rp10a - prep of organic solid and a test of its purity
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
prep of aspirin, exact masses/vols likely unnecessary but for completion's sake
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
why does the process of recrystallisation purify the aspirin?
aspirin is highly soluble in hot water and less soluble in cold water
when heated in the hot water (solvent), aspirin and impurities dissolve in the solvent
cooling the solution - cold water - causes the aspirin to crystallise out of the solution as it is less soluble
why is a small volume of ethanol used to dissolve the crude aspirin?
so as much crystallises out as possible as it cools
why is the conical flask cooled slowly when allowing the crystals to form?
to ensure the max amount of crystals form
why does scratching the side of the conical flask help the crystals form?
provides cracks/crevices which act as ‘nucleation sites’, facilitating crystal formation
why must you leave the solid aspirin to dry?
to ensure that mass is accurate and not affected by water present on it
name 7 hazardous materials present in the preparation and purification of aspirin and explain why they are hazardous:
salicylic acid (2-hydrobenzenecarboxylic acid) - corrosive, irritant
ethanol - flammable
aspirin - irritant
concentrated sulfuric acid - corrosive
ethanoic anhydride - irritant, flammable
glassware (Büchner flask/beaker etc.) - broken glassware could be sharp and cut skin
hot/boiling water - could burn skin if spilled
how can we use control measures to decrease the risks presented by salicylic acid?
wear safety goggles and lab coat to prevent irritation to eyes/skin
take care not to inhale/swallow
how can we use control measures to decrease the risks presented by ethanol?
keep away from naked flame
how can we use control measures to decrease the risks presented by aspirin?
wear safety goggles and lab coat to prevent irritation to eyes/skin
take care not to inhale/swallow
how can we use control measures to decrease the risks presented by concentrated sulfuric acid?
wear safety goggles and lab coat to prevent irritation to eyes/skin
how can we use control measures to decrease the risks presented by ethanoic anhydride?
wear safety goggles and lab coat to prevent irritation to eyes/skin
keep away from naked flame
how can we use control measures to reduce the risks presented by glassware?
keep glassware away from edge of table
how can we use control measures to reduce the risks presented by hot/boiling water?
keep beaker/kettle away from edge of table
take care when using kettle and preparing water bath
name the 3 stages of the preparation and purification of aspirin:
preparation
purification by recrystallisation
testing the purity
give the method for stage 1 - preparation:
weigh out approx 6.00 g of salicylic acid directly into a 100 cm³ conical flask
record mass of salicylic acid used
using a 10 cm³ measuring cylinder, add 10 cm³ of ethanoic anhydride to the flask and swirl the contents
add 5 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid to the flask and swirl the mixture in the flask for a few minutes to ensure thorough mixing
warm the flask for 20 mins in a 400 cm³ beaker of hot water at approx 60oC - temp should not be allowed to rise above 65oC
allow the flask to cool and pour its contents into 75 cm³ of water in a beaker, stirring well to precipitate the solid
filter off the aspirin under reduced pressure, avoiding skin contact
collect the crude aspirin on a double thickness of filter paper and allow to dry
give the method for stage 2 - recrystallisation:
using a 25 cm³ measuring cylinder, measure out 15 cm³ of ethanol into a boiling tube
prepare a beaker half filled with hot water at a temperature of approximately 75oC - temp should not be allowed to go above 78oC as this is ethanol’s bpt
use a spatula to add the crude aspirin to the boiling tube and place the tube in the beaker of hot water
stir the contents of the boiling tube until all of the aspirin dissolves into the ethanol
pour the hot solution containing dissolved aspirin into approx 40 cm³ of water in a 100 cm³ conical flask
if a solid separates at this stage, gently warm the contents of the flask in the water bath until solution is complete - avoid prolonged heating as this will decompose the aspirin
allow conical flask to cool slowly e.g. ice bath and white needles of aspirin should separate
facilitate the formation of crystals by scratching the insides of the flask with a glass stirring rod and continue cooling in ice bath
filter off purified solid under reduced pressure and allow to dry on filter paper
record mass of dry purified solid
give the method for stage 3 - testing the purity:
powder a sample of the organic solid by crushing it gently with a spatula onto the surface of some filter paper
fill a melting point apparatus provided and mount the melting point tubes ready for taking a measurement
heat the apparatus gently and observe the temp at which the solid collapses into a liquid - likely range of 100-200oC
allow melting point apparatus to cool
compare data book value with your own
stage 2 MS:
give the eqn for the production of aspirin using ethanoic anhydride:
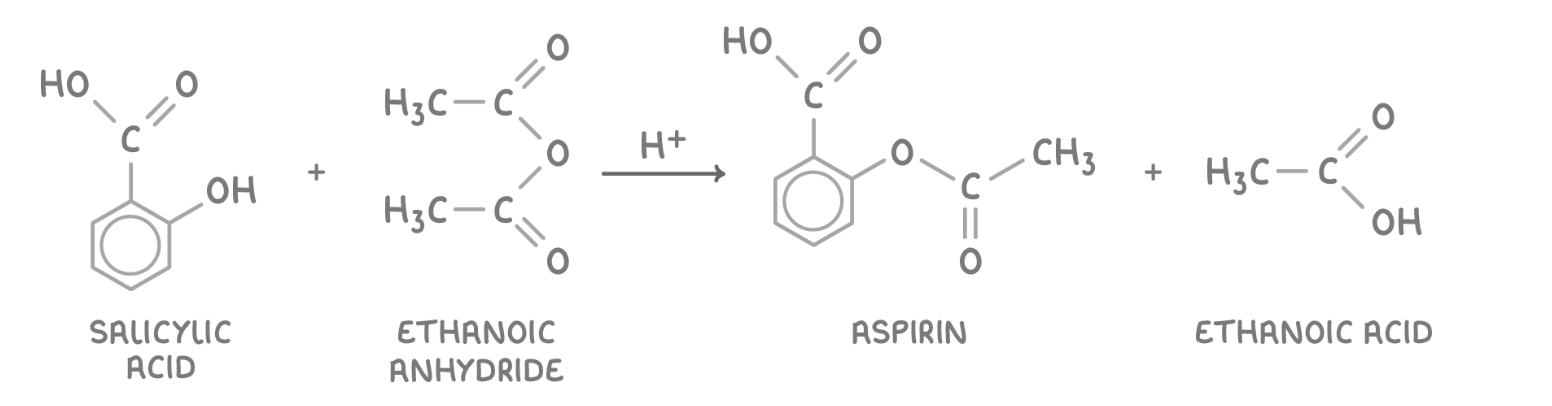
give the 2 compounds that can be used w/ salicylic acid to make aspirin - why may one be more suitable than the other?
ethanoyl chloride - less suitable as produces dangerous HCl fumes
ethanoic anhydride - more suitable as cheaper, safer: less corrosive, reacts more slowly w/ water