Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis in Neural Development
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Neurogenesis
Process of neuronal birth in the neural tube.
Gliogenesis
Process of glial cell birth in the nervous system.
Neurons
Primary communicators of the nervous system.

Glial cells
Non-neuronal cells supporting neurons.
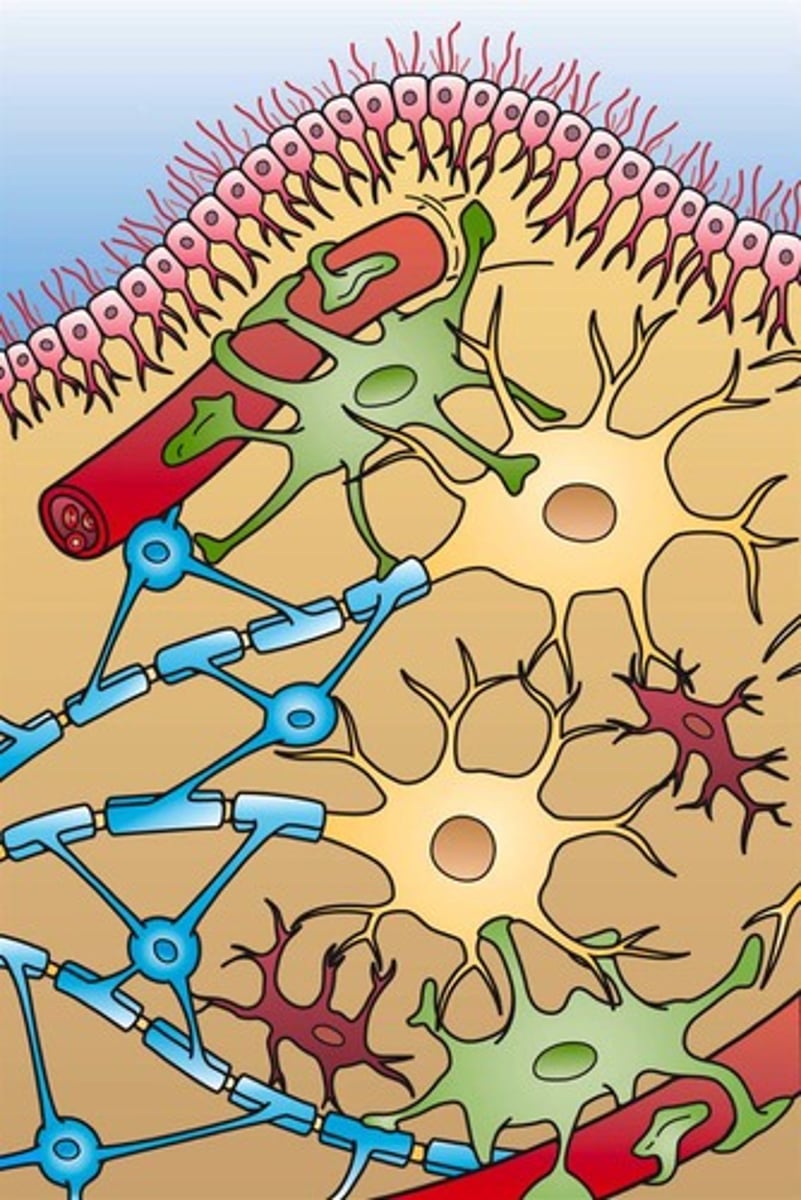
Macroglia
Includes astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in CNS.
Microglia
Immune cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells.
Schwann cells
Glial cells in the peripheral nervous system.
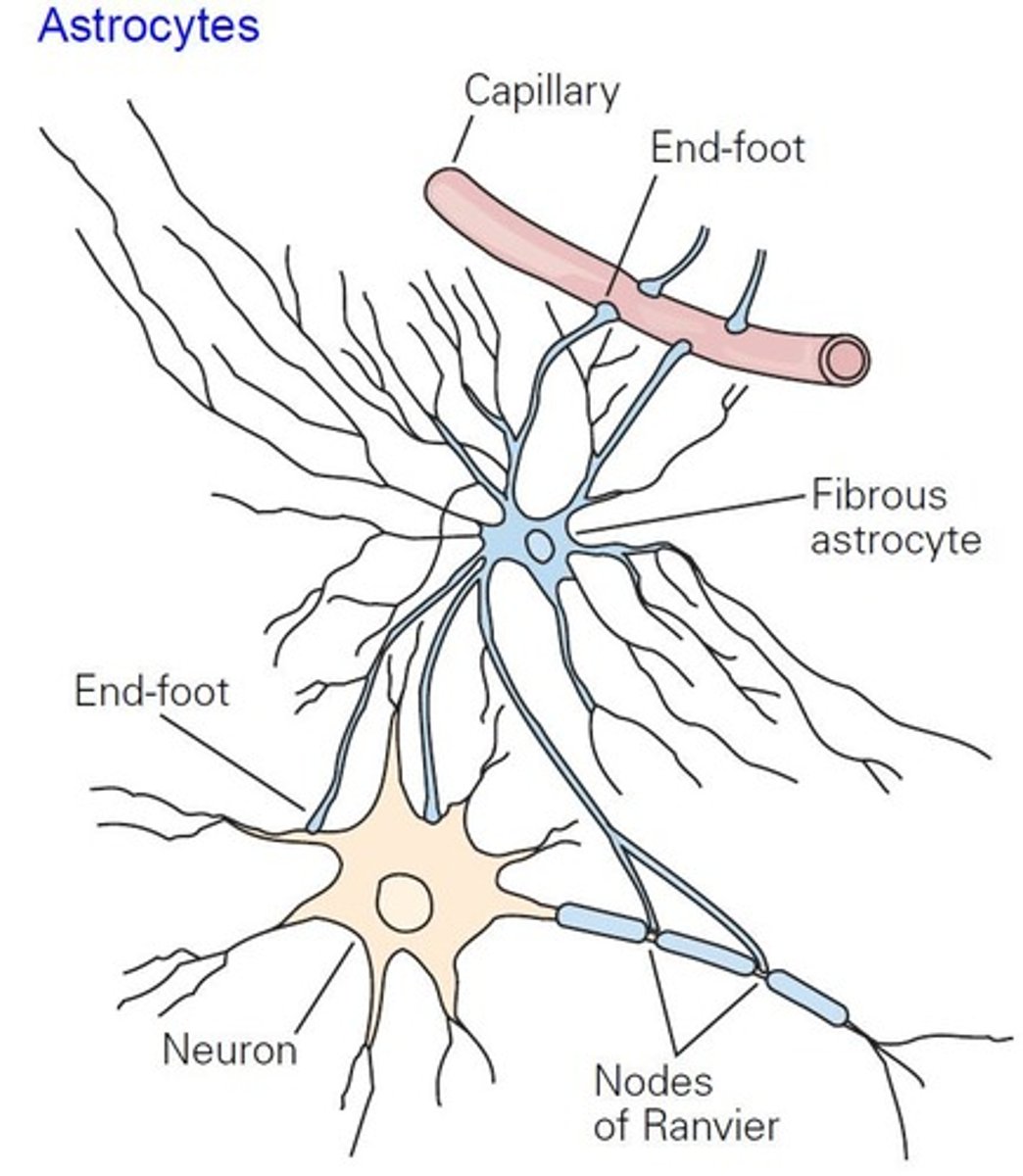
Astrocytes
Star-shaped glial cells in the CNS.
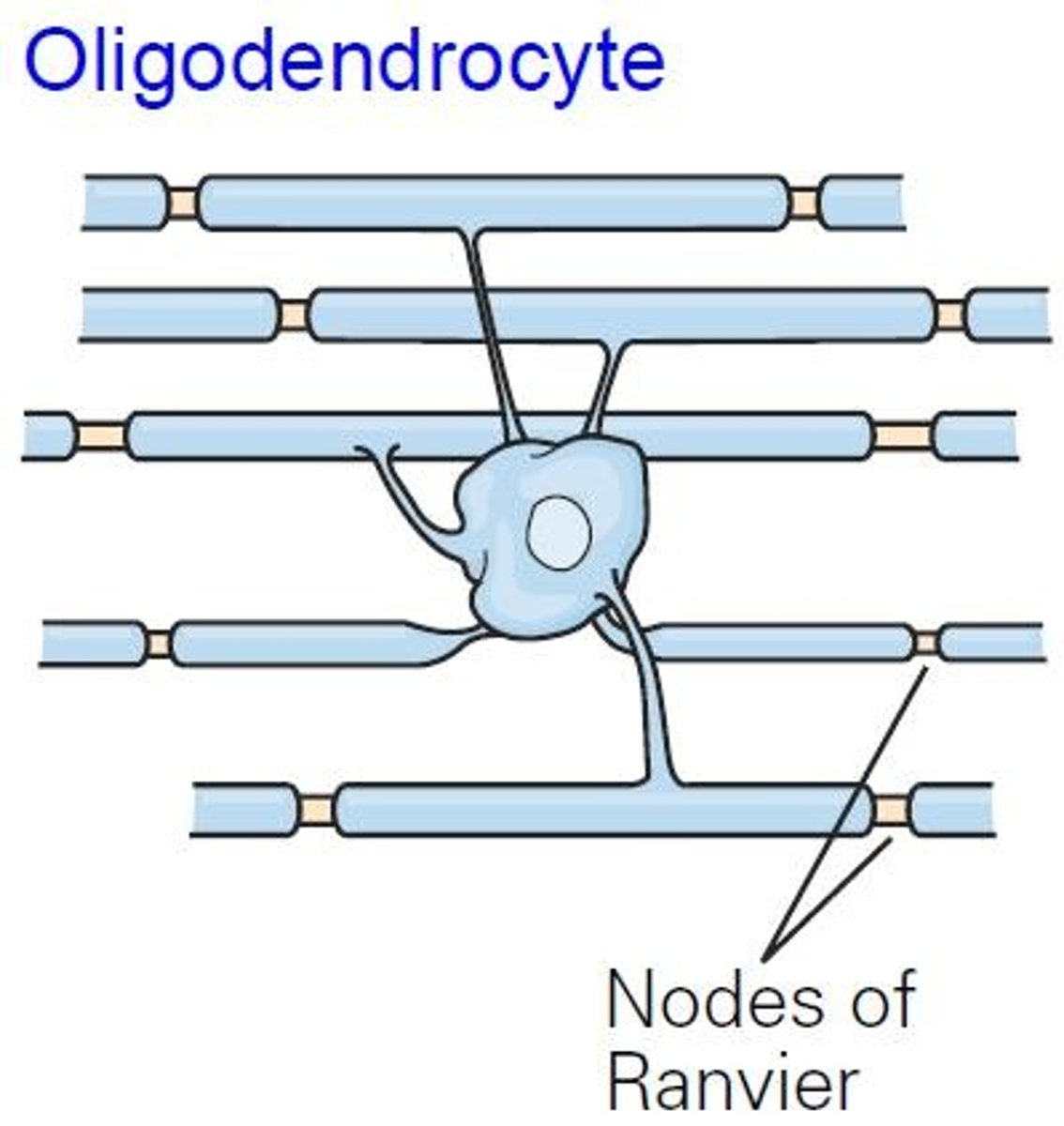
Oligodendrocytes
Glial cells that myelinate CNS axons.
Neural progenitor cells
Multipotent cells that can differentiate into neurons.
Neural stem cells
Multipotent cells that self-renew indefinitely.
Differentiation
Process of a cell becoming specialized.
Terminal differentiation
When a cell exits the cell cycle permanently.
Cell potency
Ability of a stem cell to differentiate.
Totipotent
Cells that can form an entire organism.
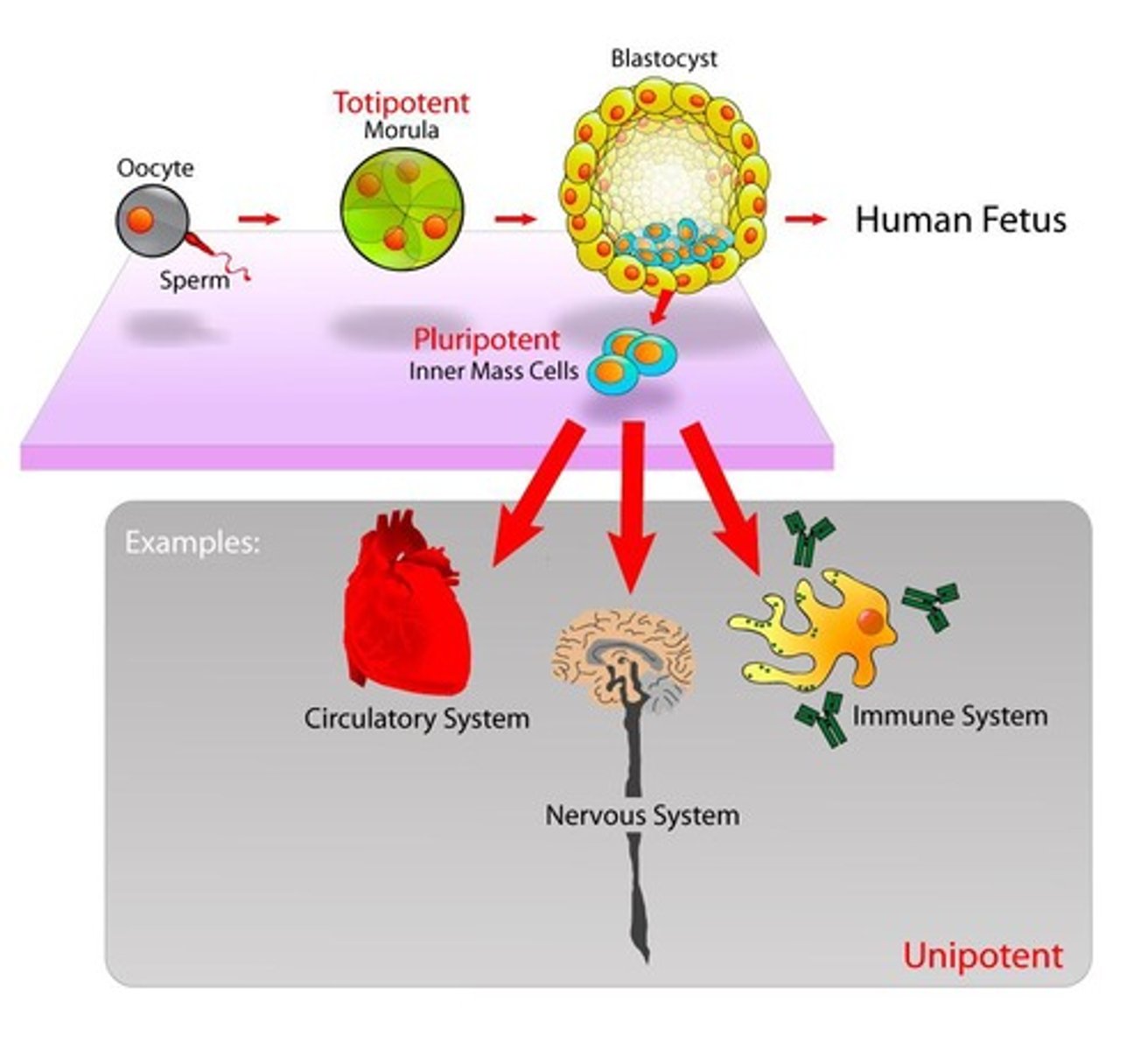
Pluripotent
Cells that can form any germ layer.
Multipotent
Cells that can differentiate into multiple cell types.
Self-renewal
Process by which stem cells replicate indefinitely.
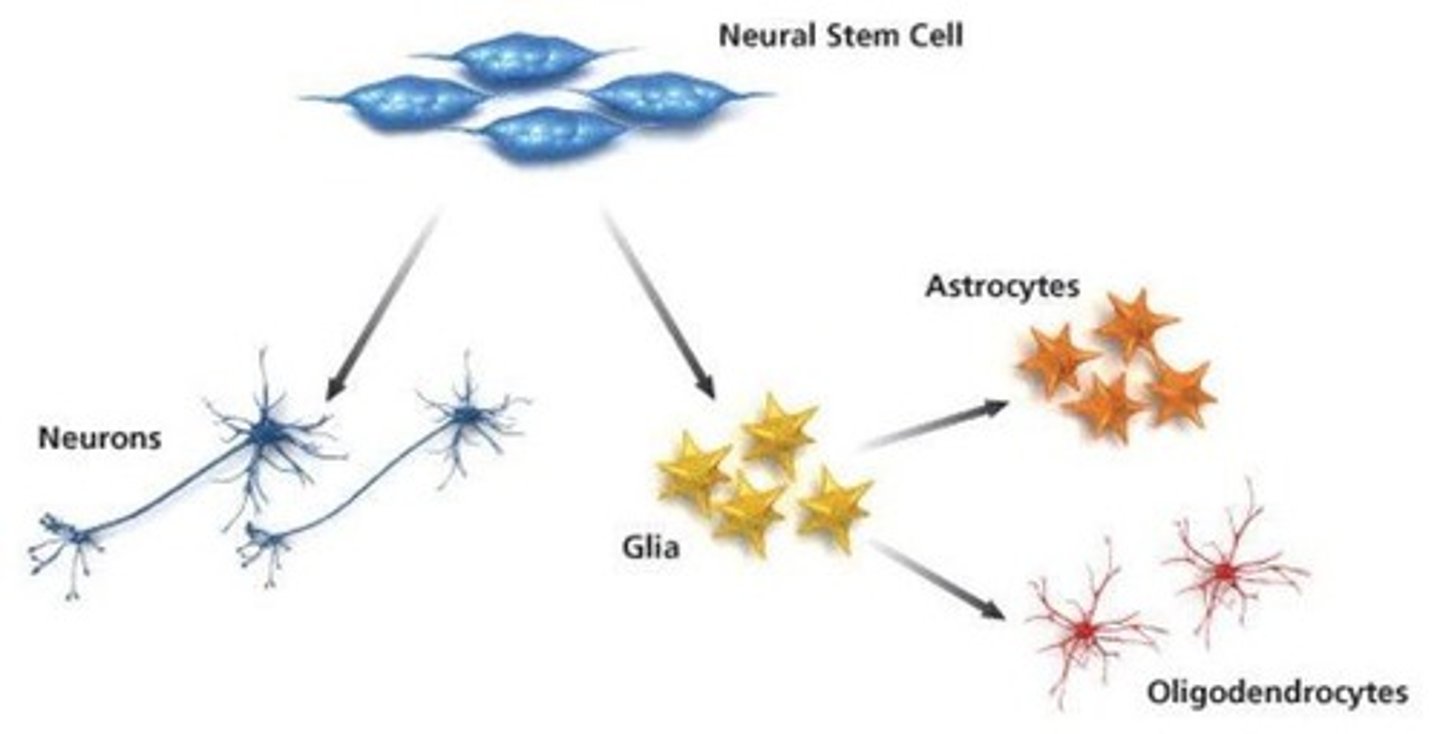
Neural stem cell (NSC)
Multipotent cells that can self-renew and differentiate.
Neural progenitor cell (NPC)
Multipotent cells with limited self-renewal capacity.
In vitro culturing
Studying cell potency by examining progeny.
Differentiation capacity
Potential of progenitor cells to become specific cell types.
Hematopoietic stem cells
Stem cells that give rise to blood cells.
Tripotent
Can differentiate into three cell types.
Bipotent
Can differentiate into two cell types.
Unipotent
Can differentiate into one cell type.
Neural progenitor cell
Cell that gives rise to neurons and glia.
Postmitotic neurons
Cells that do not re-enter the cell cycle.
Interphase
Preparation period for mitosis in cell cycle.
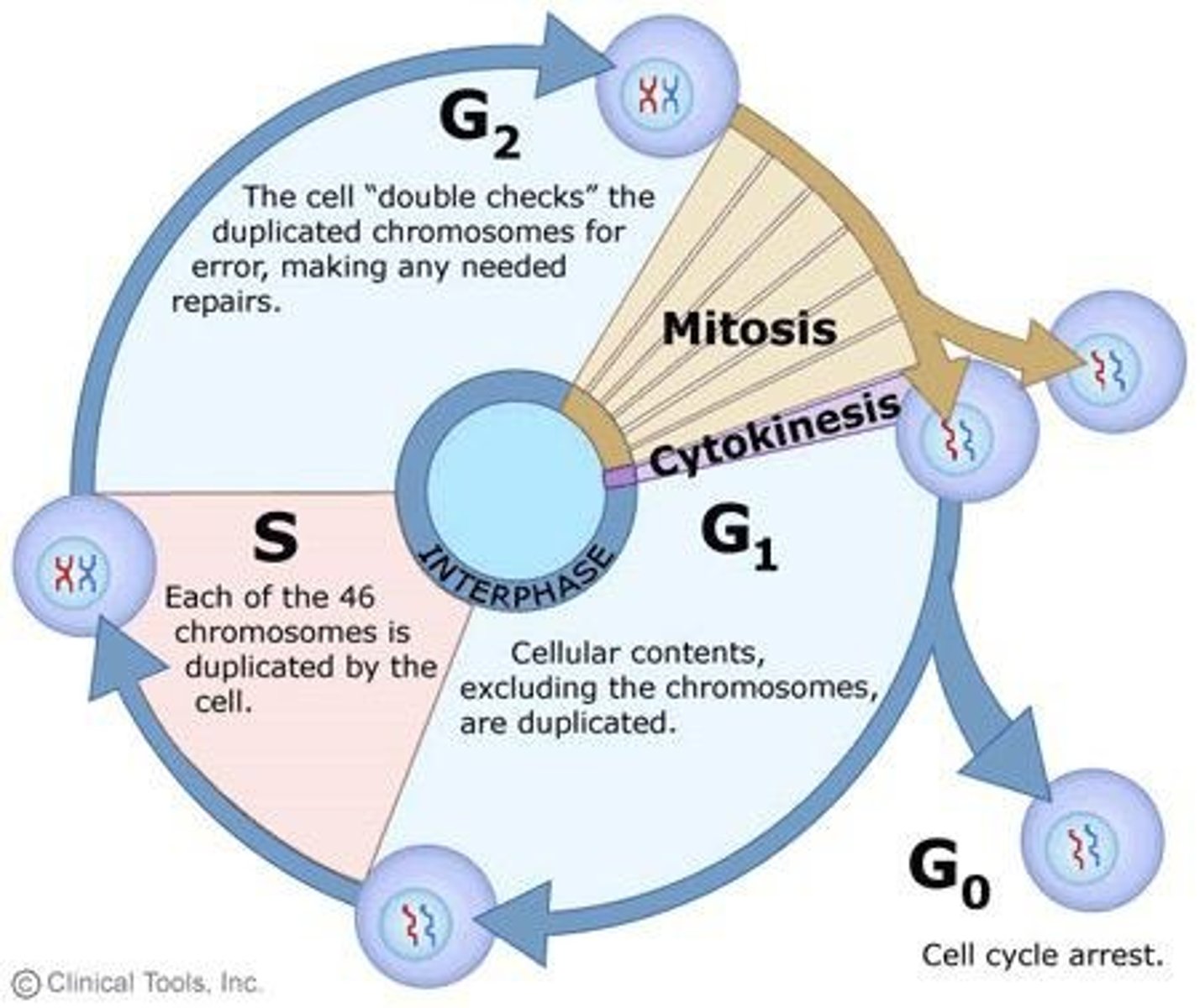
G1 phase
Growth phase where cell increases in size.
S phase
Phase where chromosomes replicate.
G2 phase
Preparation phase with rapid growth and protein synthesis.
M phase
Phase where mitosis and cytokinesis occur.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm after mitosis.
Interkinetic nuclear migration
Movement of nuclei during the cell cycle.
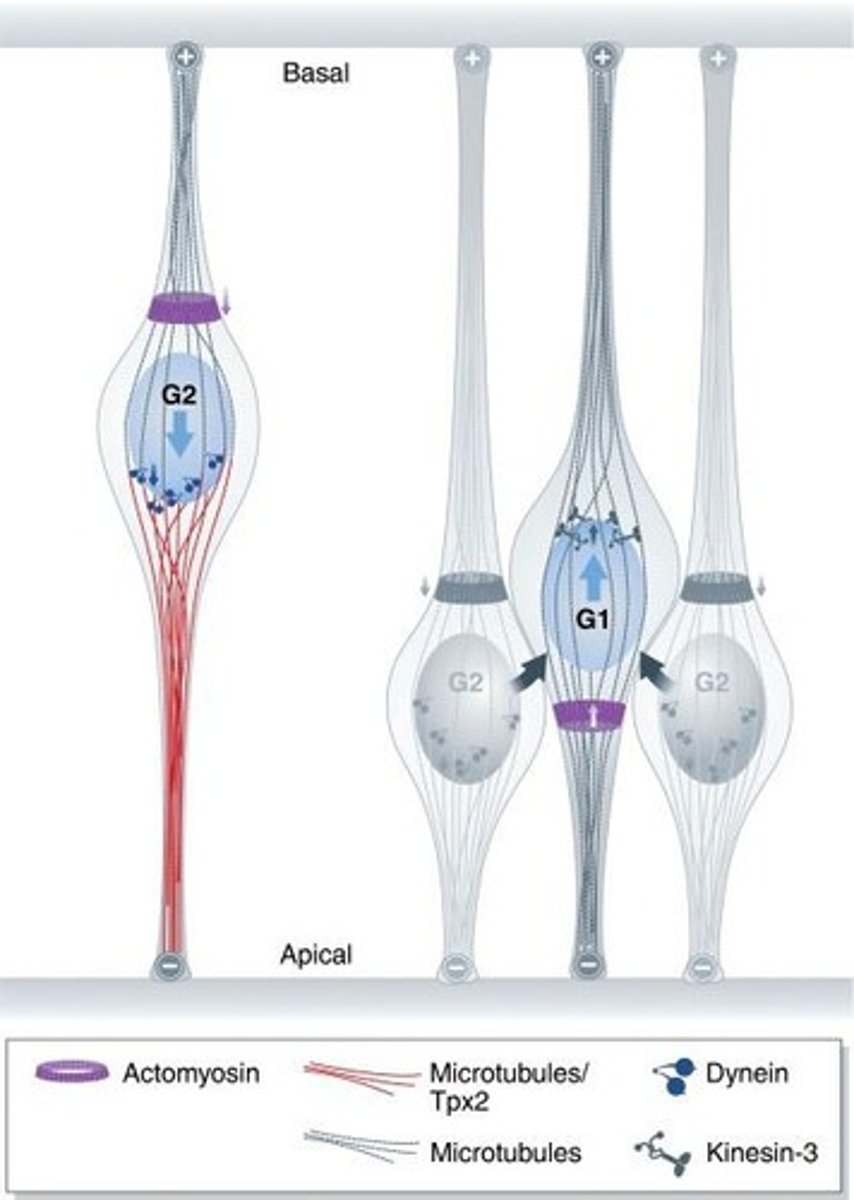
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal structures aiding in nuclear migration.
Dynein
Motor protein moving nuclei towards basal side.
Kinesin
Motor protein moving nuclei towards apical side.
Actomyosin
Protein complex that constricts microtubules.
Ventricular zone
Apical side where neural progenitors divide.
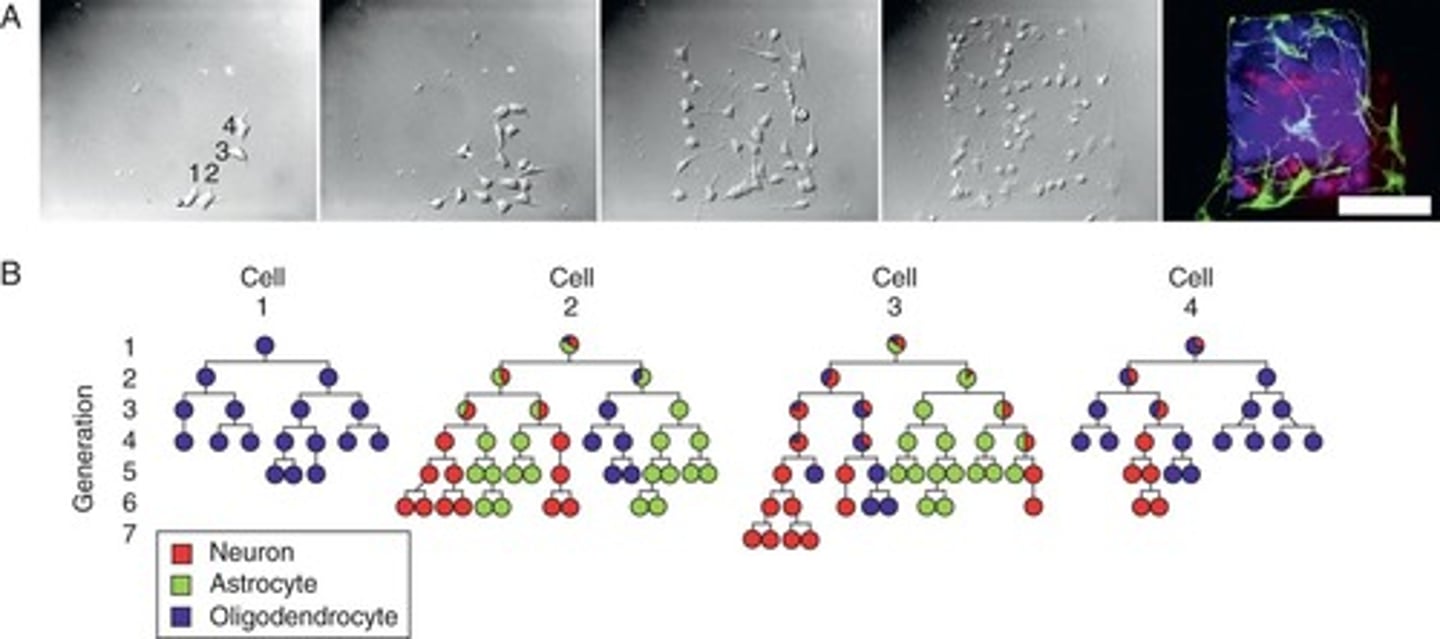
Clonal analysis
Study of cells derived from mitotic events.
Cell cycle
Series of phases leading to cell division.
Mitotic phase
Short phase where nucleus divides.
Crowded pub hypothesis
Theory on cell division influenced by environment.
Clonal analysis
Method to trace lineages of progenitor cells.
Progenitors
Cells that give rise to other cells.
Retrovirus
Virus integrating into host DNA during cell division.
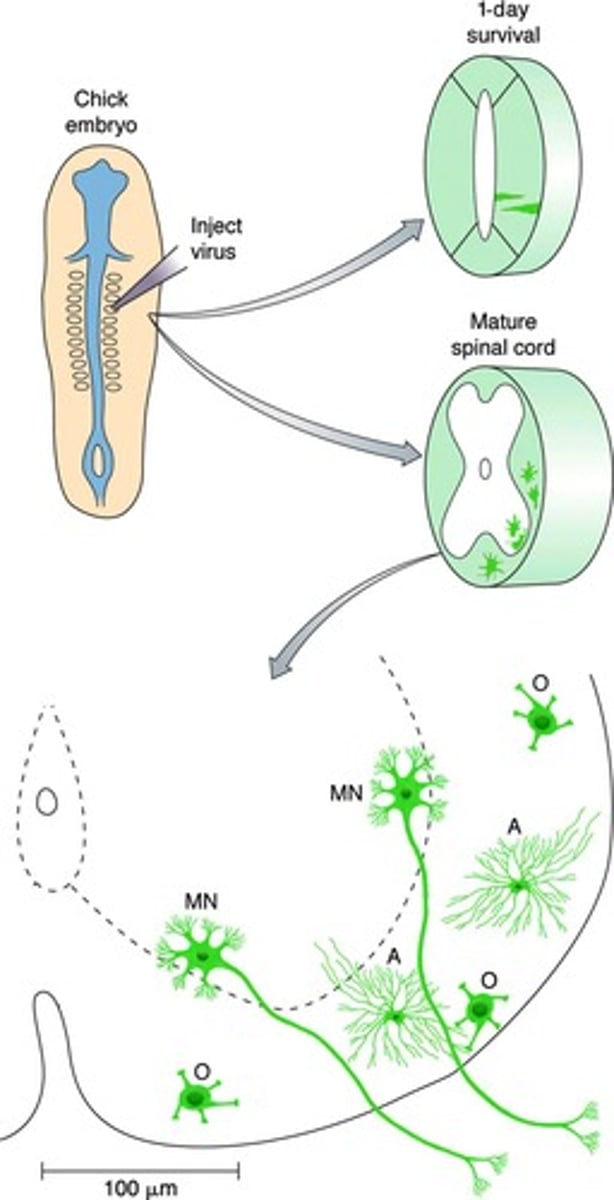
Lentivirus
Type of retrovirus used for gene delivery.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
Protein used to label cells for visualization.
Genomic DNA
Cell's complete set of DNA including genes.
Actively dividing cells
Cells undergoing mitosis, allowing viral integration.
GFP+ progeny
Descendants of progenitor cells expressing GFP.
Survival period
Time after injection before examining cells.
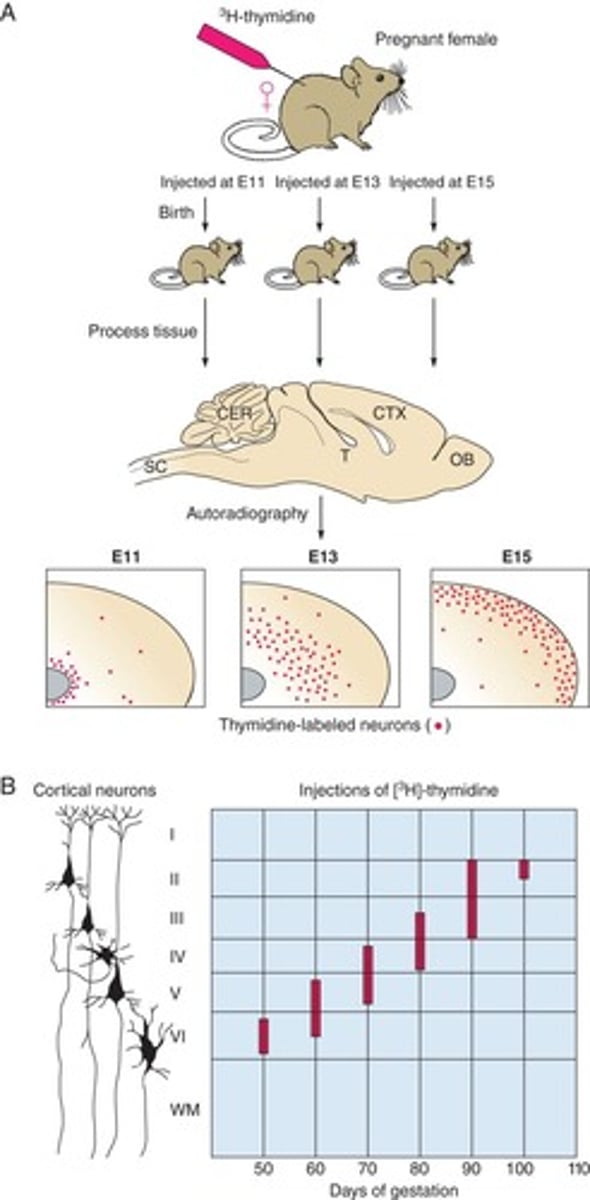
Labeled nucleotide analogs
Synthetic nucleotides used for tracking cell division.
Thymidine
Nucleotide analog incorporated during DNA synthesis.
BrdU/EdU
Modified nucleotides for detecting dividing cells.
Birth dating
Tracking cells based on their division time.
Cortical development
Formation of the cerebral cortex during embryogenesis.
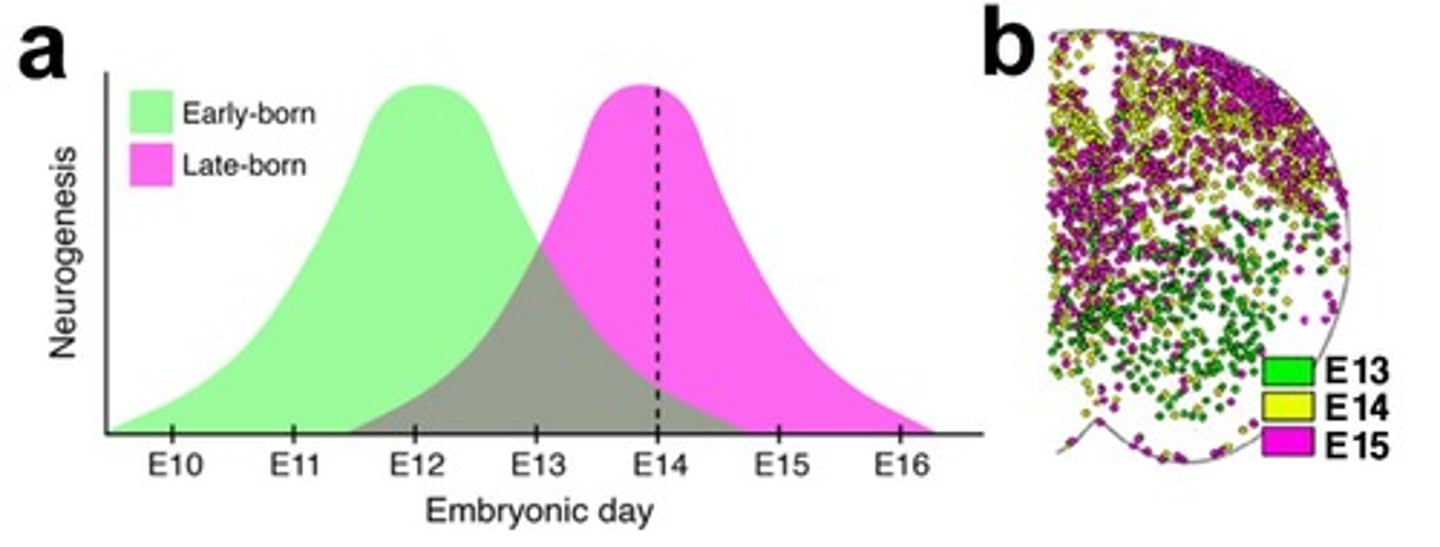
Inside out development
Neurons migrate from inner to outer layers.
Ventral spinal cord neurons
Neurons born earlier than dorsal spinal cord neurons.
Dorsal spinal cord neurons
Neurons born later than ventral spinal cord neurons.
Neural progenitor cells (NPCs)
Cells that can differentiate into neurons and glia.
Transplantation studies
Research involving transferring cells to different locations.
E14 rat embryos
Source of neural progenitors for transplantation.
Neurogenesis
Process of generating new neurons during development.
Neural Progenitor Cells (NPC)
Cells that can differentiate into various neural types.
E13, E14, E15
Embryonic days for isolating NPCs from rats.
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
Condition treated using transplanted NPCs.
Histological Analysis
Technique to determine neuronal phenotypes post-transplant.
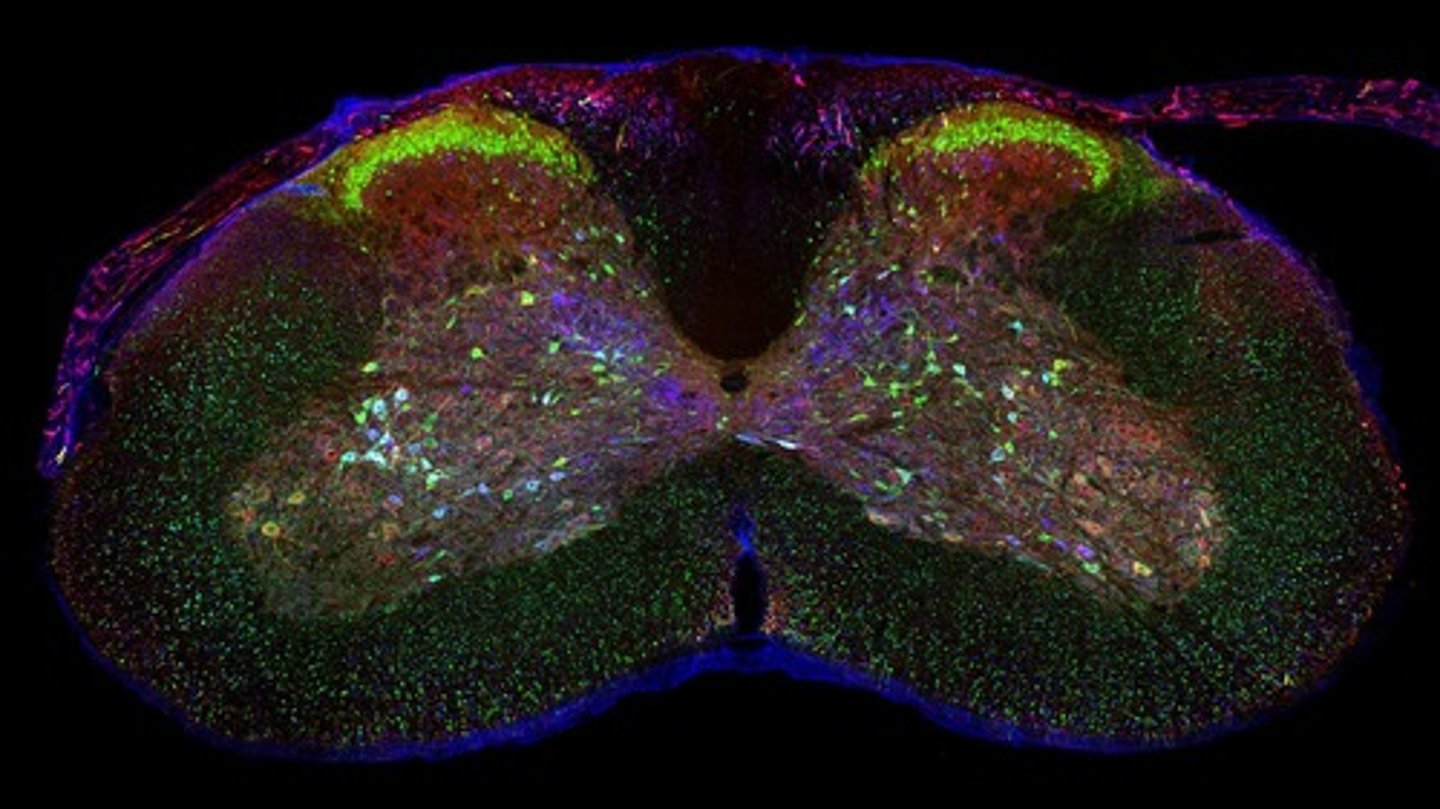
Neurons
Mature cells produced from NPC grafts.
Ventral Spinal Cord Neurons
Subtypes enriched in earlier-stage NPC grafts.
Dorsal Spinal Cord Neurons
Subtypes enriched in later-stage NPC grafts.
Developmental Stage Influence
Affects cell types in mature grafts significantly.
Neuronal Birth Dates
Larger neurons born earlier than smaller ones.
Phylogenetic Development
Older brain parts develop before newer structures.
Cell Cycle Length
Increases progressively during embryonic development.
G2 and M Phases
Remain constant in length throughout development.
G1 and S Phases
Lengthen progressively over developmental stages.
Neurogenesis Rate
Slows down as development progresses.
Quit Fraction (Q fraction)
Proportion of postmitotic neurons from cell division.
Asymmetric Cell Division
Produces one progenitor and one postmitotic cell.
Cyclins
Proteins regulating stages of the cell cycle.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
Interact with cyclins to regulate cell cycle activity.
Molecular Regulators
Identify factors affecting cell cycle progression.
Growth Factors
Regulate cell cycle, promoting or inhibiting progression.
Mitogens
Stimulate differential expression of cyclins and CDKs.
Multipotent Progenitor Cells
Can differentiate into multiple cell lineages.
Committed Progenitor Cells
Can only differentiate into neurons or glia.
Progenitor
Cell type that can differentiate into neurons or glia.
Neuron
Basic unit of the nervous system, transmitting signals.
Astrocyte
Star-shaped glial cells supporting neurons in the brain.
Oligodendrocyte
Glial cells that insulate axons with myelin.
Dorsal/Ventral Patterning
Segmentation of spinal cord into distinct progenitor domains.
Progenitor Domains
Regions in the spinal cord generating specific neuron types.
pd1 - pd6
Dorsal progenitor domains producing dorsal neurons.
p0 - p3
Ventral progenitor domains generating ventral neurons.
pMN
Motor neuron progenitor domain producing motor neurons.
Neurogenesis
Process of generating neurons from progenitor cells.
Glial Cells
Supportive cells in the nervous system, not neurons.
Ventral Interneurons
Types of interneurons generated by p0-p3 domains.