BY 124L - Plantae
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the general characteristics of plants?
eukaryotic, multicellular, photosynthetic autotrophic, chlorophylls a and b (carotenoids), store glucose as starch, cell walls made of cellulose, exhibit alternation of generations
What is alternation of generations?
plants have 2 distinct life stages; sporophyte and gametophyte dominant plants
What are sporophyte dominant plants?
diploid dominant life cycle, undergoes meiosis to produce gametes
What are gametophyte dominant plants?
haploid dominant life cycle, undergoes mitosis to produce gametes
What is a cuticle?
waxy covering that slows water loss; gas exchange via opening in the leaves (stomata); not in all plants
What is xylem?
transport water
What is phloem?
transports photosynthetic products
What is lignin?
found in secondary cell walls of woody plants and provides structures
What is the archegonia?
“uterus for plant", stores zygote until fertilization, zygote is kept moist
What are the 3 major groupings of plant phyla?
nonvascular, spore-bearing; vascular, spore-bearing; vascular, seed-bearing
What are bryophytes? (not the phylum, the grouping)
nonvascular, spore-bearing; must grow around moist environments, lack vascular tissue and rhizoids, gametophyte (haploid) dominant life cycle, homosporous, no true roots, stems, or leaves
What are rhizoids?
root hairs
What is the meaning of homosporous (bryophyta)?
spores produced by homosporous plants are indistinguishable
What are the phylums of Bryophytes?
Phylum Bryophyta, Phylum Hepatophyta, Phylum Anthocerophyta
What are the characteristics of Phylum Bryophyta (mosses)?
reproduce sexually
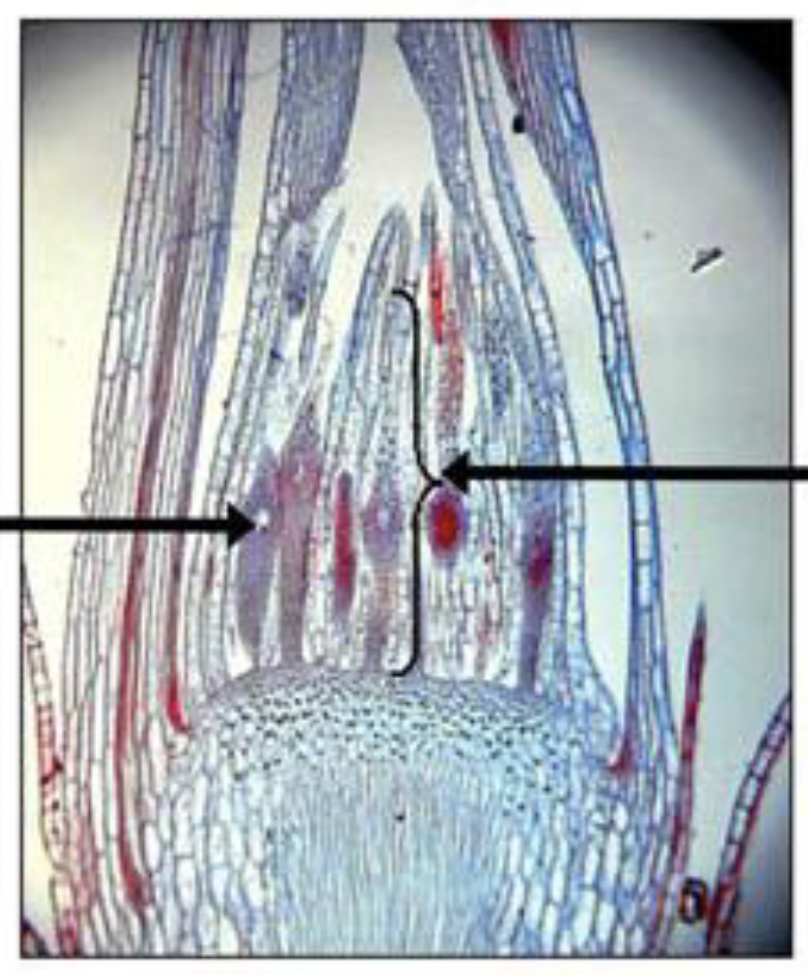
What is this?
Mnium, archegonium; Phylum Bryophyta
What is the archegonium?
female structure that holds the eggs
What is the antheridia?
male structure that holds the sperm
What is this?
Mnium, antheridia; Phylum Bryophyta
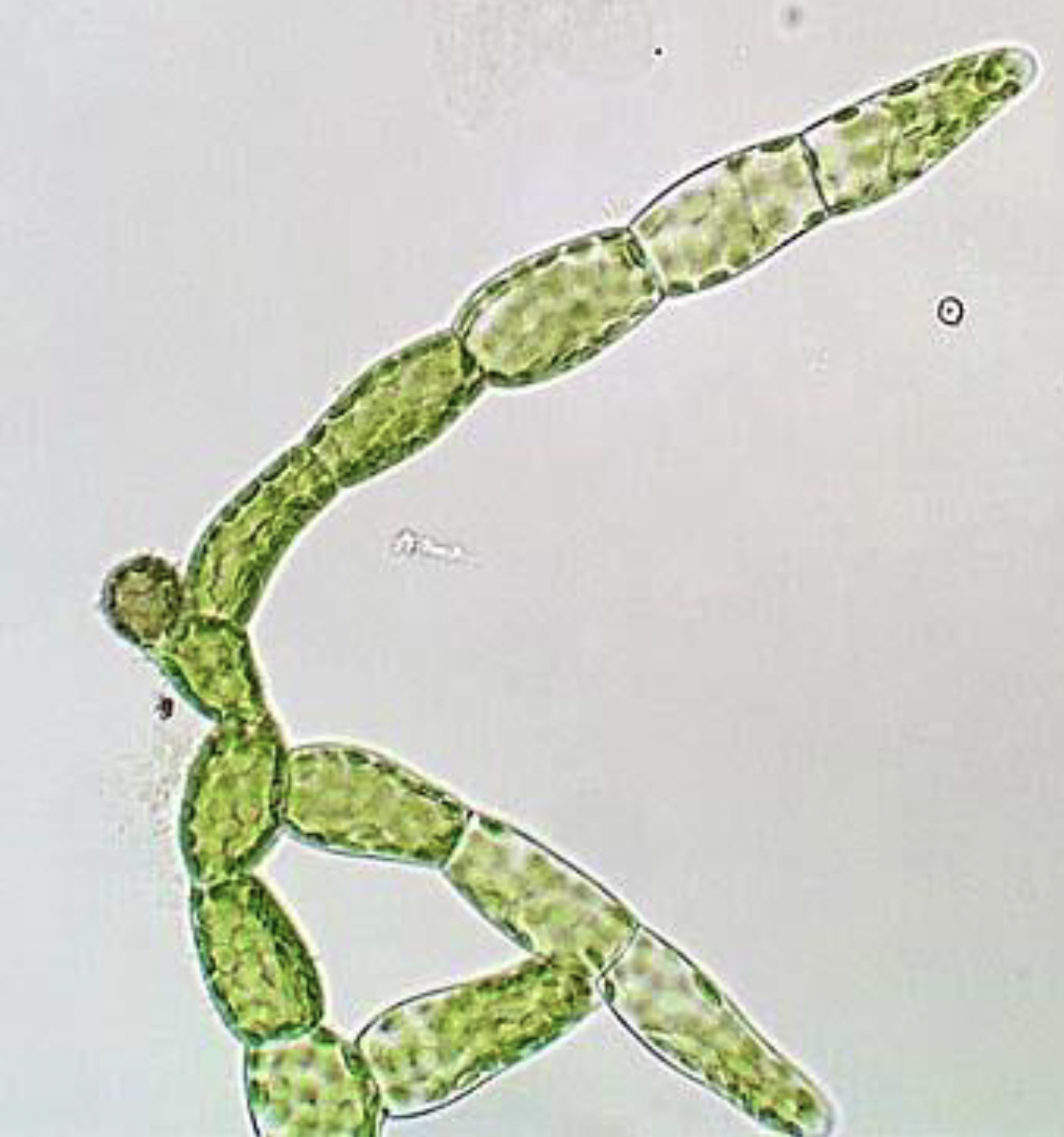
What is this?
Moss Protonema (baby moss); Phylum Bryophyta
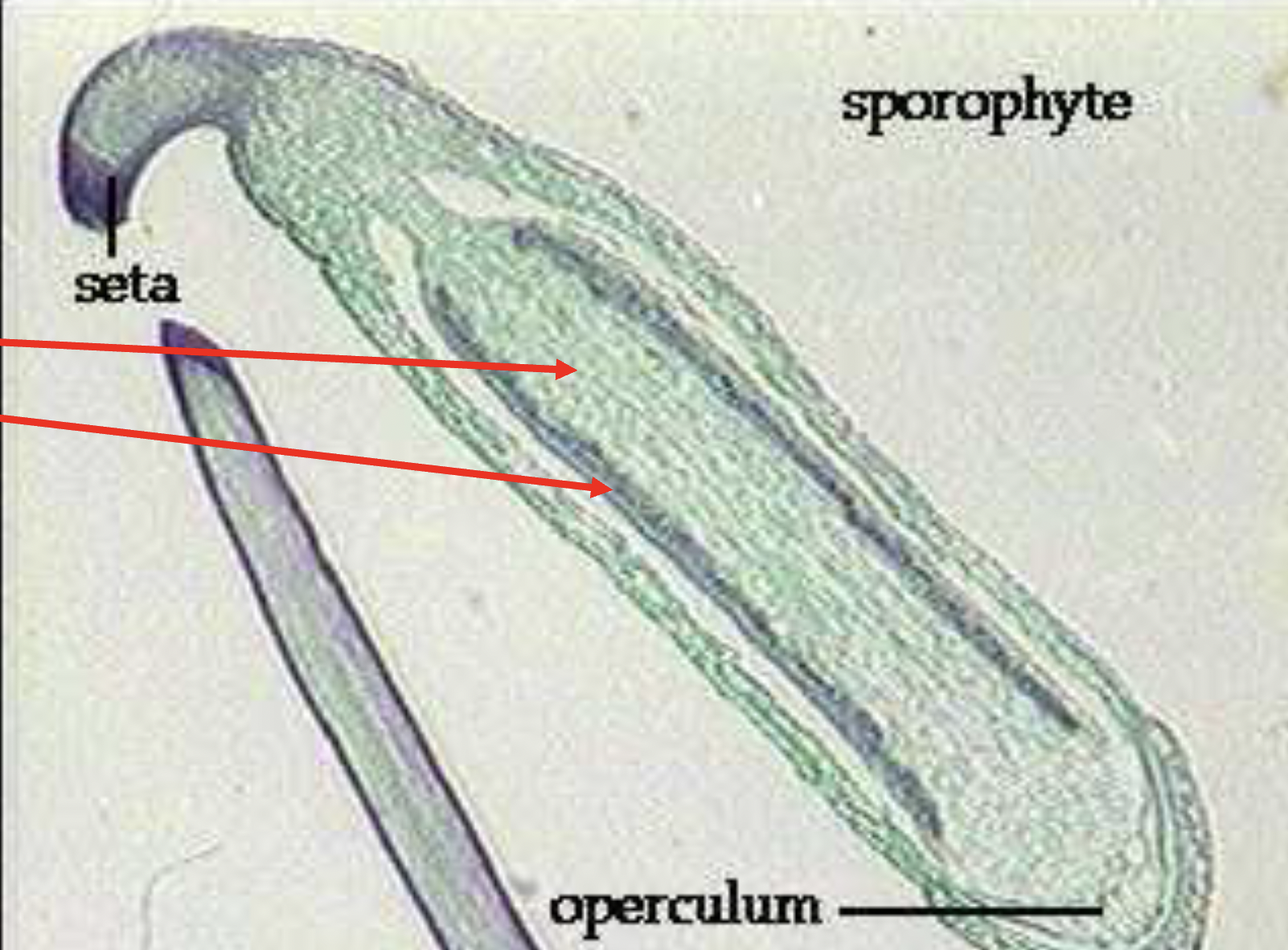
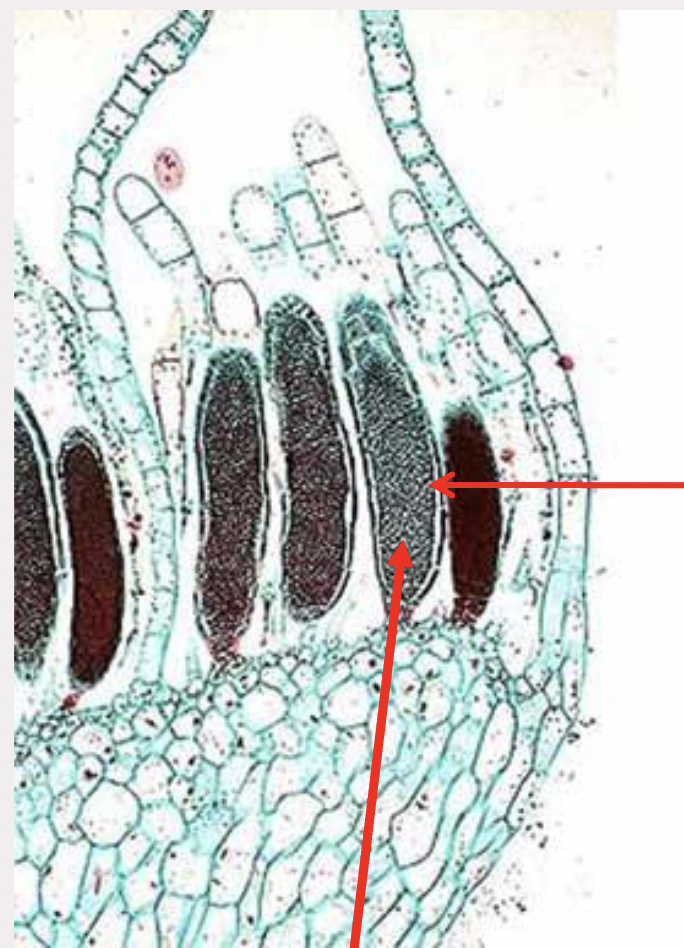
What is this?
Polytrichium capsule; Phylum Bryophyta; diploid sporophyte stage
What does sporogenesis tissue do?
makes spores
What is a seta?
stalk
What does a operculum do?
opens to let spores out
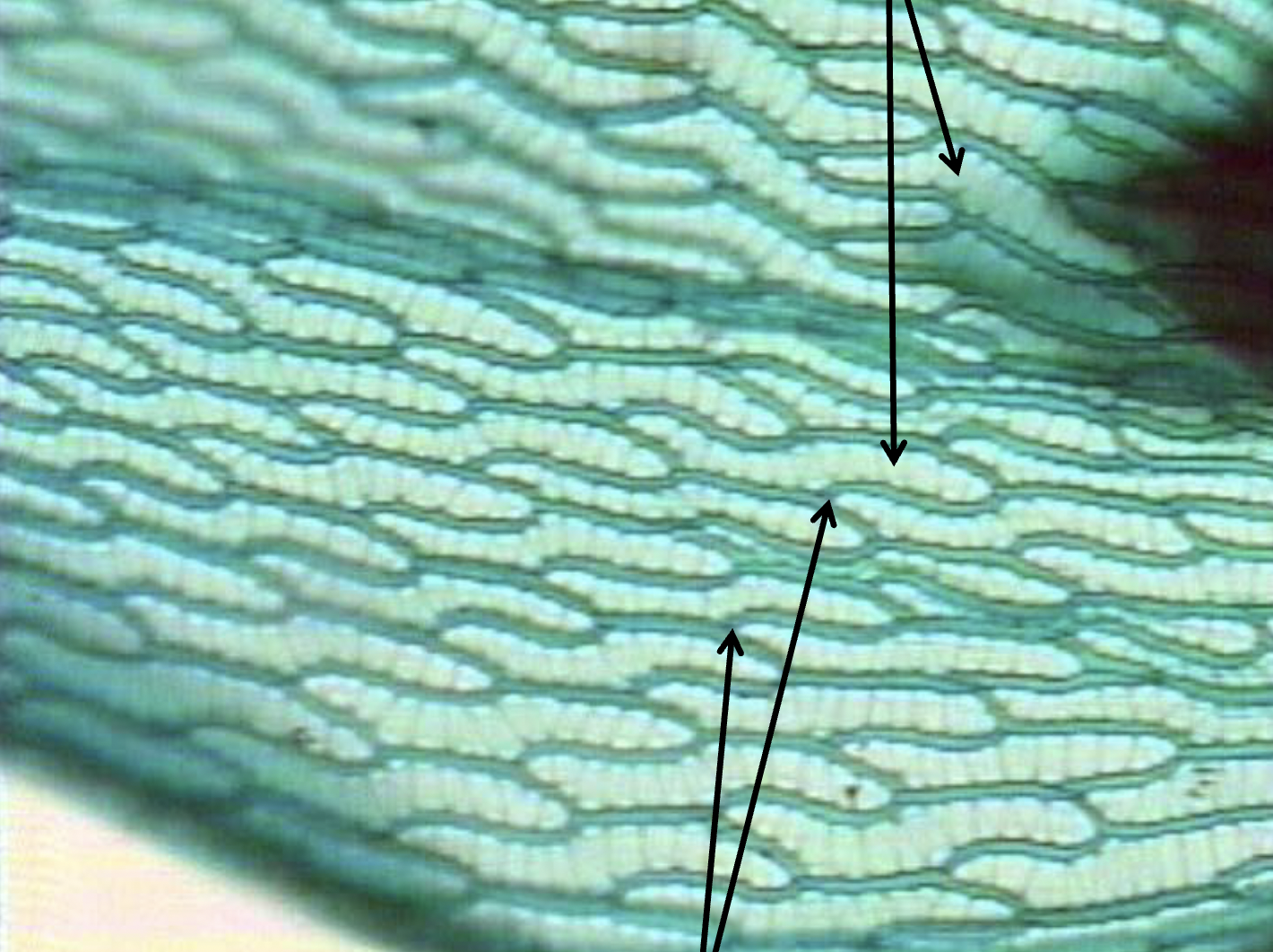
What is this?
Sphagnum Leaf
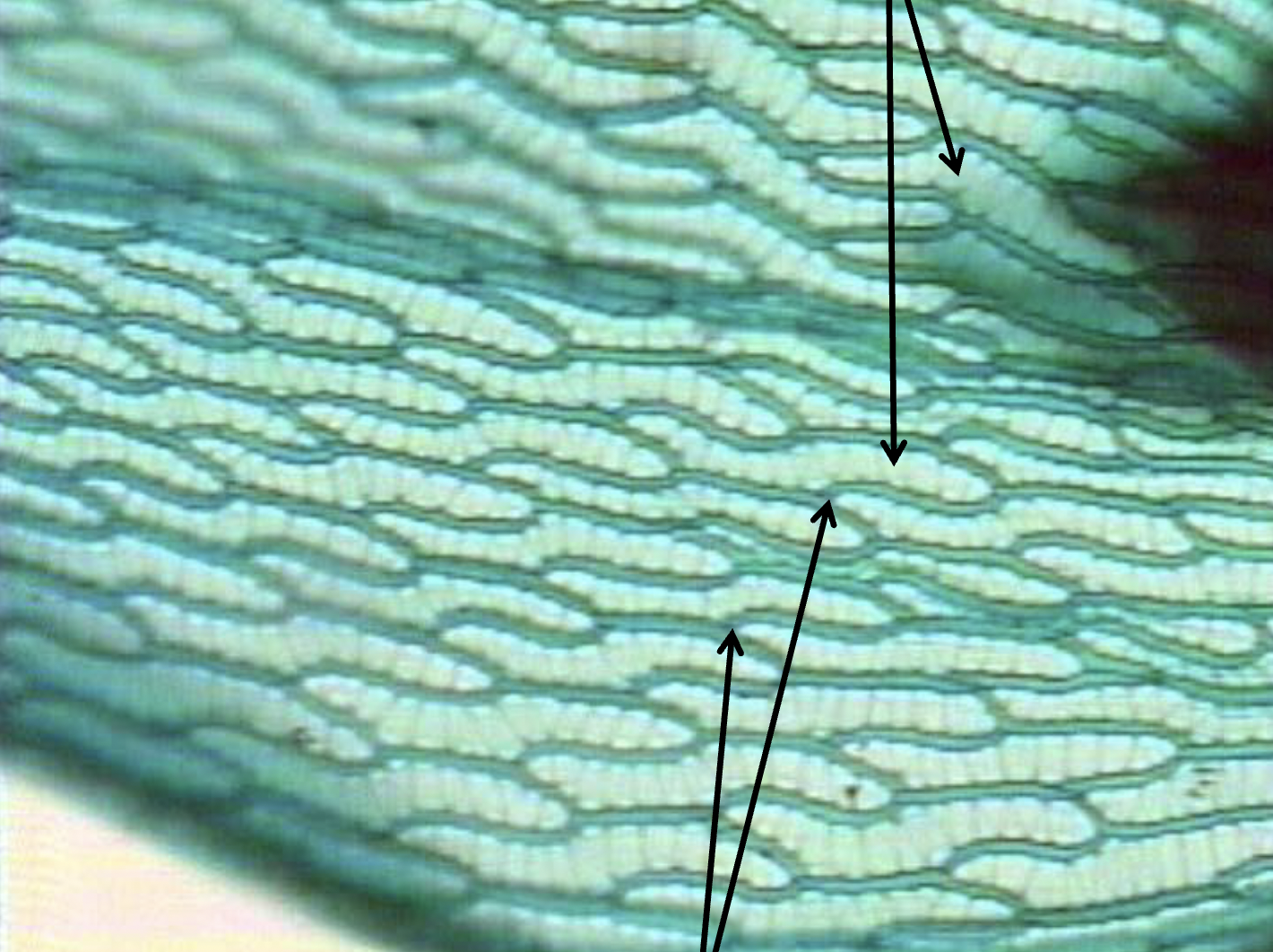
What are the dark lines and lighter spots represent?
lighter spots are dead cells (used as storage), dark lines are photosynthetic cells
What are characteristics of Phylum Hepatophyta (liverworts)?
reproduces sexually like moss, more primitive than mosses, likely similar to first land plants, flattened leafy-like appearance, can also reproduce asexually by gemmae
What is gemmae?
cup-like structures in Phylum Hepatophyta, falls off and grows into a new plant
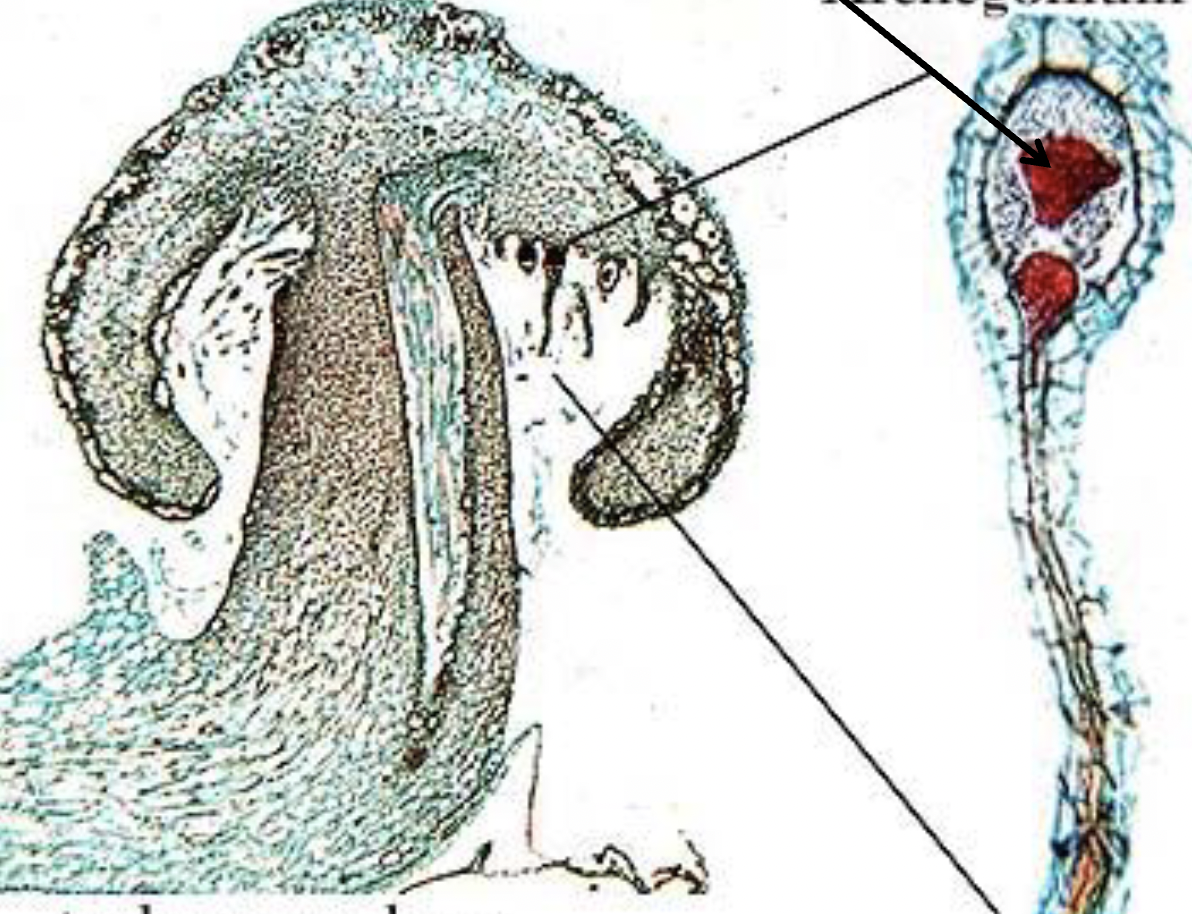
What is this?
Marchantia, Phylum Hepatophyta; arechgonium
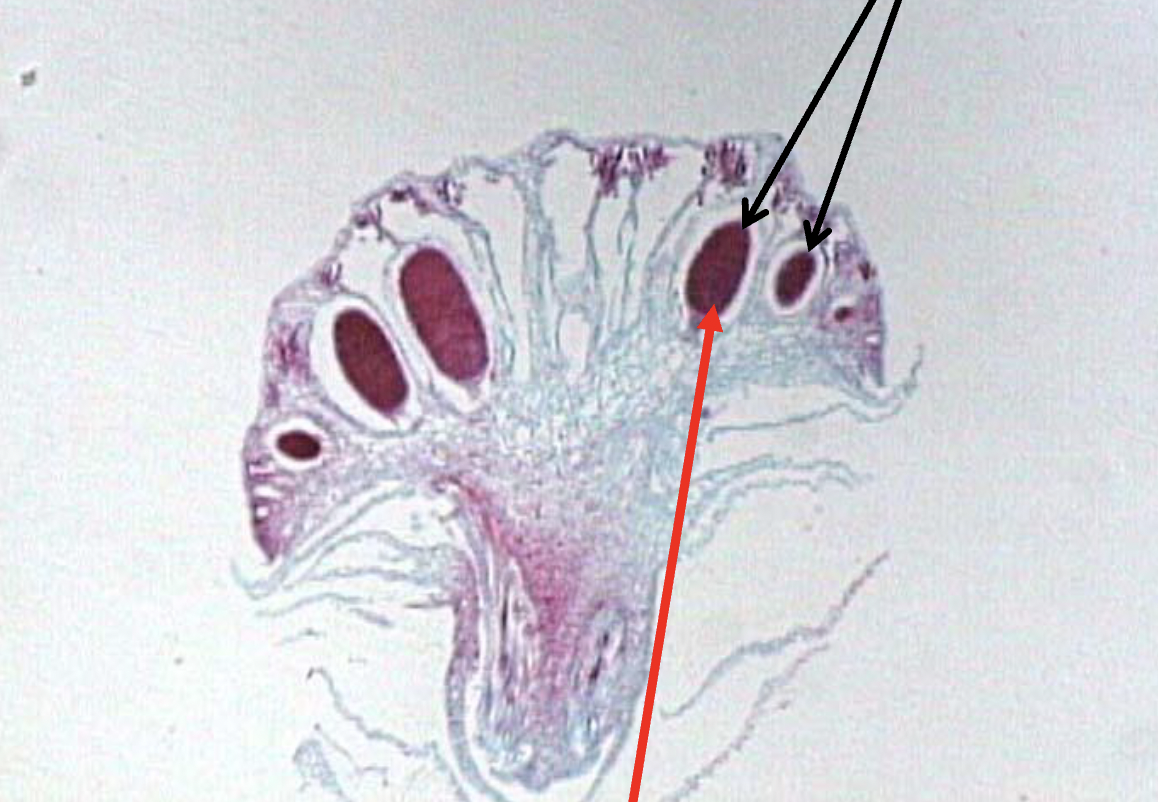
What is this?
Marchantia, Phylum Hepatophyta; antheridia
What are the characteristics of Phylum Anthocerophyta (hornworts)?
more closely related to the vascular plants compared to other bryophytes
What are lower tracheophytes?
vascular, spore-bearing; better adapted to land (still need water to grow), have vascular tissue, sporophyte dominant life cycle, homosporous, many have true roots, stems or leaves
What does homosporous mean in terms of lower tracheophytes?
produce a bisexual gametophyte that forms egg and sperm
What phylums are included in lower tracheophytes?
Phylum Lycophyta and Phylum Monilophyta
What are the characteristics of Phylum Lycophyta (Club Moss or Ground Pine)?
have true leaves, gametophyte is dependant on a symbiotic fungi (lives separately from sporophyte), some can be epiphytic, has rhizome, flagellated sperm
What does epiphytic mean?
grows on another plant
What is a rhizome?
horizontal stem
What are the characteristics of Phylum Monilophyta (Ferns)?
have true roots, stems, and leaves (rhizomes, fronds, fiddle-heads); have sori; gametes on the same plant usually mature at different times to reduce self-fertilization (sperm swims away while egg develops)
What are fronds?
on ferns, the actual long leaf
What are fiddle-heads?
baby ferns
What is a sori?
structures that produce spores on the undersides of the fronds
What are the characteristics of Phylum Monilophyta (Horsetails)?
belong to the genus Epuisetum; silica in cell walls, have roots stems and small leaves, have flagellated sperm and free-living gametophyte
What are the characteristics of Phylum Monilophyta (Whisk Ferns)?
lack true roots and leaves; appear like a green stem with yellow bulbs
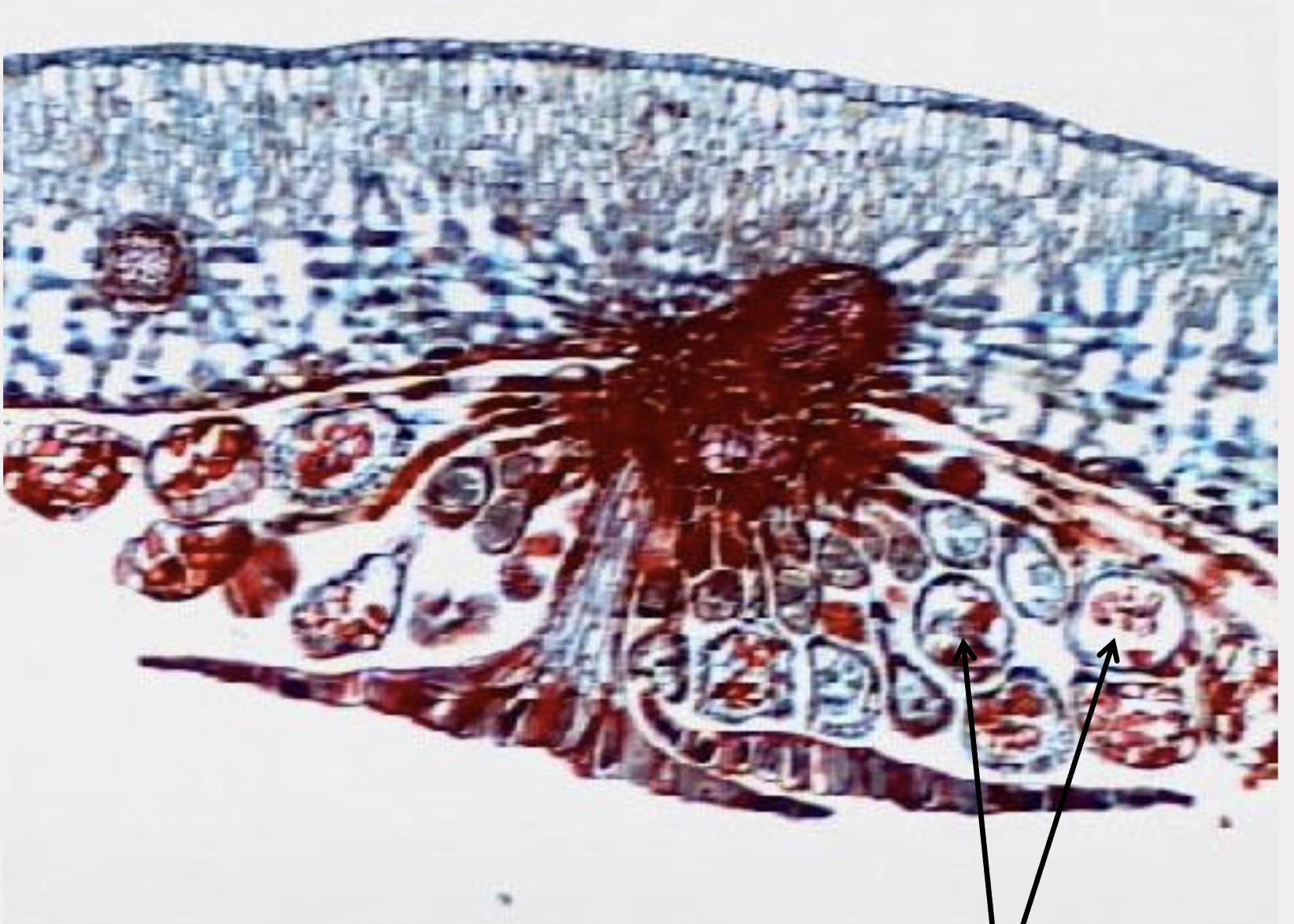
What is this?
Fern Sori; Phylum Monilophyta
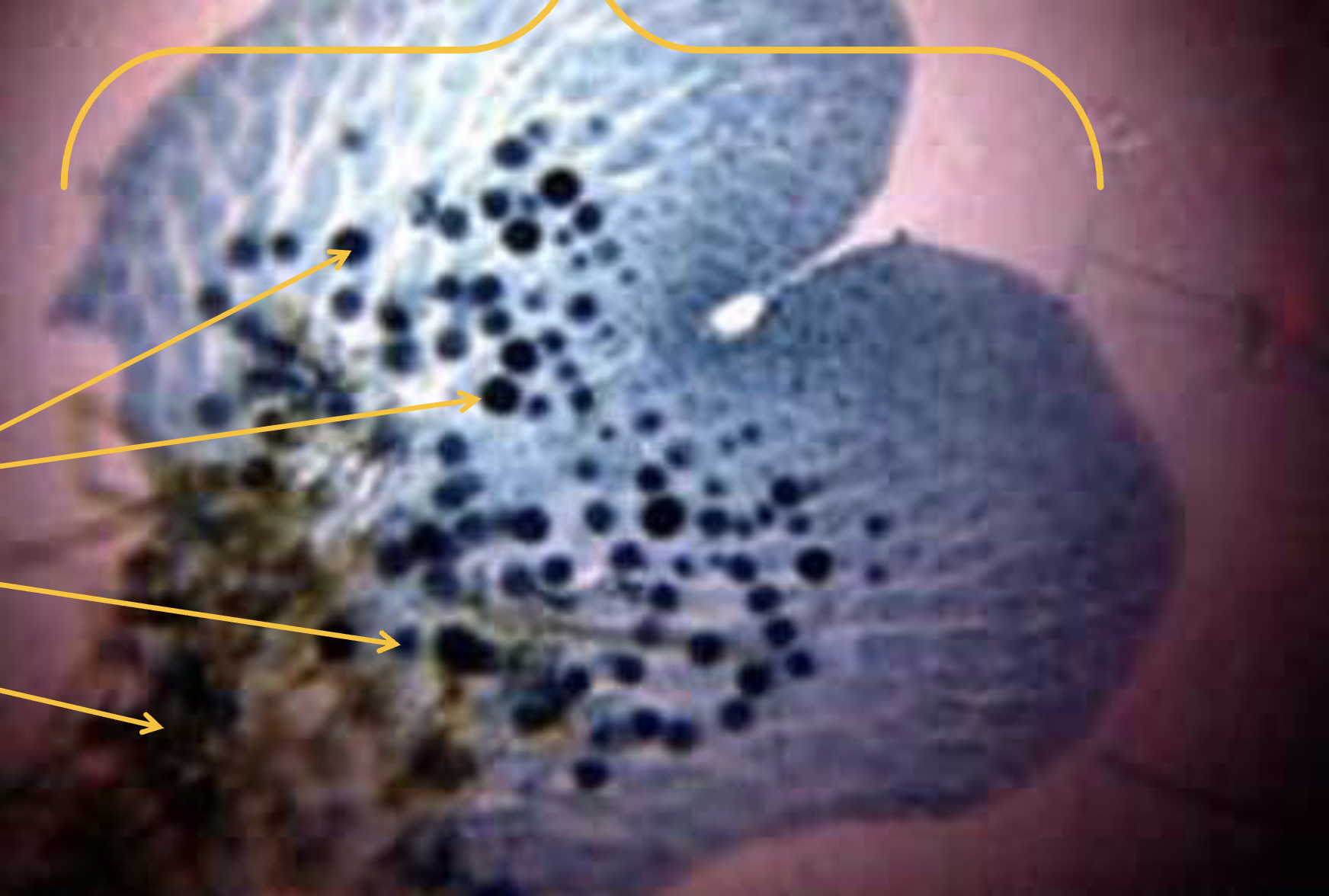
What is this?
Prothallus (gametohyte); archegonia and antheridia are black dots; Phylum Monilophyta
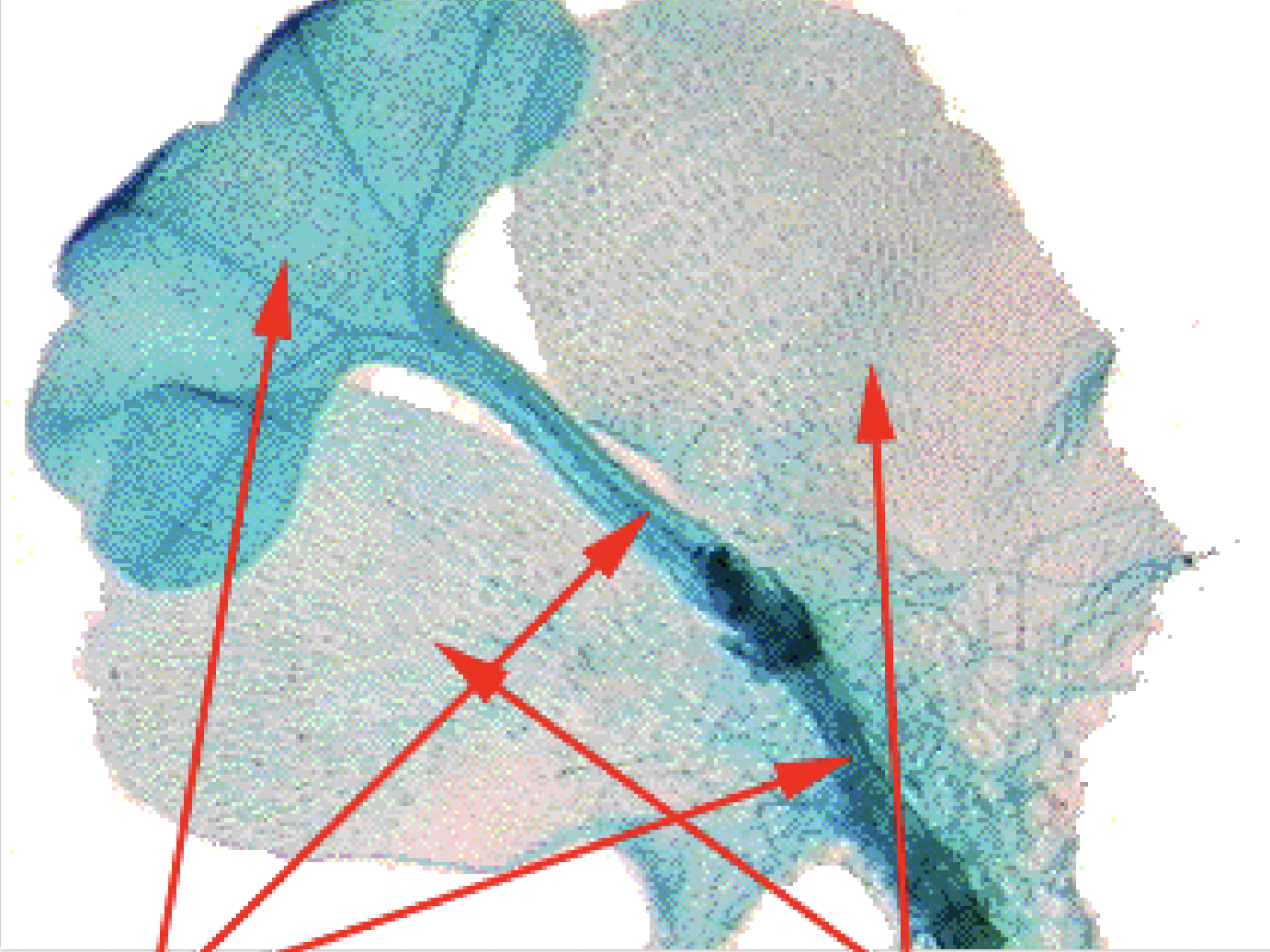
What is this?
Fern Young Sporophyte; dark is sporophyte and light is gametophyte; Phylum Monilophyta
What are the characteristics of Higher Tracheophytes?
vascular, seed-bearing; highly adapted to land, lignin in secondary cell walls, have vascular tissue (tracheids in xylem), sporophyte dominant life cycle (gametophyte is reduced, non-photosynthetic, and inside sporophyte), true roots, stems, and leaves, megaspores and microspores
What are tracheids?
in xylem; “helper cells” for xylem
What are megaspores and microspores?
spores; eggs and pollen/sperm for Higher Tracheophytes
What are gymnosperms?
“naked seed”; female gametophyte is in ovulate cone, male gametophyte is inside the pollone pone, only has tracheids in xylem
What are angiosperms?
“flowering plants”; female gametophyte is in ovary of carpel, male gametophyte is in anther of stamen, have tracheids and vessel elements in xylem, double fertilization, some are carnivorous
What phylums are included in gymnosperms?
Phylum Coniferophyta, Phylum Cycadophyta, Phylum Ginkgophyta, and Phylum Gnetophyta
What are the characteristics of Phylum Coniferophyta (Conifers)?
includes pines, firs, cedars, and spruce trees; usually occur in cooler climates, bear cones with woody protective structures (female ovulate cone), leaves are modified into needles
What are the characteristics of Phylum Cycadophyta (Cycads)?
includes the Sago Palm; cycads resemble palms but are not palms (palm trees are angiosperms)
What are the characteristics of Phylum Ginkgophyta (Ginkgos)?
only one living species (Ginkgo biloba); deciduous leaves (shed leaves); extracts used as an herbal supplement to boost memory
What are the characteristics of Phylum Gnetophyta (Gnetophytes)?
includes the Mormon tea and Ephedra; genus Welwitschia has largest known leaves of any plant
What is the phylum name for angiosperms?
Phylum Anthophyta
What are the classes included in Phylum Anthophyta?
Class Monocotyledonae and Class Dicotyledonae
What are the characteristics of Class Monocotyledonae (Moncots)?
named for having one embryonic leaf (cotyledon) during development; includes CORN
What are the characteristics of Class Dicotyledonae (Dicots)?
named for having two cotyledons during development; includes non-woody dicots (sunflowers) and woody dicots (magnolia)
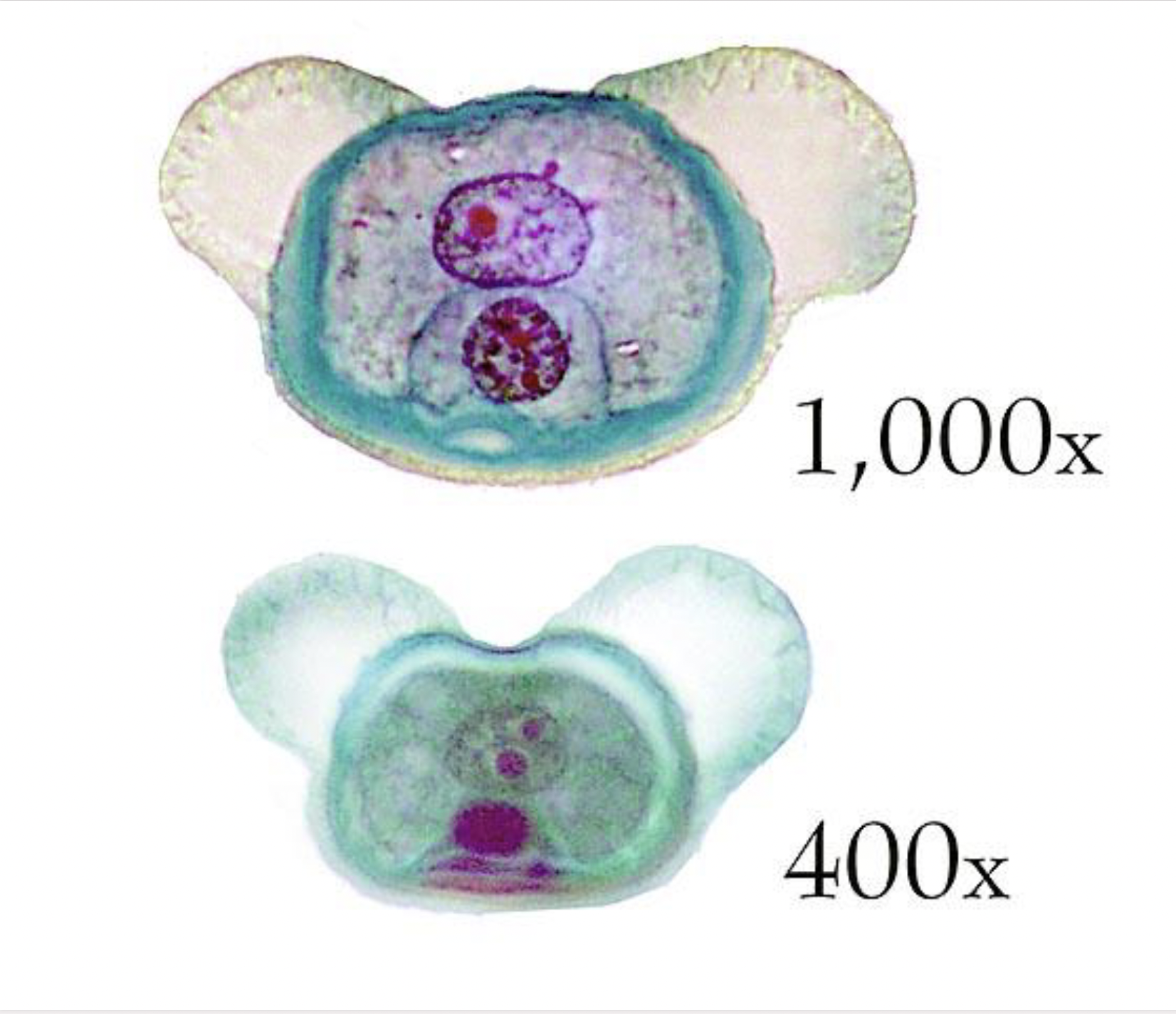
What is this?
Pine pollen; Phylum Coniferophyta
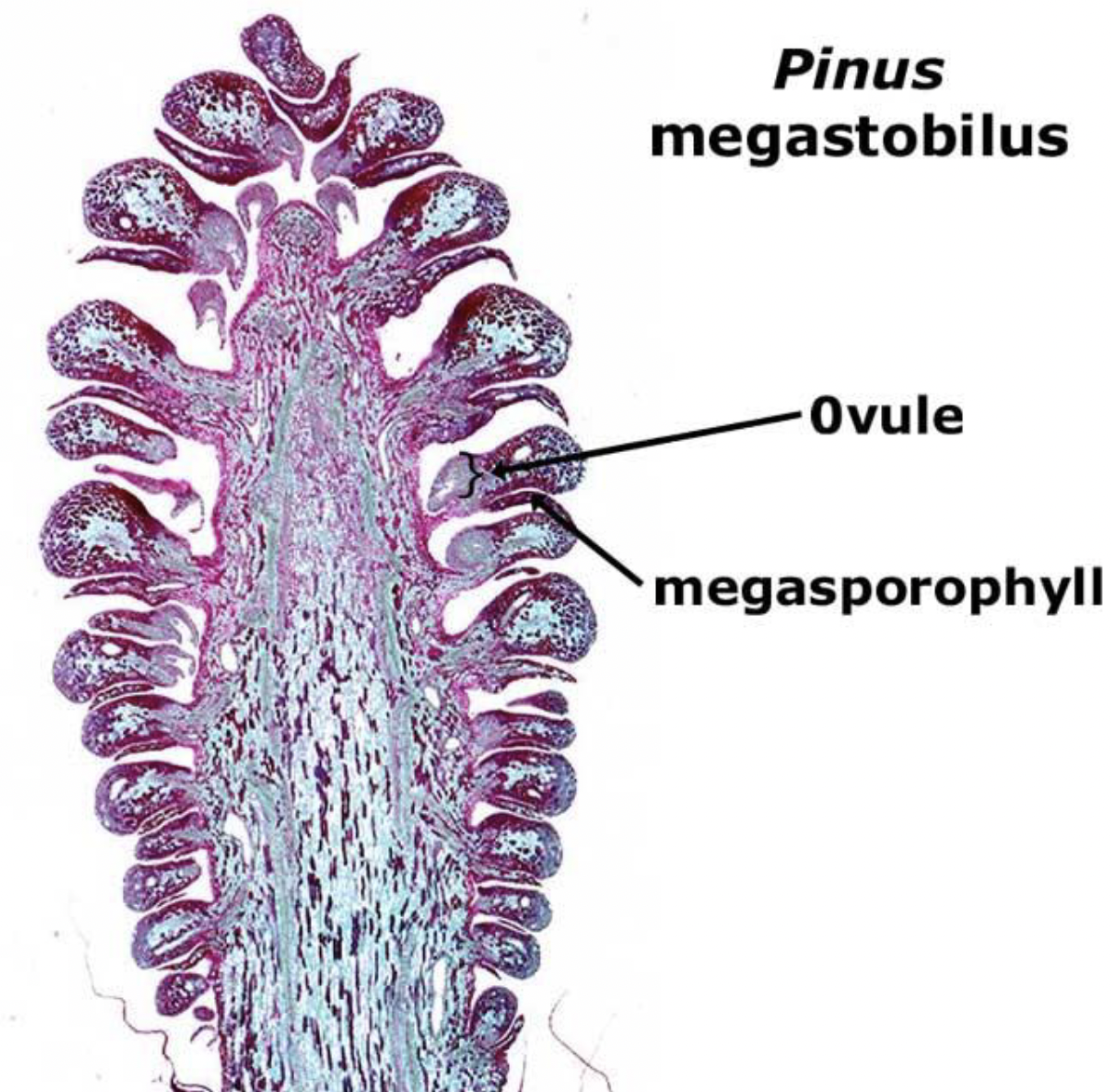
What is this?
Pine Ovulate Cone; Phylum Coniferophyta
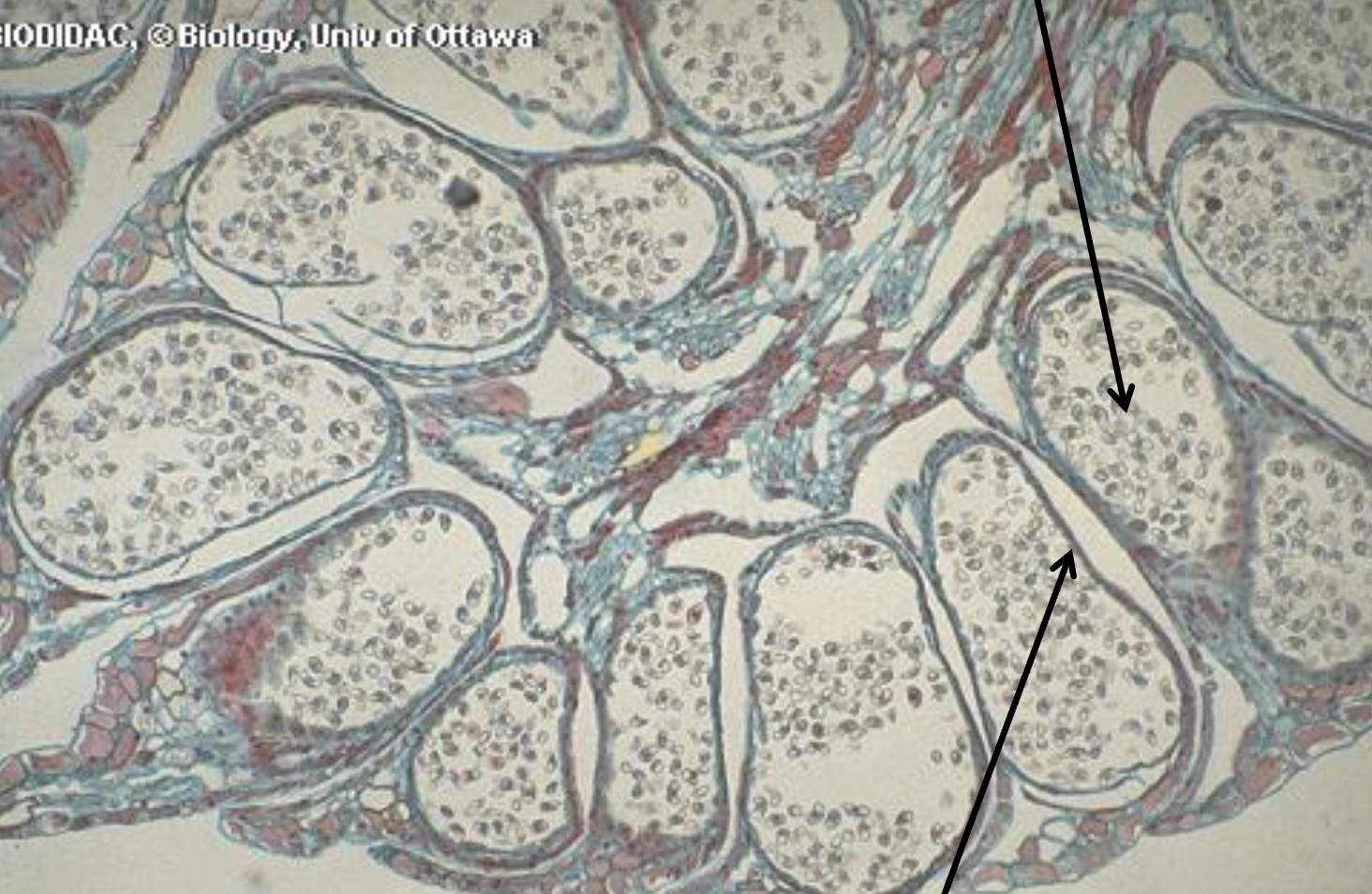
What is this?
Staminate Cone; Phylum Coniferophyta