Chem Exam 2 Actual
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
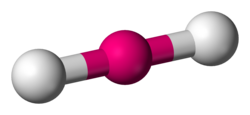
linear
180 degrees, 2 bonding sets, 0 lone pairs/ 2 bonding sets, 3 lone pairs
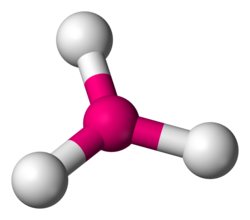
trigonal planar
120 degrees, 3 bonding sets, 0 lone pairs
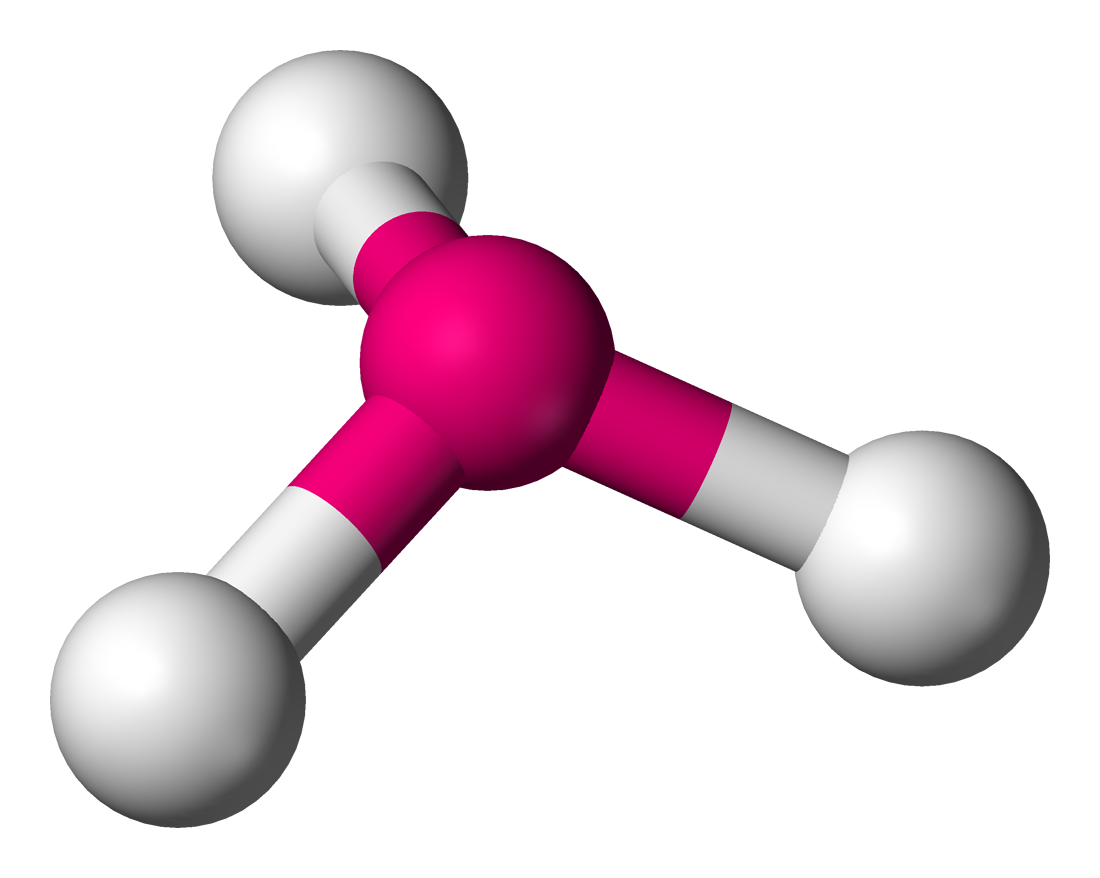
bent
less than 109.5 degrees, 2 bonding sets, 1-2 lone pairs

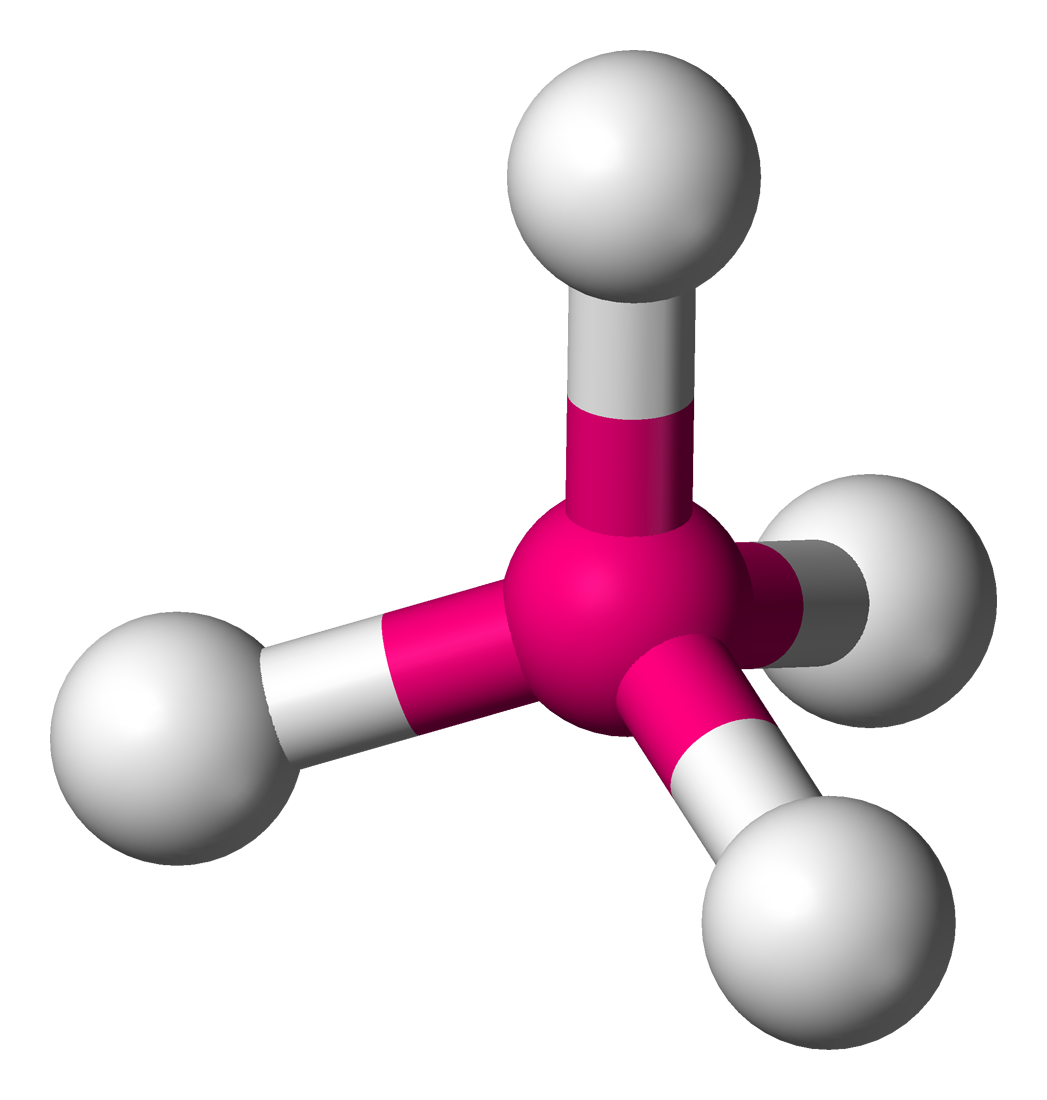
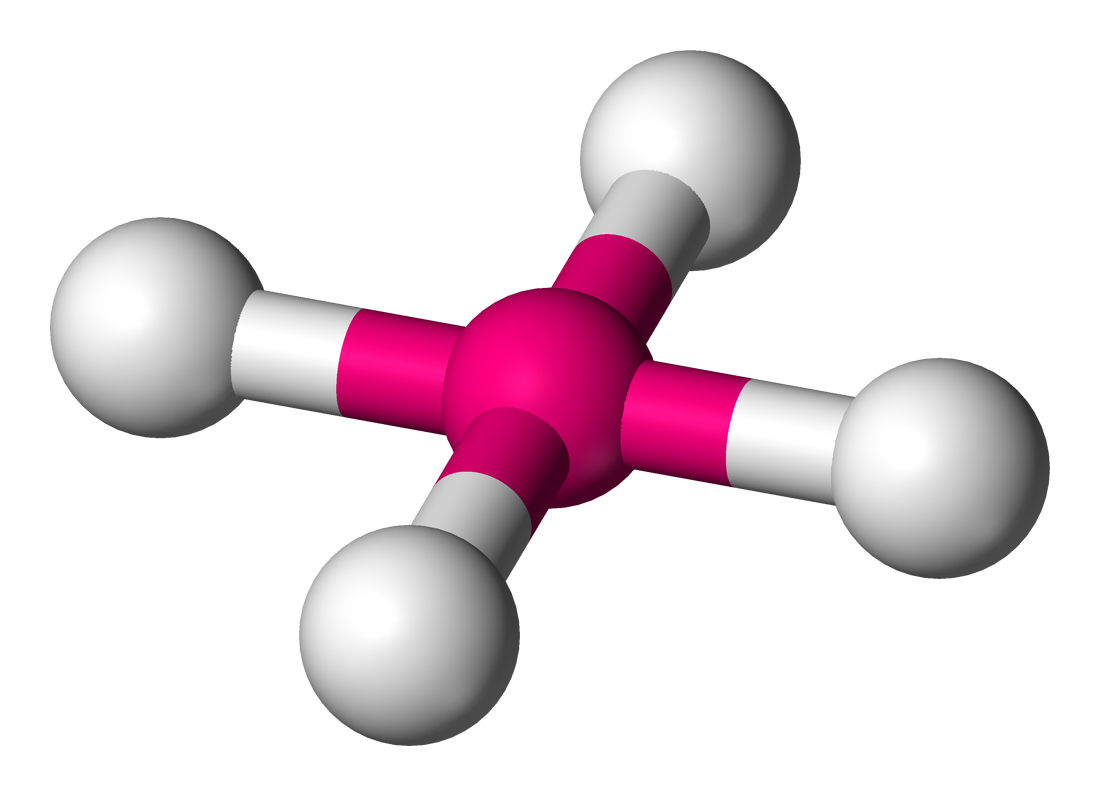
tetrahedral
109.5 degrees, 4 bonding sets, 0 lone pairs
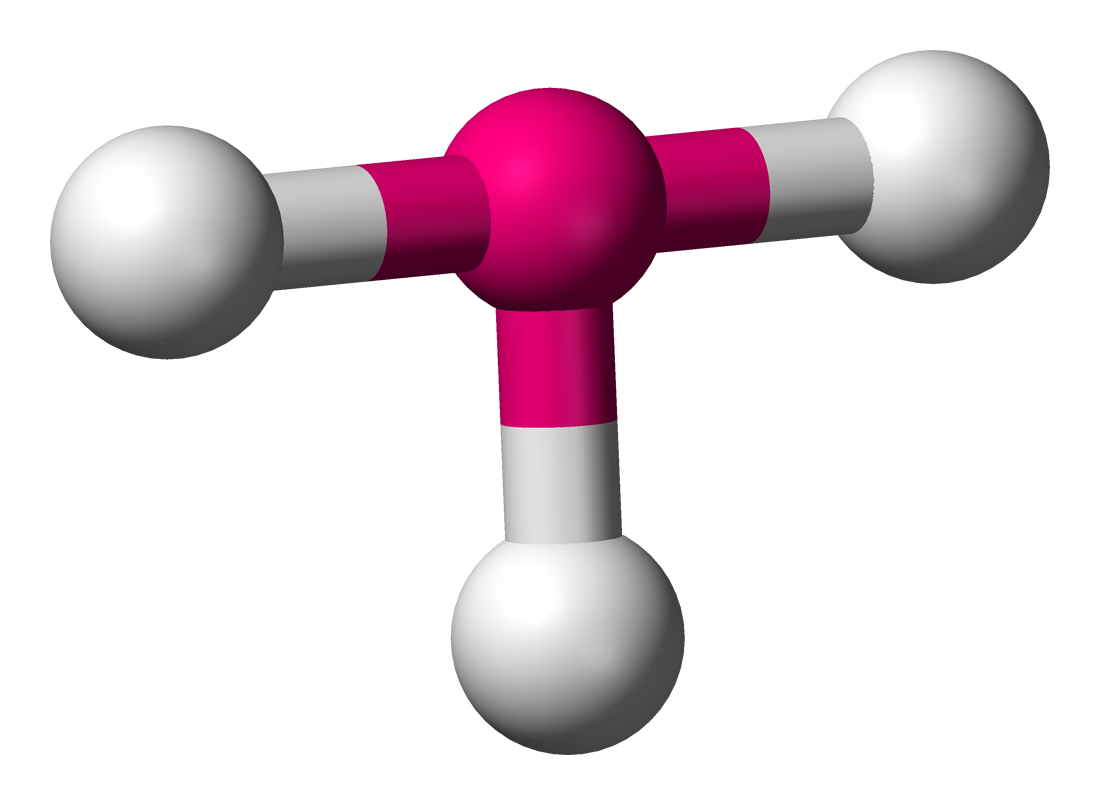
trigonal pyramidal
around 107 degrees, less than 109.5 degrees but ideal is 109.5, 3 bonding sets, 1 lone pair
trigonal bipyramidal
90 and 120 degrees, 5 bonding sets, 0 lone pairs
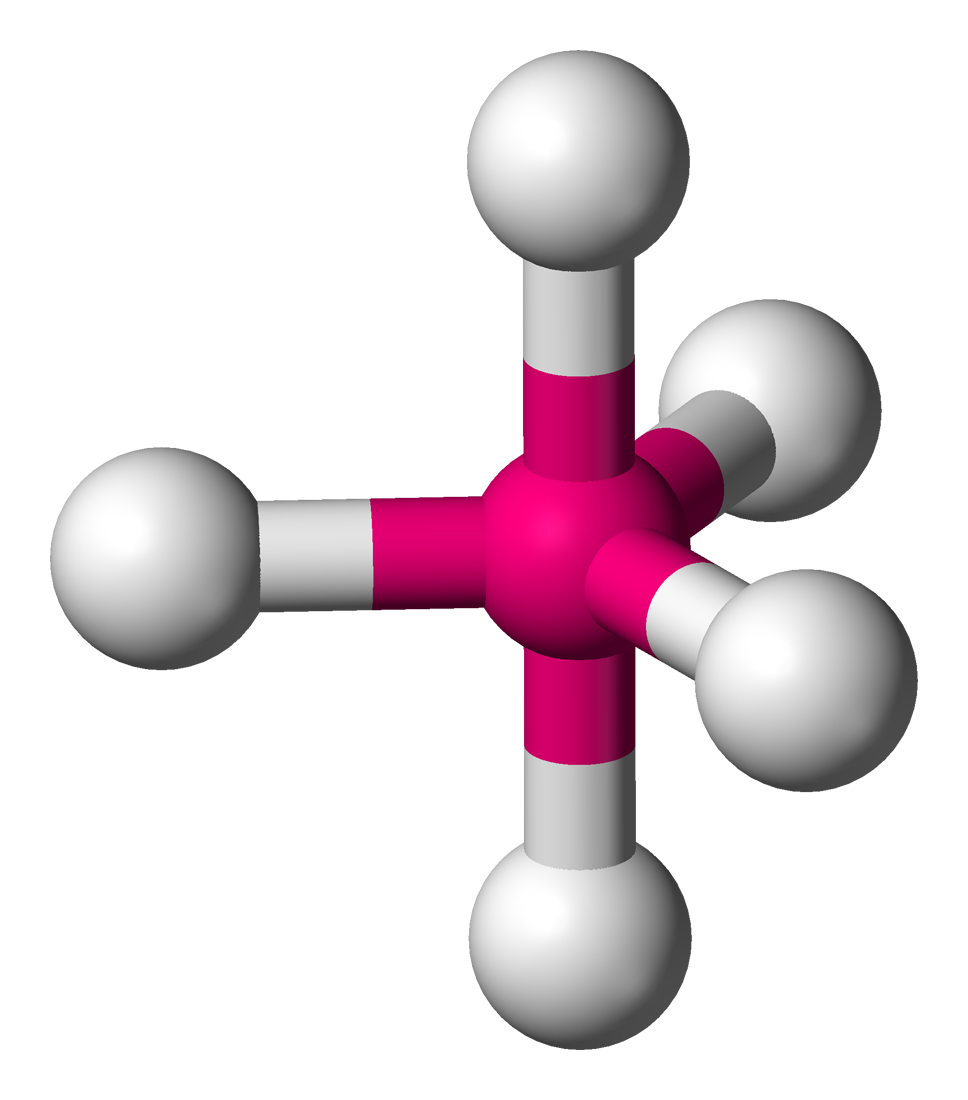
seesaw
90 and 120 degrees, 4 bonding sets, 1 lone pair
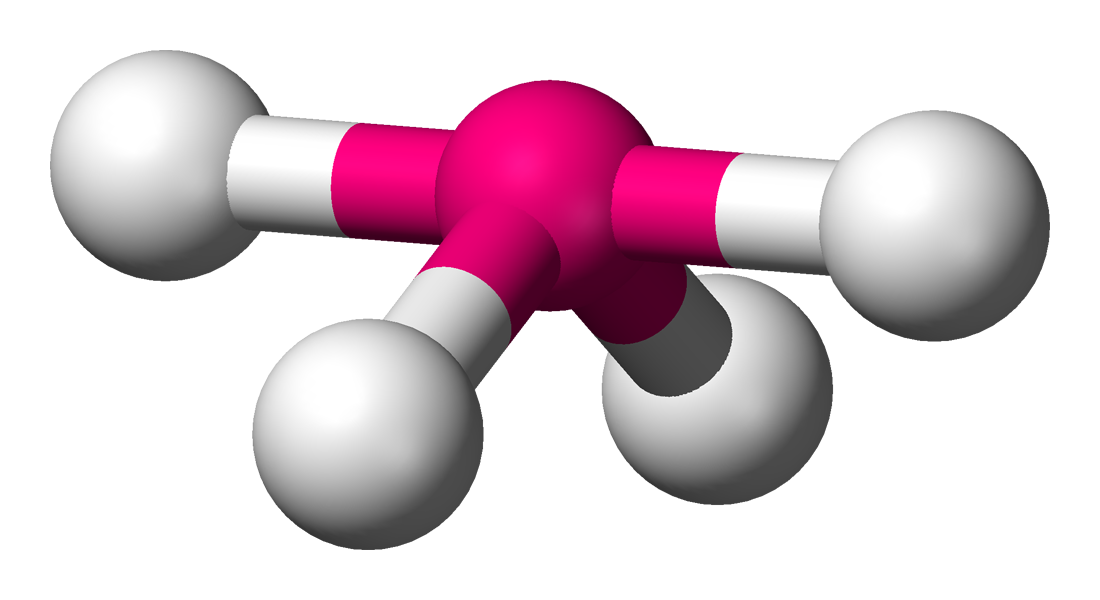
t-shape
90 degrees, 3 bonding sets, 2 lone pairs
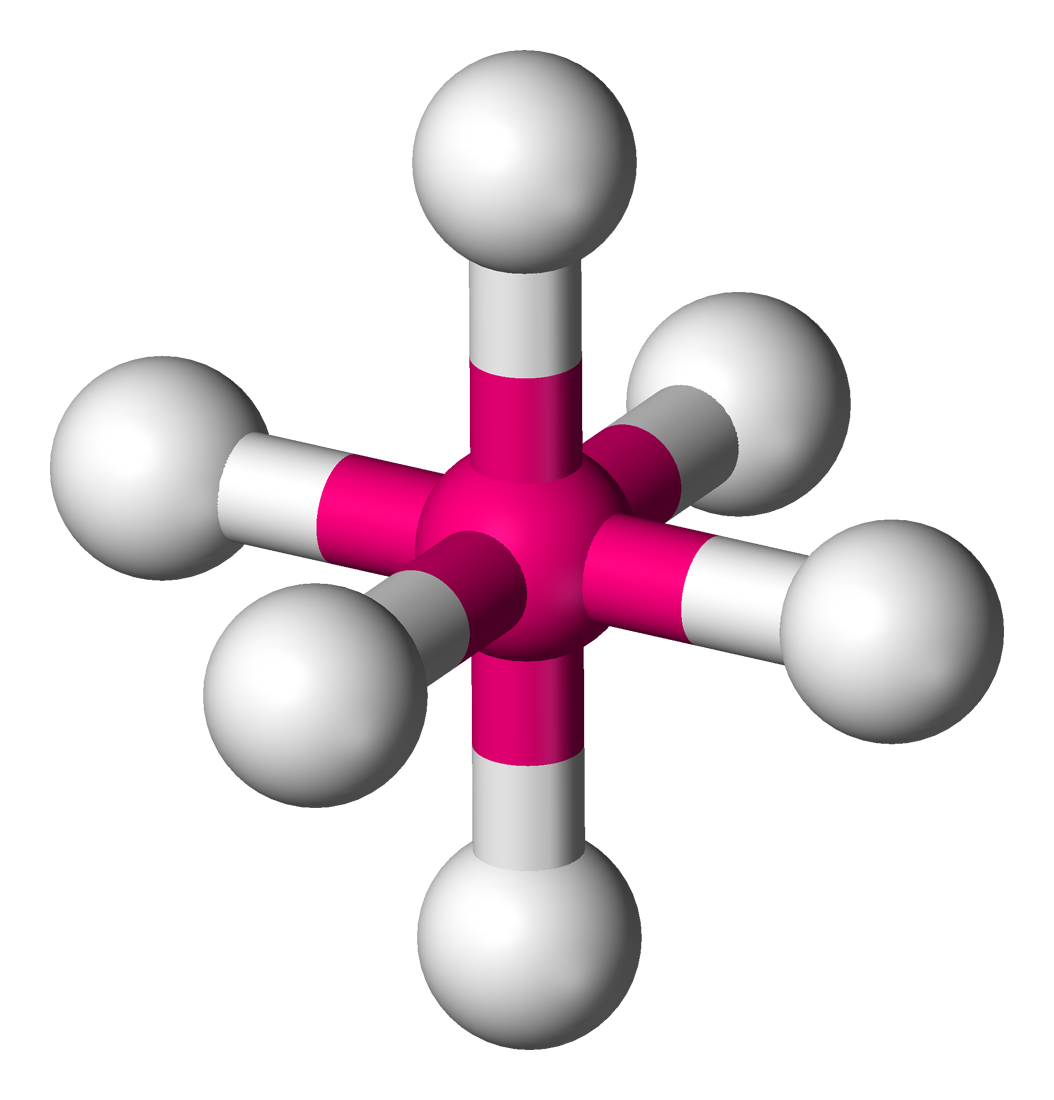
octahedral
90 degrees, 6 bonding sets, 0 lone pairs
square pyramidal
90 degrees, 5 bonding sets, 1 lone pair
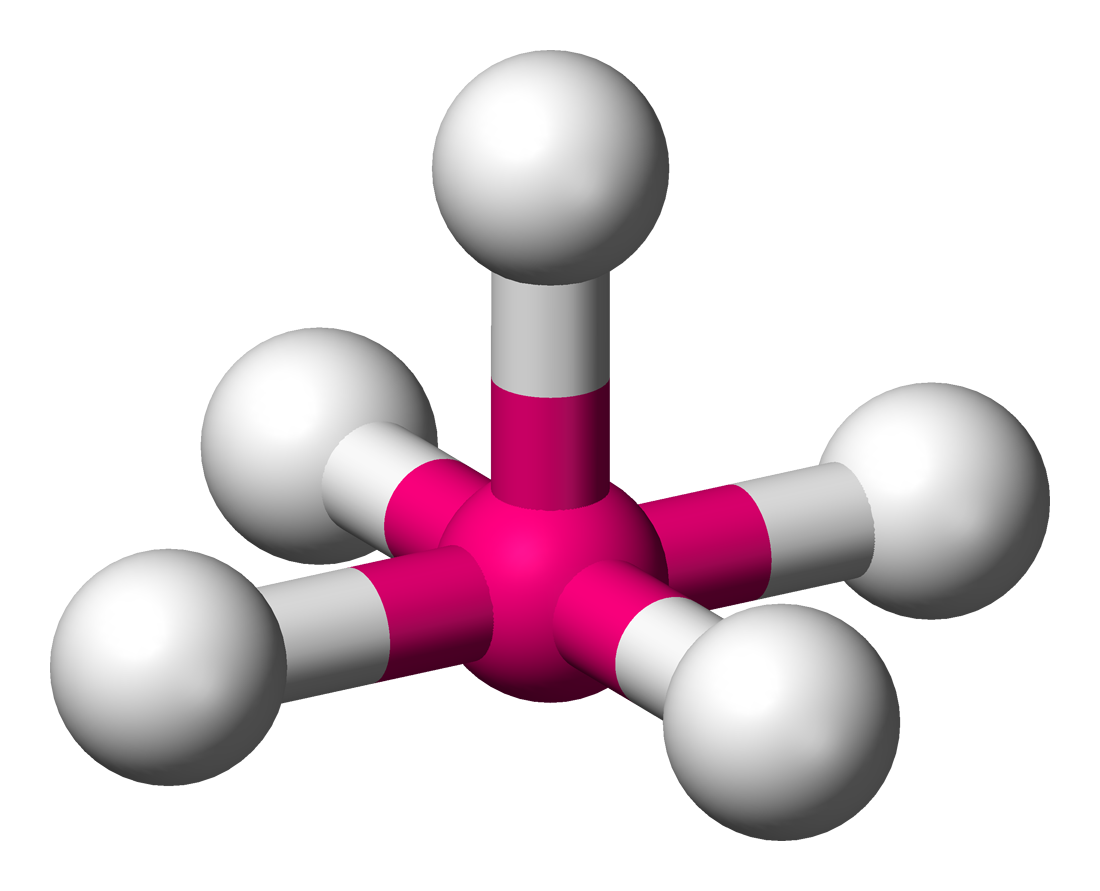
square planar
90 degrees, 4 bonding sets, 2 lone pair
average bond order
total bonds/ number of resonance structures
formal charge
valence electrons - lone electrons - bonds
sigma and pi bonds
single - sigma
double - one sigma, one pi
triple - one sigma, two pi
naming polyatomic ions
-ate: more oxygen atoms
-ite: less oxygen atoms
Per- : more oxygen
Hypo: less oxygen
naming binary ionic compound
name of metal cation + parenthesized roman-numeral indicating metal charge , anion base name + ide
naming polyatomic ionic compound
name of metal cation and polyatomic anion name (or oxyanion name)
prefixes for hydrates and polys
mono
di
tri
tetra
penta
hexa
hepta
octa
nona
deca
naming binary molecular compound
more metal-like element
more nonmettallic element
greek prefix (number of atoms of first element) + first element name then greek prefix + second element -ide
naming binary acid
hydrogen and nonmetal (hydro + nonmetal base name + ic)
naming oxyacid
hydrogen and oxyacid anion (ate: base name + -ic, ite: base name +-ous)
cis isomer
same side
trans isomer
opposite side
enantiometers
isomers that are mirror images of each other but do not super impose
coulumb’s law
lattice energy (delta H= product of ion charges/ distance between atoms
hess’s law
total enthalpy change is a sum of all enthalpy change steps
homonuclear
same element in compound
constitutional isomers
same molecular formula but different atom connectivity
conformational isomers
rotation around single bonds
diastereomers
stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other, non-identical and non-superimposable
meso compounds
organic molecules with at least two chiral centers, internal plane of symmetry, superimposable, optically inactive