Thermodynamics
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
First study my other thermodynamics set for physics and then study this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the state variables of a gaseous system?
P → Pressure
V → Volume
n → Number of moles
T → Temperature
What are extensive properties? What type of properties do you get when you add, subtract, multiply, divide and differentiate these same type of properties?
These are properties that depend on the amount of matter present in the substance. Ex:- Volume, number of moles etc
add, subtract, multiply → Extensive property
divide and differentiate → Intensive properties
If you divide an extensive property with an intensive property, you will get an extensive property
What are intensive properties?
These are properties that are fixed regardless of the matter present in the substance. Ex:- Lustre, Melting point
What are state functions?
These are properties that depend only on the initial and final states, not on the process used to get there.
What are path functions?
These are properties that depend on the initial and final states, not as well as the path taken for completing those processes
What is internal energy; What is it at the macroscopic level
It is the total amount of K.E. present in the atoms of a molecule; At the macroscopic level, it is a function of Temperature and Volume
How much is 1 Liter atm in joules?
101.3 Joules
How much is 1 Liter bar in joules?
100 Joules
What will be the formulae in the ideal gas equation for change in volume w.r.t the number of moles?
P ∆V = ∆ng*R*T
Where,
P → Pressure
V → Volume
∆ng → Difference between the Number of gas moles of the product to the number of moles of the reactants => np - nr
It is like final - initial, but for chemistry
R → Universal gas constant
T → Temperature
How much is 1 litre bar in kilojoules?
0.1 kJ
What is enthalpy? What is its formula?
It is the change in heat at constant pressure
=> Q final - Q initial
∑ Enthalpy final - ∑ Enthalpy initial
What is the formula for the relation between Cp; Cv; nCp, m; nCv, m
Where,
Cp → Specific heat capacity at constant pressure
Cv → Specific heat capacity at constant volume
n Cp → Specific heat capacity at constant pressure, per mole
n Cv → Specific heat capacity at constant volume, per mole
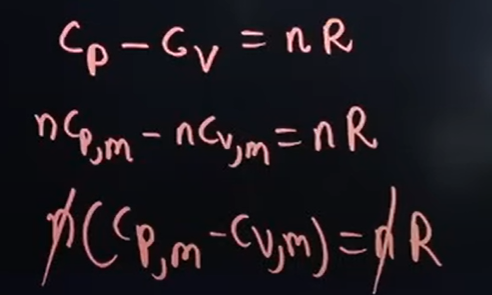
What is the relation between metre and desi metre
1m = 10 dm
What are the standard conditions
298 K and pressure = 1 atm
What are the standard temperature and pressure
273 K and pressure = 1 atm
What is the enthalpy of formation
The enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of a compound is the heat change that occurs when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
What is something that happens every time when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen during combustion
It always forms water
What is an allotrpe? Give an example
An allotrope is the different ways an atom can present itself in nature. Ex:- C (diamond) and C (Graphite) are allotropes
What is Calorific value of fuel?
The heat energy produced in calories when 1 gram of fuel is burned is called the Calorific value of fuel
What is the value for the enthalpy of neutralization

What is the limitation of the first law of thermodynamics?
It couldn’t tell us the direction of heat flow
What is Gibb’s energy; What is its formula?
It is the free energy that is present in the system that can be directed towards doing work; ΔG=ΔH − TΔS