Lec 7: Phloem
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What do palisade cells have inside them?
chloroplasts
What happens in the palisade during sugar transport from the leaf? STOP at the location before it goes out the palisade.
in chloroplasts —> calvin cycle produces G3P —> G3P moves out of the chloroplast into the palisade cytoplasm —> in the cytoplasm —> G3P makes glucose and fructose —> glucose and fructose combine (or dehydrates and synthesizes) to make sucrose
Where does the sucrose move once it is made?
Sucrose passively transport —> palisade thru the PD —> into the bundle sheath n phloem of the minor vein —> cell walls of the CC and STM
What type of sugar is glucose and fructose?
monosaccharides
What type of sugar is sucrose?
disaccharide
Who is the transport sugar?
sucrose
How does sucrose move from the cell walls of the CC and STM into their (CC’s and STM’s) cytoplasm?
phloeom loading —> sucrose co-transport protein actively transport sucrose and H+ into the CC’s and STM’s cytoplasm
Why is the transport of sucrose into the CC’s and STM’s cytoplasm active?
keep toxins out of the plant’s systemic system
Once the sucrose is in the cytoplasm of the CC and STM, is water potential high or low in their cytoplasm? Is water flowing in or out? From where?
low water potential, so water flows in from the xylem
Why is it important that the xylem and phloem are next to each other?
sugar movement bc the sugars will flow into the phloem and water will flow from the xylem into the phloem
Once the phloem is loaded with sucrose and water, how does sucrose and water flow thru the phloem and xylem?
As transpiration pulls up water in the XVMs, the water is sucked into the phloem —> in the CC’s and STM’s —> sugars are passively pushed/pressurized by bulk flow
What is a source?
where sucrose is transported out of
What is a sink?
where sucrose is transported into
Give example(s) of fall source(s) and spring source(s).
Fall - leaves and stem
Spring - tubers, rhizomes, bulbs, and roots
Give example(s) of fall sink(s) and spring sink(s).
Fall - tubers, rhizomes, bulbs,and roots
Spring - flowers, fruits, leaves, buds, and stems
Are young leaves sinks or sources? What about mature leaves?
young - sinks
mature - sources
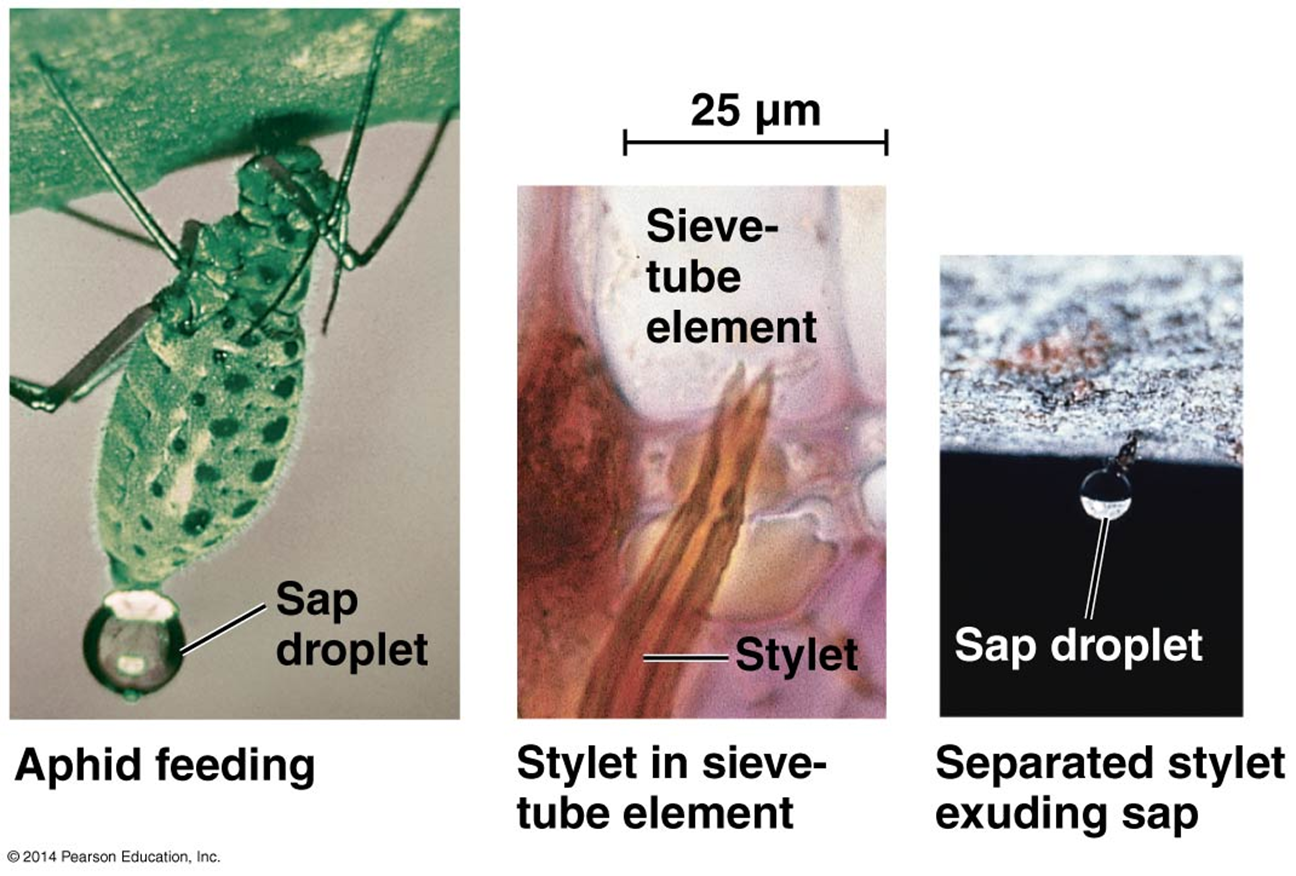
Explain the concept of these photos.
Aphid feed on the sugars in the phloem —> phloem is located near the bottom of the leaf —> Aphid stick their probosci into the STMs —> sugars are pressurized —> the sugar comes out as a sap droplet from the butt of the aphid.
Pressurized: air is forced in a airtight enviroment, till the amount of air inside is enough to increase the pressure.
After the sucrose travels from the minor veins, where does the sugar go next?
major vein —> out of the petiole —> to sinks