L3-Monomers,Polymers, monosaccharides and disaccharides
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are monomers?
Smaller units from which large molecules are made.
What are polymers?
Molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together.
Give 3 examples of monomers?
Monosaccharides, amino acids , nucleotides
What is a condensation reaction?
A reaction which joins 2 molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water (the reaction produces water)
What is a hydrolisis reaction?
Breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule.(water is a reactant)
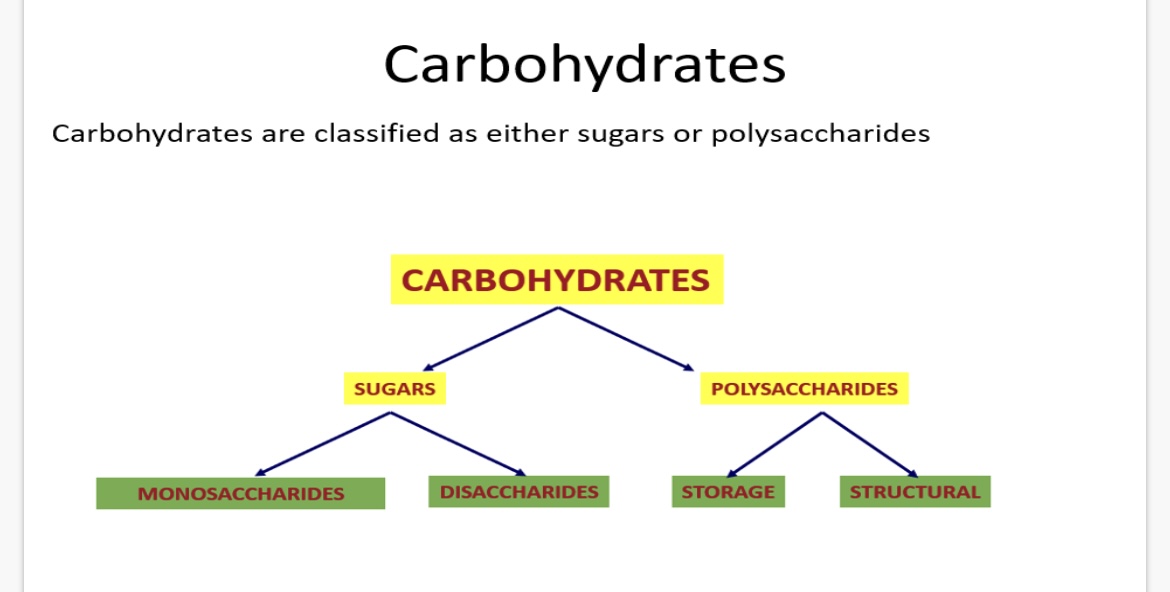
1.What are monosaccharides and give 3 examples?
2.What are disaccharides and give 3 examples?
3.What are polysaccharides(storage and structural)?
4.Give 2 examples of storage carbohydrates?
5.Give 2 examples of structural carbohydrates?
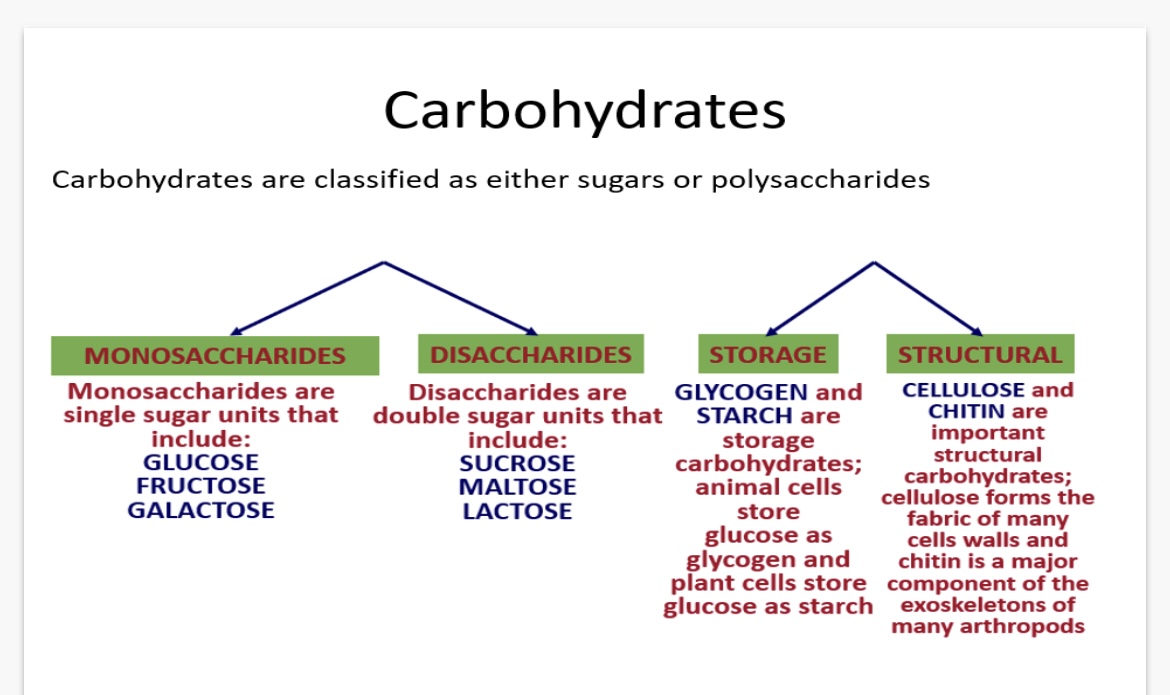
1.single sugar units e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose
2.Double sugar units e.g. sucrose, maltose, lactose
3.Complex carbohydrates made up of many monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds.
4. Glycogen (Animal cells store glucose as glycogen) and starch(plants store glucose as starch)
5. Cellulose (forms the fabric of many cell walls) and chitin(a major component of the exoskeletons of many arthropods)
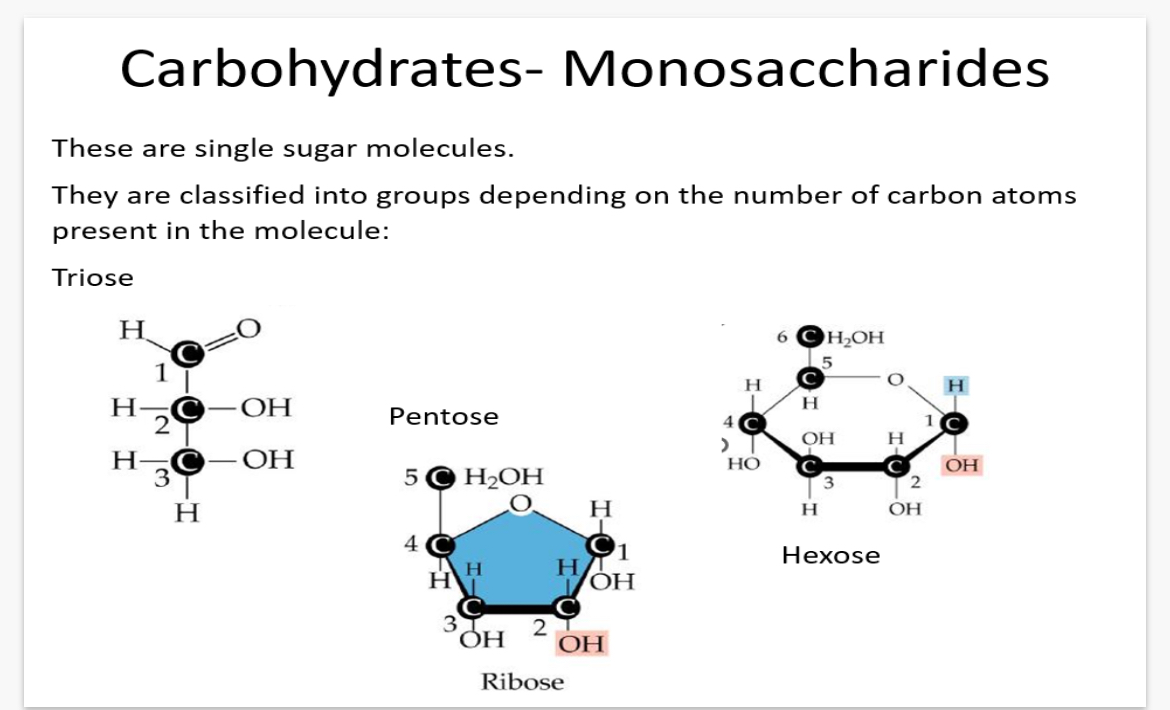
Monosaccharides are classified into groups based on the number of __1? atoms present in the molecule.
2.Give an example?
1.Carbon. 2. Triose has 3 carbon atoms in its molecule
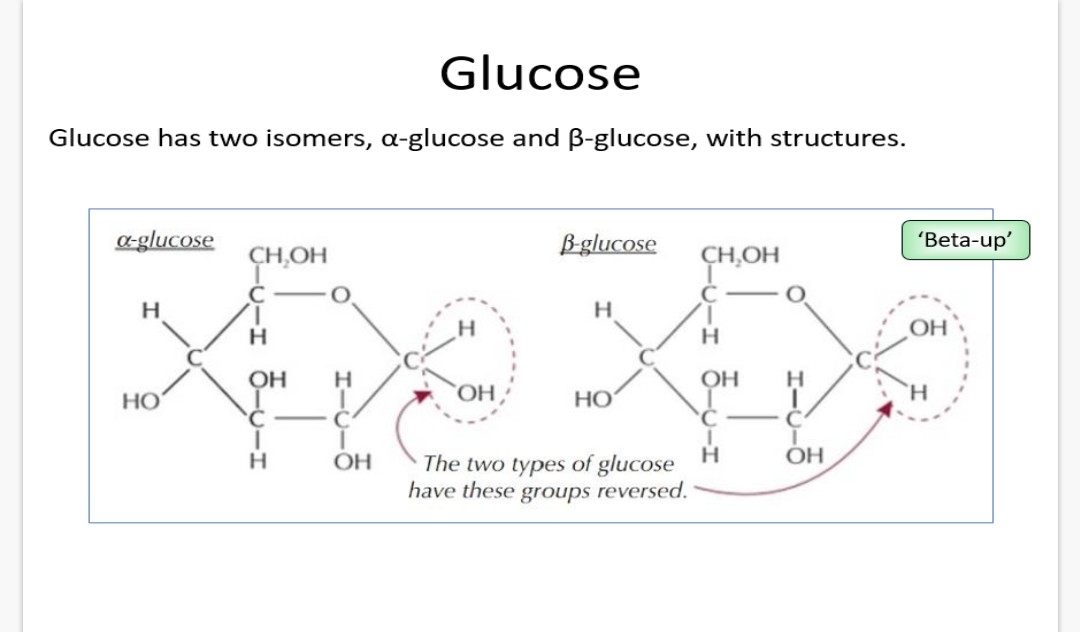
What are isomers?
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms (the difference in structures lead to variations in physical and chemical properties)
Glucose has two isomers. What are they called (ABBA)
a-glucose and B-glucose
What are hexose sugars and give 4 examples?
Monosaccharides that have 6 carbon atoms e.g. a-glucose, B-glucose, fructose and galactose
1.Give 3 roles of a-glucose?
2.Give 1 role of B-glucose?
3.Give 2 roles of fructose?
4.Give 1 role of galactose?
1. The main substrate for respiration. The form in which carbohydrate is transported in mammalian blood. Forms the polysaccharides starch and glycogen.
2.Forms the polysaccharide cellulose
3.Found in nectar and many fruits and it’s sweeter than glucose which helps to attract animals for pollination and fruit dispersal. With a-glucose, it forms the disaccharide sucrose.
4.With a-glucose, it forms the disaccharide lactose
Monosaccharides are the monomers from which larger __1? are made. A condensation reaction between 2 monosaccharides form a __2? bond.
Carbohydrates
Glycosidic
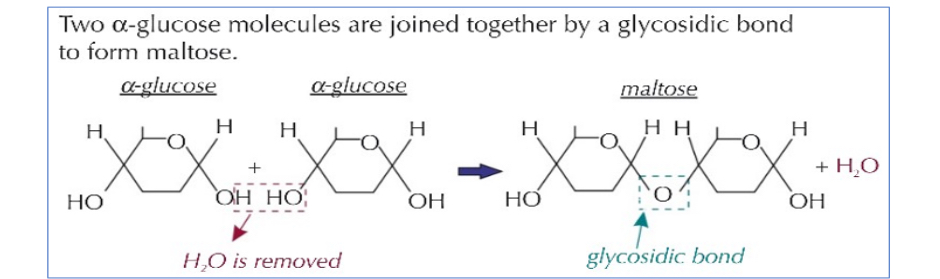
Disaccharides are formed when two __1? join together. The bond that forms is called a __2? bond and the reaction is called a __3? reaction since a molecule of __4? is produced as a by-product.
The breaking of a glycosidic bond is called a __5? reaction.
1.Monosaccharides. 2.glycosidic. 3.condensation. 4.water. 5.hydrolysis
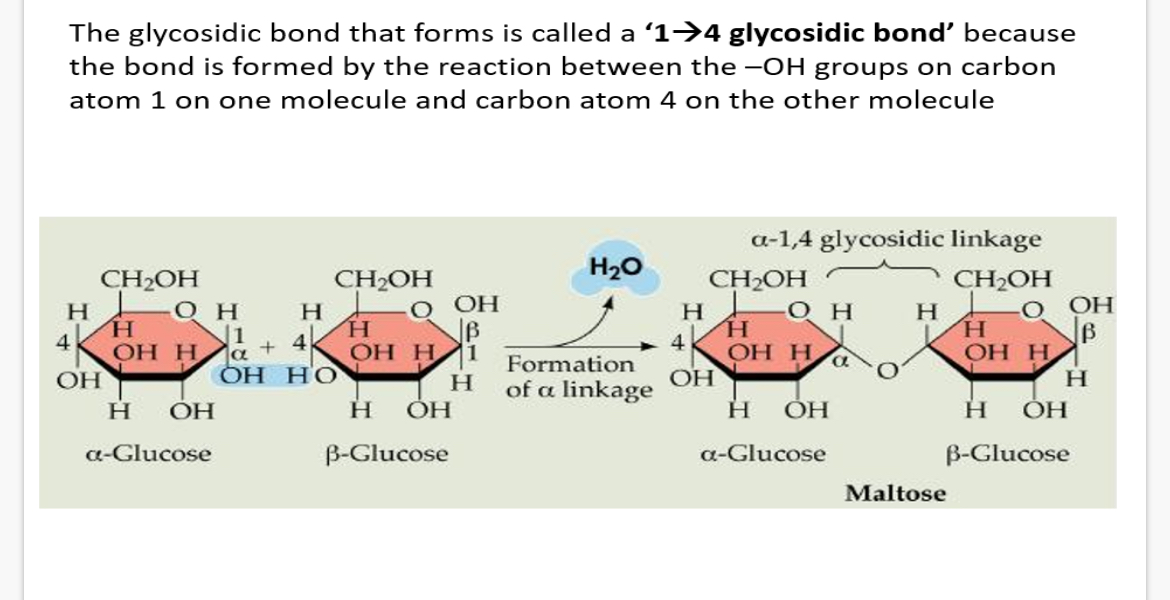
Why is the glycosidic bonds formed called a ‘1→4 glycosidic bond’?
Alpha glucose reacts with beta glucose to form cellobiose. I
Because the bond is formed by the reaction between the -OH groups on carbon atom 1 on one molecule and carbon atom 4 on the other molecule.
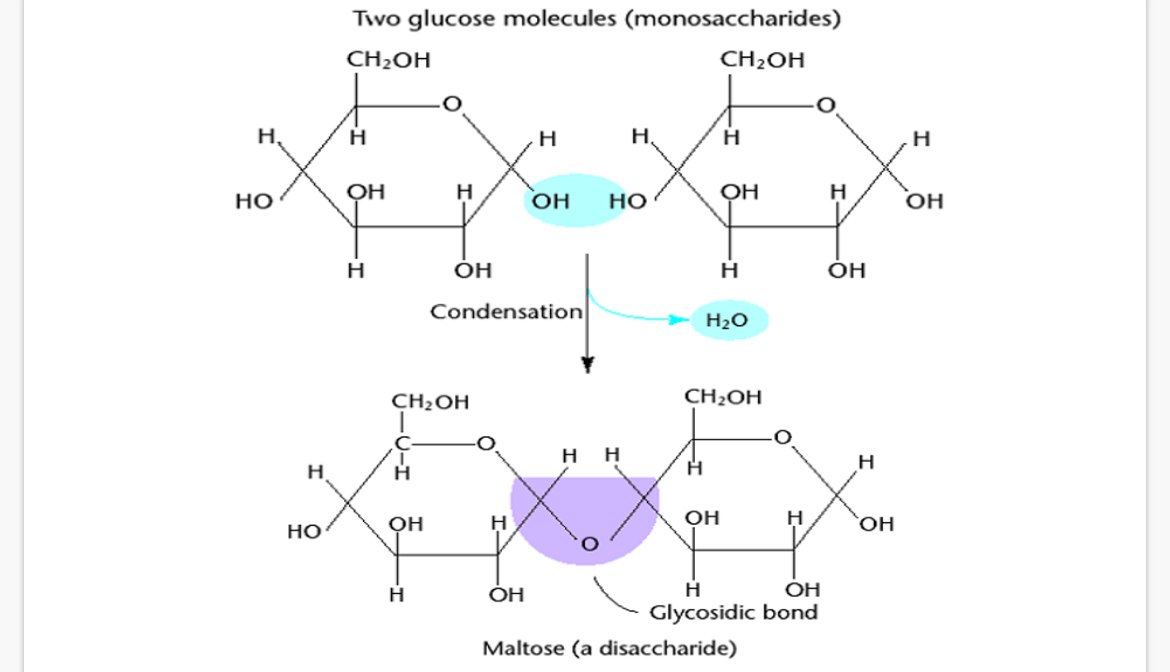
Describe how a condensation reaction occurs?(3)
1. 2 monosaccharides join together
2. A glycosidic bonds is formed between carbon 1 of the first monosaccharide , an oxygen atom and another carbon atom on the second monosaccharide.
3. Water (H2O) is produced as a by-product.
Uses of disaccharides:
1. 1 role of maltose?(a-glucose-glucose)
2. 1 roles of sucrose?(a-glucose-fructose)
3.1 role of lactose?(a-glucose-galactose)
1. Formed from the breakdown of starch in germinating seeds, where it provides energy for the growing embryo.
2.The form in which sugars are transported in the phloem of plants
3. The sugar found in milk- energy source for suckling mammals