MD 1 FORMULAS
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
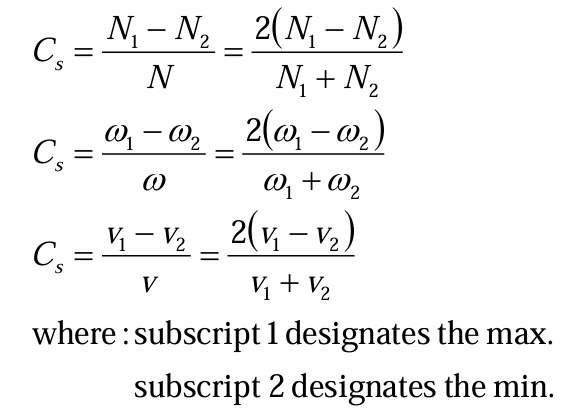
coefficient of fluctuation of speed or Cs
ultimate strength
Su = Force per stroke/A = Force per stroke/pi*d*t
energy per stroke
energy per stroke = ½ * force per stroke * plate thickness
energy per min
energy per min = energy per stroke * stroke per min
Power
Energy per min/nm
coefficient of steadiness
1/Cs
coefficient of fluctuation of energy or CE

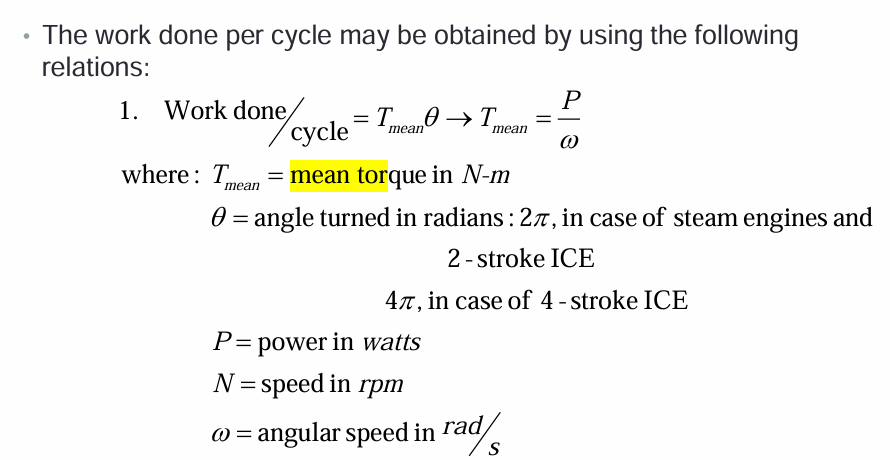
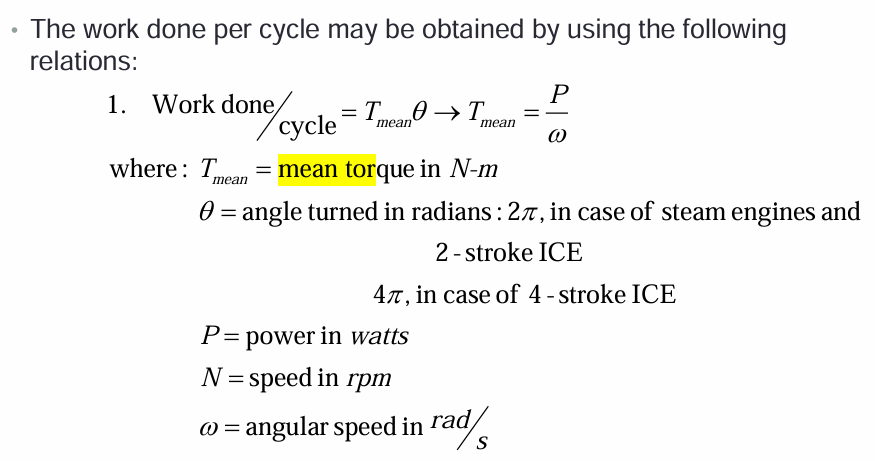
Work done per cycle using torque

mean torque
Work done per cycle using power
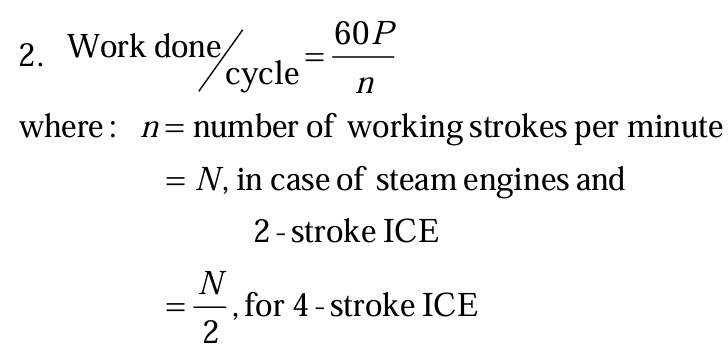
value of θ or angle turned if steam engine or 2-stroke
value of θ or angle turned if 4-stroke

value of n or number of working strokes if steam engine or 2-stroke
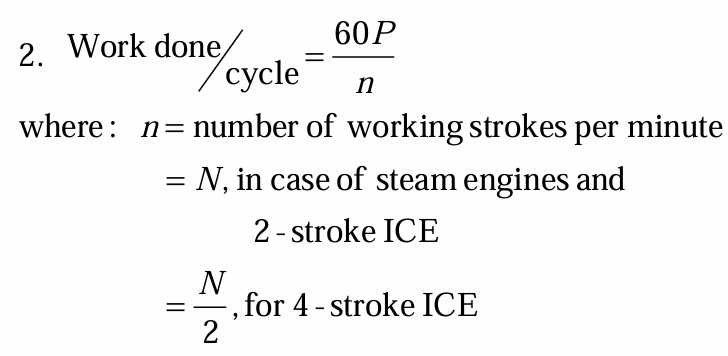
value of n or number of working strokes if 4-stroke
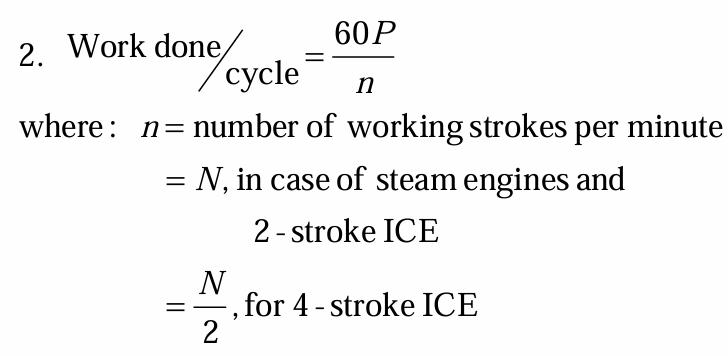
mean kinetic energy of the flywheel or KE

moment of inertia or I

change in kinetic energy or delta KE
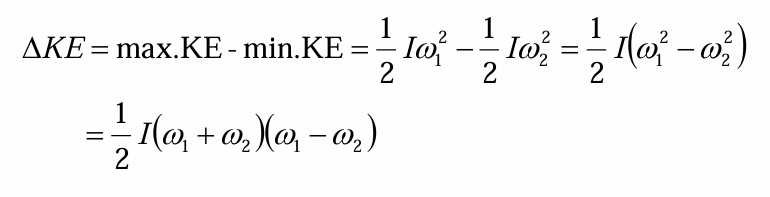
mean angular speed or omega
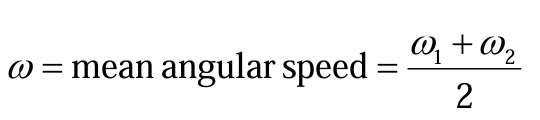
mass of flywheel
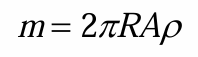
different delta KE formulas
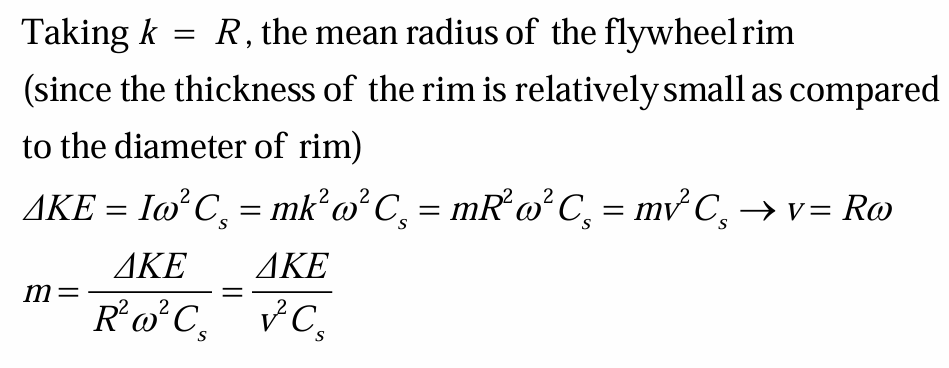
tensile stress in flywheel
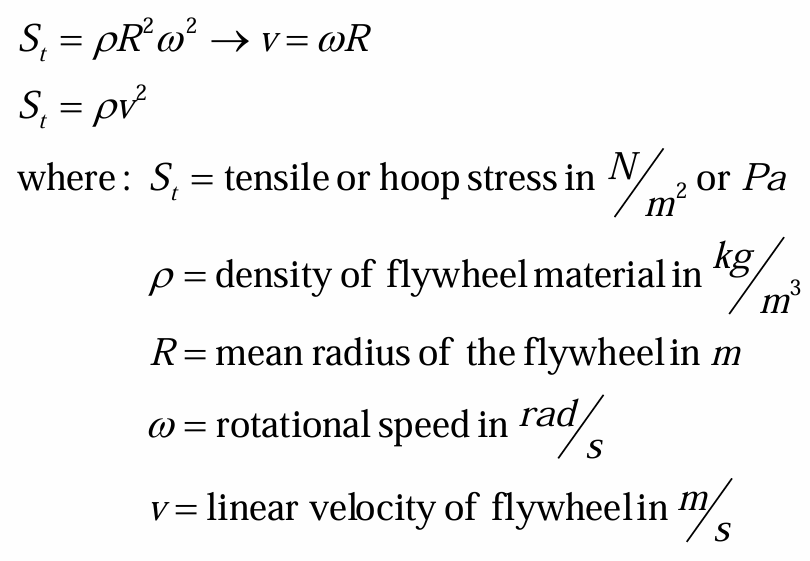
tensile bending stress in flywheel
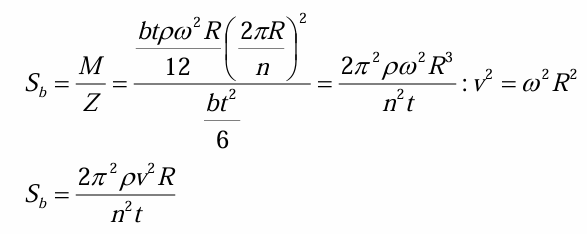
length between fixed ends in bending flywheel
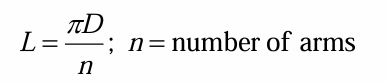
total stress in the rim

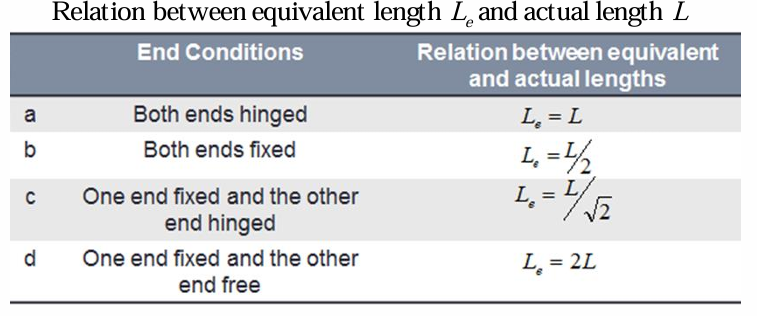
relation between equivalent length and actual length of both ends hinged
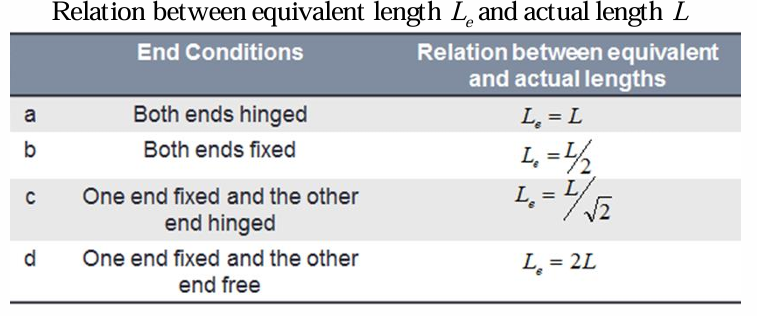
relation between equivalent length and actual length of both ends fixed
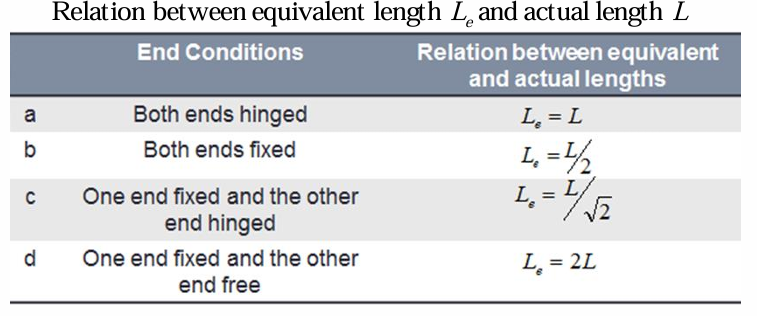
relation between equivalent length and actual length of one end fixed and the other end hinged
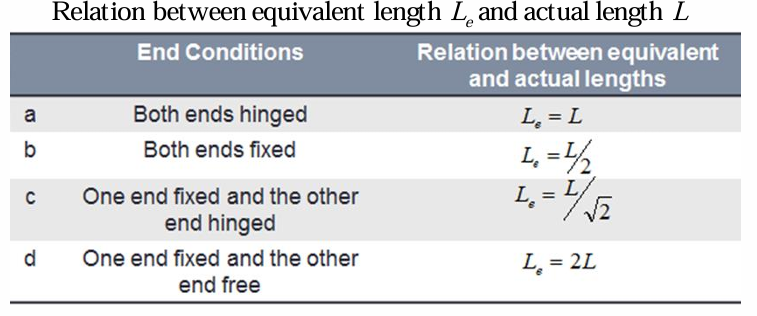
relation between equivalent length and actual length of one end fixed and the other free
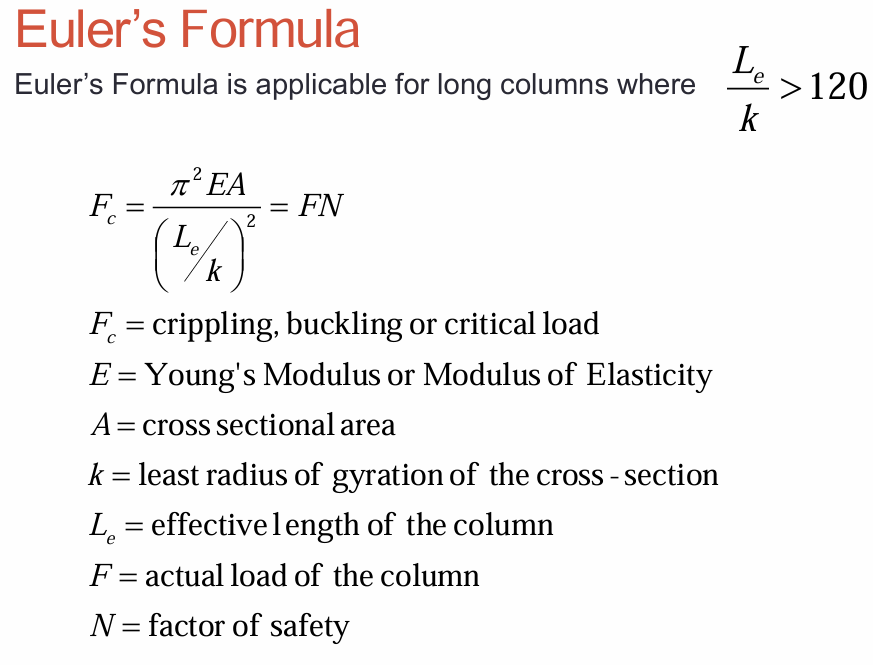
slenderness ratio

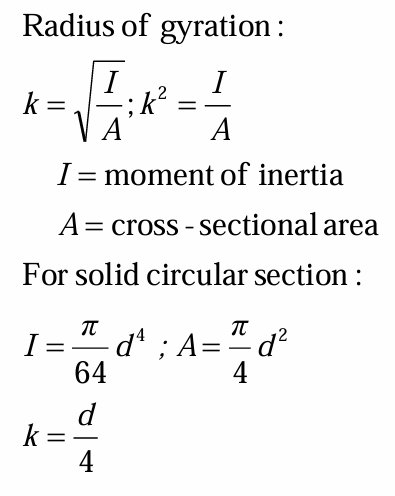
radius of gyration
Euler's formula
Johnson's formula
stresses for short compression members
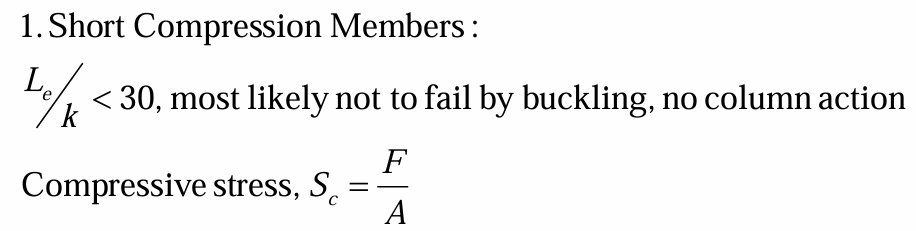
stresses for long and slender columns
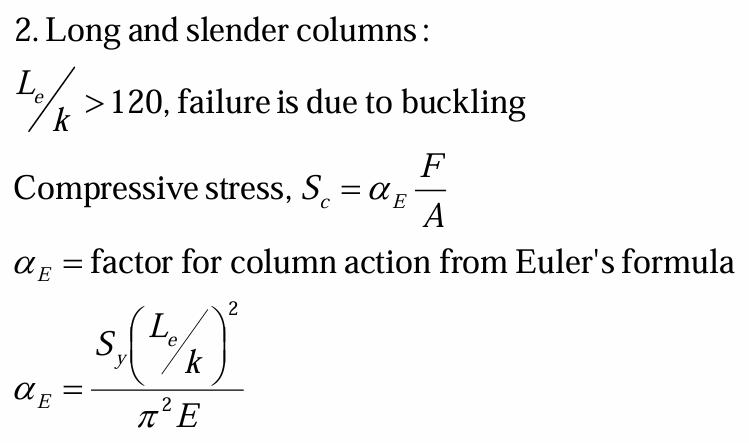
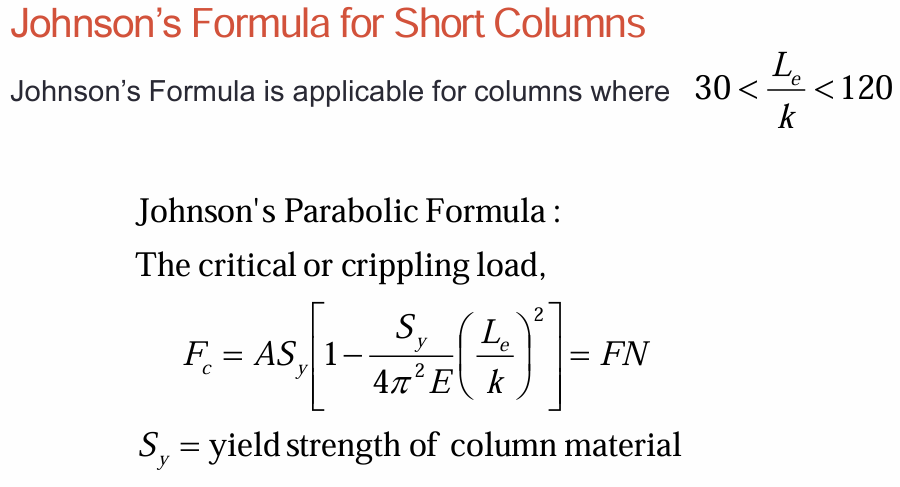
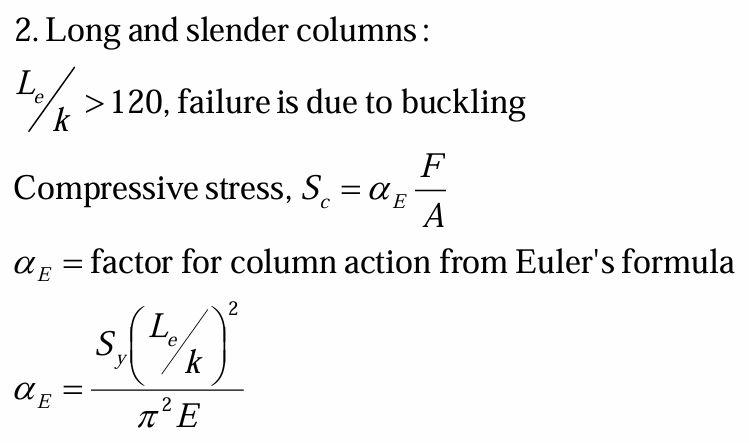
stresses for short columns

factor for column action from euler's formula
factor for column action from johnson's formula

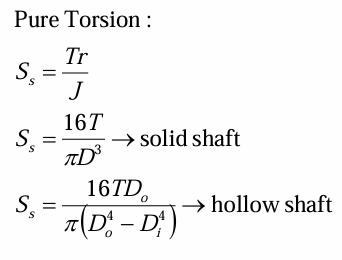
pure torsion stress in shaft
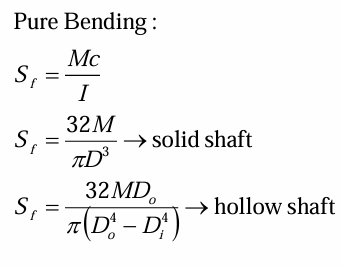
pure bending stress in shaft
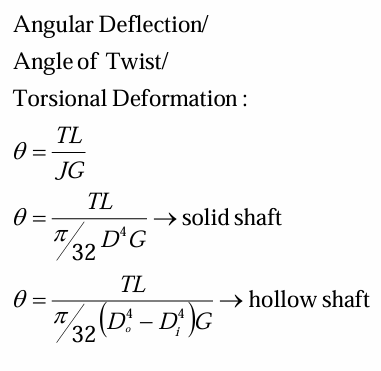
angular deflection/angle of twist/torsional deformation in shaft
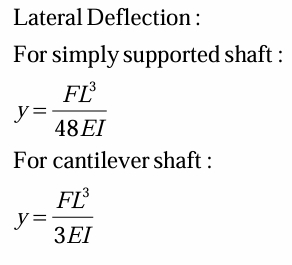
lateral deflection for simply supported shaft
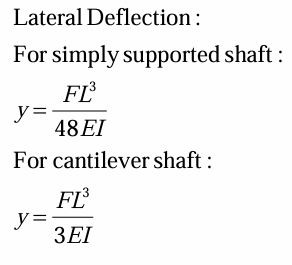
lateral deflection for cantilever shaft
yield strength and ultimate strength for shear design stress of ASME

yield strength and ultimate strength for normal design stress of ASME

design stress with keyway of ASME

equivalent twisting moment
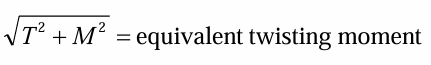
equivalent bending moment
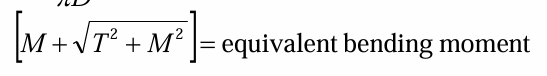
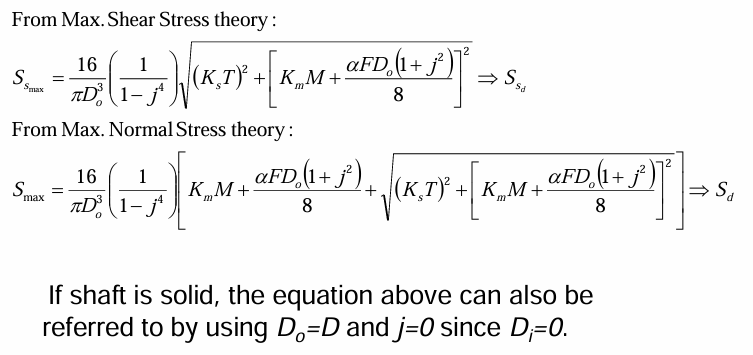
max shear stress thery for combined loads in ASME
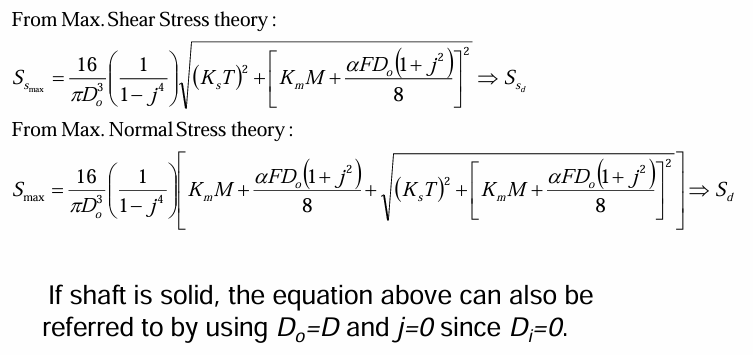
max normal stress theory for combined loads in ASME
power of main power transmitting shaft by ASME

power of line shaft carrying pulleys by ASME

power of small,short, and counter shafts by ASME

tangential force of key
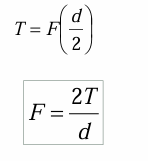
shearing stress in key

compressive or crushing stress of key

free length of spring
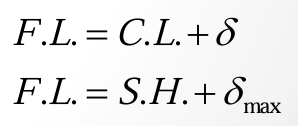
Mean Diameter
Dm = Do - Dw
axial load to axial deformation ratio for max value
Fmax/F=δmax/δ
spring index
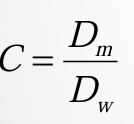
spring rate
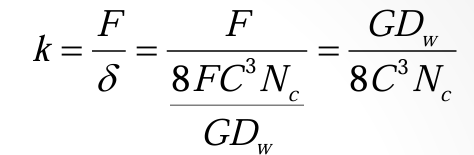
direct shear stress
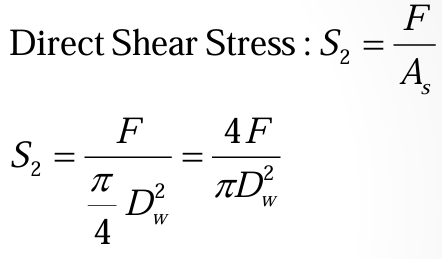
torsional stress in wire

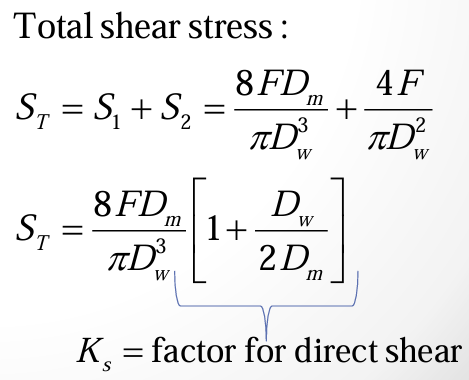
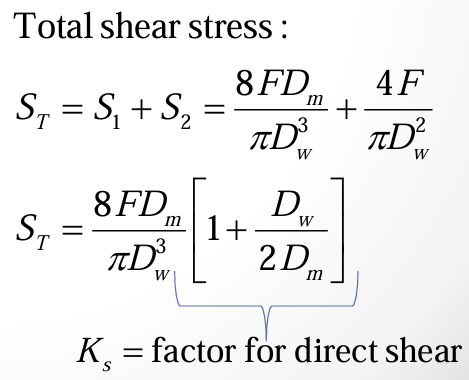
total shear stress in spring
factor for direct shear
max shear stress
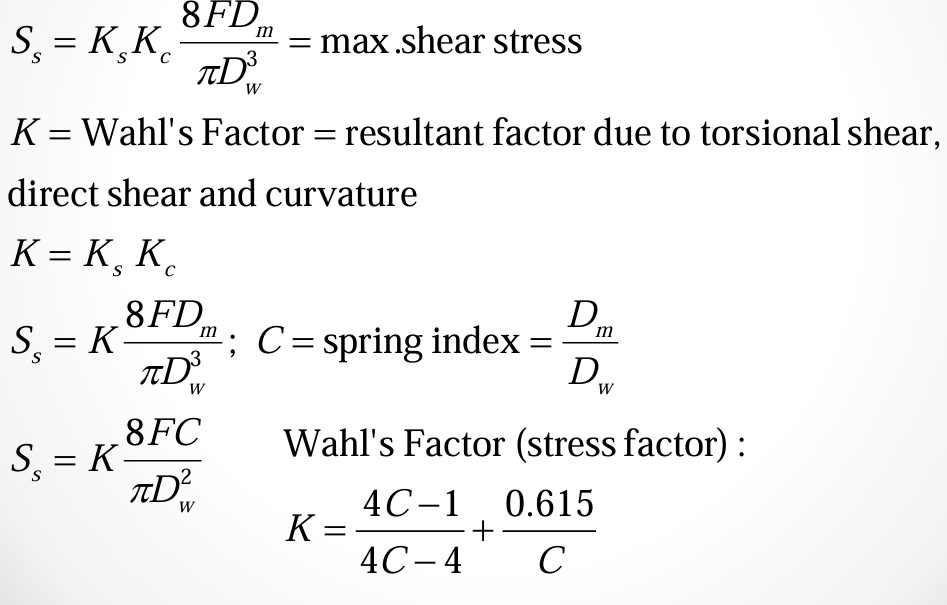
wahl's factor
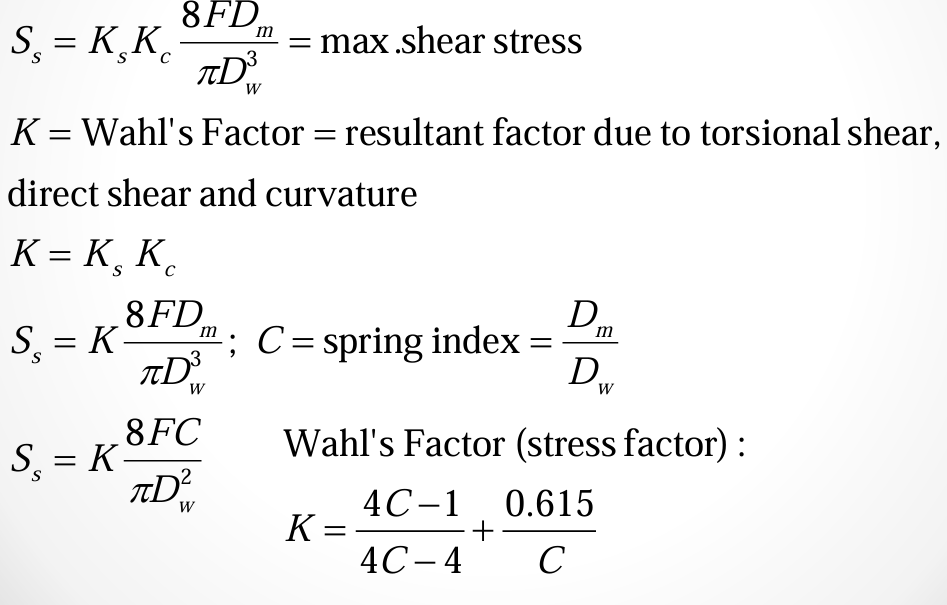
free length, total no. of coils, solid height of plain end
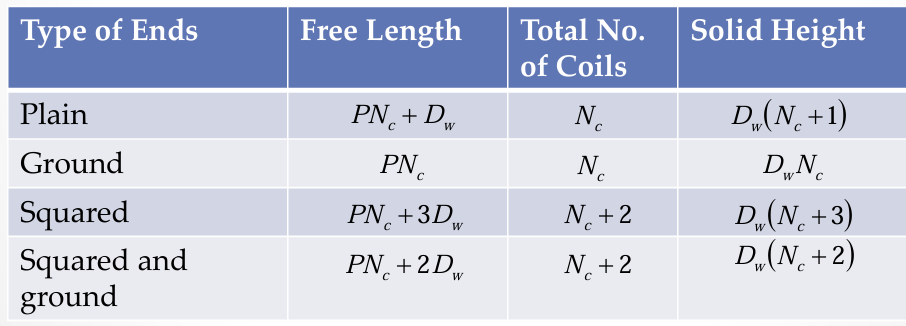
free length, total no. of coils, solid height of ground end
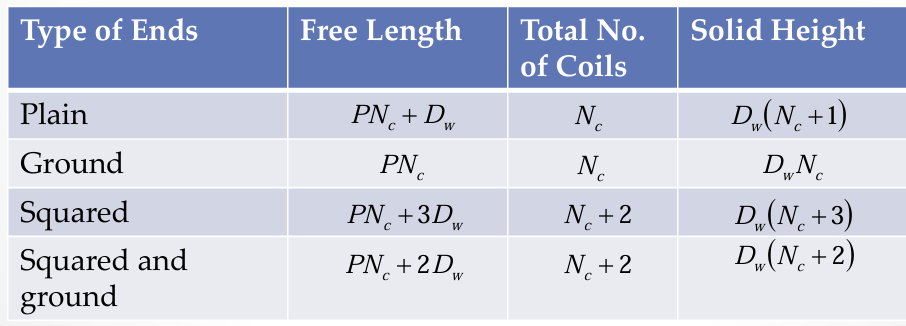
free length, total no. of coils, solid height of squared end
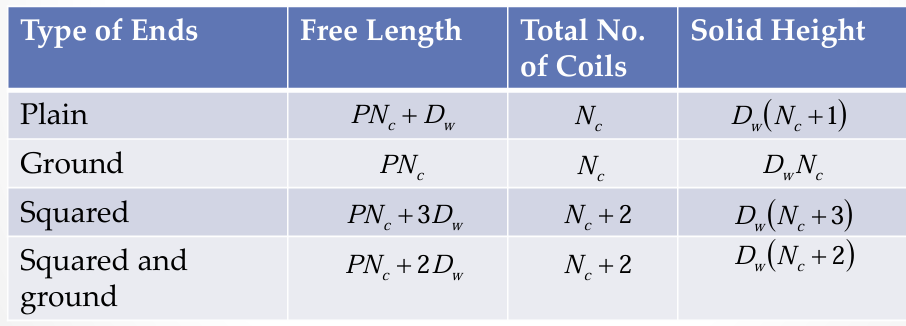
free length, total no. of coils, solid height of squared and ground end
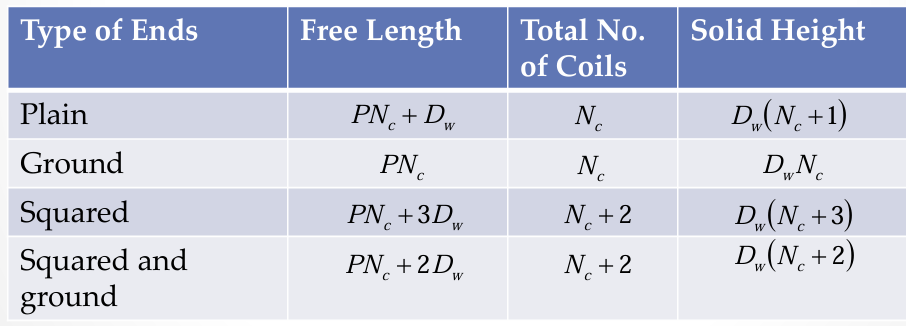
length of one coil
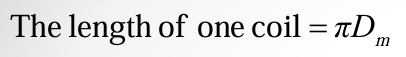
total active length of wire
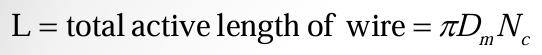
axial deflection of spring
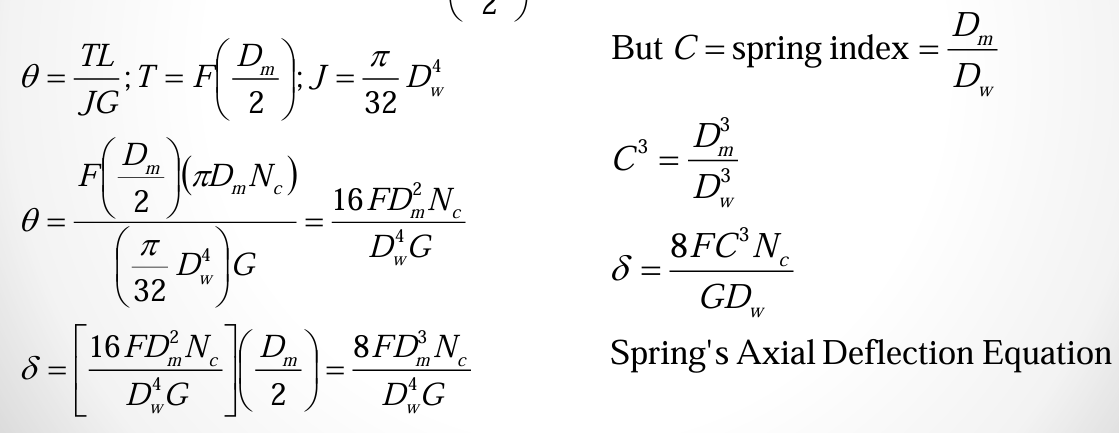
pitch angle of spring
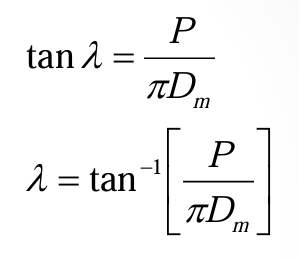
spring rate of 2 springs of same materials
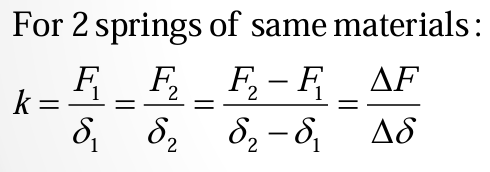
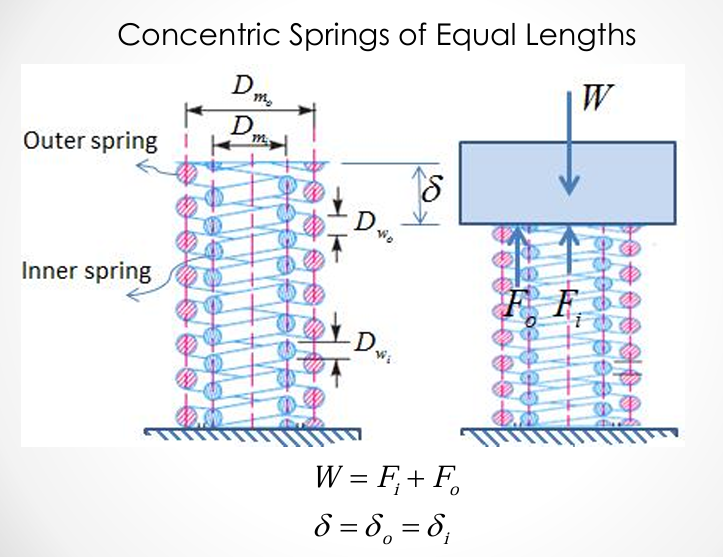
springs in parallel: concentric springs of equal lengths
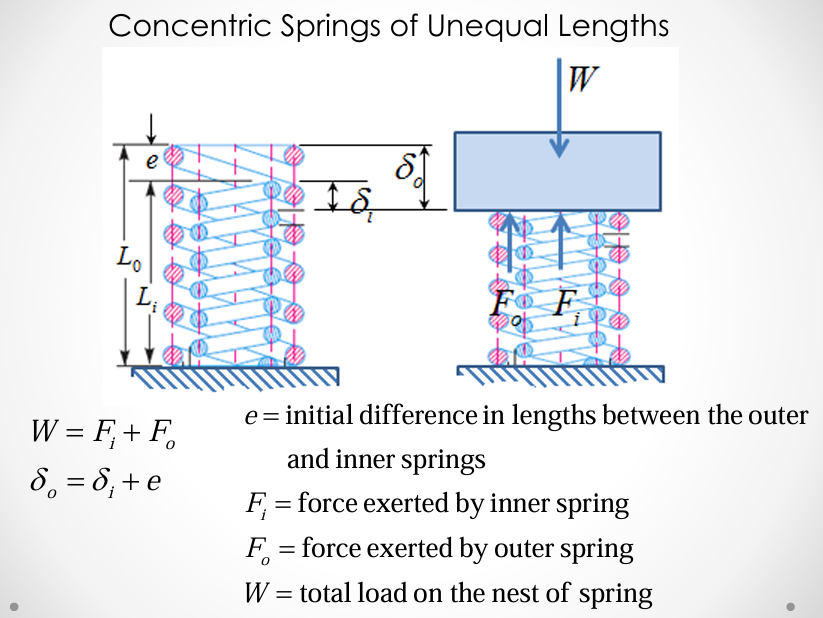
springs in parallel: concentric springs of unequal lengths
non-concentric parallel springs
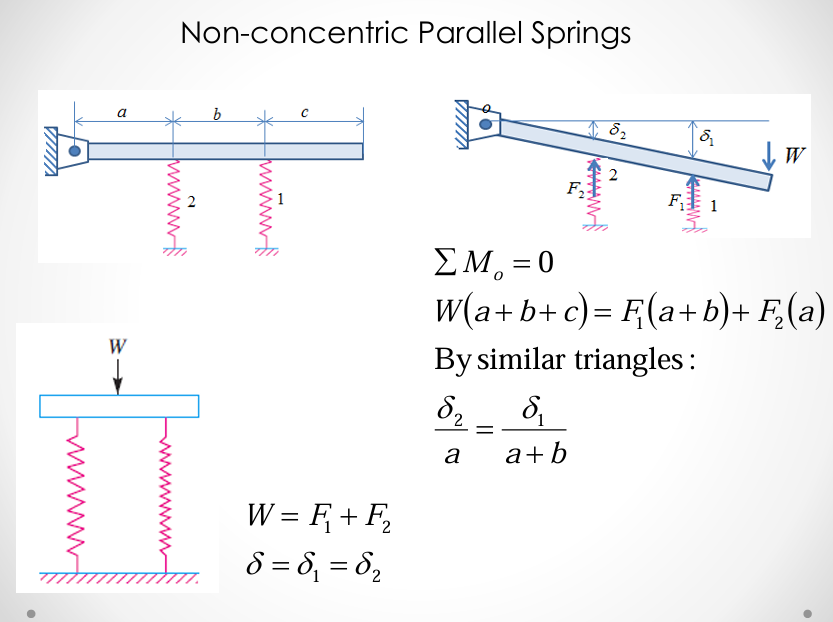
springs in series
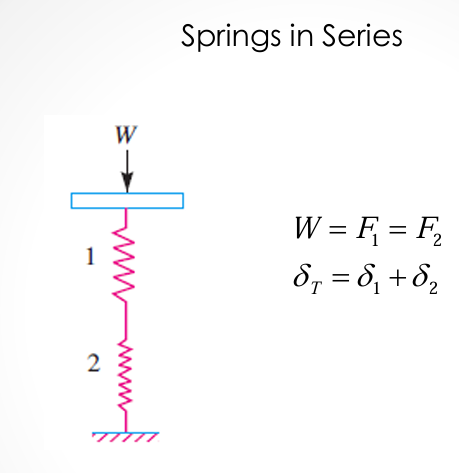
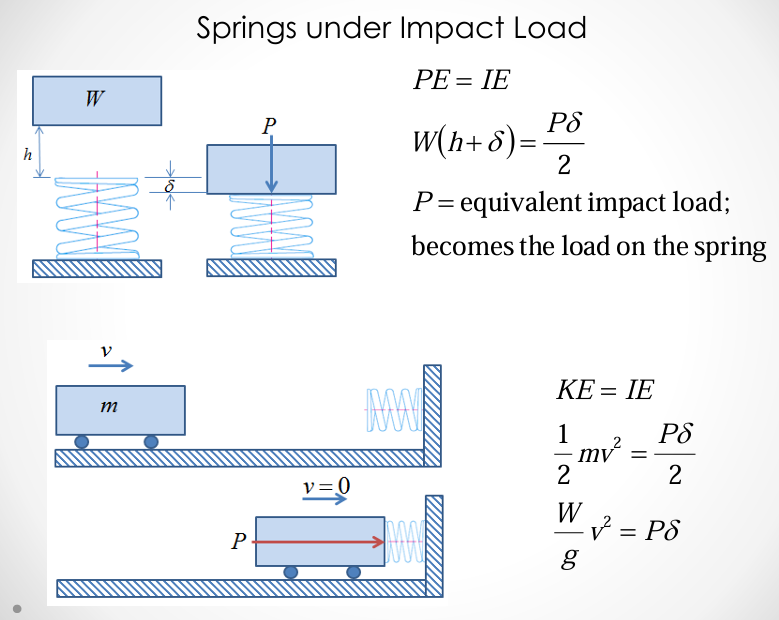
springs under impact load: potential
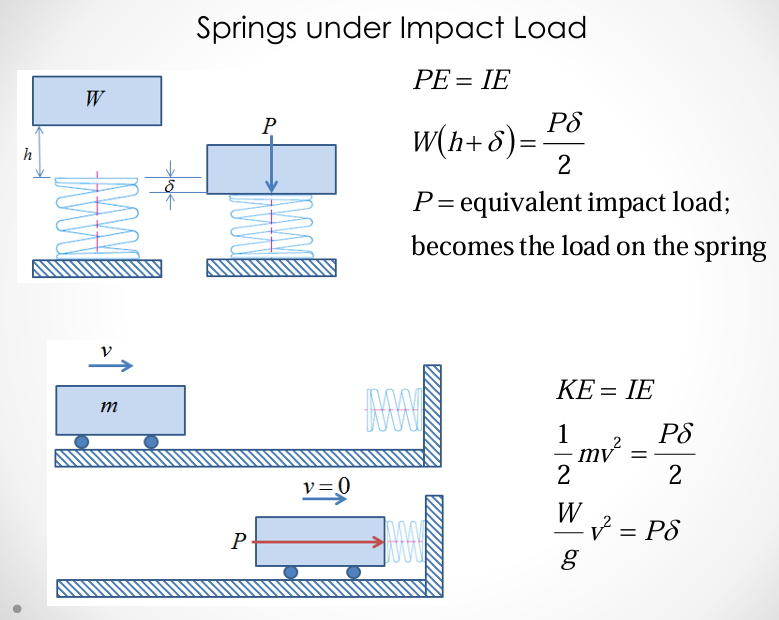
springs under impact load: kinetic
pitch
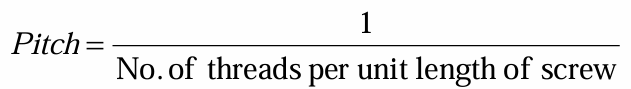
Expand tan(β+λ)
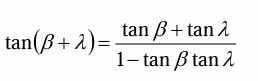
angular speed of screw or Nscrew
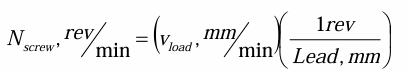
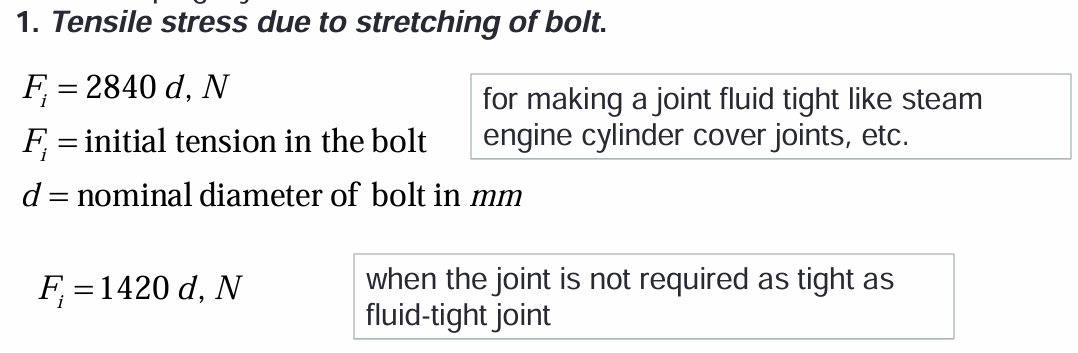
tensile stress due to stretching of bolt
maximum safe axial load for initial tensile stress
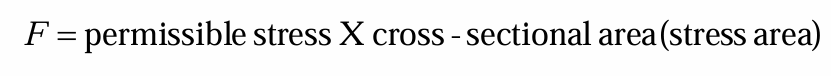
stress area for initial tensile stress

torsional shear stress caused by the frictional resistance of the threads during its tightening
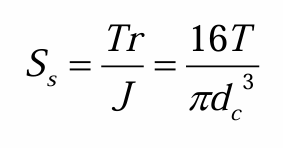
shear stress across the threads

compression or crushing stress on threads
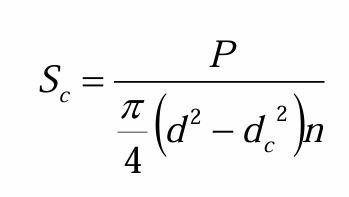
external tensile stress
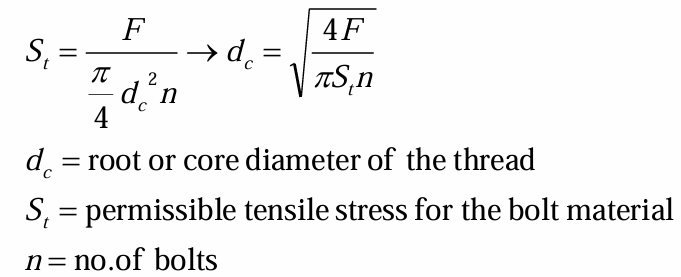
external shear stress
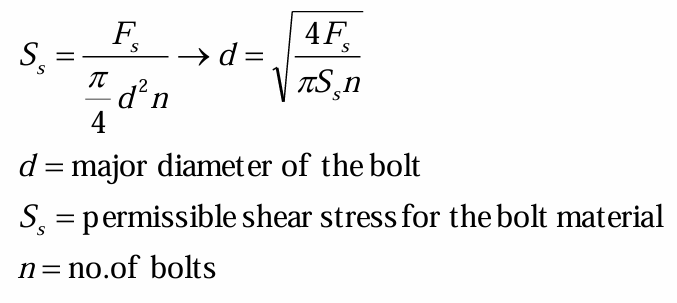
external combined tension and shear
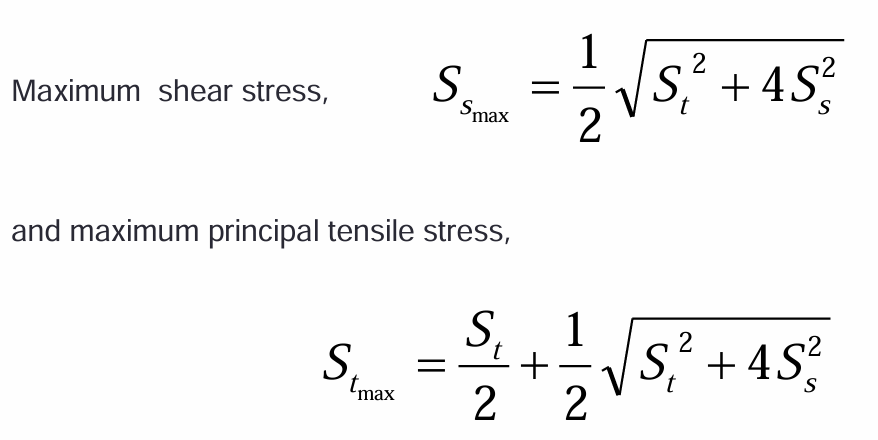
tooth depth
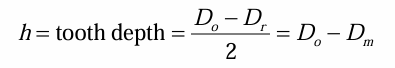
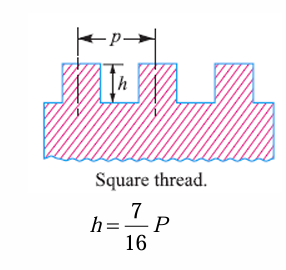
tooth depth for square
tooth depth for acme
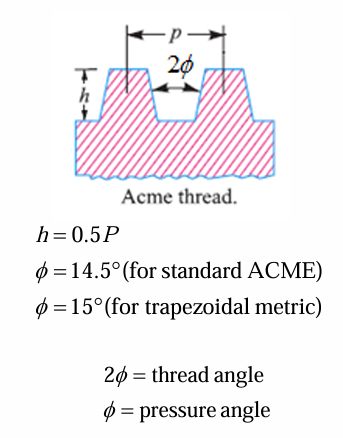
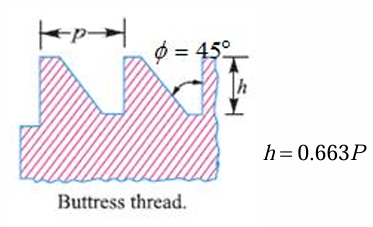
tooth depth for buttress
pressure angle for acme, square, trapezoidal metric
14.5,0,15
lead angle
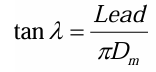
lead of single threaded, double threaded, and triple threaded screws
