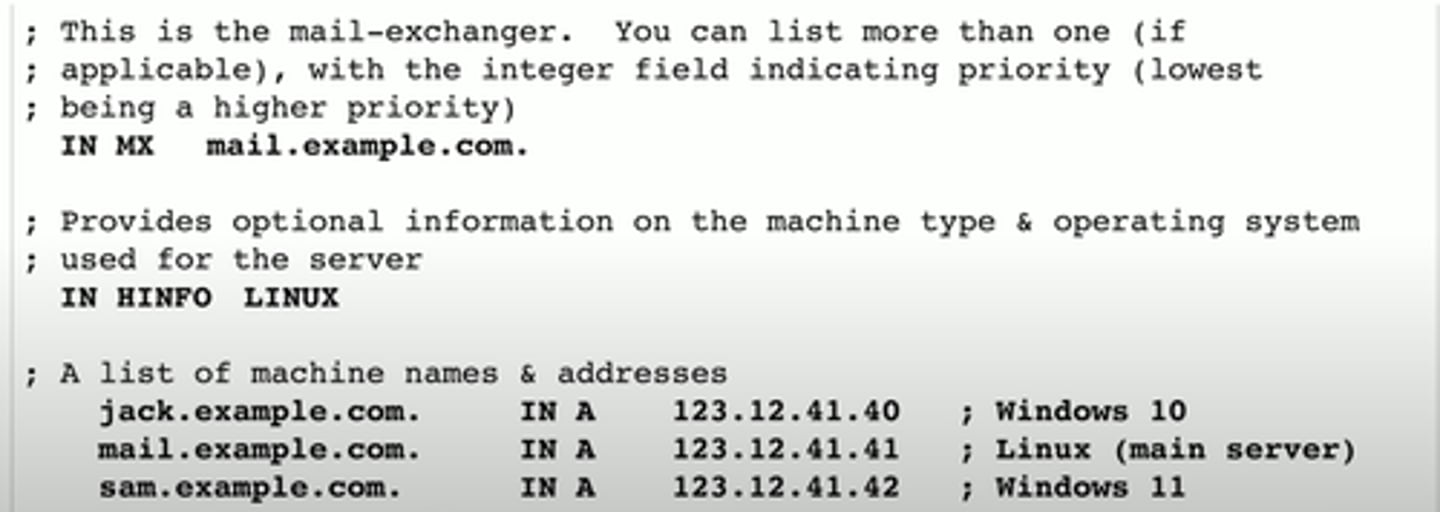
mail exchanger record (MX)
Determines the host name for the mail server
- This isn't an IP address; it's a name
MX Record
Text Record (TXT)
Human readable text information
- Useful public information
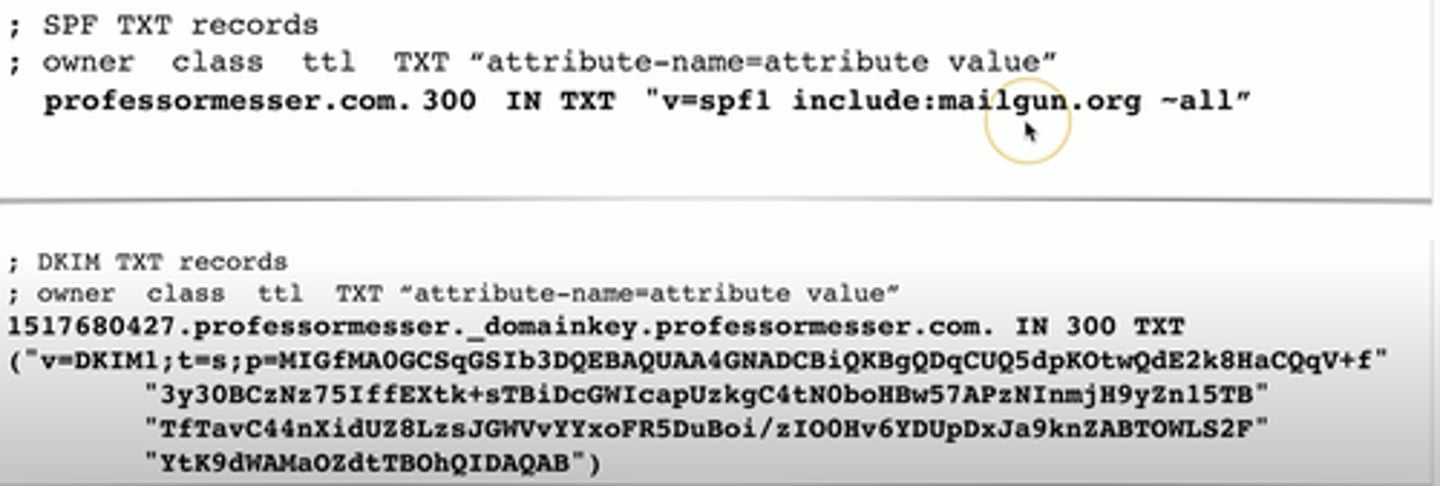
SPF protocol (Sender Policy Framework)
- Prevent mail spoofing
- Mail servers check that incoming mail really did come from the authorized host
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
- Digitally sign your outgoing mail
- Validated by the mail server
- Put your public key in the DKIM TXT record
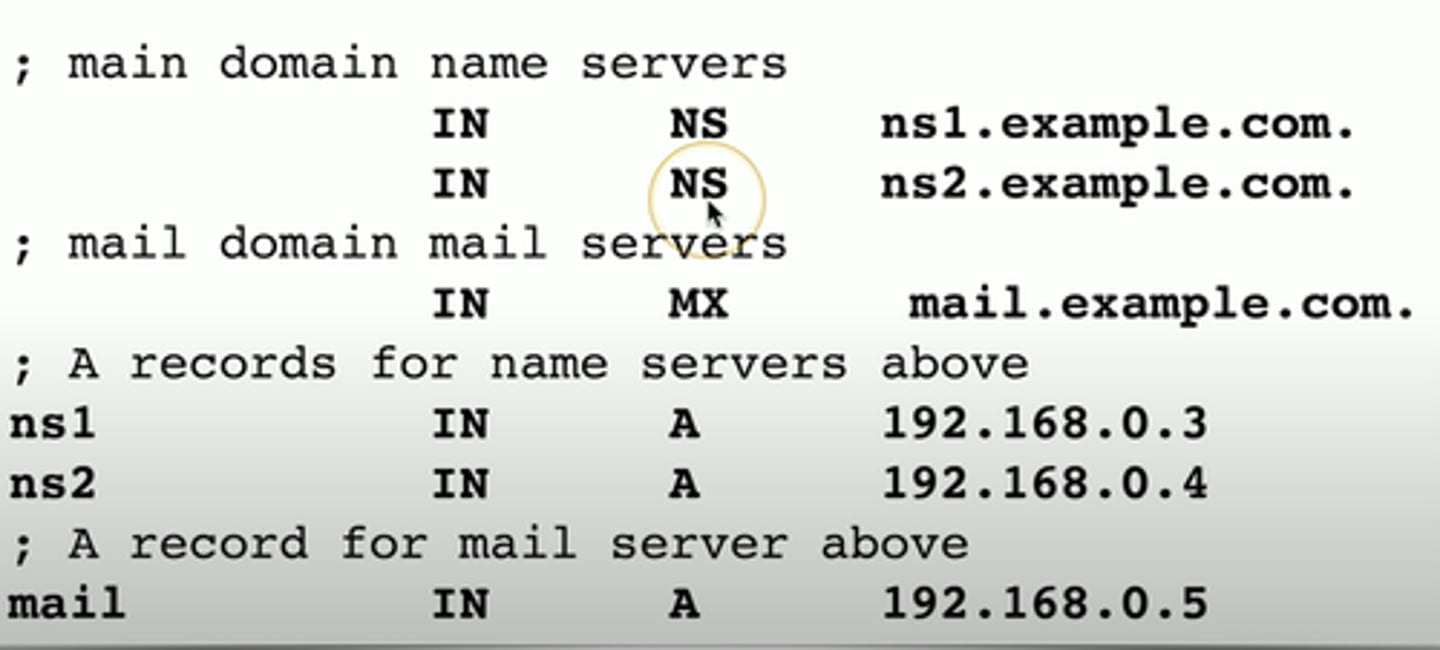
Name Server Records (NS)
List the name servers for a domain
- NS Records point to the name of the server
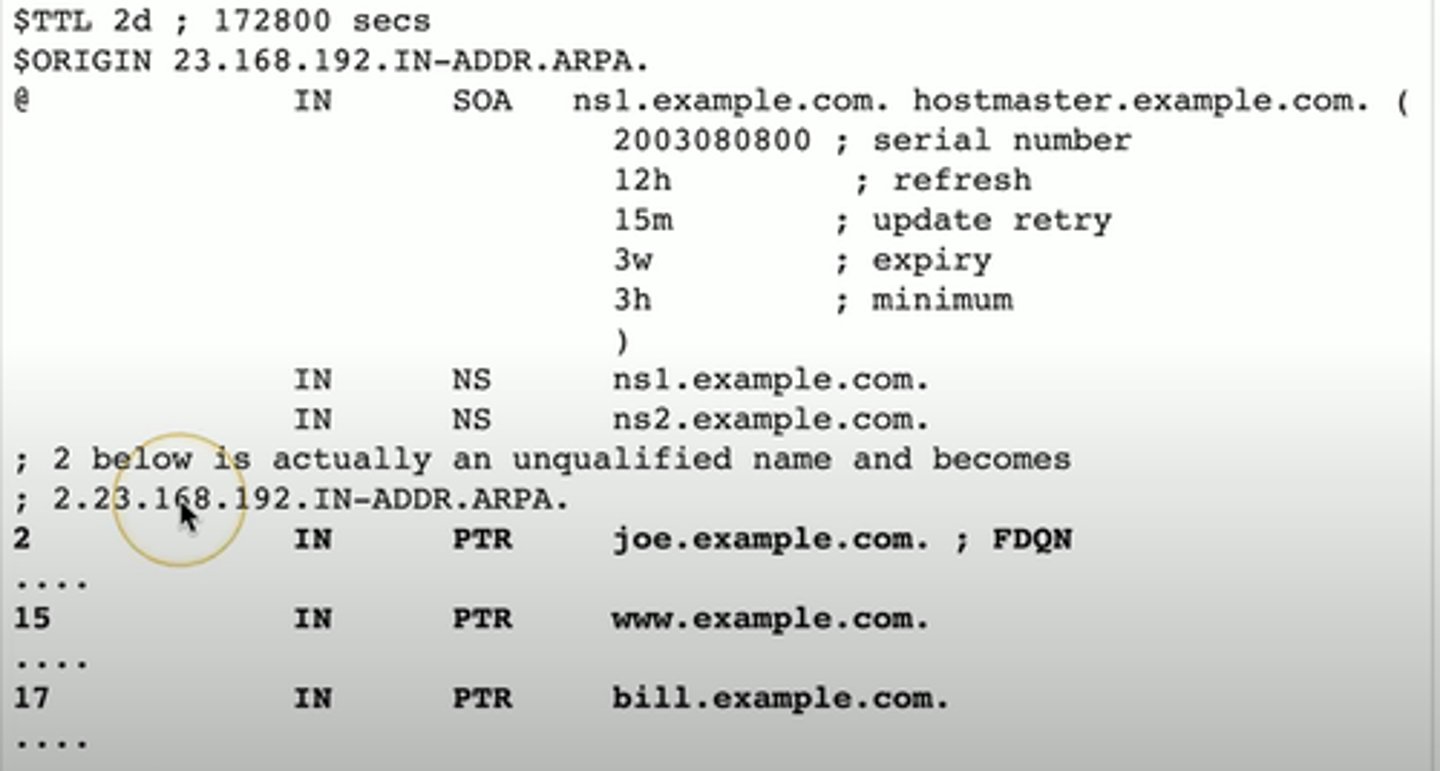
Pointer Record (PTR)
The reverse of an A or AAAA record
- Added to a reverse map zone file