Anatomy of the Skull: Bones, Sutures, and Cranial Nerves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
How many bones make up the skull?
22 bones
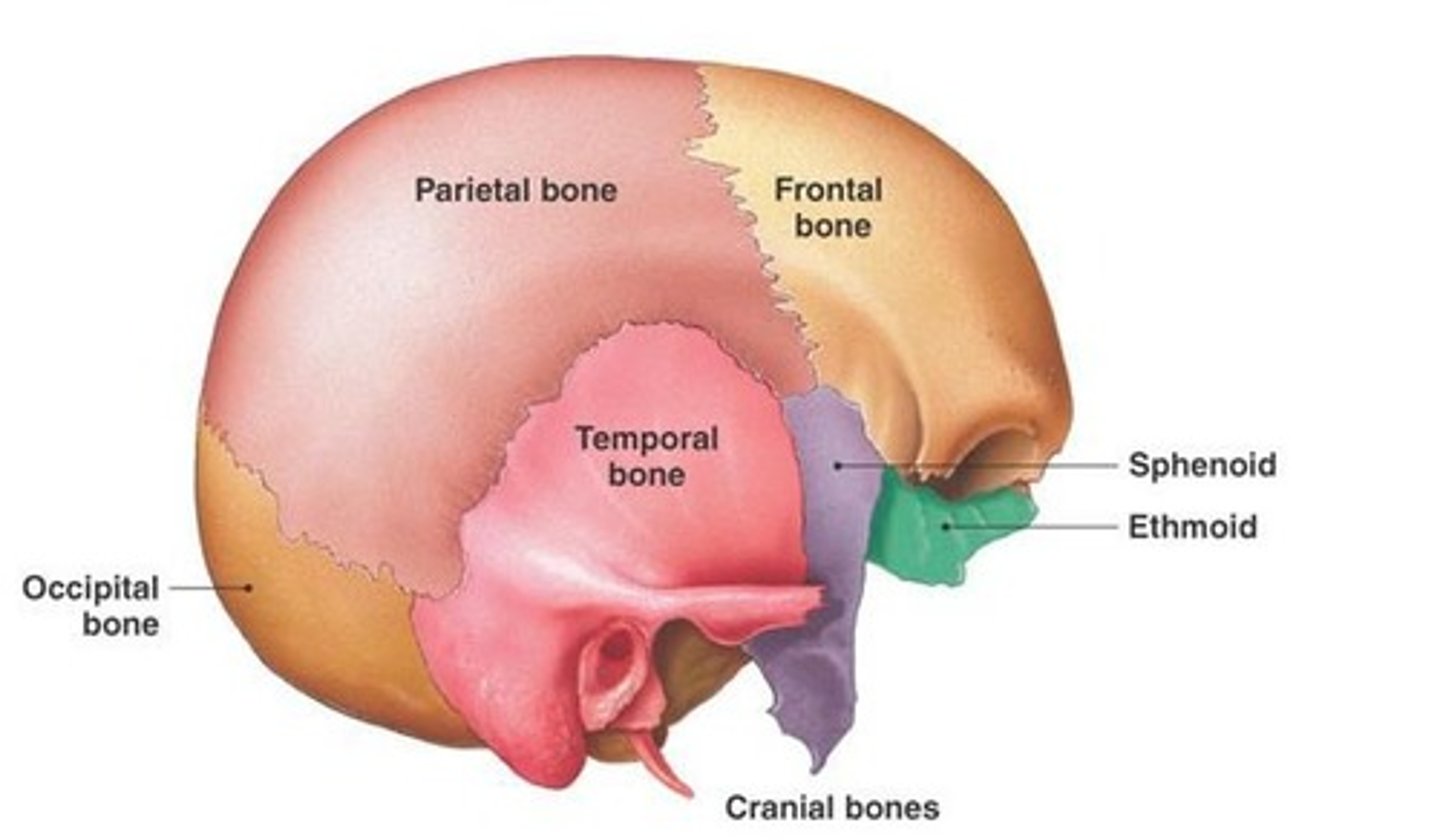
What are the two main groups of bones in the skull?
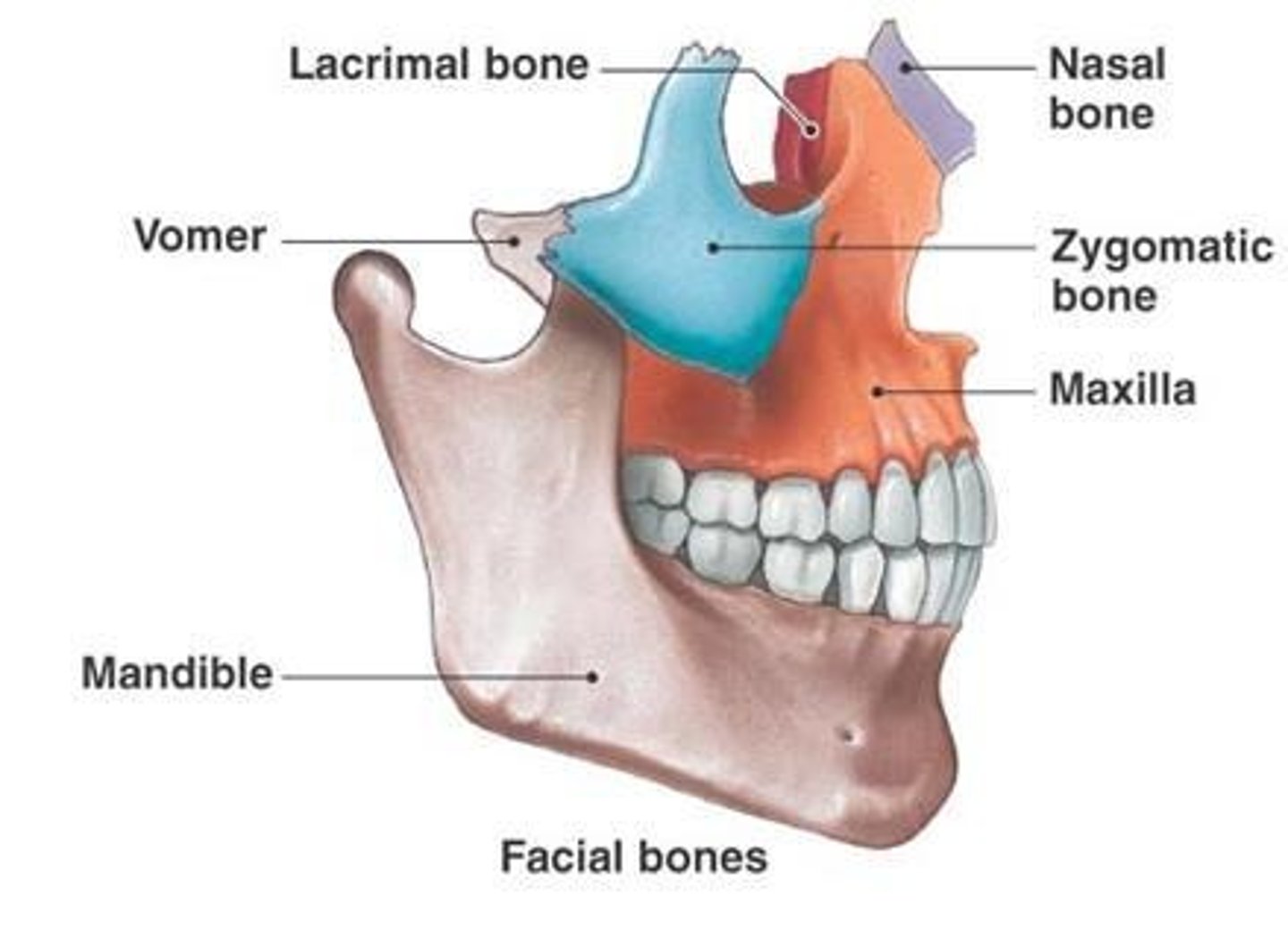
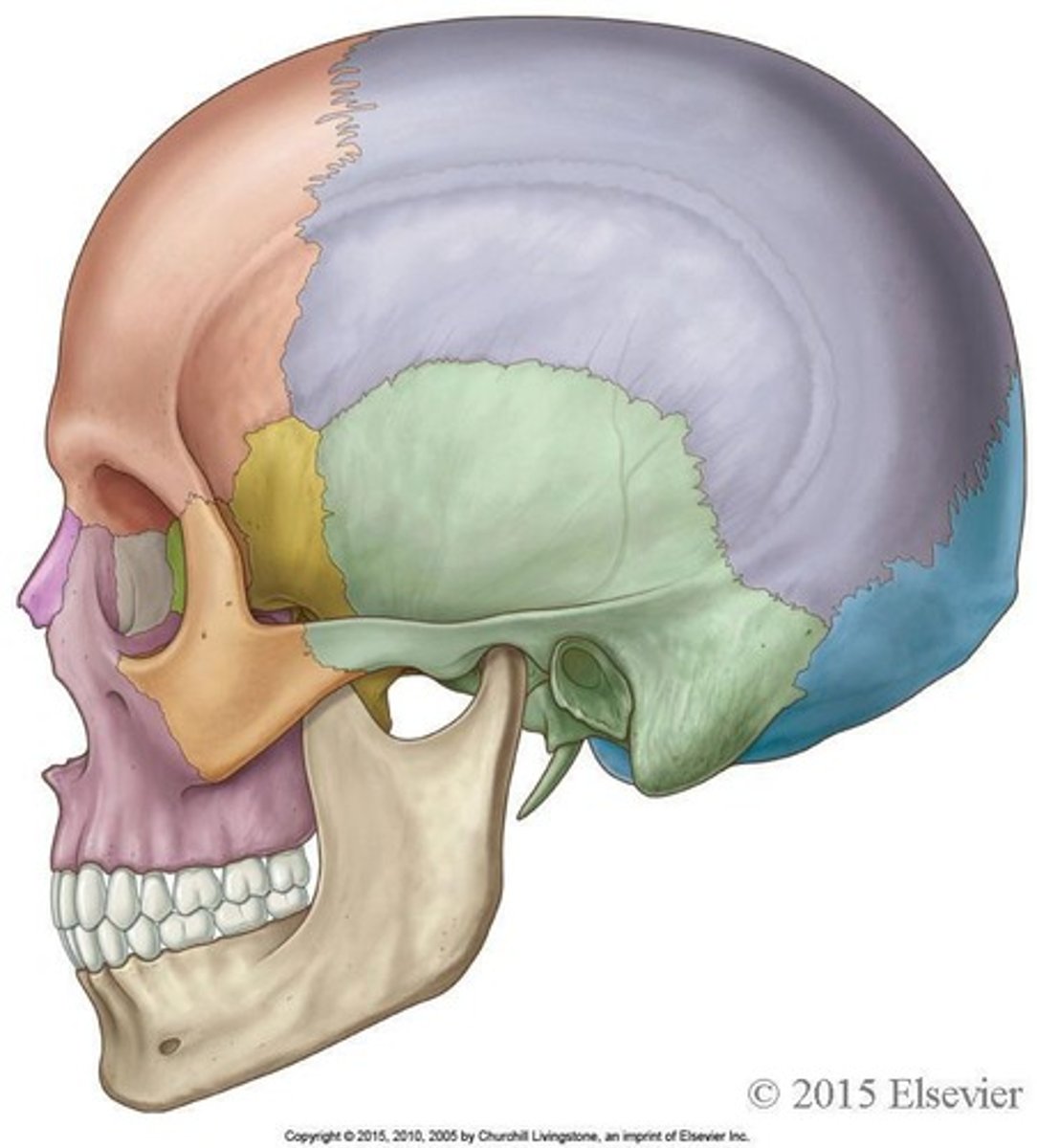
Cranial bones (8) and facial bones (14)
What are the unpaired bones of the cranium?
Frontal bone, Occipital bone, Sphenoid bone, Ethmoid bone
What are the paired bones of the cranium?
Parietal bones (2) and Temporal bones (2)
What structures compose the zygomatic arch?
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone and temporal process of the zygomatic bone
What forms the hard palate?
Palatine processes of the maxillae and horizontal plates of the palatine bones
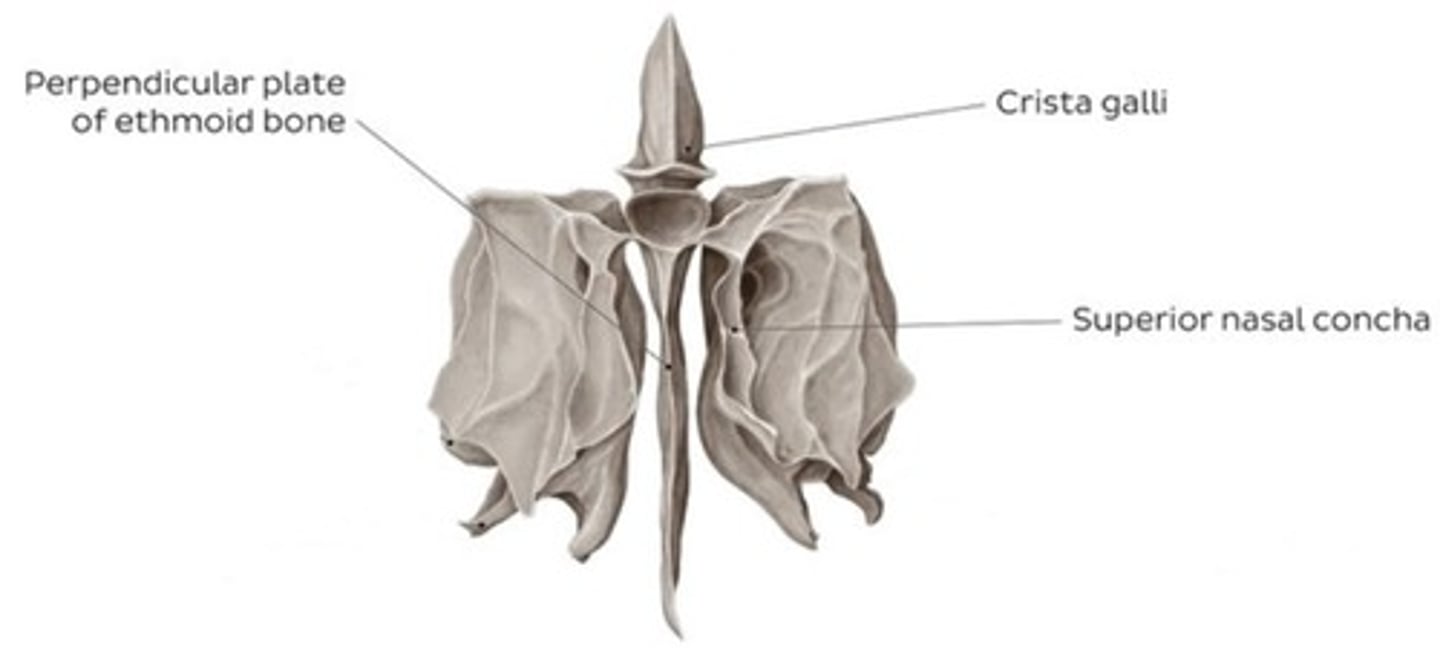
What is the nasal septum composed of?
Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, vomer bone, and septal cartilage
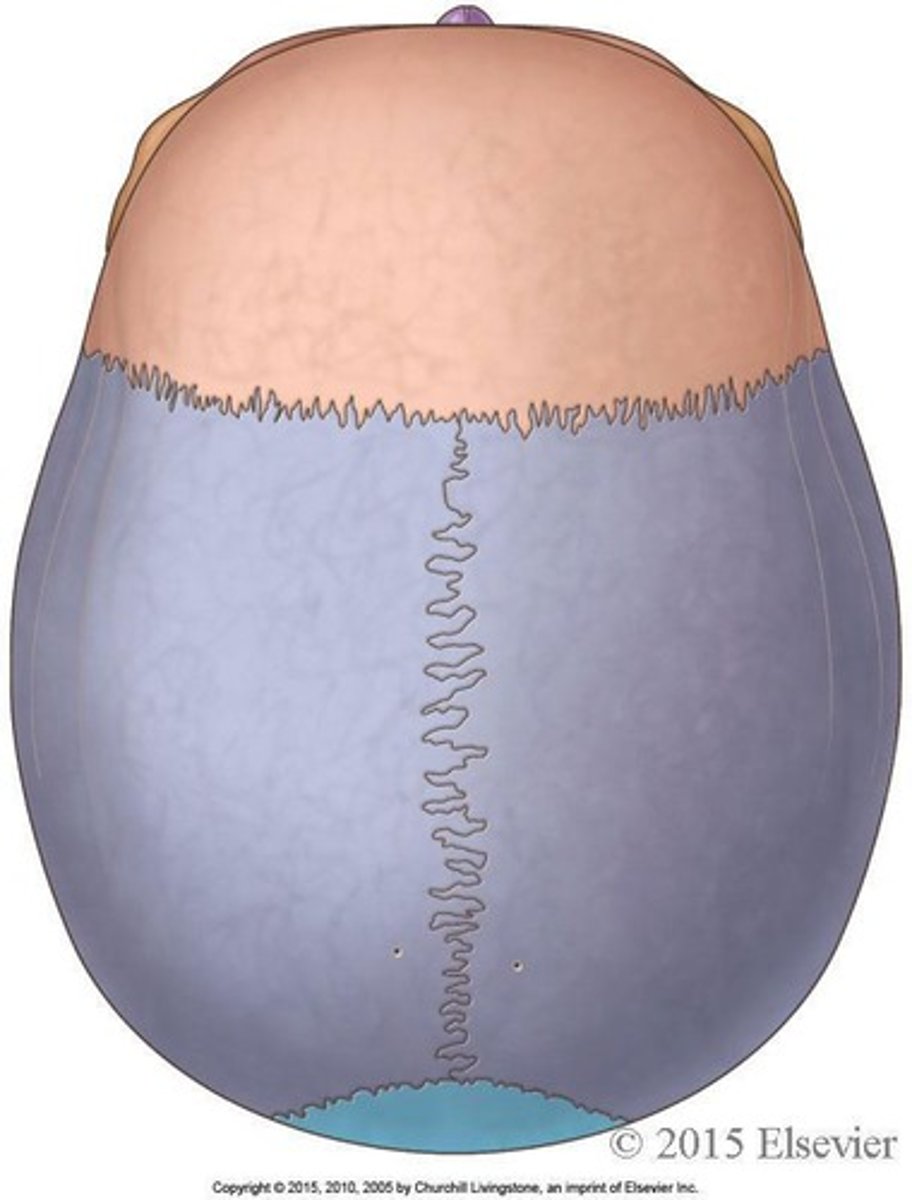
What are fontanels?
Soft fibrous areas in an infant's skull where several sutures unite, allowing for molding and bone modeling
What are the four major sutures of the skull?
Coronal suture, Sagittal suture, Lambdoid suture, Squamous suture
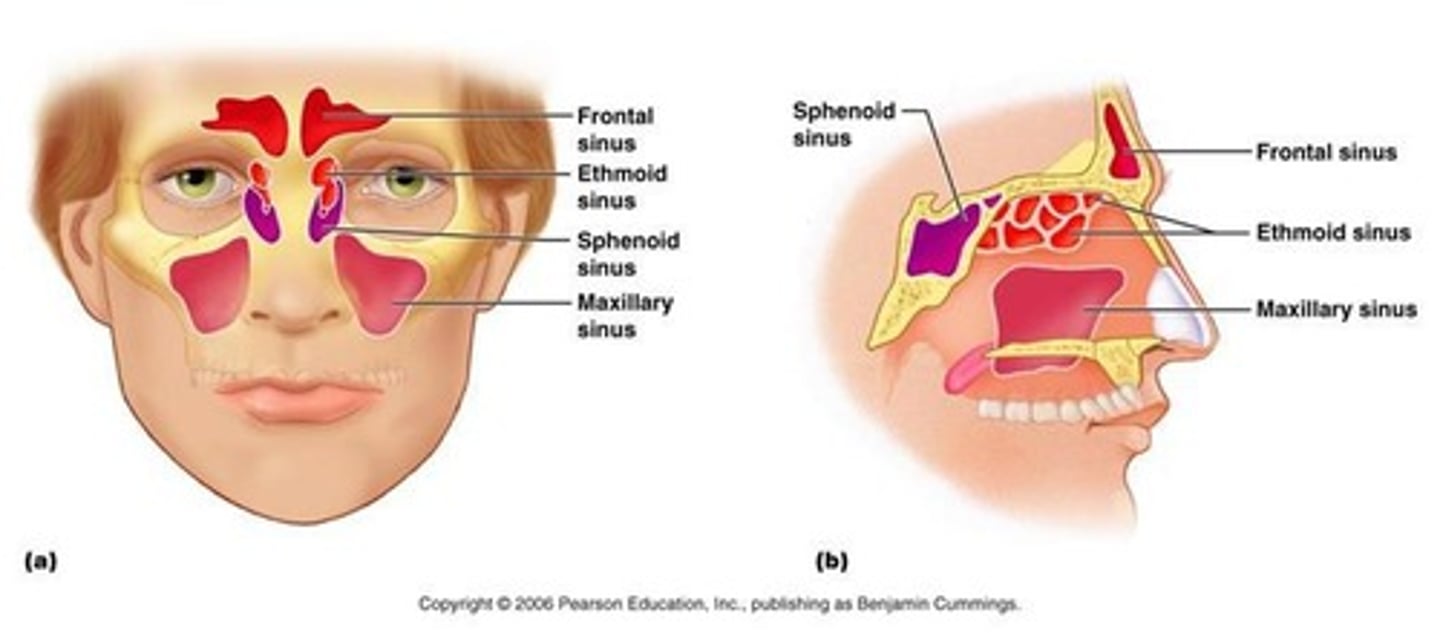
What are the paranasal sinuses?
Frontal sinus, Sphenoid sinus, Ethmoid sinus, Maxillary sinus
What is the function of the cranial fossae?
They provide a base for the brain and support the structures of the skull.
What is the significance of the foramen magnum?
It is the large opening in the occipital bone through which the spinal cord passes.
What cranial nerve passes through the optic canal?
Optic nerve (Cranial Nerve II)
Which cranial nerve is responsible for motor functions and passes through the superior orbital fissure?
Oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
What is the role of the hyoid bone?
It supports the tongue and is involved in swallowing.
What is a deviated septum?
A condition where the nasal septum is displaced to one side, often causing breathing difficulties.
What is the purpose of the cranial nerve passageways through the skull?
They allow cranial nerves to exit the skull and innervate various structures in the head and neck.
What is the anterior fontanelle and when does it close?
A soft spot on an infant's skull that closes between 12-18 months.
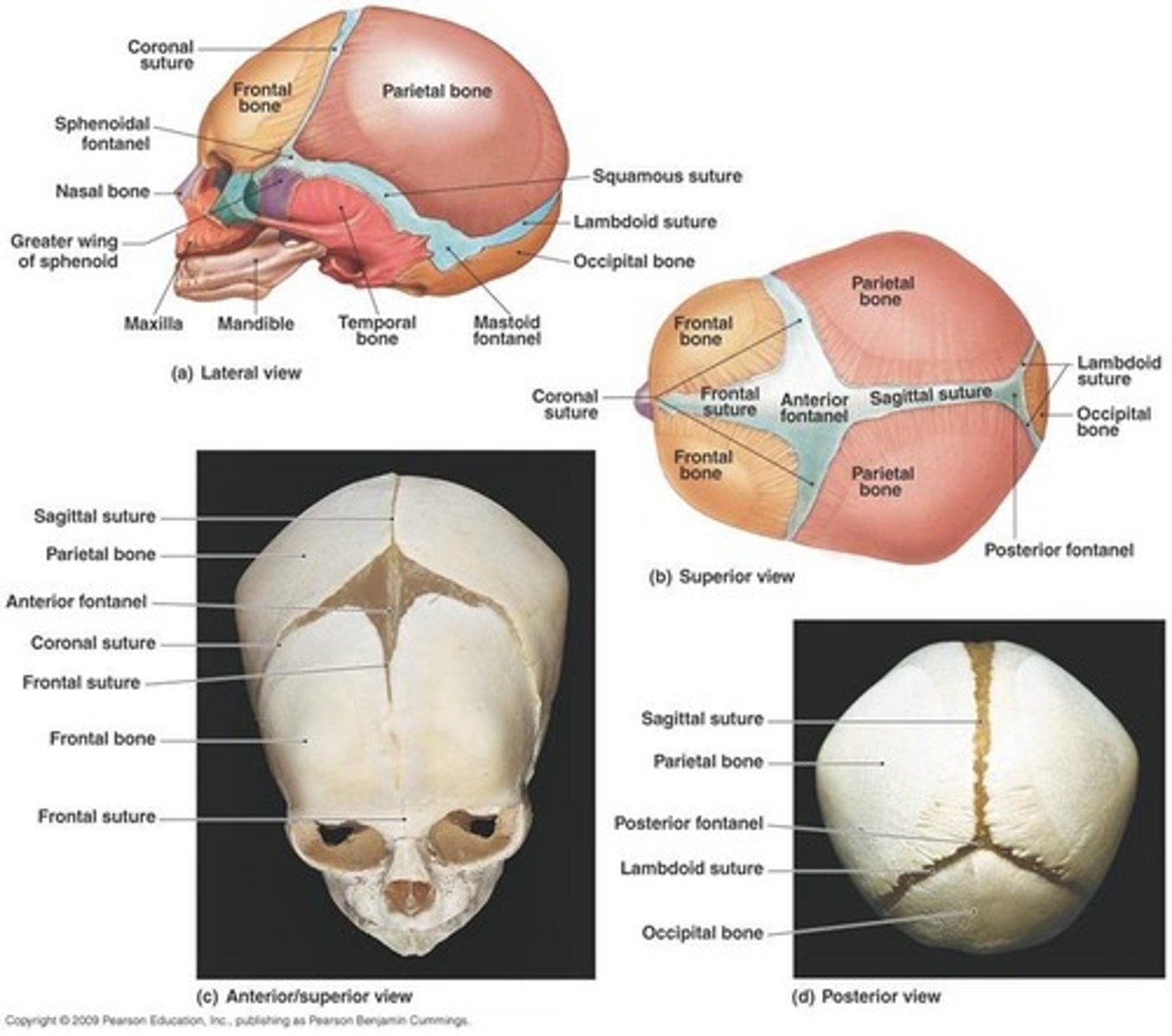
What is the posterior fontanelle and when does it close?
A soft spot on an infant's skull that closes between 6-8 weeks.
What bones make up the orbit?
Frontal bone, Zygomatic bone, Maxillary bone, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Lacrimal bone, Palatine bone
What is the significance of the external acoustic meatus?
It is the canal that leads to the eardrum and middle ear.
What is the function of the mastoid process?
It serves as an attachment point for neck muscles.
What is the crista galli?
A bony ridge in the ethmoid bone that serves as an attachment point for the dura mater.
What are the characteristics of the temporal bones?
They contain structures for hearing and balance, including the external acoustic meatus and mastoid process.
What is the significance of the jugular foramen?
It is the passageway for the jugular vein and several cranial nerves.