Unit 1: What is Psychology, History of Psychology, Contemporary Psychology, Carrers in Psychology
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Psychology
Before; The study of the soul. Now: The scientific study of the mind and behavior.
Hypothesis
A tentative explanation for a phenomenon, proposed by a researcher.
Scientific Method
A method of procedure consisting in systematic observation, measurement, experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses. Is a form of empiricism.
Psychology became accepted as its own academic discipline
Not until the late 1800
Scientific Method
Decide on a research question. 2. Conduct research. 3. Develop your hypothesis. 4. Make a plan. 5. Conduct your experiment. 6. Collect and record data. 7. Draw conclusions
Scientific Theory
A broad explanation or group of explanations for some aspect of the natural world that is consistently supported by evidence over time.
Empirical Method
A method for acquiring knowledge based on observation, including experimentation, rather than only on logical argument or previous authorities.
Critical Thinking
The active application of a set of skills to information for the understanding and evaluation of that information.
Wilhelm Wundt
German scientist, the first person to be referred to as a psychologist; viewed psychology as a scientific study of conscious experience. 1st formal lab for psychology research.
Paul Brock
Worked with brain damaged patient to understand the language processes of the brain
Hermann Helmholtz
Developed the method for measuring the speed of nerve impulses
Introspection
A process by which someone examines their own conscious experience as objectively as possible.
Voluntarism
The idea that people have free will and should know the intentions of a psychological experiment if they were participating.
Structuralism
Focus on the contents of mental processes rather than their function.
William James
Helped establish functional psychology; focused on how mental activities helped an organism fit into its environment.
Functionalism
Focuses on how mental activities helped an organism fit into its environment.
Sigmund Freud
Austrian neurologist who theorized that many of his patients' problems arose from the unconscious mind.
Psychoanalytic Theory
Focuses on the role of a person's unconscious, as well as early childhood experiences.
Unconscious Mind
A repository of feelings and urges of which we have no awareness.
Psychoanalysis
A method popularized by Freud that involves patients talking about their experiences and selves.
Drew Westen
Argued that criticisms of Freud's ideas often attack older ideas without considering later writings and the success of broad concepts he introduced.
Wertheimer, Koffka, and Köhler
German psychologists who introduced Gestalt principles to the United States.
Gestalt Psychology
Emphasizes that the relationship between individual parts forms the whole perception.
Behavior
The objectively observable outcome of mental processes.
Ivan Pavlov
Studied conditioned reflexes, where an animal produces a reflex response to a stimulus and becomes conditioned to respond to a different, associated stimulus.
Conditioned Reflex
A learning behavior where an animal or human produces a reflex (unconscious) response to a stimulus and, over time, is conditioned to produce the response to a different stimulus.
John B. Watson
An influential American psychologist who shifted the focus of psychology from the mind to observable behavior.
Behaviorism
An approach of observing and controlling behavior.
B. F. Skinner
Focused on how behavior is affected by its consequences.
Reinforcement and Punishment
States that reinforcement and punishment are major factors in driving behavior.
Operant Conditioning Chamber (Skinner Box)
A chamber developed by Skinner to carefully study the principles of modifying behavior through reinforcement and punishment.
Humanism
Emphasizes personal control, intentionality, and a predisposition for 'good' in self-concept and behavior.
Humanistic psychology
Emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans.
Abraham Maslow
Proposed a hierarchy of human needs in motivating behavior.
Maslow Hierarchy of Needs
A hierarchy of human needs that motivates behavior, arranged in a pyramid. The base includes Physiological needs (food, water, shelter), followed by Safety needs (security, stability), Love and Belongingness (relationships, intimacy), Esteem (confidence, achievement), and at the peak, Self-actualization (achieving one's full potential).
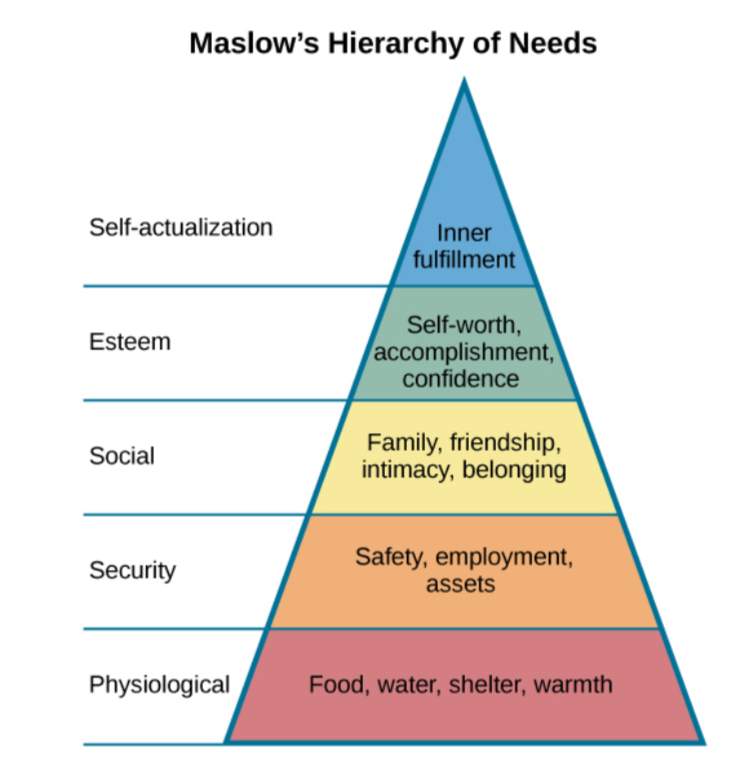
Self-actualization
A process by which we achieve our full potential.
Carl Rogers
Emphasized the potential for good that exists within all people
Client-Centered Therapy
A therapeutic technique where the patient takes a lead role in the therapy session.
Unconditional Positive Regard
Accepting the client for who they are, no matter what they might say.
Cognitive Revolution
A perspective that revived interest in the mind as a focus of scientific inquiry, emerging from new disciplinary perspectives in linguistics, neuroscience, and computer science.
Ulric Neisser
Published the first textbook entitled Cognitive Psychology.
Noam Chomsky
Argued that psychology's focus on behavior was short-sighted and it needed to re-incorporate mental functioning.
Womanless Psychology
Until the 1960s few women were able to practice psychology so they had little influence on what was studied.
Naomi Weisstein
Stimulated a feminist revolution in psychology by presenting a critique of psychology as a science.
Feminist Psychology
Includes re-evaluating the contributions of women to the history of psychology, studying psychological gender differences, and questioning the male bias present across the scientific approach to knowledge.
WEIRD
Western, educated, industrialized, rich, and democratic societies.
Multicultural Psychologists
Develop theories and conduct research with diverse populations, typically within one country.
Cross-cultural Psychologists
Compare populations across countries.
Francis Cecil Sumner
The first African American to receive a PhD in psychology in the United States.
Mamie Phipps Clark and Kenneth Clark
Conducted studies on African American children and doll preference, research that was instrumental in the Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court desegregation case.
Margaret Floy Washburn
The first woman awarded the doctoral degree in psychology.
Mary Whiton Calkins
Completed all requirements toward the PhD in psychology, but Harvard University refused to award her that degree because she was a woman.
Mary Cover Jones
Conducted a study she considered to be a sequel to John B. Watson's study of Little Albert and unconditioned fear in Little Peter, who had been afraid of rabbits.
Martha Bernal
The first Latina to earn her doctoral degree in psychology.
Inez Beverly Prosser
The first African American woman awarded the PhD in 1933 at the University of Cincinnati.
American Psychological Association (APA)
The largest organization of psychologists in the world, and its mission is to advance and disseminate psychological knowledge for the betterment of people.
G. Stanley Hall
The first president of the APA.
Association for Psychological Science (APS)
Founded in 1988 and seeks to advance the scientific orientation of psychology.
Biopsychology
Explores how our biology influences our behavior and how the structure and function of the nervous system is related to behavior.
Evolutionary Psychology
Seeks to study the ultimate biological causes of behavior.
Sensation and Perception
Scientists interested in the physiological aspects of sensory systems as well as the psychological experience of sensory information.
Cognitive Psychology
The area of psychology that focuses on studying cognitions, or thoughts, and their relationship to our experiences and our actions.
Developmental Psychology
The scientific study of development across a lifespan. Developmental psychologists are interested in processes related to physical maturation as well as changes in cognitive skills, moral reasoning, social behavior, and other psychological attributes.
Object permanence
The understanding that physical things continue to exist, even if they are hidden from us.
Jean Piaget's Theory
Focuses on cognitive changes during infancy and childhood as we move to adulthood.
Personality Psychology
Focuses on patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make each individual unique.
Personality Traits
Relatively consistent patterns of thought and behavior.
The "Big Five" or Five Factor Model
Conscientiousness, agreeableness, neuroticism, openness, and extraversion.
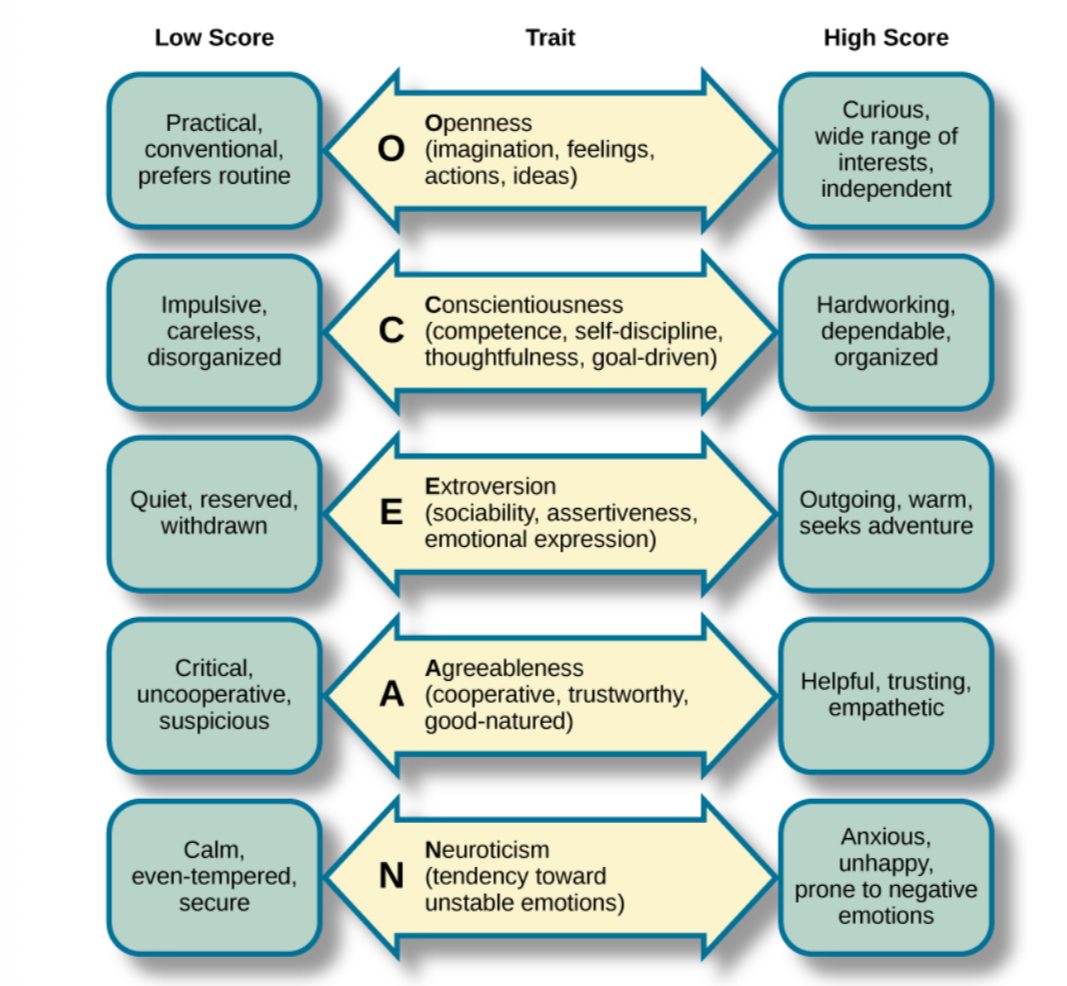
Social Psychology
Focuses on how we interact with and relate to others.
Stanley Milgram
Famous for research on obedience, particularly demonstrated by participants delivering what they believed to be lethal shocks when instructed by an authority figure.
Research Confederates
Those who pretend to be participants in a research study but are actually working for the researcher.
Industrial-Organizational Psychology (I-O Psychology)
A subfield of psychology that applies psychological theories, principles, and research findings in industrial and organizational settings.
Health Psychology
Focuses on how health is affected by the interaction of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
Biopsychosocial Model
Suggests that health/illness is determined by an interaction of biological, psychological, and social factors.
Sport and Exercise Psychology
Study the psychological aspects of sport performance, including motivation and performance anxiety, and the effects of sport on mental and emotional wellbeing.
Clinical Psychology
An area of psychology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior.
Forensic Psychology
A branch of psychology that deals with questions of psychology as they arise in the context of the justice system.
Dissertation
A long research paper or bundled published articles describing research that was conducted as a part of the candidate's doctoral training.
PsyD
Doctor of psychology degree that focuses more on application of psychological principles in the clinical context and less on research-oriented skills. Focuses on practical applications in the field.
Licensed clinical psychologists
Can administer and interpret psychological tests. Roles include assessment and therapeutic intervention.
Psychiatrists
Can prescribe medications, bridging the gap between physical and mental health treatments. Integrate medical and psychological approaches.
Faculty appointment at a college or university
Involves research, teaching, and service to the institution and profession. Shape future professionals and expand psychological knowledge.
Adjunct faculty members/instructors
Have primary careers outside of academia and serve as instructors as a secondary job. Bring real-world experience into the classroom.
Neuroscience Perspective
Views behavior from the perspective of biological functioning. Emphasizes the role of genetics and the nervous system.
Behavioral Perspective
Focuses on observable behavior, measurable actions, and reactions. How environmental factors affect behavior.
Psychodynamic Perspective
Believes behavior is motivated by inner, unconscious forces over which a person has little control. Focuses on early childhood experiences and unconscious drives.
Cognitive Perspective
Examines how people understand and think about the world. How cognitive processes influence behavior.
Humanistic Perspective
Contends that people can control their behavior and that they naturally try to reach their full potential. Emphasizes personal growth and self-actualization.
Cognitive psychology
Focuses on higher mental processes such as memory and problem-solving. How individuals process and utilize information.
Experimental psychology
Studies the processes of sensing, perceiving, learning, and thinking
Ego Ideal
Part of the superego that comprises the standards of what one would like to be.
Conscience
Part of the superego that produces feelings of guilt or moral anxiety.
Unconscious
According to Freud, it's a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that are outside of our conscious awareness. Most of the contents of the unconscious are unacceptable or unpleasant, such as feelings of pain, anxiety, or conflict.
Preconscious
Contains thoughts and feelings that a person is not currently aware of, but which can easily be brought to consciousness.
Nature vs. Nurture
Debate among psychologists regarding the relative contributions of genetic inheritance (nature) and environmental or experimental factors (nurture) to development.
Gestalt Psychology
Examines the organization of perceptual experience. Argues that the whole is different from the sum of its parts.
Developmental Psychology
Studies how people grow and change from the moment of conception through death.
Personality Psychology
Focuses on the consistency in people’s behavior over time and the traits that differentiate one person from another.
Health Psychology
Explores the relationship between psychological factors and physical ailments or disease.
Educational Psychology
Concerned with teaching and learning processes, such as the relationship between motivation and school performance.