apes agriculture + water pollution
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
malnutrition
lacks correct balance of proteins, carbs, vitamins, and minerals
undernutrition
not enough calories
global undernutrition → # of under nourishing declined but still greater than target
iron deficiency (aka anemia) symptoms + solutions
symptoms:
anemia
increased risk of death during childbirth
infections
solutions:
iron pills
eat more red meat
Vitamin A (aka beta carotene) deficiency symptoms + solutions
symptoms:
childhood blindness
increased risk of infection
solutions:
golden rice
supplements
dairy
greens
iodine deficiency symptoms + solutions
symptoms:
goiter (swelling of thyroid gland)
stunted growth
impaired mental capabilities
solutions:
iodized salt
seafood
agriculture → grains
largest part of our diet
60% of human energy intake is from corn, rice, + wheat
industrial agriculture
applies techniques of mechanization + standardization
aka agribusiness
energy subsidy
fossil fuel + human energy input per calorie of food produced
most in the form of fossil fuels + transportation
The Green Revolution
new management techniques, fertilization, irrigation, + improved crop varieties → shift in agricultural practices
mechanization
reliance on large machinery and fossil fuels
improved efficiency + higher production
drawbacks: air pollution, non-sustainability, soil compaction
soil compaction
machines drive over farmland → squishes soil down + reduces size of pores
consequences:
can’t support microorganisms
water can’t infiltrate soil + drain quickly
roots cannot push through
solution: aerate soil
waterlogging
water infiltrates soil + cannot drain → impedes plant growth
salinization
soil degradation that occurs when small amounts of salt in irrigation water becomes highly concentrated on soil surface through evaporation
organic fertilizers
composed of organic matter from plants + animals
examples:
animal manure
green manure (freshly cut green vegetation)
compost
pros:
probably free
supports soil microbes
contains all nutrients
cons:
slow release of nutrients
may contain weeds (green)
may contain pathogens (manure)
may contain salt (compost)
inorganic/synthetic fertilizer
produced commercially, normally with the use of fossil fuels
provides nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), potassium (K)
pros:
greatly increases production
cons:
no trace nutrients
doesn’t support soil organisms
runoff into bodies of water
made from nonrenewable resources
release GHG + NOx
desertification
damage to soil (compaction, salinization, waterlogging, etc.) → turns fertile areas into deserts
more common in places right next to deserts
generally irreversible → land sometimes used for nomadic grazing
consequences (mostly for humans):
loss of food production
famine
environmental refugees
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
pros:
greater yield
greater food quality
reductions in pesticides use
pest/pesticide resistance
cons:
limited restrictions (in US)
safety for human consumption
effects on biodiversity of crops → fragile food supply
furrow irrigation
process: farmers dig a trench + fill with water
pros:
cheap + easy
cons:
water loss
increased erosion
flood irrigation
process: flood field and let water soak in
pros: cheap and easy
cons: may damage plant growth, lots of water loss, increased methane production (inc. decomposition rates)
spray irrigation
process: water pumped to nozzles that spray water across field
pros: more efficient choice
cons: expensive, requires energy, water is lost (mostly through evaporation)
drip irrigation
process: hoses with small pores laid near roots/buried below soil
pros: ~100% efficient + less weeds
cons: expensive + doesn’t work for short growing crops because it takes energy to take them out and put back up every season
consequences of irrigation
waterlogging
soil salinization
soil erosion (repeated tilling and planting)
how to prevent soil erosion
contour planting
no-till agriculture
monocropping
mostly done — planting only one crop
financially beneficial
consequences:
reduced biodiversity
repeated same treatments to soil with potential depletion of nutrients and damage to helpful bacteria
increased risk of pests
increased risk of crop diseases
pesticide
kills pests
herbicide
kills weeds
insecticide
kills insects
broad-spectrum pesticide
kills many kinds of pests
selective pesticides
targets narrow range of organisms
persistent pesticides
remains in environment for a long time
pesticide treadmill
over time, pest populations evolve resistance to pesticides, which requires farmers to use higher doses/develop new pesticides
negative feedback loop
pesticide resistance
a trait possessed by certain individuals that are exposed to pesticides and survive
integrated pest management (IPM)
agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide impacts
crop rotation
intercropping
pest-resistant crop varieties
creating habitats for predators
limited use of pesticides
sustainable agriculture
growing enough food but not depleting resources
intercropping
2 or more crops planted at the same time in the same field to promote a synergistic interaction
crop rotation
crop species in a field are rotated from season to season
agroforesting
trees and vegetables are intercropped
organic agriculture
production of crops without use of pesticides/synthetic fertilizers
principles:
keep as organic matter and nutrients in soil + on farm
avoid use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
maintain soil by increasing soil mass, biological activity, etc
Concentrated Animal Feedlot Organizations (CAFO)
animals concentrated in an enclosed area and fed grain/fish meal
pros:
efficient and cheap → less land, overgrazing, and erosion
cons:
large inputs of grain, water, and fossil fuels
feedlot concerns
efficiency → 70% of corn + 80% soybeans grown go to feeding livestock; more efficient to feed humans with grains directly (10% rule)
antibiotic + growth hormone use → may lead to antibiotic resistance + hormones may pass to humans
methane → cows burp 16% of methane release
waste → only 50% of waste returned to soil as fertilizer; runoff leads to eutrophication + drinking water contamination
free-range farms
animals roam around mostly untended land + graze
pros:
less environmental impact; considered more sustainable
cons:
uses lots of land → less meat, overgrazing, threats from predators, increased erosion
fishery
a commercially harvestable population of fish within a particular ecological region
fishery collapse
decline of fish population by 90% or more
bycatch
unintentional catch of nontarget species while fishing
individual transferable quotas (ITQ)
a fishery management program in which individual fishers are given a total allowable catch of fish in a season that they can either catch or sell
aquaculture
raising marine/freshwater fish in ponds/underwater cages (~feedlot for fish)
pros:
efficient → less water/space = more fish
takes pressure off wild species
cons:
need lots of land, feed, and water
lots of waste
may destroy estuaries and wetlands
dense populations increase disease → increased use of antibiotics and risk to wild populations
septic tanks
typically in rural areas
way to manage wastewater
requires a lot of land
run by gravity
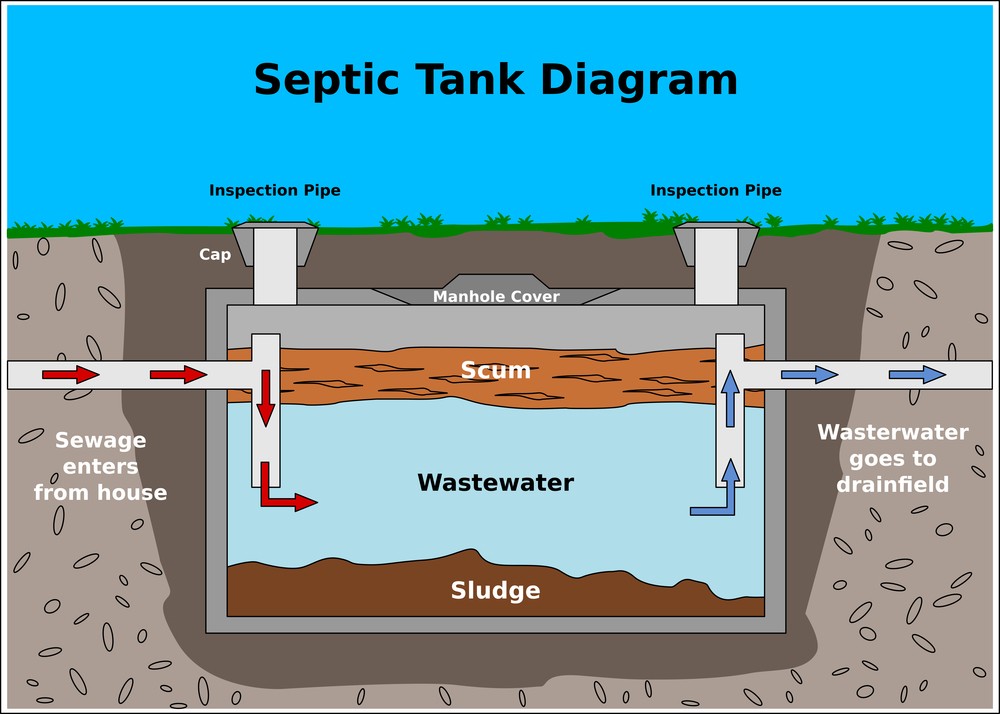
wastewater treatment process (steps + what happens in them)
1. Primary → remove solids
screens → settling basin → liquid continues to secondary
2. Secondary → break down biological oxygen demanding waste (BOD)
aeration basin → bubble air into affluent + bacteria break it down
3. Tertiary → kill pathogens
chlorine, UV light, O3 bubbles
then tested
problems with waste water treatment
open loop → unsustainable → better options = pumping water back into groundwater/sending directly to drinking water treatment plant
no treatment for stom water
not removed in waste water treatment: pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, organic compounds (VOCs), phosphates
Clean Water Act 1977
amendment to Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972
set basic structure for regulating discharge of pollutants in US
designed to protect fishing, swimming, + ecosystem health
set up National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) → regulates point sources (not runoff)
Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) → sets cap for amount of pollutant discharge
Safe Drinking Water Act
established drinking water standards
focuses on all water actually/potentially designed for drinking use
sets Maximum Containment Levels (MCLs) for drinking water
pathogen dose = 0 always
point source
1 simple, easy to identify source
eg. pipe from power plant dumping hot water
non-point source
pollution that comes from a variety of place
eg. runoff, exhaust, AMD
Nutrients
sources: agricultural runoff from fertilizer/feedlots, detergent, disturbed soil
impacts: eutrophication → dead zones
indicators: elevated N + P levels, lower dissolved oxygen levels, algal blooms (increase in organic matter)
reduction: runoff reduction (repair riparian zone), treat stormwater, improve farming techniques, use organic fertilizer, avoid detergent with phosphates
eutrophication
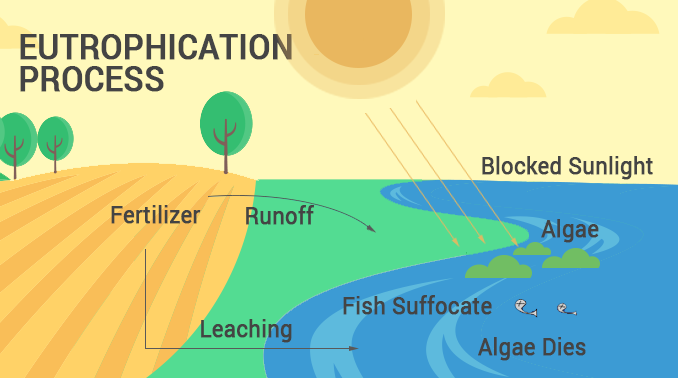
organic matter (aka BOD)
sources: agricultural runoff, sewage, papermills, food processing
effects: high temperatures reduce amount of oxygen water can hold + warm water
indicators: increased water temperature, decreased DO, fish kills
reduction: reduce runoff, cool water temperatures before releasing, maintain water flow + riparian zone (provides shade)
sediment pollution
sources: erosion, mining, construction
effects: blocks sunlight, may choke fish, increased water temperature and turbidity
indicators: increased turbidity, increased temperature
reduction: maintain soil and reduce erosion
pathogen pollution
sources: human + animal waste → raw sewage + CAFO runoff
effects: diseases → cholera, typhoid, giardia, e. coli
→ symptoms of diseases: vomiting and diarrhea
indicators: presence of fecal coliform bacteria
reduction: treat sewage, boil water, separate drinking & waste water, use filters for parasites
endocrine disruptors pollution
sources: CAFOs from added hormones & pesticides that mimic hormones
effects: interfere with functioning of the endocrine system, even in very low doses
indicators: (all in fish, amphibians, and reptiles) low sperm counts, hermaphroditism, decreased production of testosterone
reduction: decrease use of hormones in raising animals and reduce use of chemicals that mimic hormones
persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
non-polar and fat soluble
stay in environment + ecosystems for a long time
biomagnify and bioaccumulate
eg. DDT & PCB
oil spills
sources:
natural oil seeps
surface runoff
transport and extraction
indicators:
presence of oil byproducts → benzene, xylene, & other hydrocarbons
kill wildlife direct + indirectly
reduction:
improve safety standards for extracting and transporting oil
research oil spill cleanup techniques
oil spill cleanup methods
containment boom + vacuum
containment boom + absorb
dispersant
GMO bacteria → breaks down oil
plastic + solids pollution
sources:
improper waste disposal
incidental waste falling into waterways
indicators:
microplastics
problems:
wildlife eats plastic + microplastics, mistaking for food
toxins in plastics can make its way into food supply
reduction:
reduce reuse recycle
no remediation
groundwater pollution
sources:
underground storage tanks
older unlined landfills
modern landfill leaks
effects:
aquifer contamination
plume movement into surface water (at springs)
reduction:
line landfills + manure lagoons
bury waste in appropriate hazardous waste facilities
clean up superfund + brownfield sites
replace underground storage tanks
heavy metal pollution
sources:
natural deposits (arsenic, mercury)
mining
coal burning (mercury)
e-waste (cadmium, mercury, lead)
industrial processes - smelting
effects:
bioaccumulate + biomagnify
largest impact at the top of food chain
most toxic @ low doses + neurotoxins
indicators:
positive tests for metals
reduction:
minimize output of waste
temperature testing
desired range: varies, but range of tolerance for native species
impacted by:
stream flow + lake depth
thermal pollution from power plants
turbidity level
pH testing
what is measured: concentration of H+ ions → how acidic/basic
how to measure: pH probe/litmus paper
desired range: b/w 5-8
impacted by:
acid rain
AMD
buffering capacity
geology of the watershed (limestone)
nitrate testing
what is measured: ppm of nitrate ions → indicated how nutrients rich
how to measure: digital probe/nitrate titration kid
impacted by:
agricultural runoff
fertilizer
feedlots
sewage treatment plants
phosphate testing
what is measured: ppm of phosphate ions
how to measure: probe/titration kit
impacted by:
runoff
detergents
dissolved oxygen (DO)
measured by: ppm of oxygen dissolved
impacted by:
temperature
nutrient levels
turbidity
organic waste
biological oxygen demand (BOD)
what is measured: rate of oxygen use over 5 days
desired range:
pristine rivers: <1mg/L
polluted rivers: 2mg/L-8mg/L
sewage effluent: >20mg/L
impacted by: