Genetics Exam 1 (Organization of DNA and Packing)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
DNA in Prokaryotes (5)
dsDNA
Circular
Chromosomes, may contain plasmids
Found in nucleoid (no nucleus)
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Bacteria can acquire genetic material from the environment (versus a parent cell)
ex) antibiotic resistance gene
What allows for all DNA material to fit inside cell?
Supercoiling
Twist
One strand crosses over the other
Writhe
Both strands cross over itself
What causes writhe?
As dsDNA is twisted or untwisted, bond angles and length constraints cause it to writhe
Positive supercoiling
More twist added
“overwound’
Found ahead of transcription or replication bubbles and in thermophilic organisms
Negative supercoiling
Less twist added
“unwound”
Most DNA in cells is negatively supercoiled
What controls superpoiling
Highly conserved family of proteins called topoisomerase
How do topoisomerases work (3 steps)
Cuts DNA
introduced + or - twist in DNA
then reseals DNA
Type I Topoisomerase
Nicks 1 strand
Type II Topoisomerase
Nicks 2 strands
DNA in Eukaryotes (4)
Linear chromosomes found in nucleus
Circular chromosomes found in mitochondria and chloroplasts
Wound around histones
C-value
C-value
The amount of haploid DNA in base pairs in an organism
C-value paradox
Increased C-value does not mean increased complexity
Chromatin
DNA and associated protein in the nucleus
Each chromosome exists as _____
Chromatin
each chromosome is precisely positioned into its territory within the nucleus
How DNA is arranged and positioned plays a large role in gene expression regulation
Histones
Make up chromatin
help pack DNA pack into chromatin
HIGHLY conserved
Nonhistone proteins
Various function (replication, repair, transcription, recombination)
may or may not be highly conserved
_____ is supercoiled around histone
dsDNA
Octomer
Two of each subunit: H2A, H2B, H3, H4
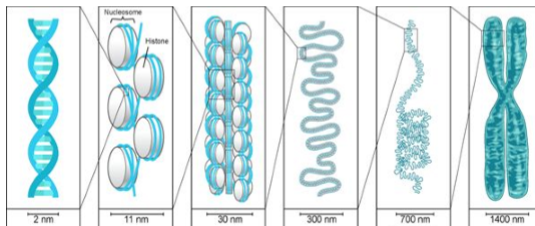
Higher order chromatin structure in eukaryotes (6)
DNA - 2 nm
Nucleosome (beads under string) - 11 m
Chromatine - 30 nm
Chromatine Loops - 300 nm
Condensed chromatine loops - 700 nm
Chromosome: 1400 nm
DNA size
2 nm
Nucleosome (Beads under string) size
11 nm
Chromatine size
30 nm
Chromatine Loop Size
300 nm
Condensed Chromatine Loop size
700 nm
Chromosome size
1400 nm
Packing along chromosomes is less uniform during _____
interphase, but still highly organized
10 nm fiber (tight or loose)
loose
30 nm fiber (tight or loose)
tight
Lower levels of transcription (tight or loose)
tight
Higher level of transcription (tight or loose)
loose
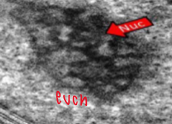
Euchromatin
open and accessible to transcription machinery, expressed

Heterochromatin
Packed tight; closed and silenced
Two types of heterochromatin
1.) Constitutive heterochromatin
2.) Facultative heterochromatin
Constitutive heterochromatin
present in ALL cells at the SAME position on the chromosome
typically repetitive DNA
ex) centromeres and telomeres
Facultative heterochromatin
can VARY between cell type, developmental stage, homologous chromosome
Euchromatin becomes heterochromatin under certain conditions
ex) one of the two X chromosomes in XX mammals (wild-type genetic female) is deactivated to form a Barr body
Distribution of sequences in a genome (2)
1.) Unique-sequence DNA
2.) Repetitive DNA Sequence
Unique-sequence DNA
One or only a few copies of the sequence in the genome
could be heterochromatin OR euchromatin
Makes up 60% of eukaryotic genome
ex) genes that encode protein
Repetitive DNA sequences
Repeated SEVERAL to MILLIONS of times in the genome
Could be dispersed (ex. transposons, rRNA genes)
Could be tandemly repeated (in a row)
Often heterochromatin
ex) satellite DNA of telomeres and centromeres
satDNA
satellite DNA
centromere
separate differently from rest of genome during centrifugation
huge stretch of repeats
Centromere
Constriction points of a chromosome where 2 sister chromatids
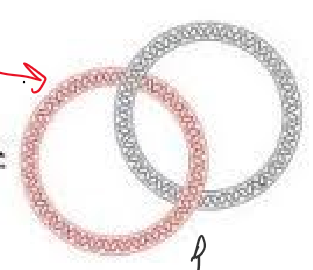
Catenated
Interlinked strands
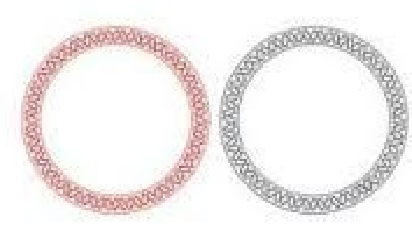
Decatenation
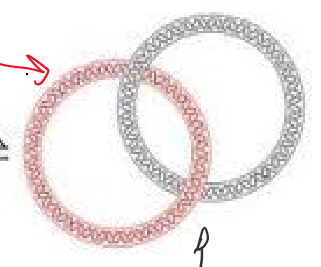
What type of topoisomerase was used
Type II
Draw a beads-on-a-string model of chromatin
do it..
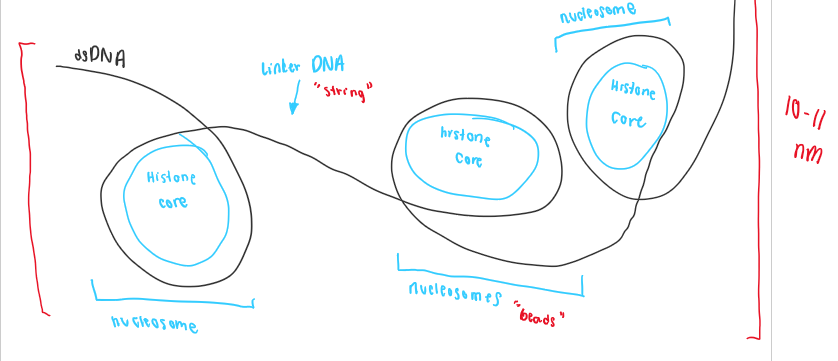
beads-on-a-string size and/or can also be called
10 nm fiber
a _____ shows the complete set of chromosomes during mitosis
karyotype
Satellite DNA
Is NOT found outside the nucleus
Is NOT used to describe very small
Is NOT less subject to breakage than other chromosome regions
Is NOT only found in telomeres
Why is satellite DNA called “satellite”
separates separately from main band after centrifugation
What is centromeres made of
heterochromatin, it’s satellite DNA, it does NOT contain genes
What are telomeres made of, where are they located
Heterochromatin
Located at the ends of linear chromosomes —> protects the ends
Repeated DNA sequences
The # of repeats for telomeres depends on
Organism’s age
Exonucleases