EX2 Alpha Agonists/Antagonists (P'col)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Non-selective (α1 and α2) Blockers
Phenoxybenzamine
Phentolamine
Selective α1 Blockers
Prazosin
Terazosin
Doxazosin
Tamsulosin
a blocker mechanism
Inhibition of vascular and other peripheral α-adrenergic receptors
Decrease in BP
Pharmacokinetics → Non-competitive inhibition (phenoxybenzamine)
Action slow in onset but irreversible
Competitive inhibition (as caused by all others)
Relatively fast in onset and can be reversed
a blocker ADR
nasal congestion
difficulty in ejaculation
Reflex tachycardia
Systemic extracellular fluid retention
Orthostatic hypotensive symptoms
Phenoxybenzamine
Long-acting, irreversible inhibitor of both α1- and α2-receptors
Pheochromocytoma (a rare tumor, usually benign, that forms in the adrenal gland (above the kidney) and causes it to release too much adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline, leading to dangerously high blood pressure, pounding heart, headaches, and sweating)
Treatment of sweating and hypertension associated with pheochromocytoma
Used during the preoperative period prior to surgery
Also used to treat patients with inoperable pheochromocytoma
Phentolamine
Non-selective, Reversibly inhibits both α1 and α2 receptors, Short acting
Clinical Uses
Pheochromocytoma
Extravasation management
Local anesthesia reversal
Hypertensive crisis (off-label use)
ADR GI
Prazosin
Prototype of the selective α1- adrenergic blocking agents
for HTN
Used in combination with
diuretics, β-blockers or other
antihypertensive agents
Attractive drug for hypertensive
patients with BPH
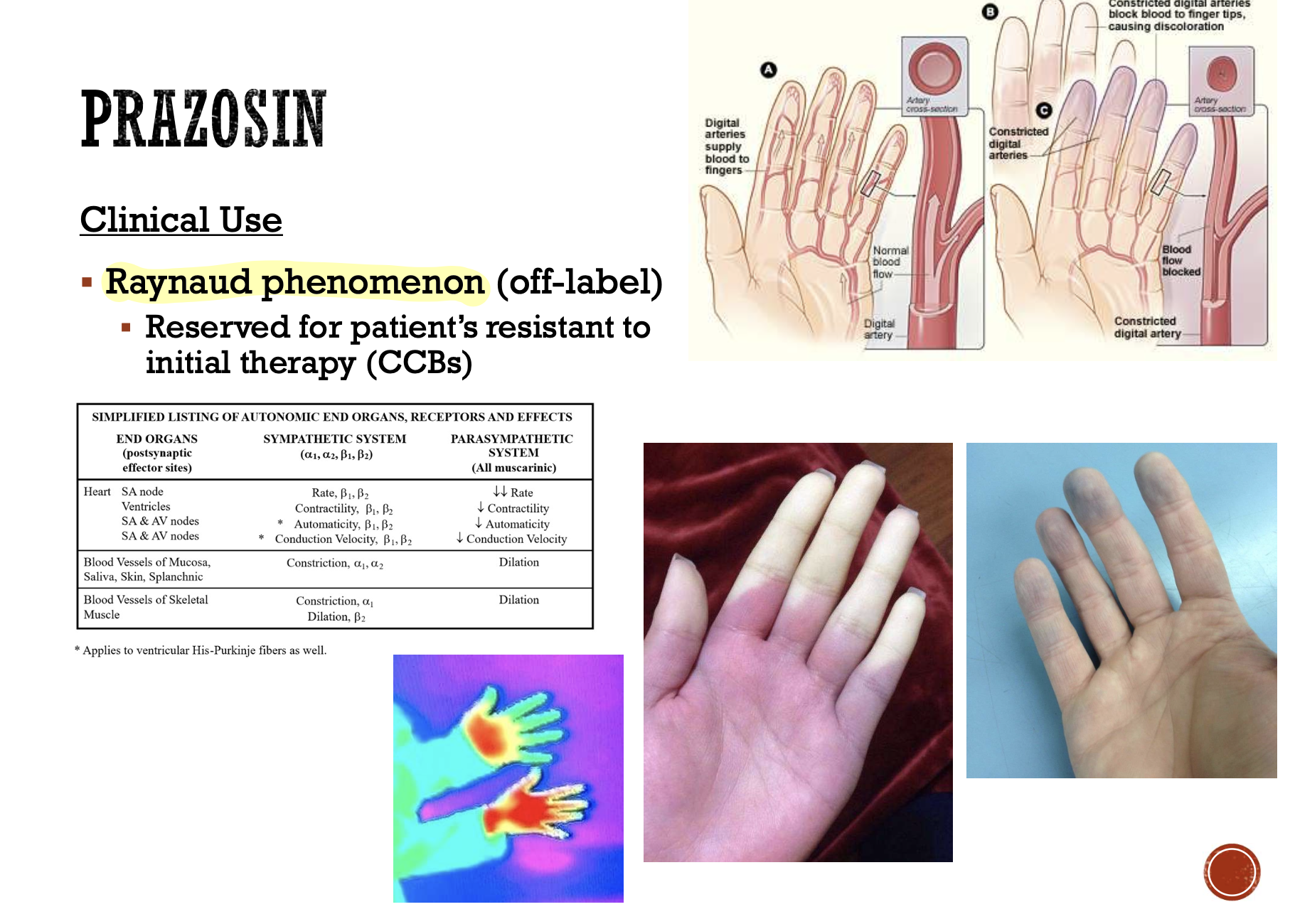
Raynaud phenomenon (off-label)
PTSD-related nightmares and sleep disruption (off-label)
Likely by inhibition of central α1-receptors
ADR: Orthostatic hypotension with syncope, ECF retention, tachycardia
Doxasosin and Terazosin
Newer α1-receptor blockers
Mechanism of action, side effects and uses are almost identical to prazosin
half-lives are much longer than prazosin
Helpful in BPH and long term HTN
Tamsulosin (silodosin dont need to know too)
blocking the subtype A alpha-1
receptor (α1A)
Main subtype in smooth muscle of the bladder neck and prostate
for BPH
ADR: abnormal ejaculation
Centrally-Acting Sympathetic Neuronal Blockers
Methyldopa
Clonidine
Guanfacine
Centrally-Acting Sympathetic Neuronal Blockers effects
α2-receptor agonists
More prominent effects at CNS α2 sites
Act on vasomotor centers, thereby decreasing sympathetic outflow to peripheral organs like heart, blood vessels, and kidney
Methyldopa
a2 adrenergic agonist
Enzymes that convert Dopa to DA to NE
Dampening outflow of sympathetic nerve activity
to peripheral CV tissues
Results in a decrease of:
Renal renin release
Heart rate
Cardiac output
Peripheral resistance
limited to treatment of hypertension in pregnancy
ADR - peripheral fluid retention, dry mouth, sedation, positive coombs test, hemolytic anemia
Clonidine
direct α2 adrenergic agonist
Like methyldopa, decreases sympathetic outflow from CNS vasomotor centers
Primary hypertension (mechanisms similar to methyldopa)
Not recommended for the initial treatment of hypertension
Used as patch
ADR - Dry mouth and sedation, Sexual dysfunction, Rebound hypertension
Clonidine other clinical uses
ADHD
Pain management (epidural)
Inhibits release of neurotransmitter in afferent pain fibers
Opioid withdrawal (off-label)
Imidazoline receptors
Vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (off-label)
Apraclonidine for decreasing postsurgical intraocular pressure
Guanfacine
not 1st choice
Primary Hypertension
α2 antihypertensive use similar to clonidine
Slightly less sedation and less tendency toward withdrawal (rebound)
syndrome
Not recommended for the initial treatment of hypertension
ADHD → Reserved for children and adolescents who respond poorly to or have unacceptable side effects with a trial of stimulants or atomoxetine