Epilepsy- Krysiak
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is SUDEP?
Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy—> sudden, unexpected death in a person with epilepsy, where underlying cause of injury/death unknown
T/F: pts. with epilepsy ALL experience seizures
T
T/F: all individuals who experience a seizure will be diagnosed with epilepsy.
F
A chronic disorder of brain function characterized by the recurrent and unpredictable occurrence of seizures is called…
epilepsy
Some seizures are provoked bc of systemic, toxic, or metabolic problems.
What’s a symptom of these problems?
fever (ex: febrile seizures)
Do febrile seizures qualify as epilepsy?
No –> they’re provoked by fever and don’t recur once the fever resolves
Most common cause of childhood onset and older-age onset epilepsy?
childhood—> genetic issues
older-age—> acquired structural injury (ex: stroke)
The etiologies of epilepsy can be classified into what 6 categories?
Which the most common?
genetics
structural
infectious- most common
metabolic
immune
unknown
note: many epilepsies can belong to 2+ categories
What are some triggers for epilepsy?
hyperventilation
photo stimulation (flashing lights)
others: stress, sleep deprivation, hormones, drugs
What is the underlying general process of epilepsy? aka what happens to the neurons?
neuronal hyperexcitability + hyper synchronization
What can lead to hyperexcitability in the neuron?
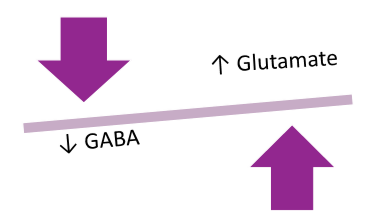
describe glutamate and GABA as inhibitory or excitatory
neurotransmitter changes/imbalances
glutamate= excitatory
GABA= inhibitory
others: alteration in ion channels, and ions in general
To reduce seizure generation, would we want to increase or decrease GABA and glutamate?
INCREASE GABA (increase inhibition)
DECREASE GLUTAMATE (decrease excitation)
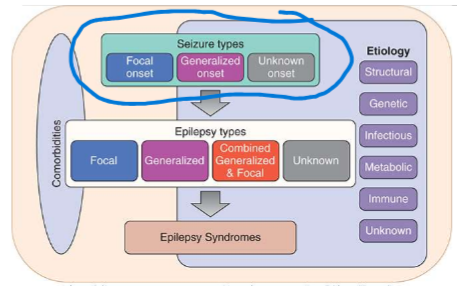
Seizures are classified based on what 3 things?
(not that imp, more of an FYI)
where seizures start in the brain
level of awareness during seizure
other seizure features- nonmotor/motor symptoms
Describing WHERE a seizure starts helps to classify it.
What are the 3 categories and describe them?
focal seizures- one hemisphere of brain, unilateral, may or may not lose consciousness
generalized seizures- both hemispheres of brain, bilateral, loss of awareness/consciousness
unknown
Describing the motor symptoms of a seizure helps to classify it.
What are some examples of motor and non-motor symptoms?
(idk how imp)
motor: rhythmical jerking (clonic), limp/weak muscles (atonic), twitches (myoclonus), rigid/tense muscles (tonic)
non-motor: sensations, emotions, thinking, etc.
Most generalized seizures have __________ motor movement.
a. unilateral
b. bilateral
(idk how imp)
b.
How is epilepsy DIAGNOSED? WHAT are the conditions?
at least 2 unprovoked seizures occurring greater than 24 hours apart
1 unprovoked seizure and a probability of further seizures—> similar to the general recurrence risk (at least 60%) after 2 unprovoked seizures over the next 10 years
aka if a pt. only had 1 seizure but they have high risk features
diagnosis of epilepsy syndrome

What are the diagnostic laboratory tests for epilepsy?
TRICK QUESTION—> THERE ARE NONE
Obtaining what serum levels may HELP (not diagnose) confirm seizures?
serum prolactin—> must be taken within 10-20 minutes of seizure
What scans can HELP (not diagnose) confirm a seizure? gold standard?
electroencephalogram
video EEG gold standard
CT
MRI
Is pharm therapy for epilepsy curative or for symptoms?
(FYI)
for symptoms
Nonpharm therapy for epilepsy?
keto diet
vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)- device used as adjunctive therapy in pts. 12+ with focal seizures refractory to AEDs
surgery
ALL anti-epileptic drugs have increased risk for what condition?
suicide
What drugs are 1st gen, 2nd gen, and 3rd gen AEDs? (Anti-epileptic drugs)
FYI
1st gen | 2nd gen | 3rd gen |
|
|
|
Answer the following about Carbamazepine (CBZ):
drug interactions
what’s unique about it’s metabolism?
BBW
ADRs
common
serious/rare
long term
inducer of CYP3A4, 1A2, 2B6, 2C9/19
auto-inducer (aka induces its own metabolism)
BBW—> increased risk of SJS/TEN with HLA-B*1502, aplastic anemia, and agranulocytosis
ADRs
common: CNS effects
serious/rare: blood dyscrasias, hepatotoxicity, DRESS rxns
long term: hyponatremia from SIADH, metabolic bone disease
What are the advantages/DISADVANTAGES of using Carbamazepine?
advantages: useful in comorbid bipolar disorder and trigeminal neuralgia
disadvantages
avoid in absence seizures
screen for HLA-B*1502 allele
fetal harm
Answer the following about Oxcarbazepine (CBZ):
drug interactions
is it metabolized like carbamazepine?
ADRs
common
serious/rare
D/I
inducer of CYP3A4, inhibits CYP2C19
may decrease lamotrigine levels, increase phenytoin levels
not the same metabolism as carb—> not auto-inducer
ADRs
common: CNS effects, GI, hyponatremia, rash
serious/rare: SJS, TEN, DRESS, blood dyscrasias
What are the advantages/disadvantages to using oxcarbazepine?
(idk how imp really)
advantages: useful in bipolar disorder, ER useful
disadvantages
hyponatremia
HLA-B*1502
Phenytoin uses what kind of pharmacokinetics?
michaelis-menten kinetics (saturates metabolizing enzymes at higher doses)
Having low what may cause phenytoin levels to be falsely low or normal?
low albumin (<3.5 g/dl)
What are the ADRs of phenytoin?
BBW
common
serious/rare
long term
BBW- phenytoin IV admin rate should NOT exceed 50mg/min
common: nystagmus (eyes moving a lot), decreased coordination, mental confusion, dizzy, insomnia, HA
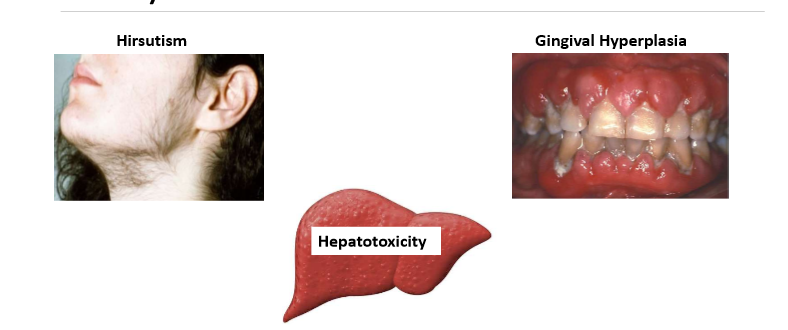
serious/rare: blood dyscrasias, rash, DRESS, angioedema, hepatotoxicity, purple glove syndrome with IV admin, extravasation
long term: connective tissue changes and skin thickening, HIRSUTISM, GINGIVAL HYPERPLASIA, HEPATOTOXICITY
What are the advantages/disadvantages of phenytoin?
FYI
advantages: oral or IV available, ER formulations
disadvantages:
avoid in absence seizures
can increase BS in DM
HLA-B*1502 risk factor
dose adjustments and monitoring
What is the prodrug of phenytoin?
Fosphenytoin
For administration of fosphenytoin it cannot exceed ________ PE/minute.
150mg
What are the ADRs of lamotrigine?
BBW
common
serious/rare
BBW: serious skin reactions including SJS/TEN, increase risk with high dosing, quick dose escalation OR when used w/ valproic acid
common: n/v, somnolence, tremor, ataxia, diplopia, alopecia
serious/rare: DRESS, blood dyscrasias, HLH
Ethosuxamide is the DOC for __________________.
absence seizures
ADRs of Ethosuxamide?
serious skin rxns (SJS/TEN), blood dyscrasias, DRESS, psychiatric abnormalities
ADRs of Gabapentin?
weight gain, sedation, dizzy, angioedema
List the AEDs that belong to each MOA:
MOA | drugs |
sodium channel blockers | |
calcium channel blockers | |
GABA enhancers | |
Glutamate inhibitors/ synaptic vesicle modulators |
MOA | drugs |
sodium channel blockers |
|
calcium channel blockers |
|
GABA enhancers |
|
Glutamate inhibitors/ synaptic vesicle modulators |
|
Benzos (clonazepam, clobazam) have what BBW? What long-term ADRs?
concurrent use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, and death
long term ADRs: dependence/tolerance
ADRs of phenobarbital?
common
serious/rare
long term
common: CNS effects, dependence, tolerance, hangover effect
serious/rare: respiratory depression, apnea, bradycardia, hypotension (IV), hepatotoxicity
long term: metabolic bone disease, folate deficiency, behavior changes
If albumin is low, the true valproic acid level will be _______than it appears.
a. higher
b. lower
a.
Answer the following about valproic acid:
drug interactions?
ADRs
BBW
common
serious/rare
D/I:
CYP2C9 inhibitor
ADRs:
BBW: hepatic failure, fetal harm, pancreatitis
common: GI, weight gain, alopecia, thrombocytopenia, POCS, blurred vision
serious/rare: hyperammonemia, DRESS, bleeding
Advantages/disadvantages of using valproic acid?
advantages: useful in bipolar disorder, migraines
disadvantages:
C/I in severe hepatic dysfunction, mitochondrial disorders, urea cycle disorders
caution pancreatitis, bleeding disorders
C/I in pregnancy when treated for migraine prophylaxis
Advantages/disadvantages to using Levetiracetam?
advantages: NO SIGNIFICANT DRUG INTERACTIONS, XR useful
disadvantages: may worsen depression, PTSD, anxiety, thought disorders
What are the ADRs of Levetiracetam?
common
serious/rare
common: CNS effects, agitation, aggression, depersonalization, hostility
serious/rare: psychosis, hallucinations
Answer the following about Lacosamide:
ADRs
Interactions
advantages/disadvantages
ADRs: prolongs PR interval, increased risk of arrhythmias (obtain ECG prior)
common: n/v, diplopia, blurred vision, euphoria
Interactions: caution with medications that prolong PR interval (B blockers, CCB, digoxin) due to risk of AV block and bradycardia
advantages/disadvantages
advantages: minimal interactions
disadvantages: ECG prior to use, not rec in severe renal/hepatic impairment, fetal harm
When is topiramate C/I?
trokendi XR only: alcohol use 6 hrs before or after dose— pts. with metabolic acidosis who are taking metformin
What are the ADRs of topiramate?
common
serious/rare
long term
common: CNS effects
serious/rare: kidney stones, hypo/hyperthermia, oligohidrosis, metabolic acidosis, hyperammonemia with valproate, fetal harm
long term: weight loss/anorexia, renal stones
(lowkey: Zonisamide has similar ADRs)
When is Zonisamide C/I?
sulfa hypersensitivity
When is cannabidiol used?
oral solution useful for tx of refractory seizures in LGS and Dravet syndrome
BBW of Felbamate?
hepatic failure, aplastic anemia
Vigabatrin has a REMS program bc of what side effect?
vision loss
Eslicarbazepine is a major active metabolite of ___________________.
oxcarbazepine
T/F: The efficacy of newer AEDs is considered comparable to older AEDs.
true
What medications require SLOW titration?
Lamotrigine, topiramate, clobazam, phenobarbital
When starting AEDs, is mono or combination therapy preferred?
start with monotherapy
What is the definition of drug resistance in epilepsy?
basically failure to control seizures after 2 medications
Is concentration monitoring a therapeutic endpoint or a tool to optimize therapy?
tool to optimize therapy, NOT a therapeutic endpoint
ALL AEDs act on the same part of the body so have a risk of what side effects?
act on brain—> so CNS side effects are a risk (sedation, dizzy, blurred vision, double vision, ataxia)
also have a risk of suicidal thoughts/behaviors
Review:
Hypersensitivity reactions (SJS/TEN/DRESS) are most associated with aromatic anticonvulsants such as…
Carbamazepine
oxcarbazepine
ethosuximide
lamotrigine
phenobarbital
phenytoin
primidone
Review:
What AEDs have a increased risk of osteoporosis/osteomalacia?
phenytoin
phenobarbital
Carbamazepine
oxcarbazepine
felbamate
valproic acid
What are the main counseling points with AEDs?
can cause suicidal thoughts/actions
do not stop taking this medication without consulting your healthcare provider
seizure meds can impair judgement, thinking, coordination
avoid drugs that lower seizure threshold
use caution with generic substitutions
avoid st. johns wort with ALL anticonvulsants
According to guidelines, when can AED withdrawal be considered?
seizure free 2-5 yrs
history of single type of focal seizure or generalized seizure
normal neuro exam/IQ
normal EEG
T/F: When discontinuing AEDs, it should be done abruptly.
FALSE—> gradually
In the elderly what is the DOC for focal onset seizures?
Lamotrigine
What AEDs can decrease efficacy of oral contraceptives?
Carbamazepine
oxcarbazepine
topiramate
rufinamide
lamotrigine
clobazam
felbamate
What should be supplemented in any women of childbearing age who is taking an AED?
folic acid
In pregnancy, what AEDs have increased clearance?
LAMOTRIGINE, carbamazepine, phenytoin, levetiracetam
What AEDs should NOT be used in pregnancy?
valproic acid
topiramate (cleft palate)