Intergumentary System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
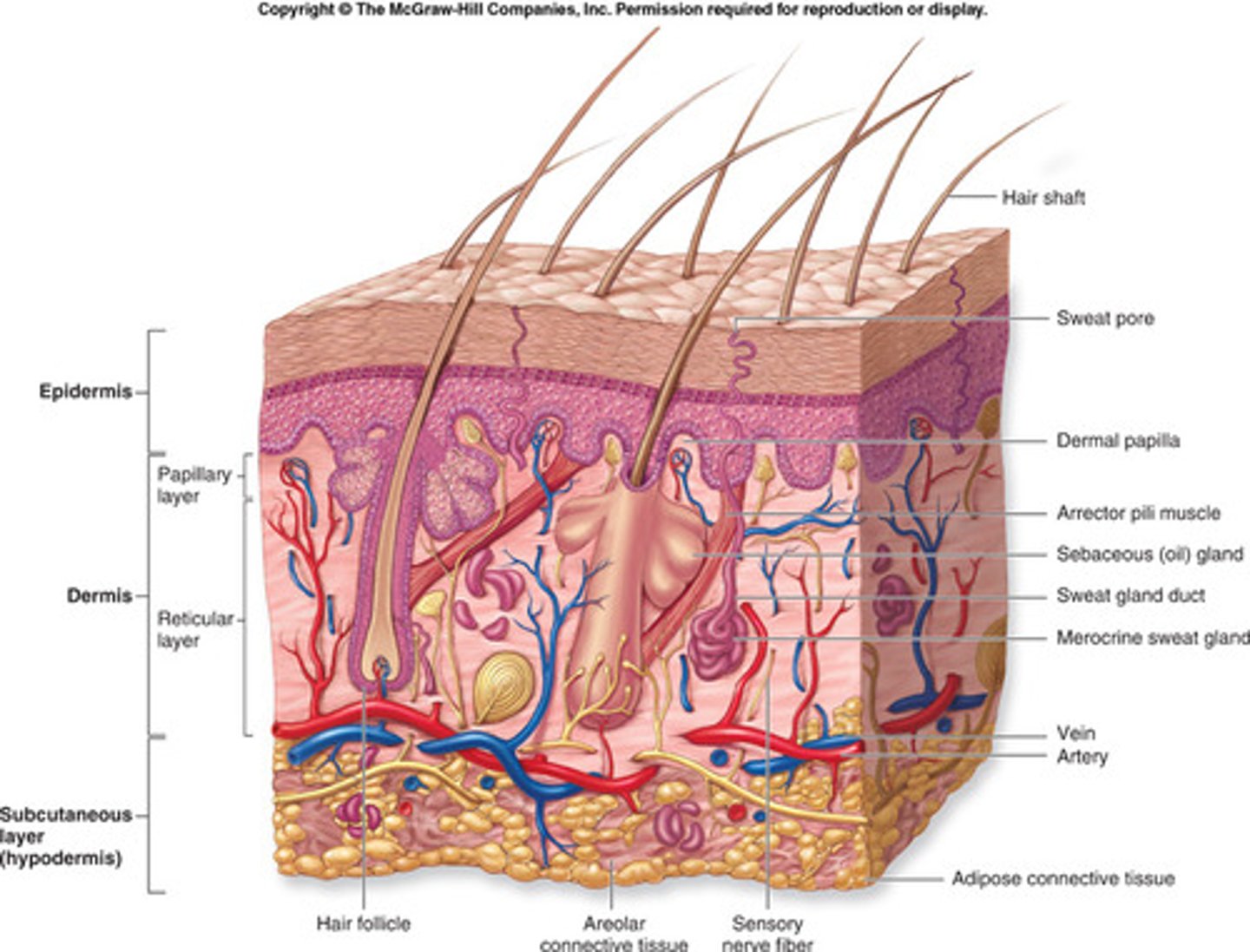
skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands
integumentary system
Protection of bacteria, UV; body temperature regulation through sweat glands; Excretion of salts and urea, Production of Vitamin D, and sensory reception
Functions of Skin
(produce the fibrous protein keratin). These cells are connected by desmosomes.
Keratinocytes
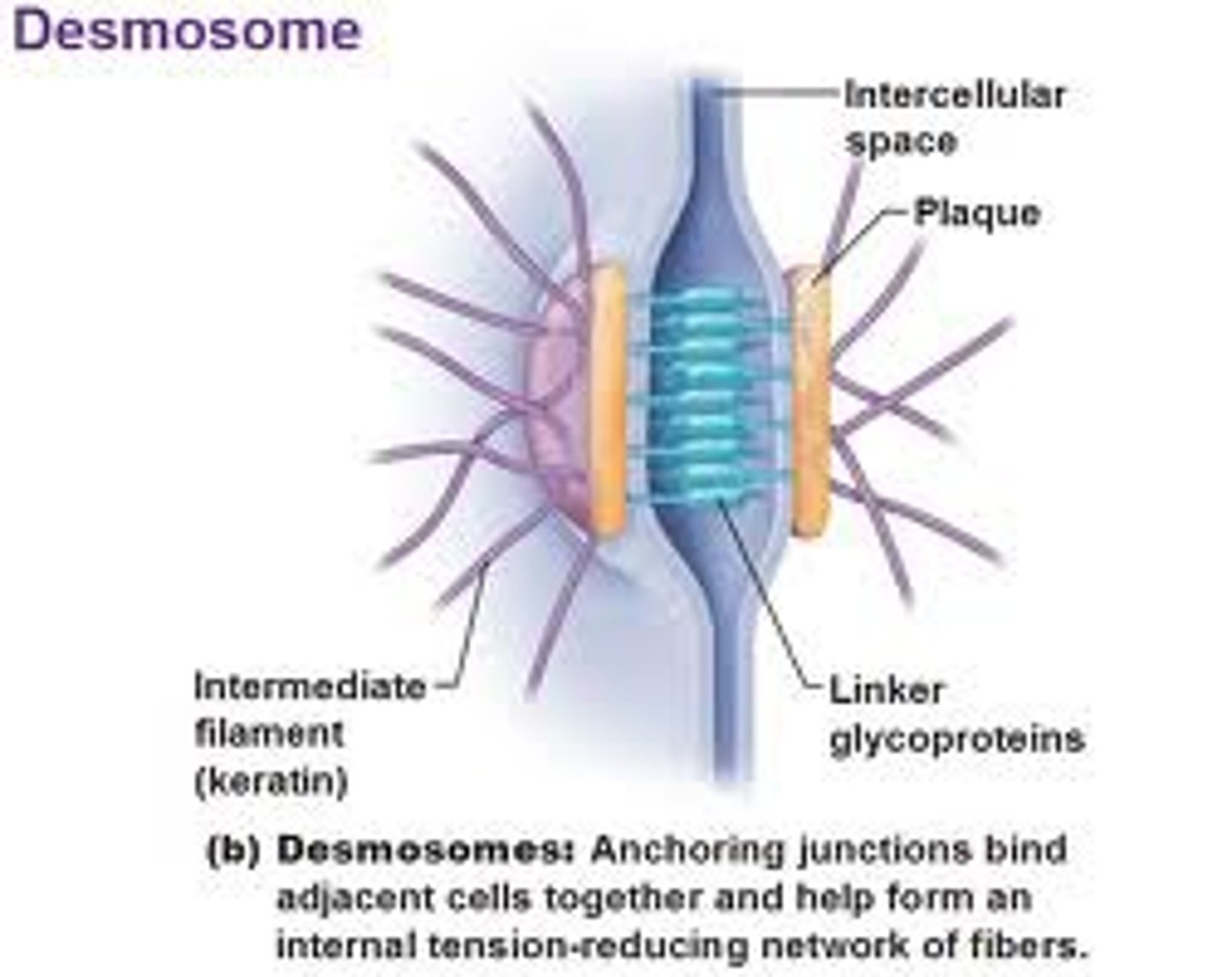
Anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart
Desmosomes
immune cells
dendritic and macrophages
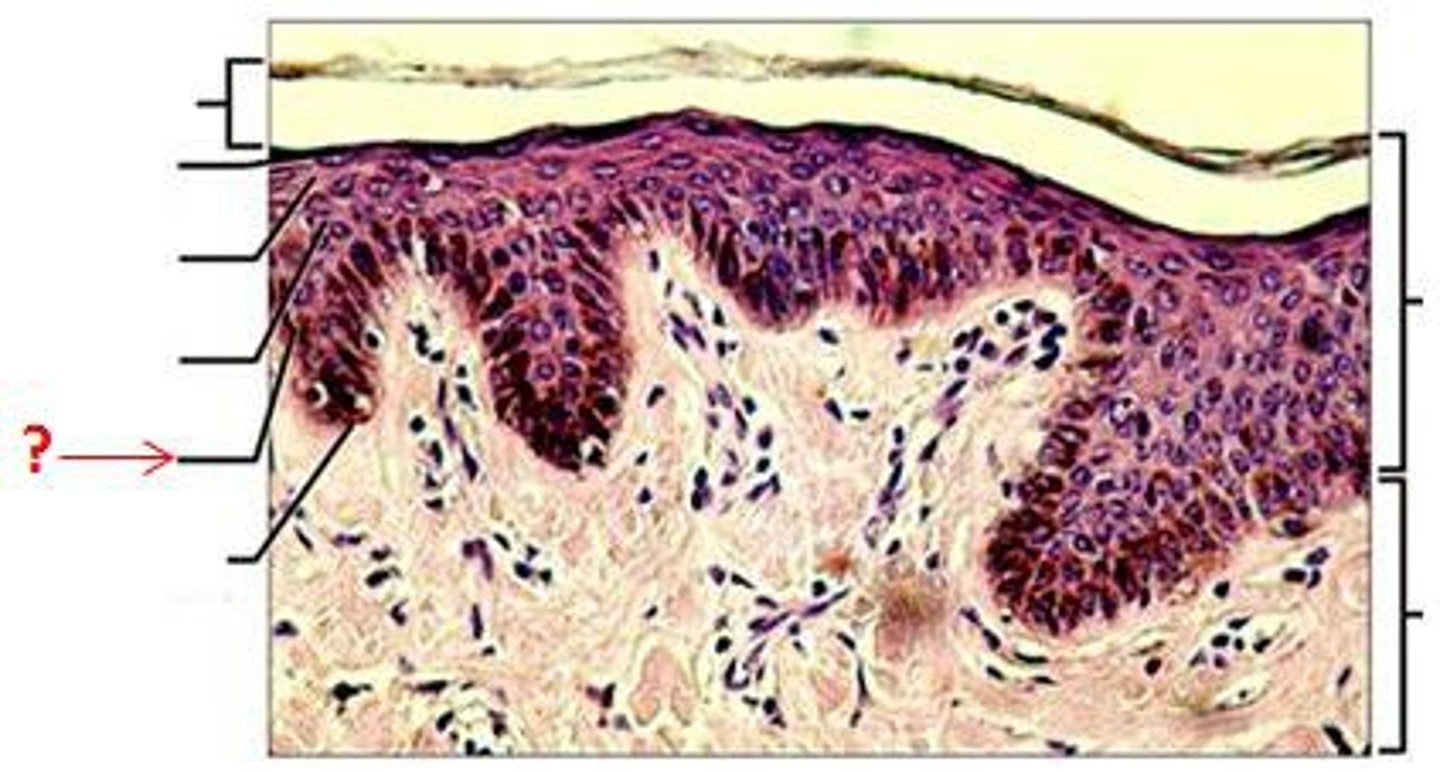
Row of cells along the dermis, Consists of a row of stemcells (youngest keratinocytes) and they rapidlydivide.
Stratum Basale
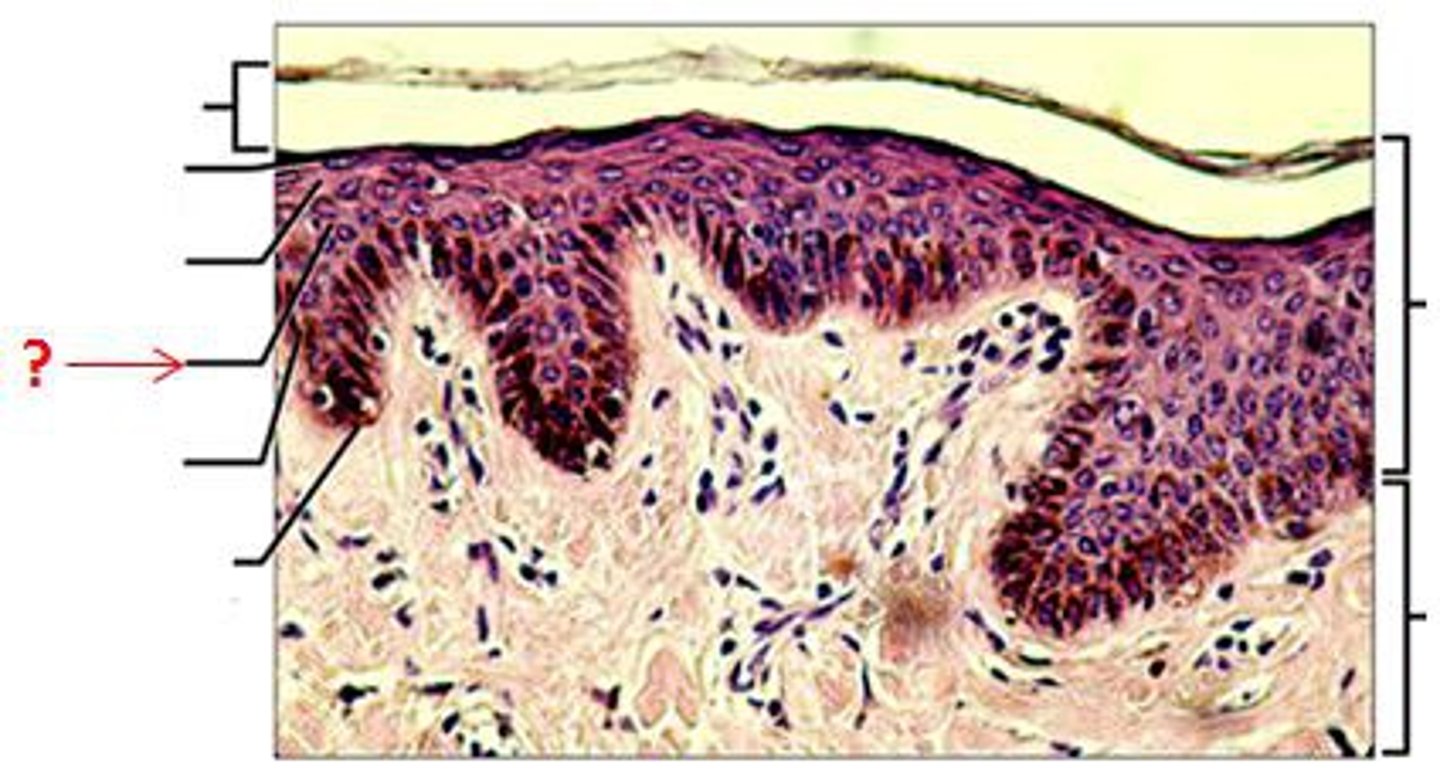
Several layers of keratinocytes with manydesmosomes and intermediate filaments- Dendritic cells and macrophages are found here
Stratum Spinosum
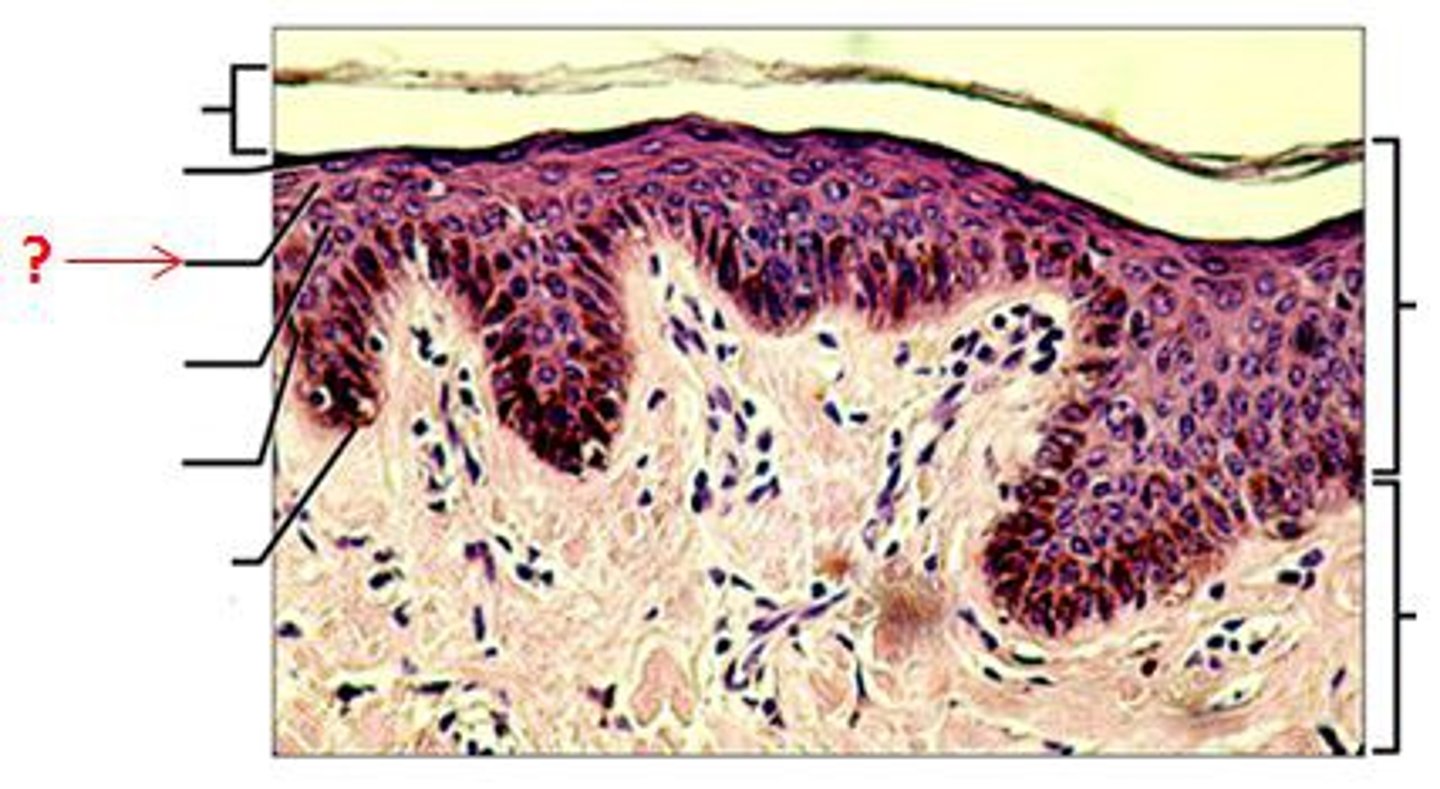
A thin layer of flattened keratinocytes. Any layer above this layer is too far from the vascularization of the connective tissue to survive. Cells contain granules that help waterproof and thicken the plasma membrane
stratum granulosum
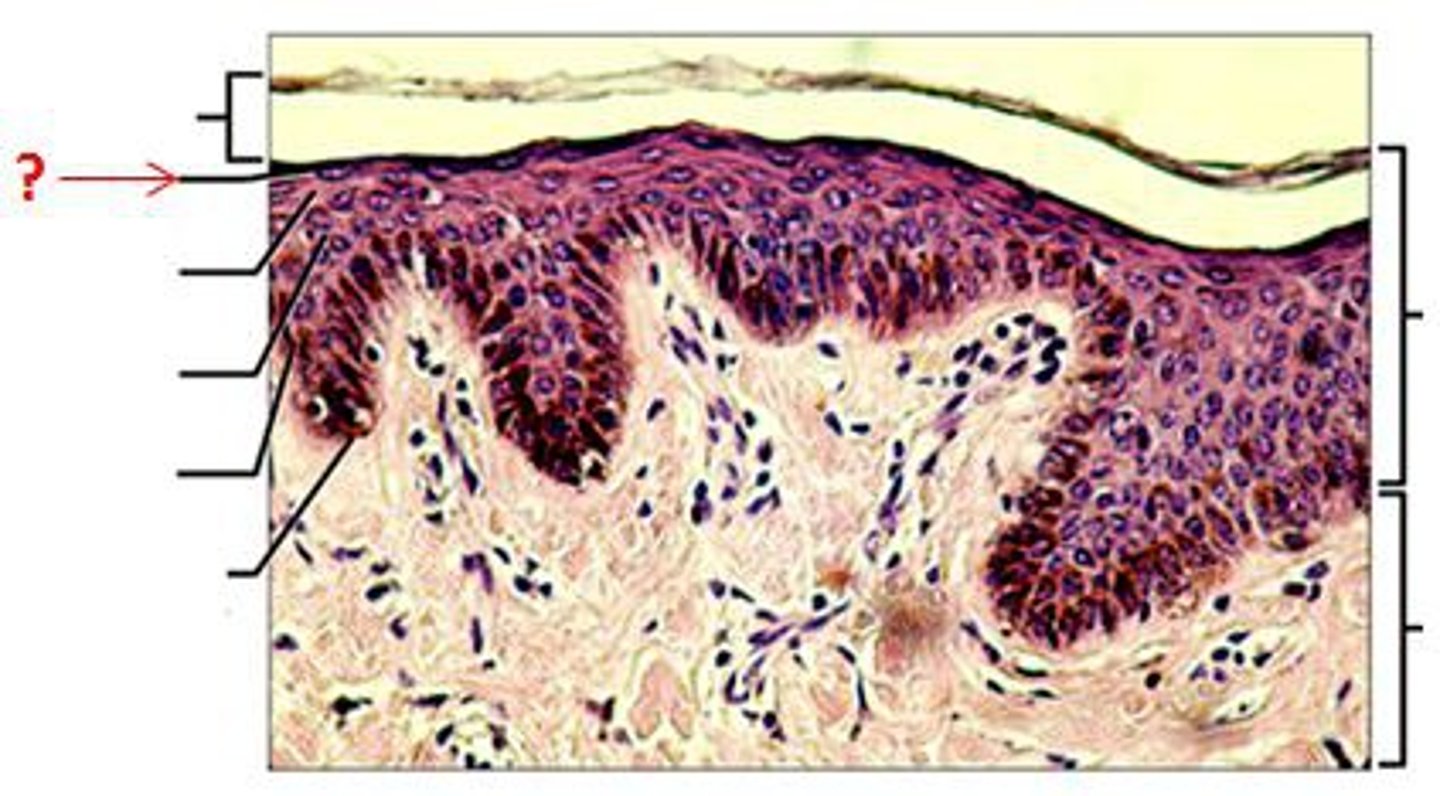
(occurs in thick but not thin skin) Consists of a few rows of flat dead keratinocytes
Stratum Lucideum
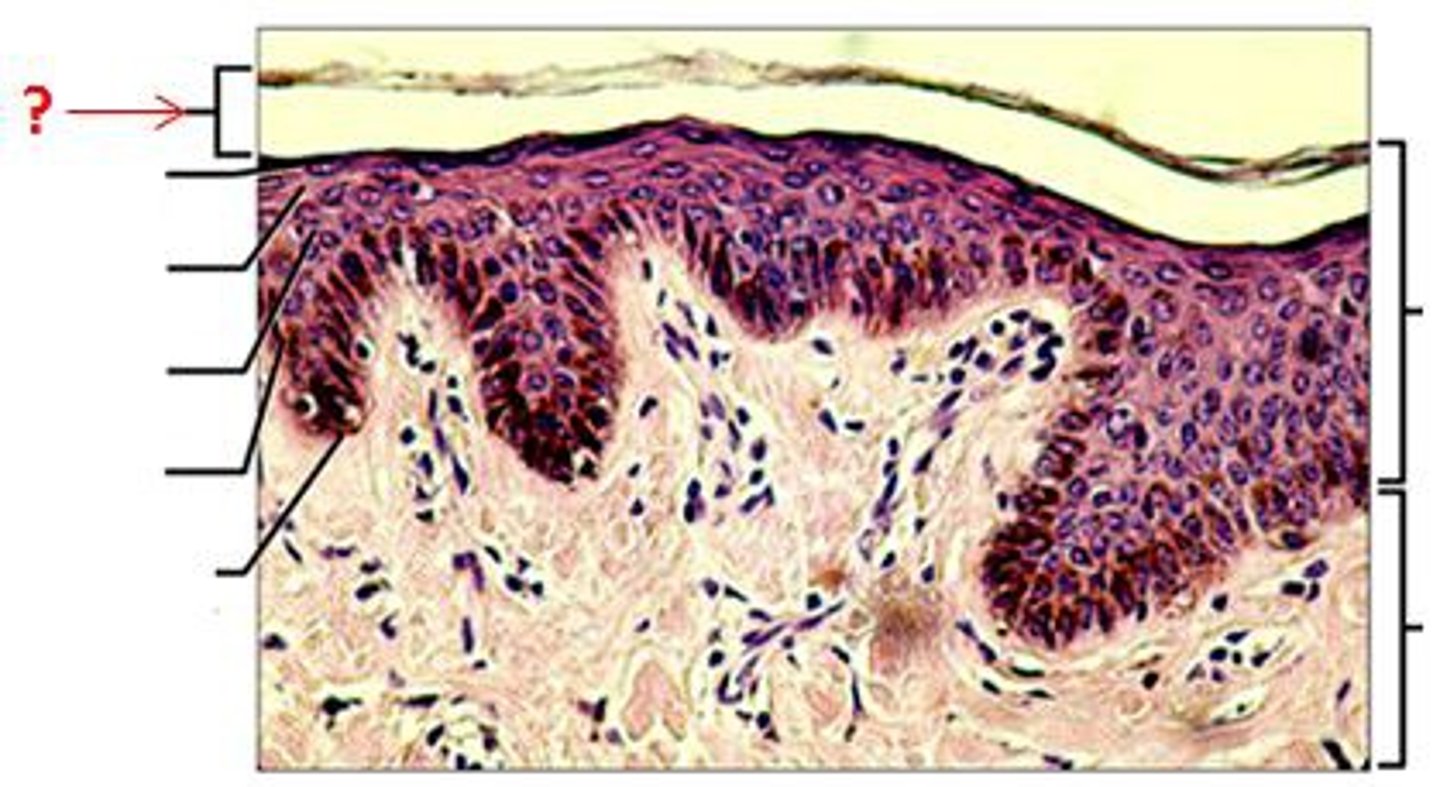
Dead keratinocytes that are flat sacs filled with keratin. Also has intermediate filaments embedded in "glue" from the granule
Stratum Corneum
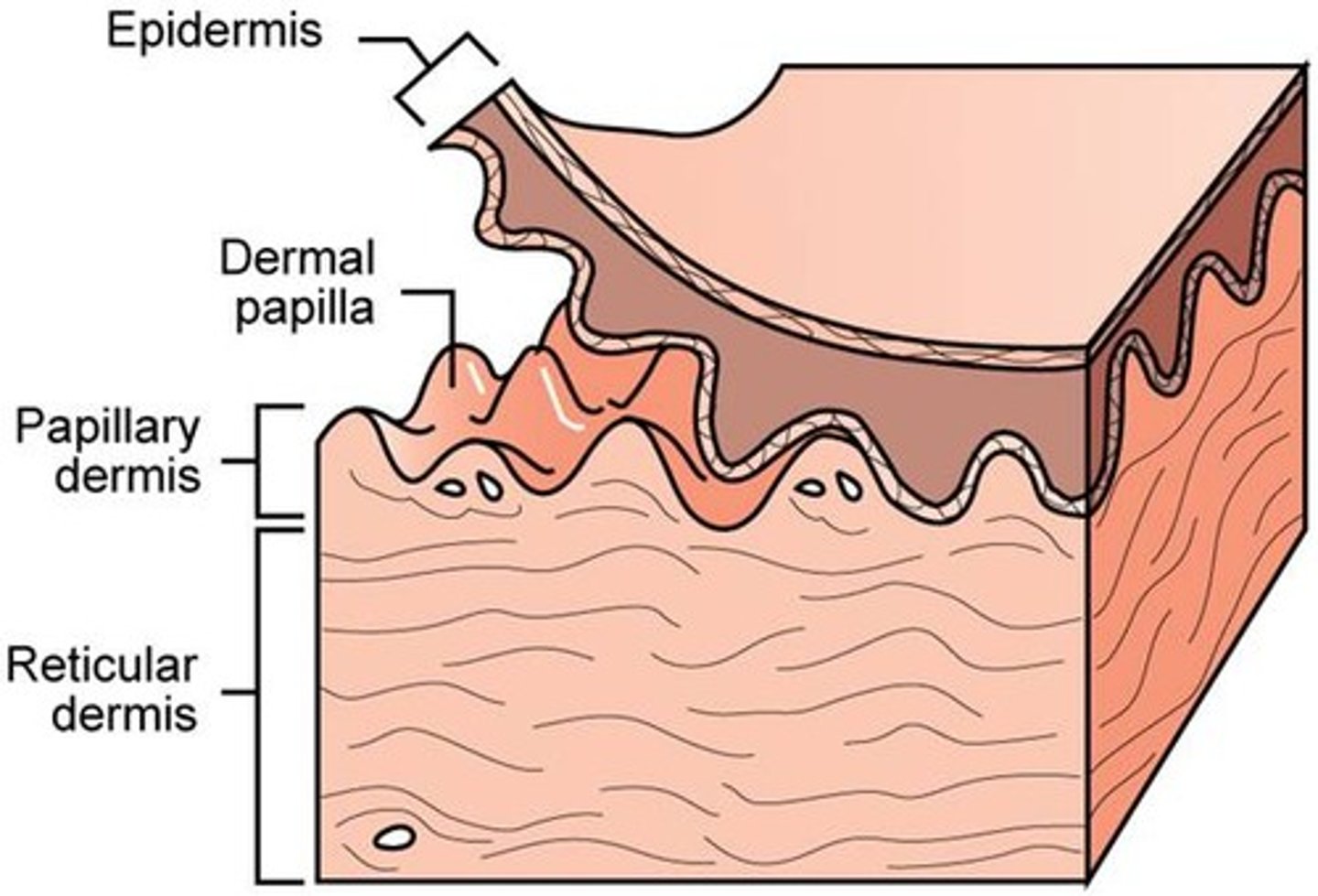
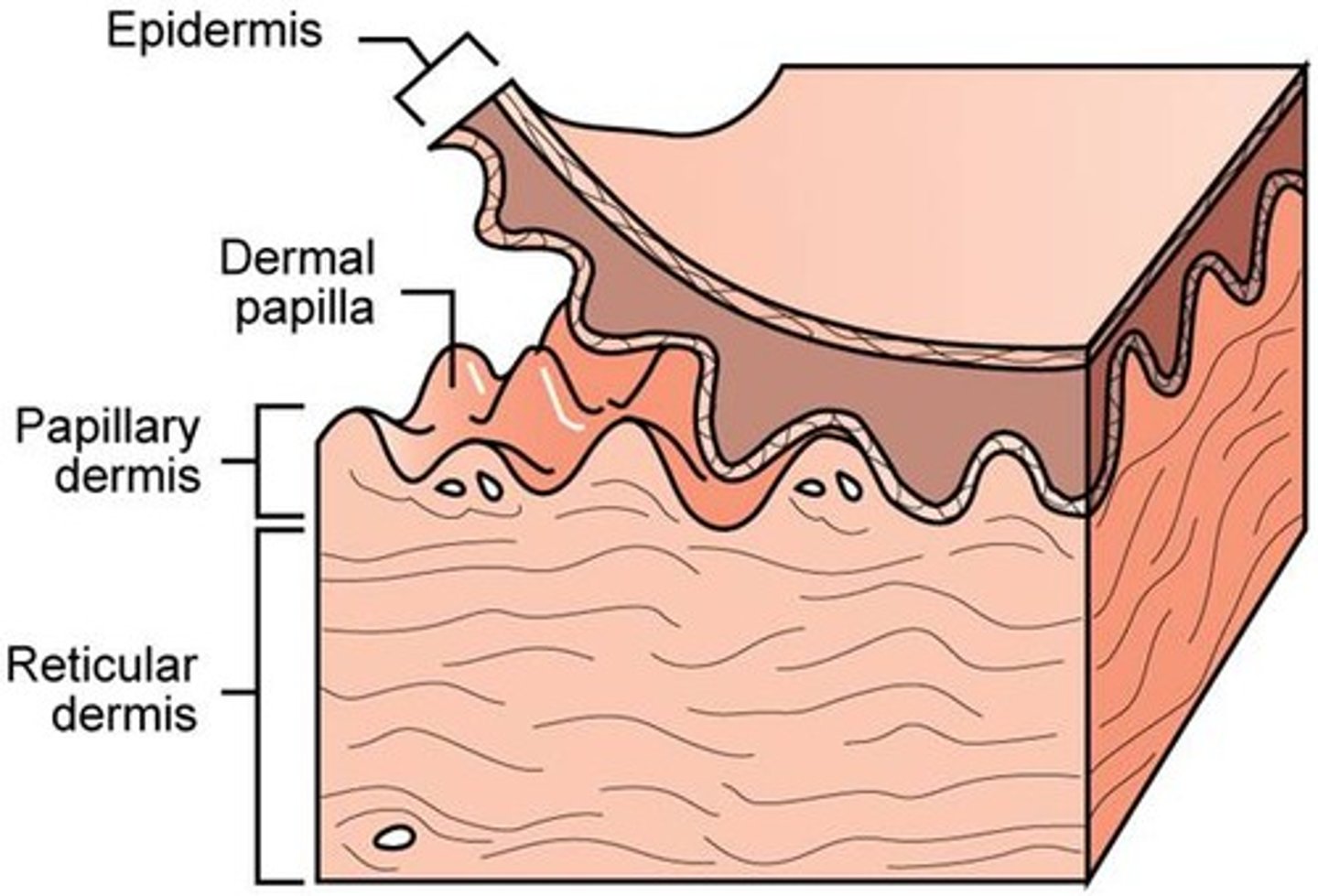
middle layer of skin divided into the papillary layer, and reticular layer
Dermis
s composed of areolar connective tissue (thin collagen and elastic fibers)
Papillary Dermis
Composed of Dense Irregular connective tissue.
Reticular Dermis
Oil Glands, found everywhere except palms and soles, secrete sebum (oil), they are holocrine glands (explode, releasing contents), have no lumen
sebacious glands
Secretion process of sebacious glands. The central cells of the gland become engorged with lipids and burst.
holocrene secretion
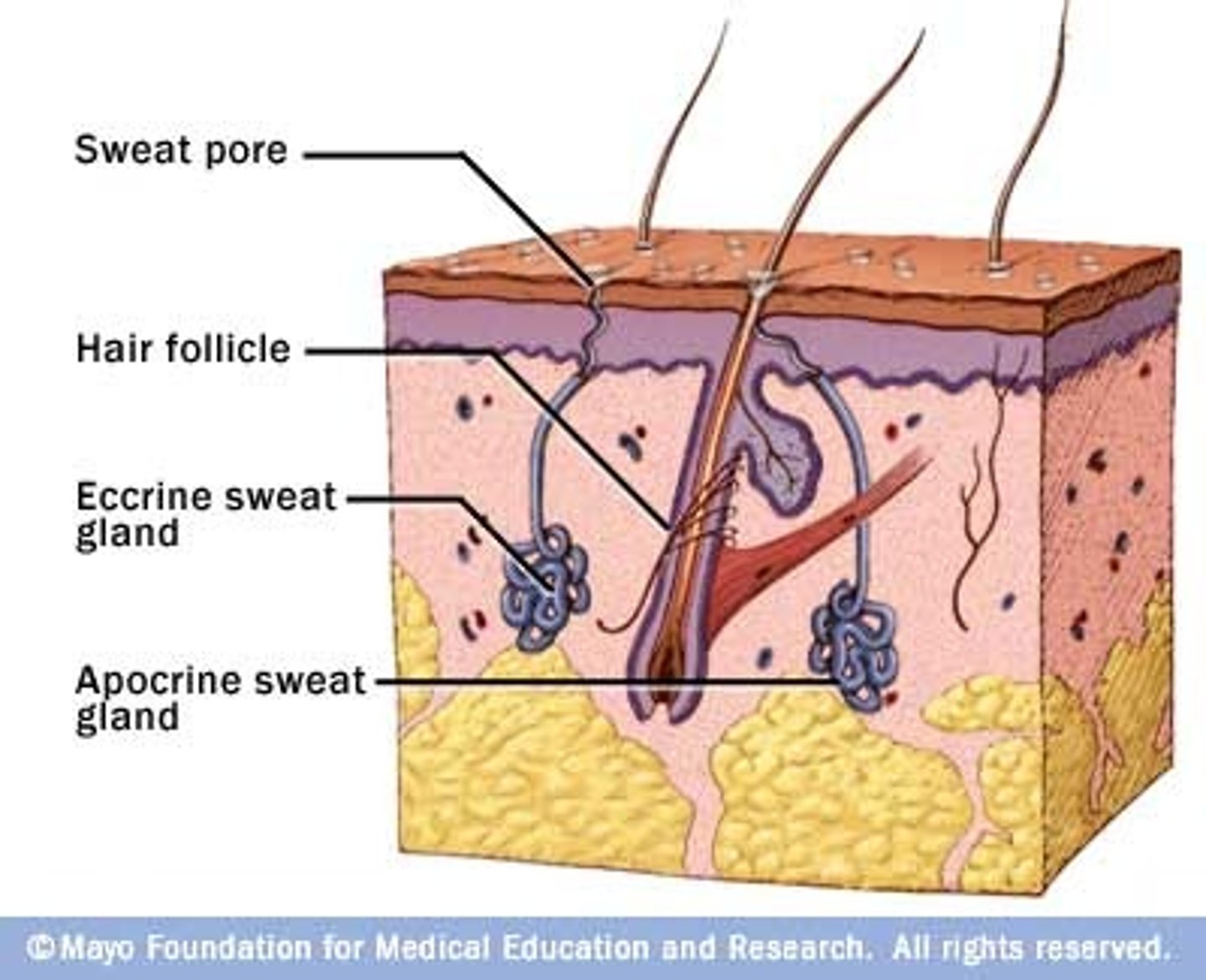
sweat glands made mostly of water, sweat comes from a filtrate of the blood
eccrine sweat glands
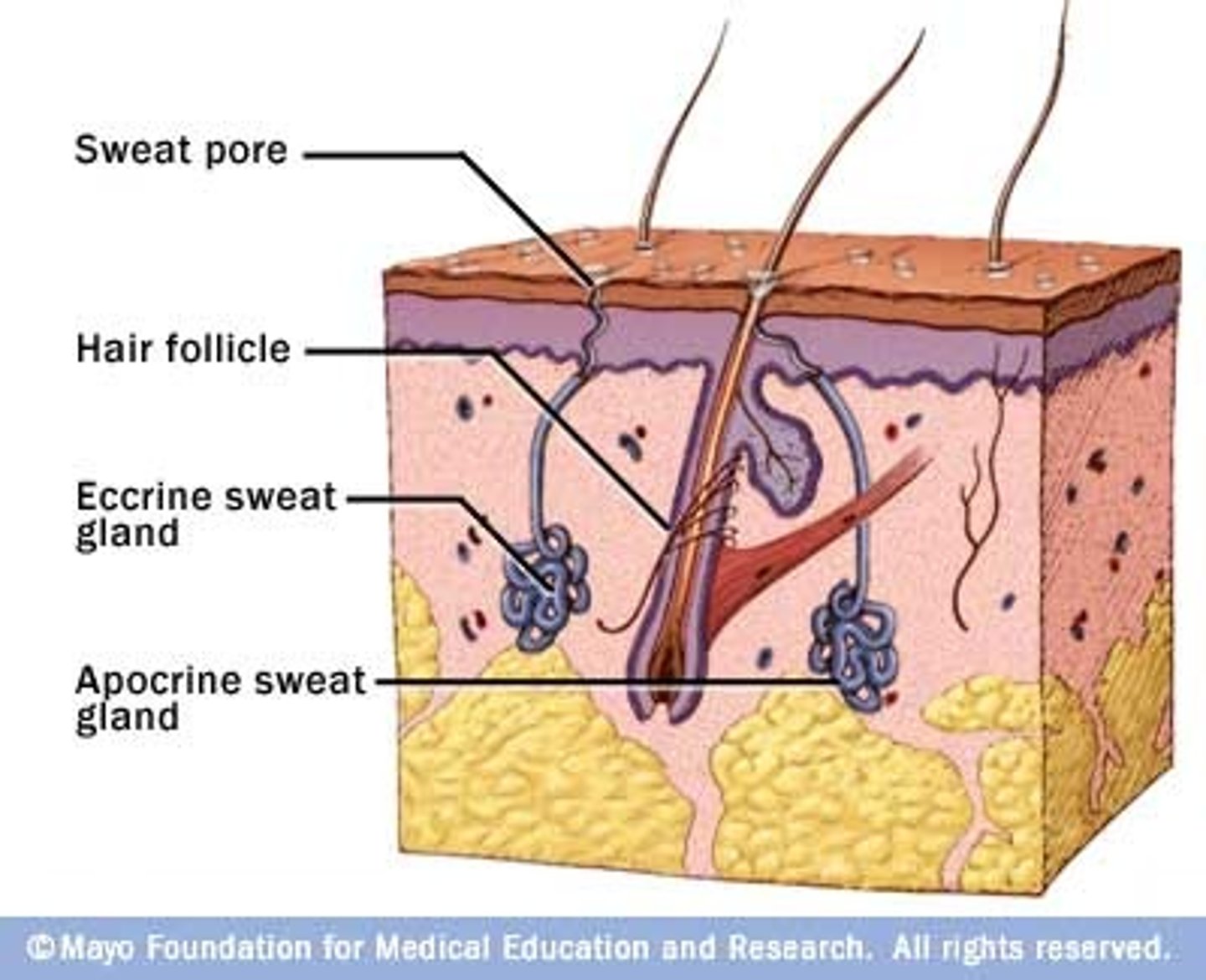
sweat glands only active after puberty; secrete a milky sweat with lipids and proteins, located in the armpits and groin, connected to hair follicle
appocrine sweat glands
Nails, hair, hair follicles, sebaceous (oil) glands,and sweat glands, all deriving from epithelial cells
skin appendages
Body hair of women and children• Fine, less coarse
Vellus Hair
Scalp hair, pubic hair, and axillary hair.• Longer and coarser.• Males, face, chest, arms and legs (under the control of androgens)
Terminal Hair
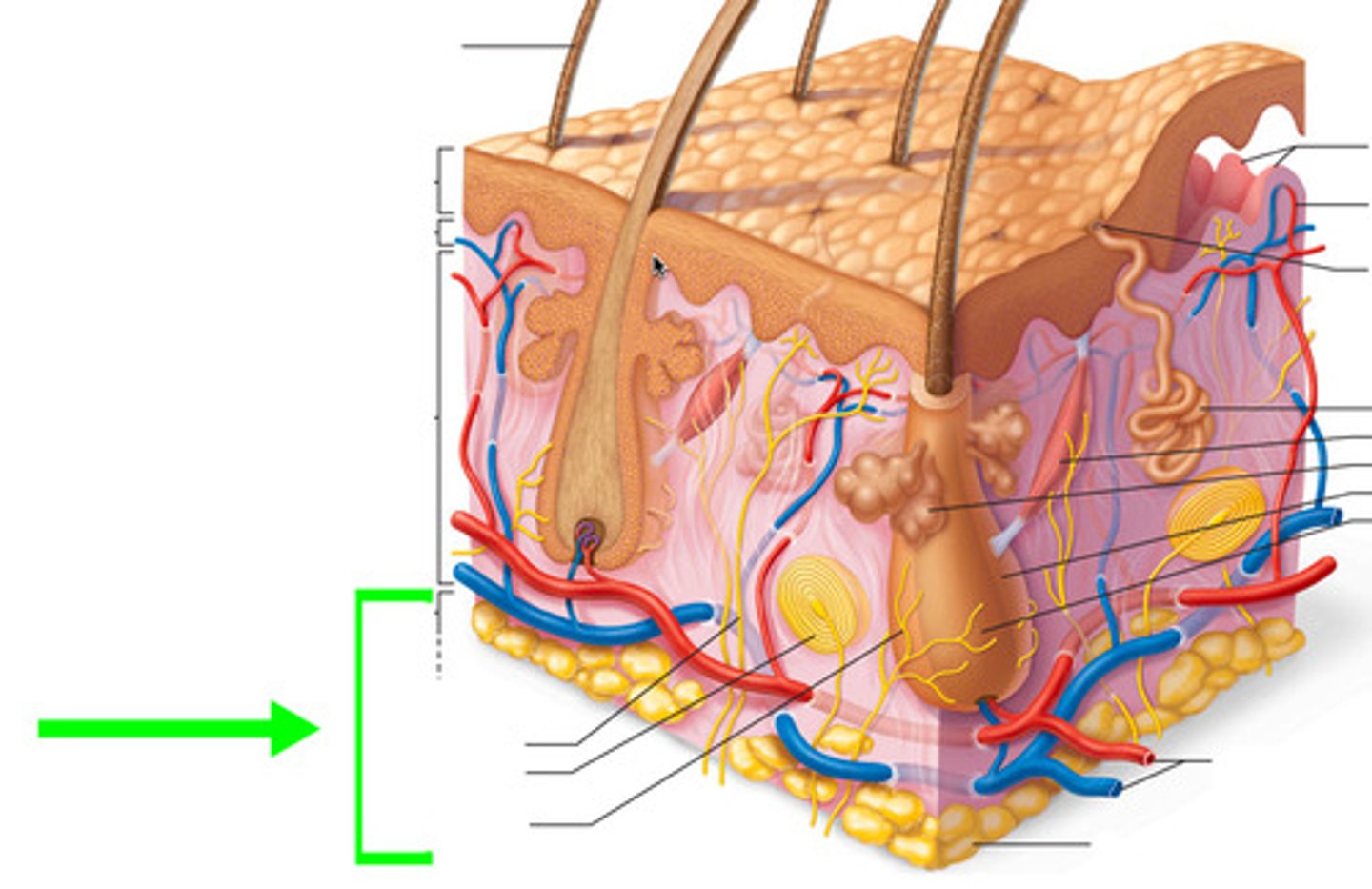
Consists of adipose and areolar connective tissue (mostly adipose)• Functions for energy storage and insulation
Hypodermis
The most serious form of skin cancer
Melanoma
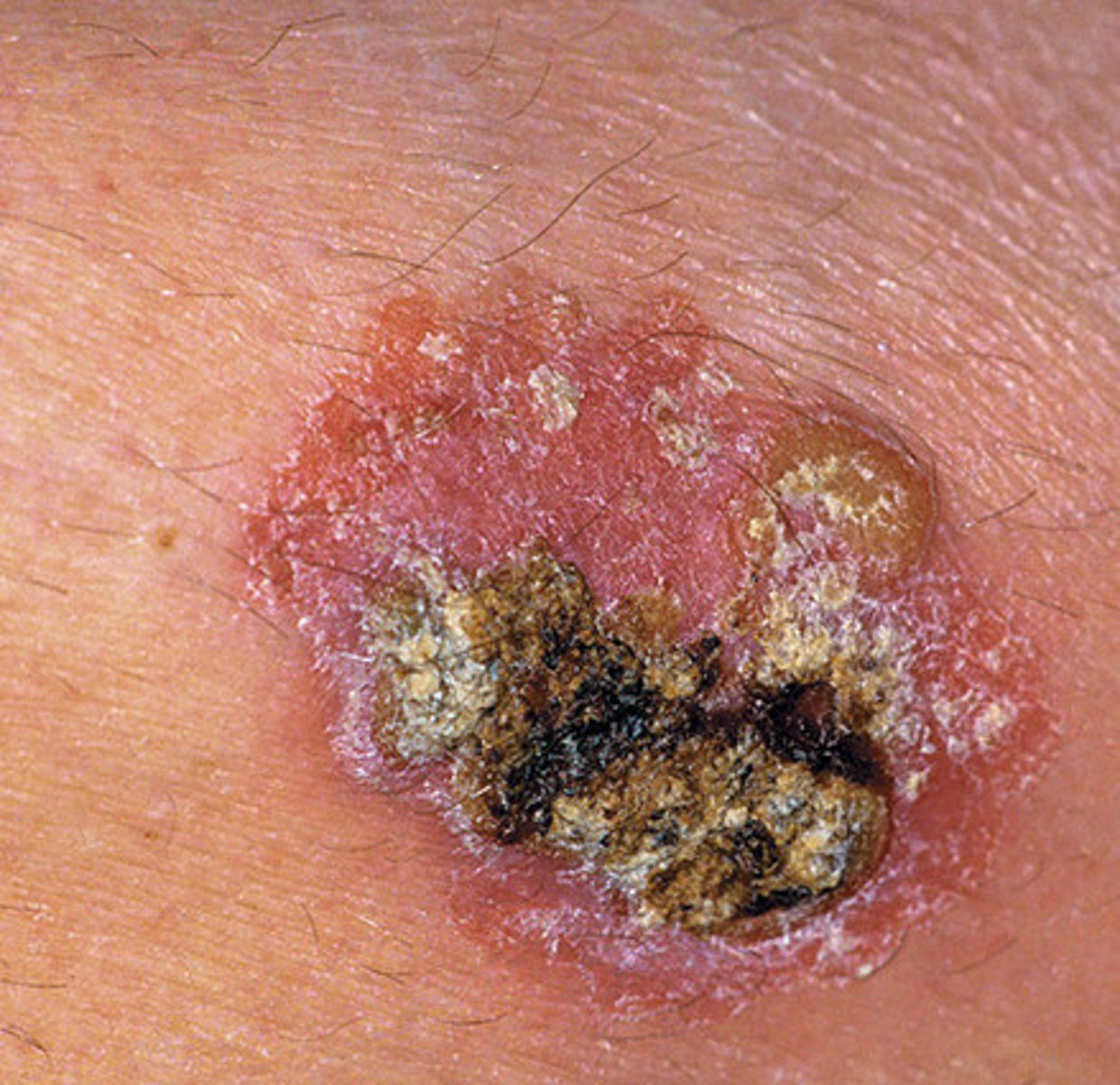
malignant tumor of the squamous epithelial cells in the epidermis
squamous cell carcinoma
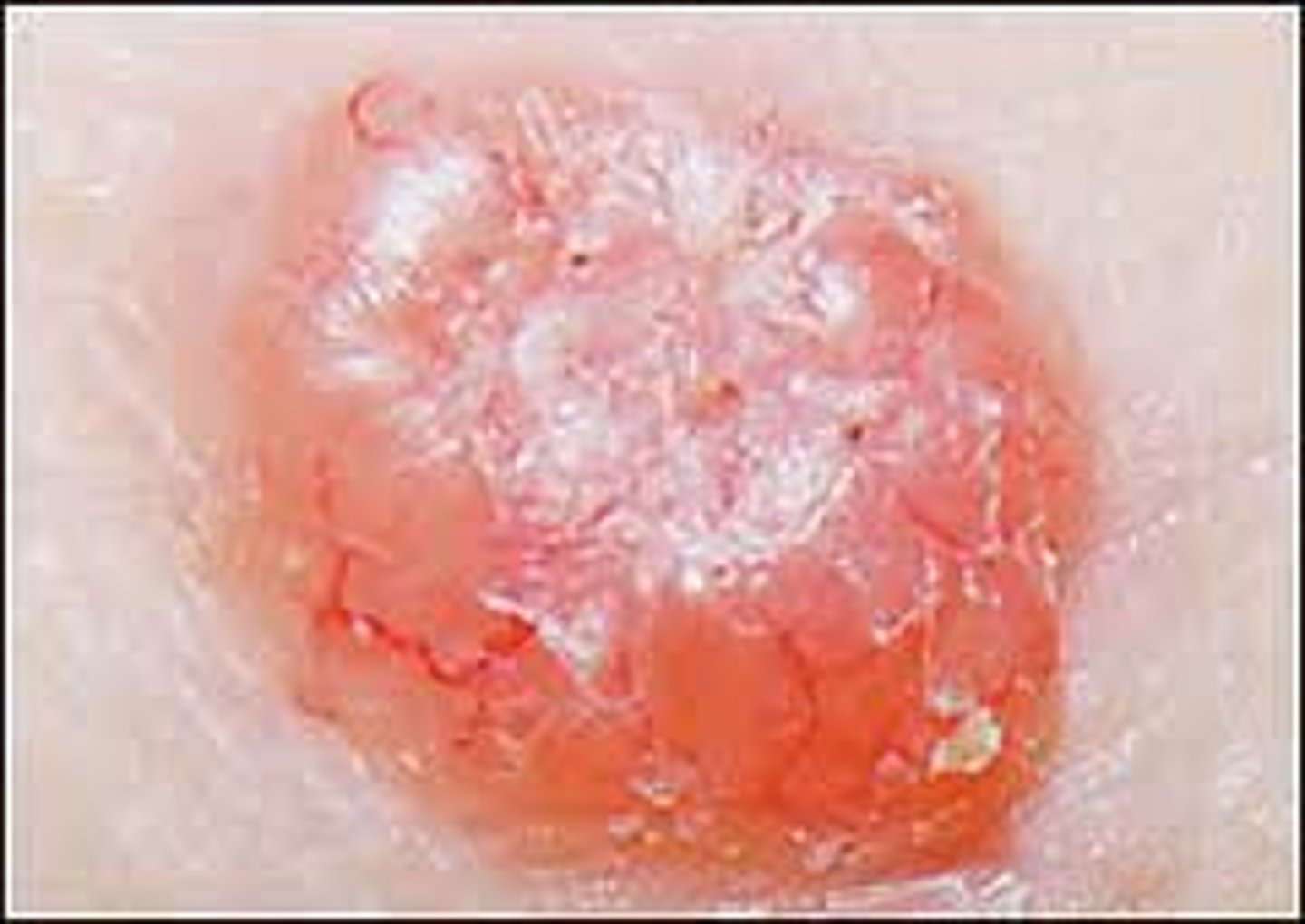
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer; often characterized by light or pearly nodules.
basal cell carcinoma
stratified squamous tissue
what tissues is the epidermis made out of?
loose areolar tissue
what tissues is the papillary dermis made out of?
dense irregular connective tissue
what tissues is the reticular dermis made out of?
adipose tissue
what tissues is the hypodermis made out of?