Theory of Evolution - Honors Biology 9
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
mutation
a change in an organisms coding region of DNa leading to a new allele
somatic mutation vs germline mutation
somatic is developed after conception, to cells other than sperm and egg. germline is inherited for the egg and sperm during conception
natural selection and adaptations
when an allele makes an organism able to survive and reproduce in a given environment. adaptations help certain organisms survive and reproduce increasing allele frequency
gene flow
the gain or loss of alleles from a population by the movement of individuals or gametes into or out of an established population
immigration
to join or enter an area
emigration
to exit an area
migration
both enter and exit a population
genetic drift
the population variation decreases due to chance, changing the allele frequency of the gene pool
Founder Effect (Genetic Drift)
a decrease in genetic variation caused by the formation of a new population by a (random) small number of individuals from a larger population
Bottleneck Effect (Genetic Drift)
a change in allele frequencies of a new population caused by a sudden decrease in population size due to a random event - usually a natural disaster (not due to fitness or lack of an adaptation)
Non-Random Mating (Sexual Selection)
the selection of mates other than by chance/convenience. Females choose their mates so males have to compete.
5 conditions of natural selection
Must be variation
Must be competition
Some organisms will survive the competition and some won’t
Some organisms will reproduce and some will not (aren’t long enough or nobody chooses to mate with them)
Those that survive and reproduce pass on their genes and unique traits to their children and evolve (increasing favorable allele frequency
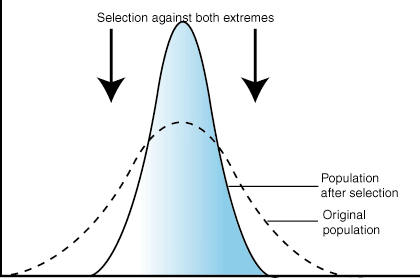
Stabilizing Selection
when natural selection selects against the extremes and favors the intermediate/average
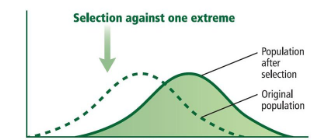
Directional Selection
natural selection favors one extreme over the other and the average
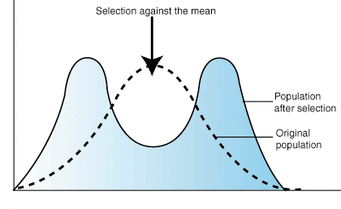
Diversifying/Disruptive Selection
favors both the extremes
How do we know if evolution is occurring?
If the allele frequency is different than the value expected from the Hardy-Weinberg equation (allele frequency stays the same)
allopatric speciation
when the ancestral population becomes separated by a geographical (physical) ex: Grand Canyon and ground squirrels
sympatric speciation
a species evolves into two different species without a physical barrier ex: mating season doesn’t align
5 characteristics of a population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
No Natural Selection
No migration
No mutation
Random Mating
Large Population Size
punctuated equilibrium
a new species undergoes changes quickly from the parent species, then remains largely unchanged for a long time
Gradual Speciation Model (Gradualism)
species diverge gradually over time in small steps with intermediate organisms
why is the significance of reproductive isolation in speciation>
It is critical for the maintain diversity
Prezygotic Barriers
prevent mating/fertilization between species (no zygote is formed)
Postzygotic Barriers
occur after mating and fertilization but present hybrid offspring from being viable or fertile
Temporal Isolation (Sympatric Speciation)
species that breed during different times of day, different seasons, or different years cannot mix gametes
Behavioral Isolation
unique behavior patterns and rituals isolate species and they can no longer identify members of the species or attract males of the same species
Mechanical Isolation
morphological (physical) differences can prevent successful mating (spiral penis can’t fit into a vagina)
5 Pieces of Evidence for Evolution
Fossil Record
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative Embryology
Comparative Biochemistry
Biogeography/Geographic Distribution
Homologous Structure (Comparative Anatomy)
a trait that was passed on from the common ancestor to all of the organisms from that point on
Analogous Structure
when structures arise independently - usually due to the different species living in similar environments
Vestigial Structure
modern organisms that have organs that serve little or no function ex: eye sockets on a fish with no eyes
comparative biochemsity rule
more similarities in DNA = the more closely related the organisms are
biogeography/Geographic distribution
the distribution of species on Earth provides evidence that informs our understanding of both the evolution of life and the monument of continents across the globe via plate tectonics
macroevolution
large-scale changes ex:the origin of extinction of a species
speciation
the process of Evolution that creates 2 different species
hybrid
the offspring resulting from the cross between parents of different species
microevolution
small-scale changes ex:mutation, gene flow, non-random mating, etc.
covergent evolution
when organisms that are not closely related evolve independently to have similar kinds of traits
divergent evolution
when related species graduallybecome different
coevolution
the evolution of one species in response to new adaptations that appear in another species (as one species changes, it causes another to change) ex: pollinators and plants, predator and prey, parasits and hosts