Atomic Structure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Atom
Smallest part of an element
Compounds
Two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
Mixture
Consists of two or more elements or compounds that are not bonded together.
Are the chemical properties of each substance in the mixture changed?
No, they are unchanged
Mixtures can be separated by physical processes such as: 5
filtration
crystallisation
simple distillation
fractional distillation
chromatography
These physical processes do not involve chemical reactions and no new substances are made.
pure
a substance that consists of only one element or compound
what is filtration used for?
give an example
used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid.
e.g. separating sand and water or excess reactant from a reaction mixture.
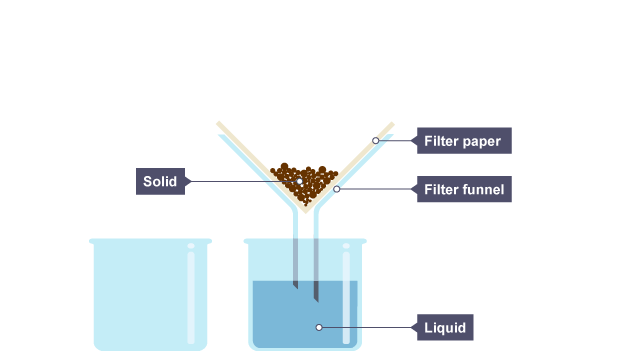
give the method for filtration (3) + draw diagram
Set up apparatus as shown
Pour the solid and liquid mixture into the filter funnel
the liquid drips through the filter paper but the solid particles are caught in the filter paper.
What is crystallisation used for?
give example
Used to produce solid crystals from a solution.
e.g. obtain copper sulfate crystals from copper sulfate solution.
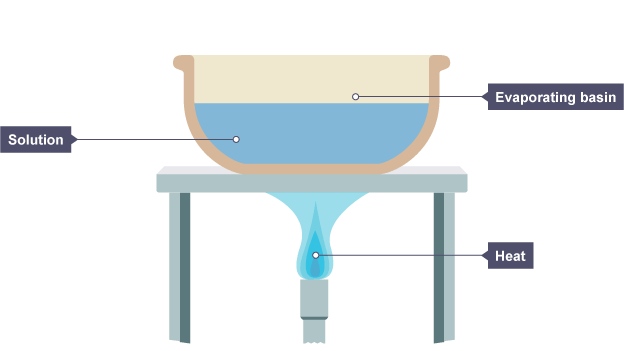
give the method for crystalisation(2) + draw diagram
Place the solution in an evaporating basin and gently heat it with a Bunsen burner.
remove the heat when insoluble crystals start to form.
what is simple distillation used for?
give an example
Used to separate solvent from a solution.
e.g. pure water from seawater
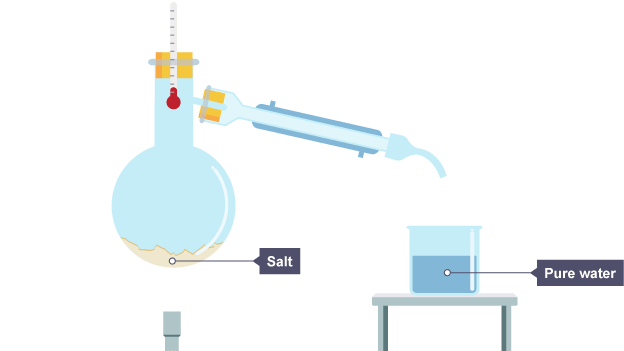
method and diagram for simple distillation
Salty water is heated
the water vapour cools in the condenser and drips into a beaker
The water has condensed and is now in the beaker, the salt stays behind
What is fractional distillation used for?
give example
Used to separate different liquids from a mixture of liquids.
e.g. separating different fractions from crude oil
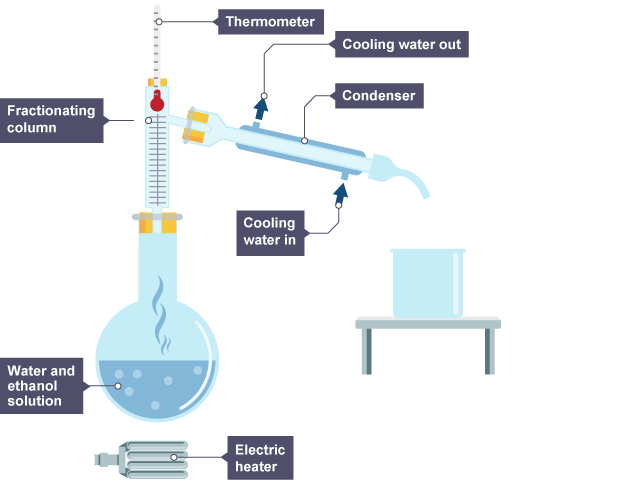
method for fractional distillation + draw labelled diagram
Vapours rise through a column which is hot at the bottom, and cooler at the top.
Vapours condense when they reach a part of the column that is below the temperature of their boiling point.
each liquid is led away from their column
Write the chronological order of the discoveries of the model of atoms over time.
Dalton - tiny indivisible spheres
Discovery of the electron led to the plum pudding model of the atom - ball of positive charge with electrons in it - JJ - Thompson.
Results from the gold foil experiment led to the conclusion that mass of an atom was concentrated in the centre and that it was positively charged. - Geiger, Marsden, Rutherford
Niels Bohr then adapted the nuclear model by suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances.
Later experiments led to the idea that the positive charge of the nucleus could be subdivided into smaller particles, called the proton.
James Chadwick provided evidence to show the existence of neutrons within the nucleus, 20 years after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea.
radius of an atom
0.1nm (1 ×10^-10m)
radius of the nucleus
less than 1/10,000 of the atom itself (about 1×10^-14m)
relative atomic mass
The average mass of the isotopes of the atom relative to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
relative isotopic mass
mass of an isotope relative to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
relative molecular mass
The average mass of a molecule relative to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom.
List the name of the processes in the Mass Spectrometer
Ionisation
Acceleration
Ion Drift
Detection
Describe the two ways to ionise substances before they go in the mass spectrometer
Electrospray Ionisation - The sample is dissolved in a solvent and pushed through a small nozzle at high pressure. A high voltage is applied to it, causing each particle to gain a H+ ion. The solvent is removed, leaving a gas of positive ions.
Electron impact ionisation - The same is vapourised and an ‘electron gun’ is used to fire high energy electrons at it. This knocks one electron off each particle so they become +1 ions.
Explain what happens in stages Acceleration and Ion drift.
The positive ions are accelerated by an electric field. All ions have the same kinetic energy. Lighter ions accelerate more.
How does the ion detector use the data to calculate the mass/charge values needed to produce a mass spectrum
it detects the current created when the ions hit it
records how long they took to pass through the spectrometer.
How to calculate the relative atomic mass using mass spectra
Y-axis shows the percentage abundance of each isotope
X-axis shows the mass number of each isotope
Use these values to calculate the relative atomic mass in the usual way.
mass/ charge ratio
mass number of an atom/ molecule
3 rules for electron configurations
Electrons fill up the lowest sub-shells first. (4s is below 3d and so it fills up first.)
Electrons fill up orbitals in a sub-shell singly before they start sharing.
For the configurations of ions, just add or remove electrons from the highest energy occupied sub-shell.
Factors effecting ionisation energy
Nuclear charge
Shielding
Distance from the nucleus
Define first ionisation energy
The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove 1 electron atom each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions.
Draw the graph of the ionisation trend of period 3
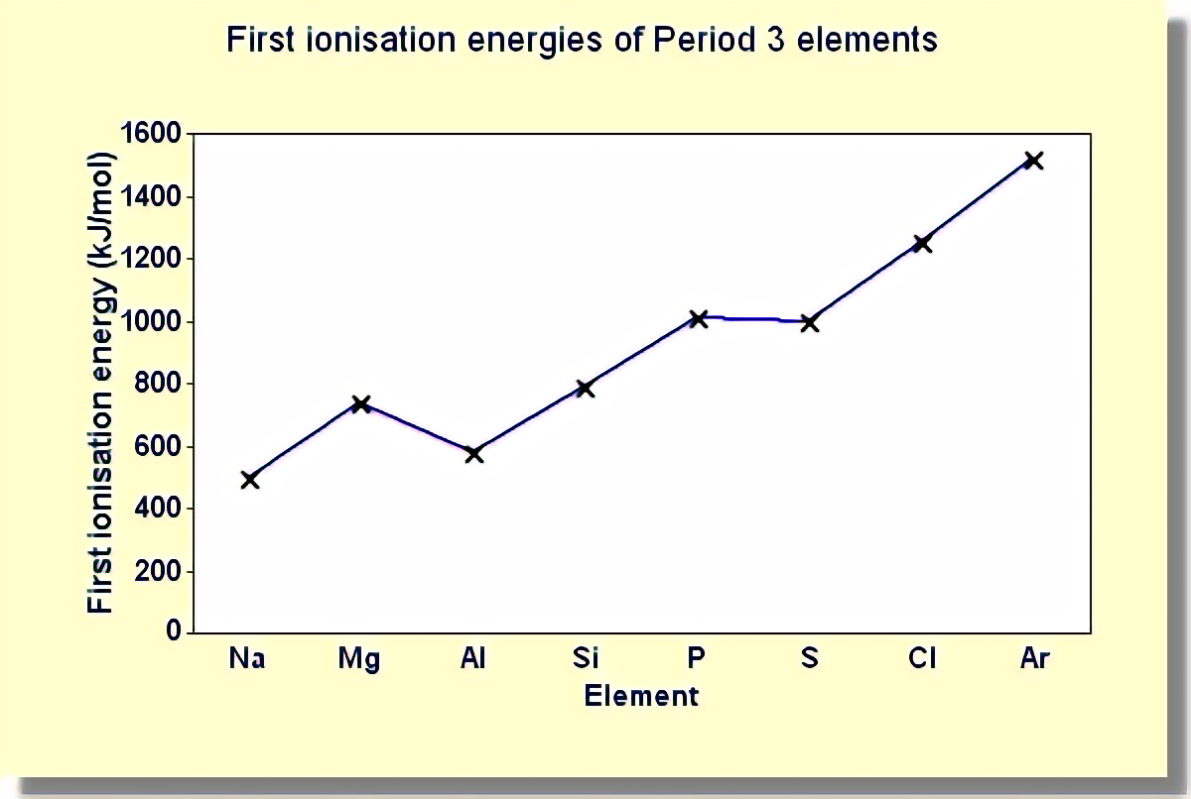
Explain the dip at group 3
Aluminium’s outer electron is in a 3p orbital rather than a 3s. 3p orbitals have slightly more energy than the 3s orbital, so the electron is, on average, to be found further from the nucleus.
The 3p orbital has additional shielding provided by the 3s electrons
These two factors together are strong enough to override the effect of the increased nuclear charge, resulting in the ionisation energy dropping slightly.
Explain the dip at 6
electron pair repulsion
Explain the difference between relative molecular mass and relative formula mass.
Relative molecular mass refers to the mass of a molecule determined by the total of the atomic masses of its constituent atoms, whereas relative formula mass applies to ionic compounds AND giant covalents based on the formula unit.
Explain how a mass spectrum can be used to determine relative molecular mass.
A molecular ion, M+ is formed in the mass spectrometer when one electron is removed from the molecule.
This gives a peak in the spectrum with a mass/charge ratio equal to the relative molecular mass of the molecule.
This can then be used to identify an unknown compound.