Coastal Systems and Landscapes - A Level AQA Geography
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Atmosphere
The air that surrounds the earth
Lithosphere
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
Hydrosphere
All the water on earth
Biosphere
The part of Earth where life exists
Isolated system
A system that can exchange neither energy nor matter with its surroundings.
Closed system
There is input, transfer and output of energy but NOT matter.
Open system
Inputs and outputs of both energy and matter
Input
Energy/matter entering a system
Output
Energy and/or matter leaving a system
Store/component
A section of a system in which matter can remain, be added to or removed from
Flow/transfer
Movements between stores/components within a system
Boundary
The edge of a system
Dynamic Equilibrium
When the inputs and outputs of a system are balanced and stores remain the same
Negative feedback
When a system acts by lessening the effect of the original change and ultimately reversing it
Positive feedback
When a change in a system is further amplified, causing a snowball effect
Inputs to the Coastal System
-Energy from waves, wind, tides and sea currents
-Sediment
-Geology of coastline
-Sea level change
Components of the Coastal System
-Erosional landforms and landscapes
-Depositional landforms and landscapes
Outputs of the Coastal System
-Dissipation of wave energy
-Accumulation of sediment above tidal limit
-Sediment removed beyond local sediment cells
Marine Factors
Waves, winds, tides, salt spray and currents
Subaerial Factors
Temperatures and weather
Human factors
Pollution, management, buildings, recreation
Tectonic Factors
Coastal uplift, volcanic activity
Geological Factors
Structure and lithology
Biotic Factors
Vegetation, coral reefs etc.
Climatic Factors
Winds, weather, climate change, glaciation
Geomorphic Factors
Rivers, glaciers, mass movement
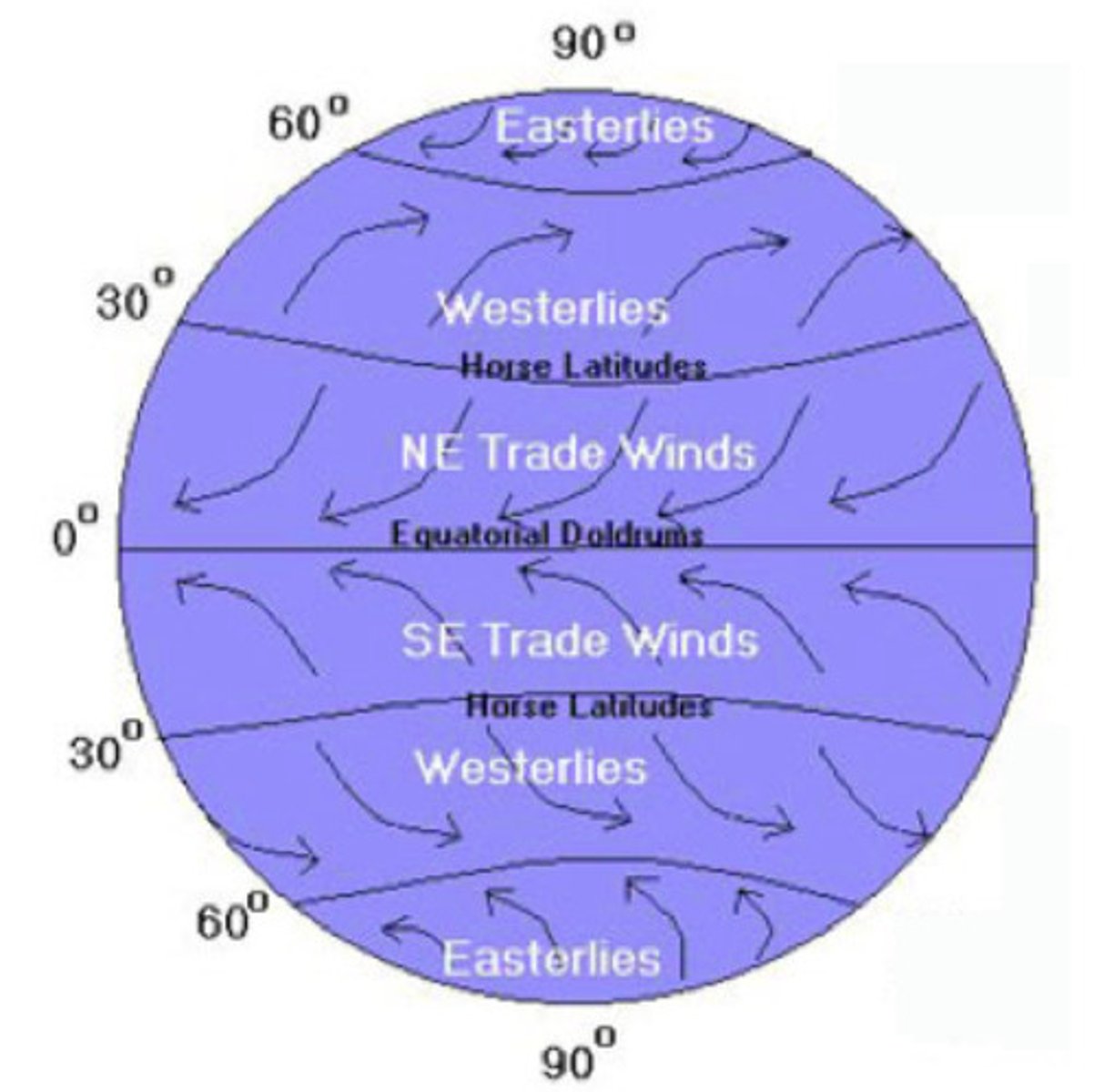
Wind Map North to South
Easterlies, Westerlies, Horse Latitudes, NE Trade Winds, Doldrums, SE Trade Winds, Horse Latitudes, Westerlies, Easterlies
How are waves formed?
Wind blows over the surface of the water, creating drag and gaining grip, with the friction causing disturbance and forming waves as a result. Circular to elliptical orbit, crest of wave rises and steepens, breaks.
How does fetch influence waves?
Makes the waves more powerful, increases wave energy
Wave Crest
Highest point of a wave
Wave Trough
Lowest point of a wave
Wave Height
the vertical distance from the crest of a wave to the trough
Wavelength/Amplitude
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
Wave Period
the time required for one cycle
Wave frequency
The number of waves passing a fixed point per second.
Swell waves
Waves in open water, characterised by long wavelengths and reduced height. Travel long distances, up to 15m
Storm Waves
Large waves generated by strong winds that travel short distances
Constructive Waves
The swash is stronger than the backwash therefore the material is moved up the beach and much is left there.
Destructive Waves
The backwash is stronger than the swash therefore material is dragged back down the beach and moved along the coast.
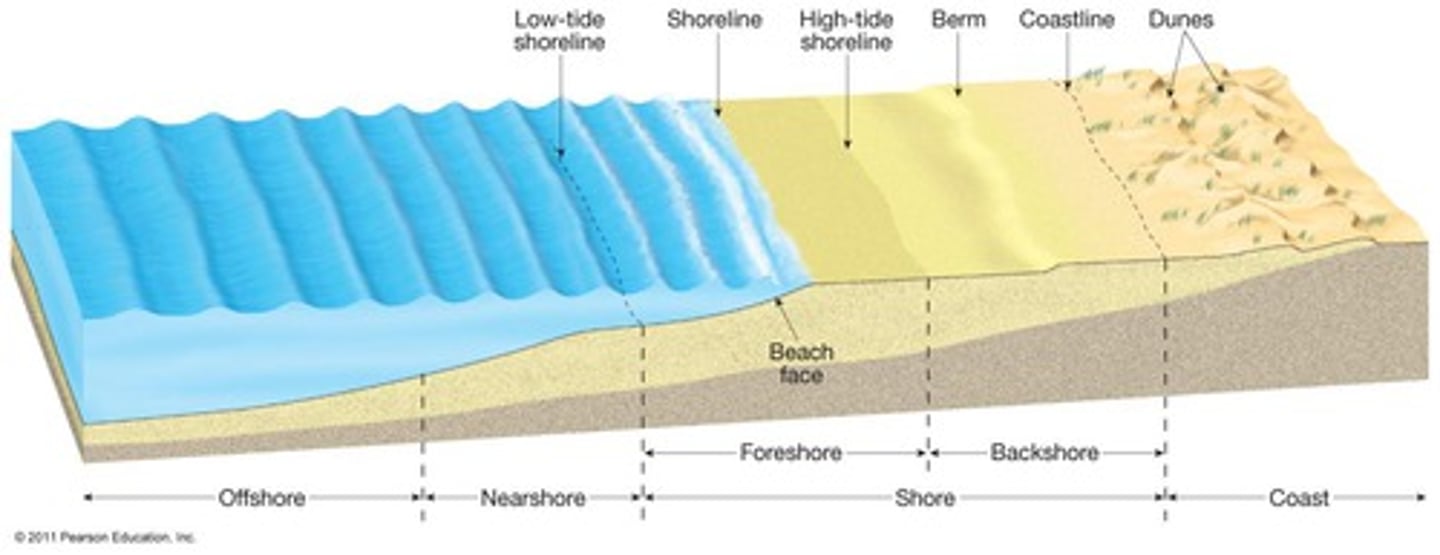
Zones of a Coastline
Wave refraction
Slowing and bending of progressive waves in shallow water - concentrate on headlands, negative feedback
Spring tides
tides that have the greatest tidal range due to the alignment of the earth-moon-sun system.
Neap tides
tides with minimum daily tidal range that occur during the first and third quarters of the moon.
Tidal range
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide
Macro tidal
Tidal range of more than 4m
Meso tidal
Tidal range between 2 m and 4 m.
Micro tidal
Tidal range less than 2m
Storm surges
A wall of water that is pushed ashore by a storm. Low pressure raises sea levels, winds push high sea towards coast
Longshore currents
movement of water near & parallel to shore
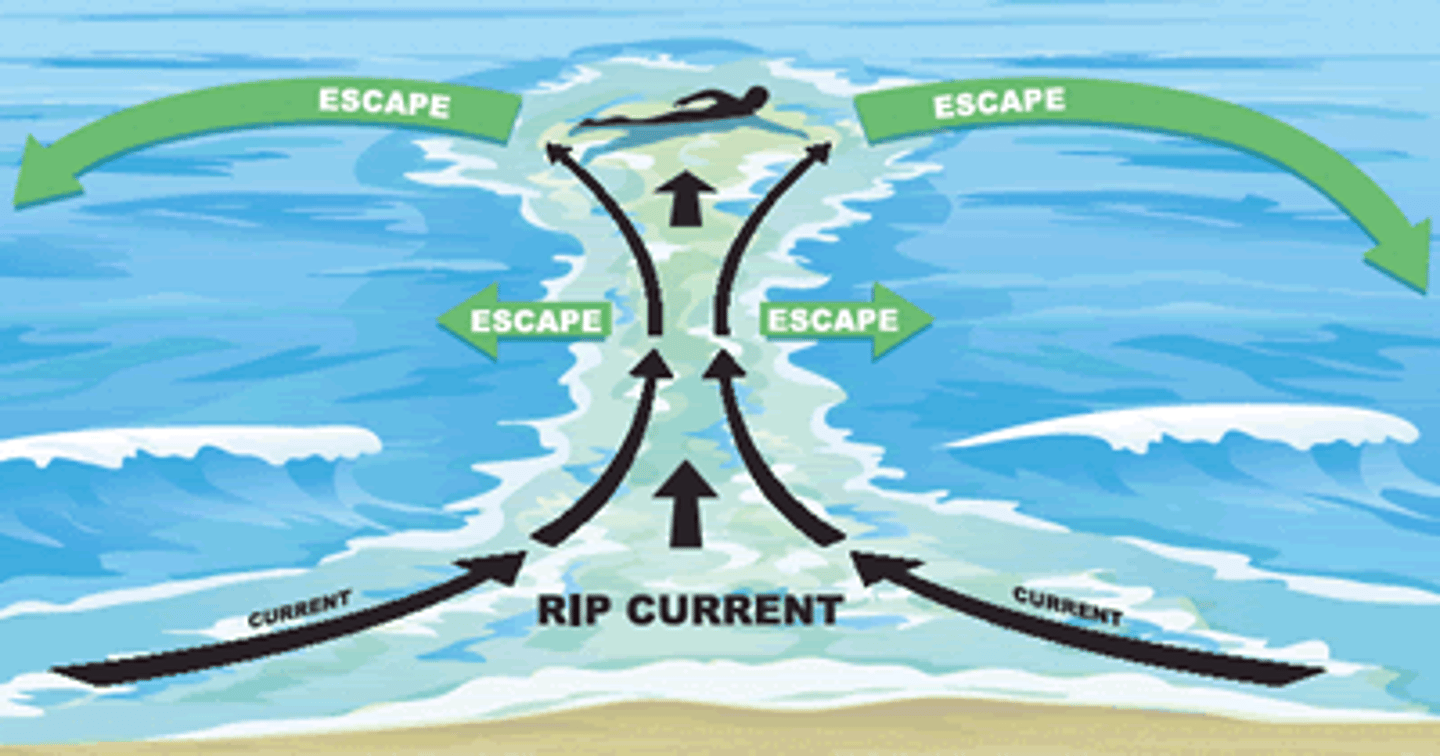
Rip currents
Narrow streams of water that break through sand bars and drain rapidly back to sea
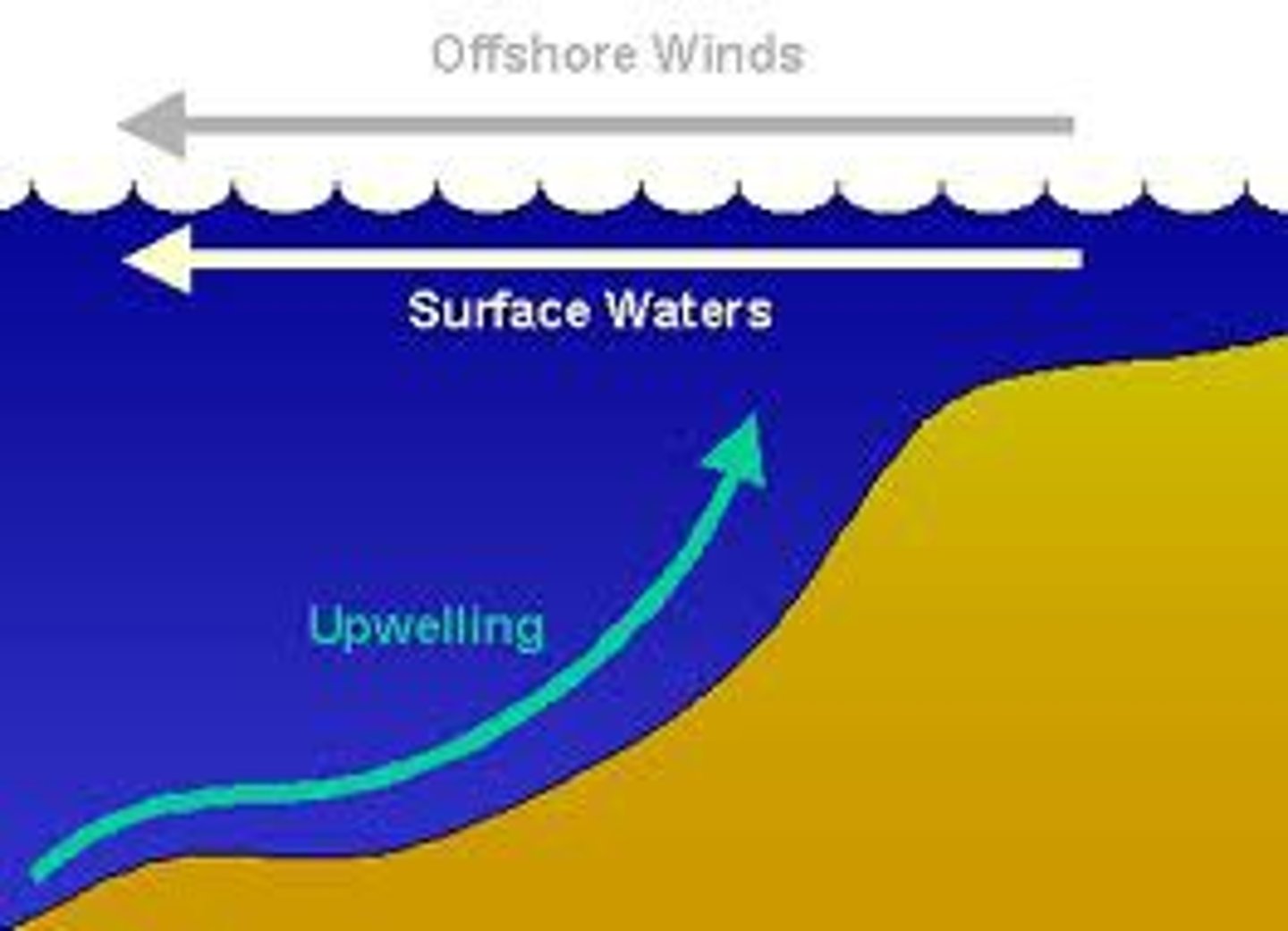
Upwelling
the upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents