EXAM 1 - Lecture 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what are large biological molecules that make up all living things
macromolecules
what are examples of macromolecules
protein, carbs, lipids, nucleic acids
molecules that are comprised of smaller subunits called monomers and are defined as the basic structures of macromolecules are known as
polymer
examples of polymer
polypeptides, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, lipids
subunits of macromolecules that are comprised of atoms bonded together are known as
monomer
what atoms are commonly found associated with macromolecules
C,H,O,N,P,S
a particular combination of atoms that are consistently found together in a variety of different macromolecules is known as
function group
be able to identify functional groups on molecules
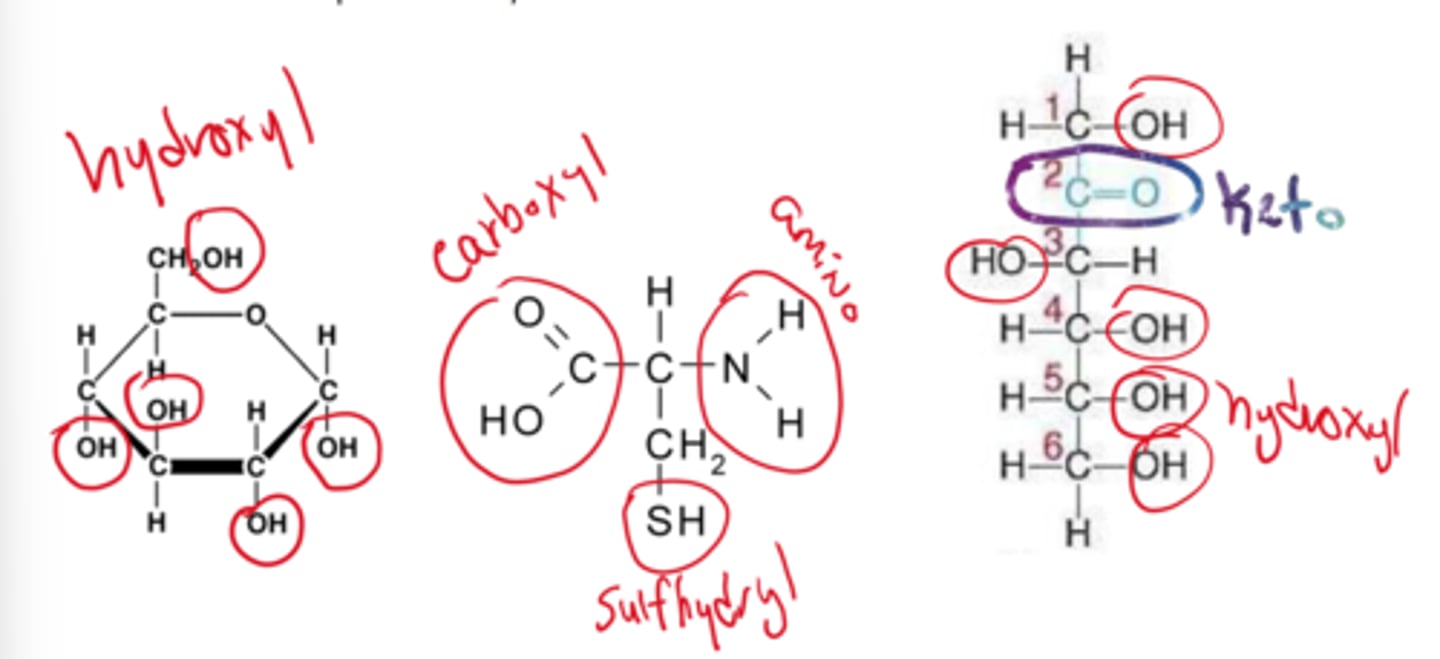
what type of bond is the strongest
covalent
what bond is the weakest
van der waals/hydrophobic
what type of bond shares electrons
covalent
what bond transfers electrons from one atom to another
ionic
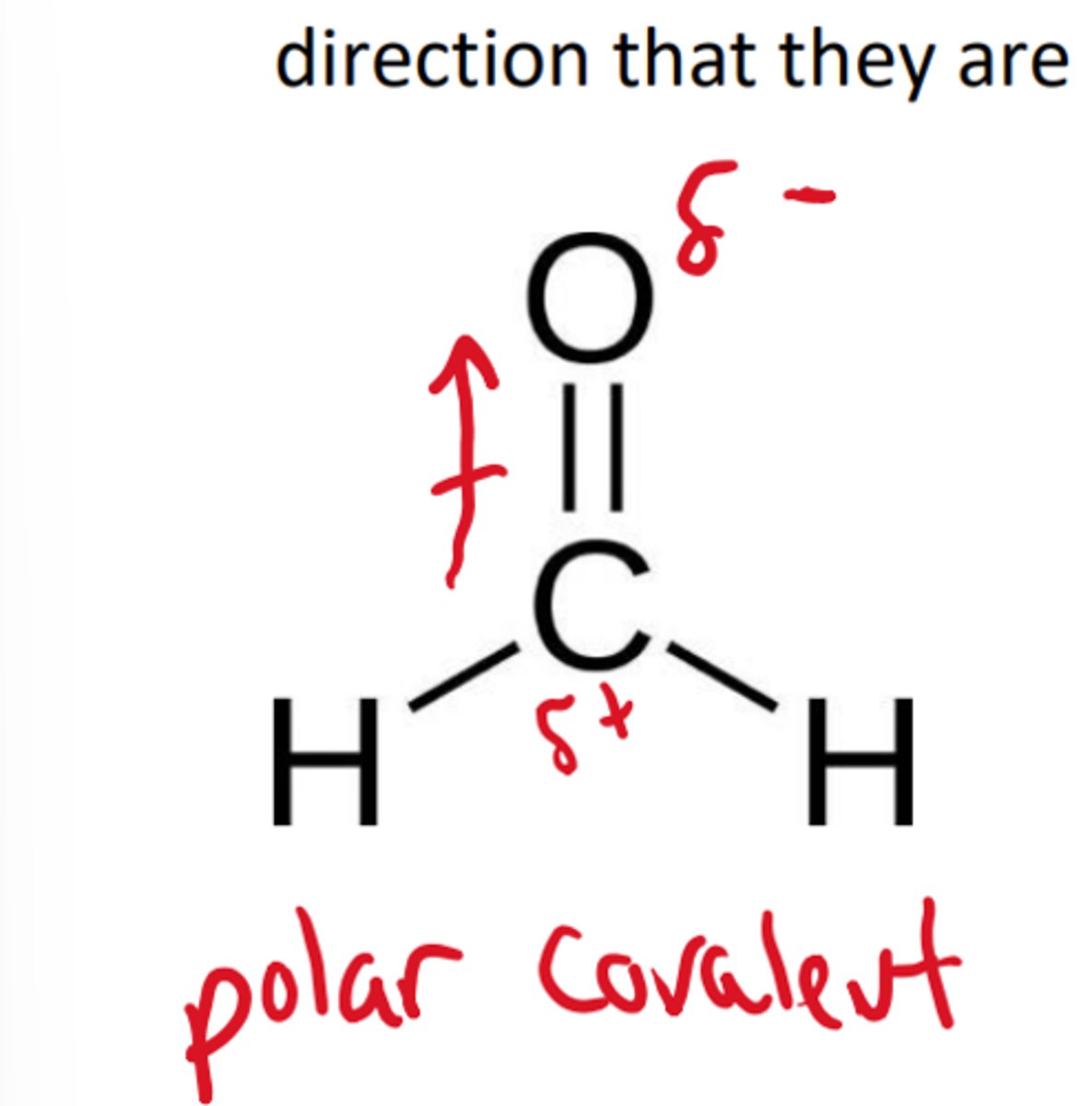
what type of covalent bond shares electrons equally amongst two atoms
non-polar covalent
what type of covalent bond shares electrons unequally
polar covalent
the attractive force that an atom exerts on an electron is known as
electronegativity is the
electrons will be drawn ____ the more electronegative atom
towards
which atoms are the most electronegative
oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, and chlorine
polar covalent molecule diagram
ionic bond molecule diagram
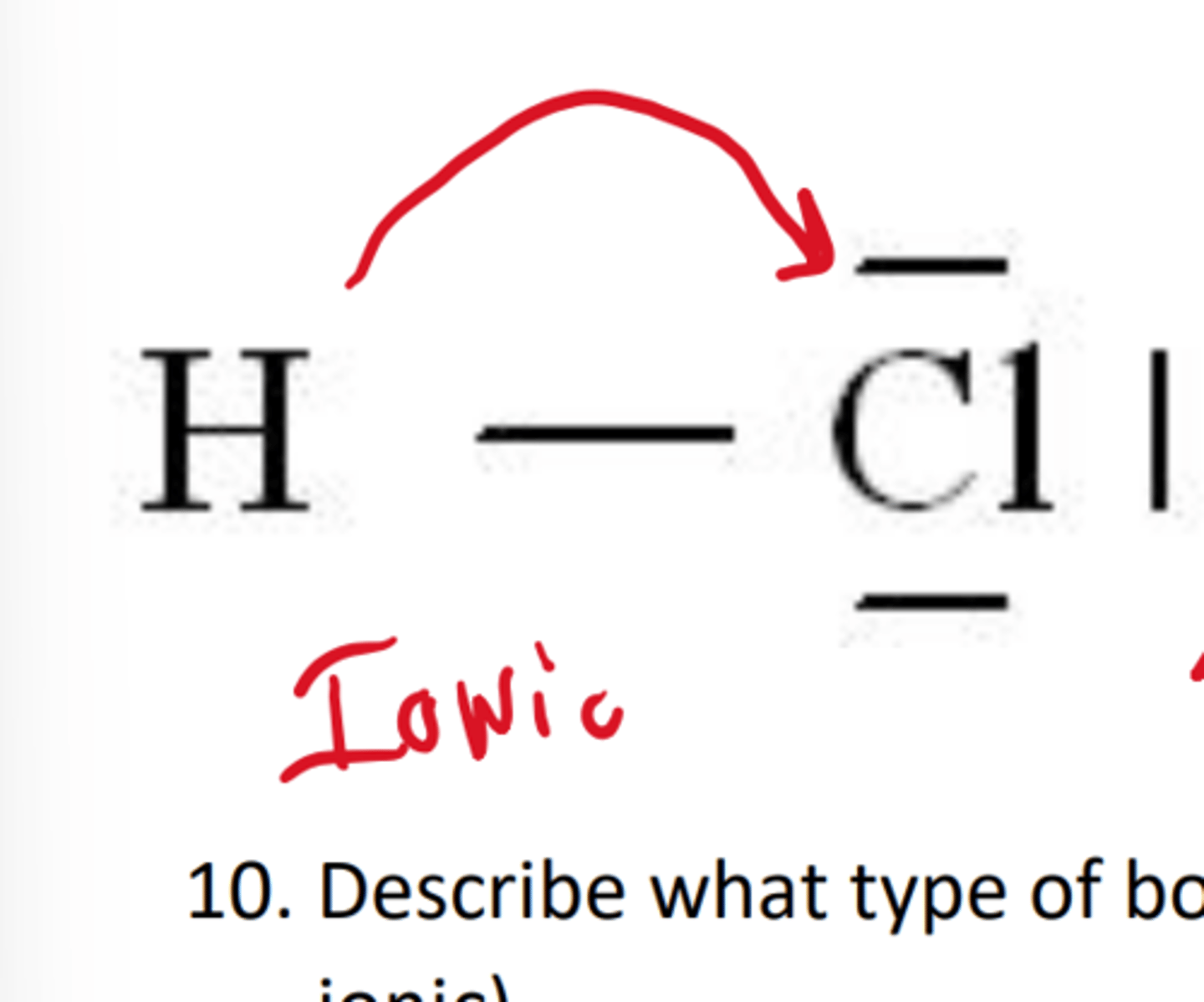
a charged atom or group of atoms is known as an
ion
a positive ion is called
cation
a negative ion is called
anion
when does a redox reaction occur
when one atom loses or gives up an electron to another atom
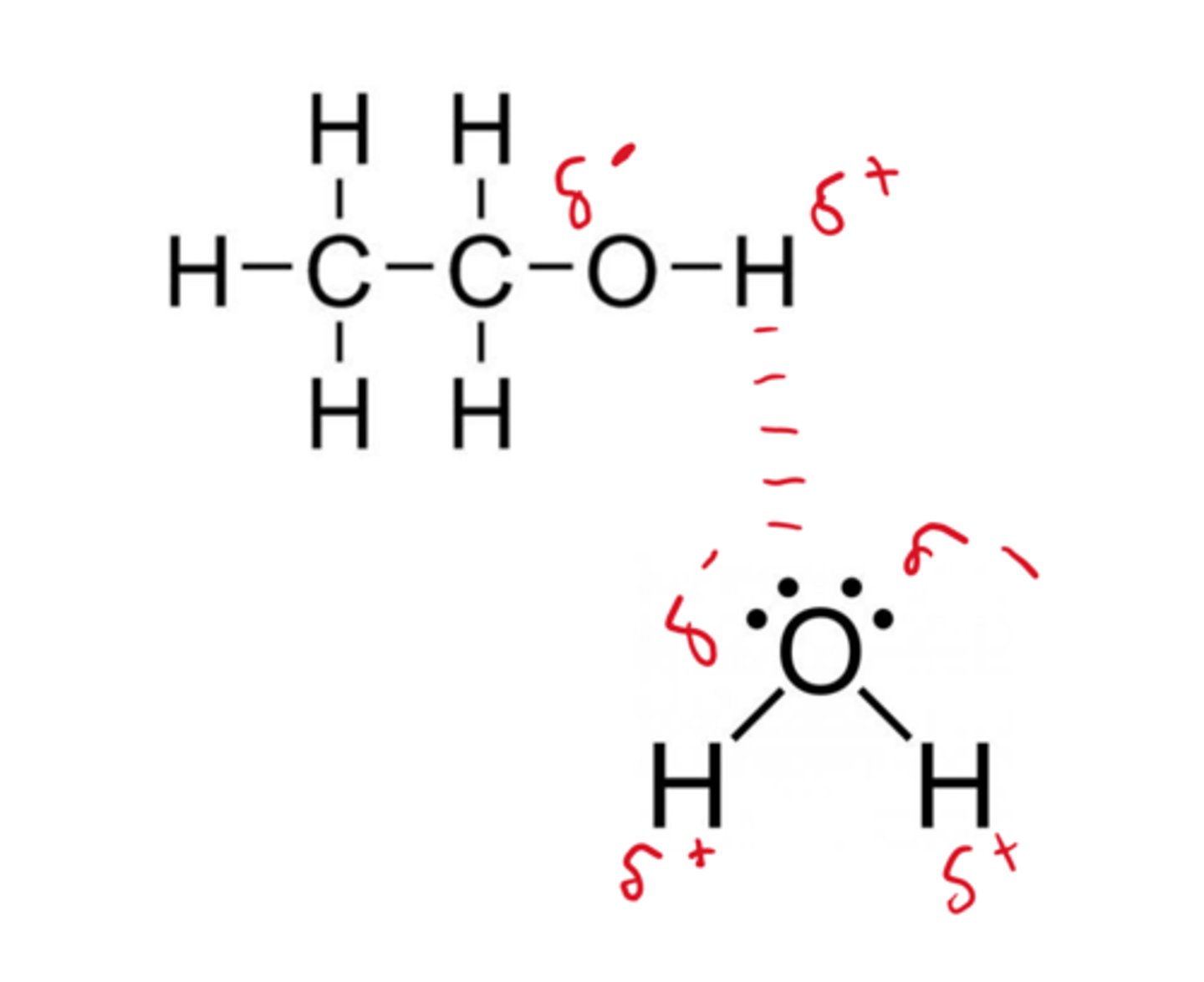
an interaction between an H atom that is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and the unbonded electrons of a second electronegative atom is known as a
hydrogen bond
hydrogen bond diagram
Which of the following solutions would have the highest concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)?
a. Water with a pH of 7
b. Sodium bicarbonate with a pH of 9
c. Beer with a pH of 4
d. Sodium hydroxide with a pH of 1
C
the difference between water and sodium bicarbonate is 2 pH scale points. This means that sodium bicarbonate is 2/10/100 times more acidic/basic/neutral than water
100, basic