On ramps chem unit 1 review
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Rutherford's gold foil experiment demonstrated that
the positive charge in an atom must reside in a dense core much smaller than the atom (the nucleus)
Rutherford’s foil experiement proved the existance of the nucleus
Which scientist is associated with the discovery of the electron?
JJ Thompson discovered the electron in 1897 by demonstrating that cathode rays were negatively charged
One of hte most profound ideas proposed by Max Planck was
Electron energies are quantized— he showed that the structure of nature is discontinuous and was restriced to discreet values, forming the conclusion that electromagnetic energy could only be used in quantized form
when an atom absorbs a photon of light, electrons
move up an energy level
an electron moving from the 3rd energy level to the 1st energy level will
emit a photon, when an electron moves down energy levels, they release energy in the form of light
the electromagnetic spectrum
is divided into 7 named regions, each containing a range of wavelengths
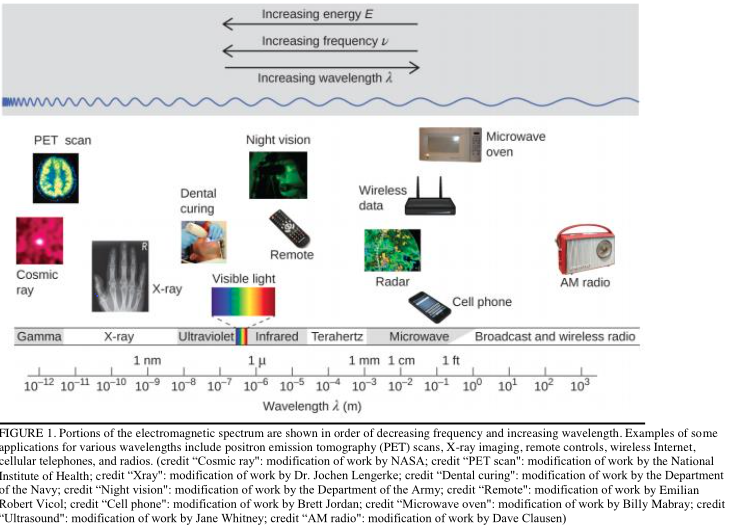
wavelength and frequency are
inversely proportional
light propogates in
both electric and magnetic fields
radio waves
lowest energy level, cause nuclei to flip their spin
microwaves
low energy radiation, contains enough energy to cause entire molecules to rotate
Infrared radiation
higher energy, causes vibrations in molecules, can change mode of vibration
UV and visible light
energetic enough to excite the valence electrons, ionizing radiation
x-rays and gamma rays
highest energy, can penetrate the inner shell electrons

delta E is change in energy
v is the frequency (s^-1)
lamda is wavelength (m)
c is speed of light (3×10^8 m-s)
h is panks constant (6.6×10^-34)
destructive interference of two waves occur when
the two waves are exactly out of phase
the three failures of classical physics
emission spectra of hydrogen
blackbody radiation
photoelectric effect
The photon…
teh model of light as a particle
E=hv
wave particle duality
the question of if light is a wave or a particle?
One of the pieces of evidence supporting energy quantization was the line spectra of elements. Why does this demonstrate energy quantization?
There are sharp emission lines demonstrating discrete energy levels.
the photoelectric effect
use of a photon to produce an electron
Increasing the brightness (i.e. more photons of the same energy) of the light shined on the metal _____ the number of ejected electrons.
increases
Increasing the _____ of light can increase the speed of the ejected electrons.
frequency
In the 20th century, quantum mechanics addressed the failures of classical mechanics by introducing the concept of the wave-particle duality. Why was classical mechanics able to explain the world just fine up until then?
Macroscopic objects can be modeled purely as particles because their wavelength is so small compared to their scale that it can be neglected for most purposes and still gives a good description of their behavior.
You shoot a beam of 4.5 eV light at a metal surface and notice that electrons are being released from the metal. What will happen if you then increase the intensity of the 4.5 eV light?
more electrons would be released
light behaves like
both a particle and a wave
Einstein's explanation for the photoelectric effect led to what major breakthrough in science?
wave particle duality of light
Which of the following experiments most directly supports de Broglie's hypothesis of the wave nature of matter?
Electron diffraction by a crystal
Even though all matter exhibits a wave-like quality, we can really only observe the wave properties of
very small objects like subatomic particles.
n- principle quantum number
explains energy levels and sitance of electrons from the nucleus
l- angular momentum number
explains shape of atomic orbital
s-1
p-3
d-2
f-4
ml- magnetic moment
explains orientation of atomic orbital
s-0
p- -1 0 1
d- -2 -1 0 1 2
f- -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
ms- electron spin
explains orientation of electron spin
if the last electron is an up arrow it’s +1/2 or if it’s negative it’s -1/2
The Rydberg constant is 3.3 x 1015 Hz. This value is also
the ionization frequency of hydrogen
What is the frequency of light released when an electron moves from the 2nd energy level to the 1st energy level in hydrogen (don't reach for a calculator, you should be able to estimate 3/4s of a number like 3.3).
2.5 x 1015 Hz
Schrodinger's solution to the wave equation that agreed with the Rydberg constant proved what?
Electrons have a wave like character and can be solved with wave equations.
The complication to the Schrodinger equation in multi-electron systems arises because:
electrons repel each other
Aufbau principle
Always fill electron orbits starting with the orbits that are closest to the nucleus. This is the lowest energy or ground state configuration.
pauli exclusion principle
Never put more than 2 electrons in a single orbit. This is actually the consequence of a larger idea promoted by Pauli that no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers.
huds rule
bus seats, fill up one by one before doubling up