Care of Clients with Problems in Oxygenation (Heart as a Pump)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Last updated 4:41 PM on 9/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
Hypercoagulability
Injury
Stasis
Injury
Stasis
What are the three components of the Virchow’s triad?
2
New cards
Myocardium
The thickest layer of the heart
3
New cards
Closure of the semilunar valves
Which event is responsible for the S2 heart sound?
4
New cards
Hemoptysis
Failure of the left side of the heart can lead to which of the following symptoms?
\
A. Varicose veins
B. Ascites
C. Hemoptysis
D. Hepatomegaly
\
A. Varicose veins
B. Ascites
C. Hemoptysis
D. Hepatomegaly
5
New cards
Infarction
A complete obstruction of blood flow in the coronary arteries could result in myocardial:
6
New cards
SA Node, 60-100
The ___ Node is the main pace-maker of the heart and fires spontaneously at ________ beats per minute.
7
New cards
Left Anterior Descending Artery
Most common site of atherosclerosis
8
New cards
Stroke volume
This refers to the amount of blood pumped by the heart every beat.
9
New cards
Afterload
Vascular resistance
10
New cards
Preload
Ventricular stretch/blood volume prior to systole
11
New cards
Contractility
Force of contraction (inotropic activity)
12
New cards
Vagus Nerve (stimulates parasympathetic NS)
Which cranial nerve does Valsalva Maneuver stimulate? Also the longest cranial nerve
13
New cards
True
True or False: Valsalva Maneuver slows down heart rate
14
New cards
increases
What happens to the preload and afterload during a general vasoconstriction?
15
New cards
decreases
What happens to the preload and afterload during a general vasodilation?
16
New cards
Contractility
Inotropic activity is also known as
17
New cards
Inotropes
Norepinephrine, dopamine, and dobutamine are examples of
18
New cards
Frank-Starling Law
What law indicates that the more stretch, the stronger the contraction until a physiological limit has been reached (like a balloon or rubber band)
19
New cards
RAAS (Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system)
The system that regulates BP through hormones
20
New cards
Chest pain (PQRST)
Dyspnea
Dizziness, syncope
Edema
Fatigue
Palpitations
Cough, hemoptysis
Weight gain and skin changes
Dyspnea
Dizziness, syncope
Edema
Fatigue
Palpitations
Cough, hemoptysis
Weight gain and skin changes
The common complaints related to CV disease (assessment)
21
New cards
A
The pt. is experiencing chest pain that is characterized with a squeezing feeling in the chest for about 15 minutes. Which of the ff is/are he/she most likely experiencing? Select all that apply
A. Stable Angina
B. Unstable Angina
C. Acute Coronary Syndrome
D. Myocardial Infarction
A. Stable Angina
B. Unstable Angina
C. Acute Coronary Syndrome
D. Myocardial Infarction
22
New cards
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: When the pt. is experiencing angina that does not go away after administering three nitrates, you should rush them to the hospital.
23
New cards
Substernal
Anterior Chest
Vague
Exacerbated by (1) Exertion, (2) Extreme emotions, (3) Eating large meals, and (4) Extreme cold
Relieved by Rest \[or nitrates\]
Short Duration
Anterior Chest
Vague
Exacerbated by (1) Exertion, (2) Extreme emotions, (3) Eating large meals, and (4) Extreme cold
Relieved by Rest \[or nitrates\]
Short Duration
What are the characteristics of anginal pain? (SAVERS)
24
New cards
FALSE: Patients with MI experience impending doom due to cerebral hypoxia
TRUE or FALSE: In Angina, there is a feeling of impending doom
25
New cards
Sedentary lifestyle
Age
Diet
Smoking
Alcoholism
Genes
Gender (Male = lifestyle; Female = after menopause)
Age
Diet
Smoking
Alcoholism
Genes
Gender (Male = lifestyle; Female = after menopause)
Risk factors of CV disease
26
New cards
Hypertension
Diabetes
Hyperobesity
Hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Hyperobesity
Hyperlipidemia
What are the four metabolic disorders?
27
New cards
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea - blood backflow to the lungs
What can be implied from the number of pillow the patient is using while sleeping?
28
New cards
S3
Heart sound that is also known as ventricular gallop (pahabol)
29
New cards
S4
Heart sound that is also known as atrial gallop
30
New cards
Diaphragm
Which part of the stethoscope should you use to auscultate S1 and S2 sounds?
31
New cards
Bell
Which part of the stethoscope should you use to auscultate S3 and S4 sounds?
32
New cards
Murmurs
Swooshing sounds upon auscultation of the heart
33
New cards
Thrills
What do you call the palpable vibrations
34
New cards
Arterial
Arterial or Venous?: Insufficient organ perfusion
35
New cards
Venous (edema)
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Heaviness
36
New cards
Arterial
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Sharp stabbing pain
37
New cards
Venous (stasis)
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Reddish color
38
New cards
Arterial
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Pale skin
39
New cards
Arterial
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Cold to touch
40
New cards
Venous
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Warm to touch
41
New cards
Arterial
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Non-healing wound
42
New cards
Venous
Arterial or Venous Insufficiency?: Edema
43
New cards
CK Total (?)
The most cardiac specific biomarker
44
New cards
Troponin
The most cardiac sensitive biomarker
45
New cards

What are the different diagnostic/laboratory examinations related to altered CV function?
46
New cards
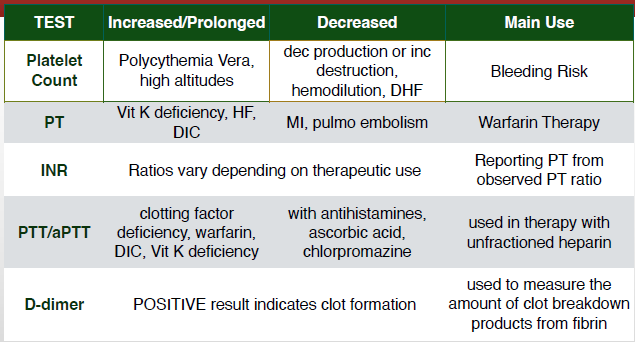
What are the different coagulation studies?
47
New cards
True (triglycerides can be fat that is converted from sugar)
TRUE or FALSE: When you have high triglycerides, you are advised to reduce your rice consumption
48
New cards
True; The desirable level of cholesterol in the blood is
TRUE or FALSE: The first thing to assess in the lipid profile is the cholesterol levels
49
New cards
Echocardiography
Also known as the ultrasound of the heart (Ultrasound cardiography)
50
New cards
Ejection Fraction
Percent of EDV ejected with each heartbeat
51
New cards
Femoral artery
What artery is the access in cardiac catheterization?
52
New cards
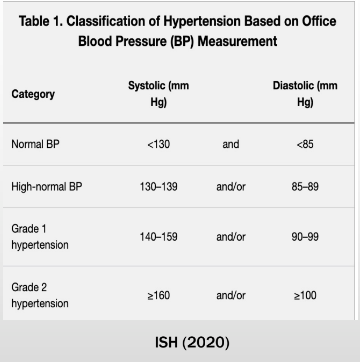
False
TRUE or FALSE: 130-139 mmHg over 85-89 mmHg is considered Stage 1 HTN in International Society of Hypertension (2020)
53
New cards
Hypertension
What is the no. 1 risk factor of coronary artery disease?
54
New cards
Sclerosis
Plaque: Atheroma = Hardening: ________
55
New cards
True
True or False: All heart diseases lead to decreased cardiac output
56
New cards
Insufficient Tissue perfusion
Backward: Backflow = Forward: ___________________________
57
New cards
Injury
What component of the Virchow’s triad is present in Coronary Artery Disease?
58
New cards
Stasis
What component of the Virchow’s triad is present in Mitral Stenosis?
59
New cards
Backflow/Leaking mitral valve
Mitral Stenosis: Narrowing/Narrowed mitral valve = Mitral Regurgitation: ______________
60
New cards
False: insufficient filling or low preload
True or False: Increased heart rate means increased cardiac output
61
New cards
Shock
What happens if there is a lack of oxygenated blood supply to multiple organs?
62
New cards
Decreased Cardiac Output
Activity Intolerance
Activity Intolerance
Give the two main nursing diagnoses regarding CV diseases
63
New cards
reduction of oxygen DEMAND / cardiac workload
promotion of OXYGEN supply
hemodynamic MONITORING (non-invasive)
prevention of COMPLICATIONS
REHABILITATION (cardiac rehab)
promotion of OXYGEN supply
hemodynamic MONITORING (non-invasive)
prevention of COMPLICATIONS
REHABILITATION (cardiac rehab)
Management of Impaired Cardiac Function; Interventions (DOMCoRehab)
64
New cards
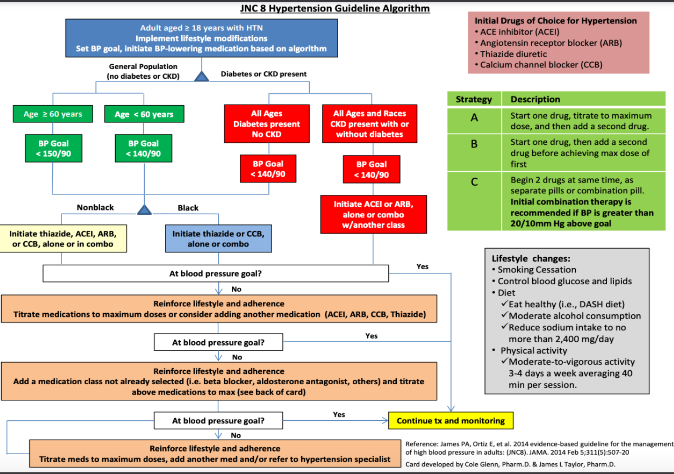
ACE Inhibitor (ACEI) → -PRIL (AcePril = credits to ley)
Angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) → -SARTAN (e.g. Losartan)
Thiazide Diuretic (e.g. HCTZ or hydrochlorothiazide)
Calcium channel blocker (CCB) → -DIPINE (e.g. Amlodipine)
Angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) → -SARTAN (e.g. Losartan)
Thiazide Diuretic (e.g. HCTZ or hydrochlorothiazide)
Calcium channel blocker (CCB) → -DIPINE (e.g. Amlodipine)
Initial Drugs of Choice for Hypertension based on JNC 8 hypertension guideline algorithm
65
New cards
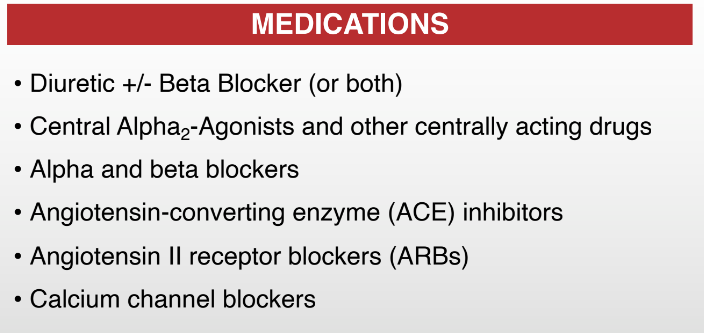
Diuretic → to be taken in the morning to avoid nocturia
Alpha2 → causes vasodilation
Alpha1 → causes vasoconstriction
Beta blockers → -OLOL
ACE → -PRIL
ARBs → -SARTAN
Calcium channel blockers → -DIPINE
Alpha2 → causes vasodilation
Alpha1 → causes vasoconstriction
Beta blockers → -OLOL
ACE → -PRIL
ARBs → -SARTAN
Calcium channel blockers → -DIPINE
Give all medications for hypertension
66
New cards
\[D\]ecrease myocardial \[O\]xygen \[D\]emand and \[I\]ncrease \[O\]xygen \[S\]upply
What is the main goal/intervention for a patient with Angina? (DOD-IOS)
67
New cards
TRUE; Self-Care Deficit (Hygiene) r/t easy fatiguability
TRUE or FALSE: Self-care deficit (hygiene) is also a possible nursing problem in CV function alteration
68
New cards
Anticoagulants (Heparin/Warfarin)
Antiplatelets (Aspirin)
Antiplatelets (Aspirin)
To prevent clot formation, what medication/s is/are administered in a pt. w/ angina?
69
New cards
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents (e.g. Propranolol)
Calcium channel blockers (e.g., Amlodipine)
Calcium channel blockers (e.g., Amlodipine)
To reduce cardiac workload, what medication/s is/are administered in a pt. w/ angina?
70
New cards
VS, respiratory distress
Pain
ECG
Pain
ECG
What should you monitor in a patient with angina?
71
New cards
Arrhythmia
What is the most common complication of myocardial infarction?
72
New cards
True
TRUE or FALSE: When the pt. has myocardial infarction, you should be ready to provide BLS any time.
73
New cards
1\. Ineffective myocardial tissue perfusion
2\. Risk for ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
3\. Risk for fluid imbalance
4\. Death anxiety
2\. Risk for ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
3\. Risk for fluid imbalance
4\. Death anxiety
What are the different nursing and collaborative problems regarding myocardial infarction?
74
New cards
True; To DECREASE myocardial oxygen demand and INCREASE oxygen supply
TRUE or FALSE: Angina and Myocardial infarction have the same main/goal and intervention.
75
New cards
Morphine Sulfate; It is a CNS depressant to treat SNS stimulation which increases both HR and BP
To manage the pain of a pt. w/ myocardial infarction, what medication/s is/are administered?
76
New cards
To avoid straining that causes vagal stimulation
Why is a pt. with myocardial infarction in complete bed rest (CBR) with no bathroom privileges (BP)?
77
New cards
Thrombolytic Therapy (E.g., Streptokinase, Urokinase)
What do you call the therapy used to manage myocardial infarction? (Hint: It dissolves the clot)
78
New cards
Balloon angioplasty \[with Stent to maintain patency)
What do you call the percutaneous coronary intervention to repair the artery associated with the MI?
79
New cards
NTG, Aspirin, Beta-blockers
What are the other medications administered to patients with MI?
80
New cards
It prevents constipation, because constipation can cause straining which leads to vagal stimulation
Why is lactulose administered to a patient with MI?
81
New cards
Assess indicators of CO, especially changes in level of consciousness.
What should you do first in patients with dysrhythmia?
82
New cards
1\. Decreased CO
2\. Anxiety
3\. Cardiac arrest, heart failure, thromboembolic events
2\. Anxiety
3\. Cardiac arrest, heart failure, thromboembolic events
Give nursing and collaborative problems secondary to dysrhythmias
83
New cards
Antiarrhythmics (e.g. Amiodarone)
What are the medications for patients with dysrhythmia?
84
New cards
False; it stops/resets the beating of the heart
(defib to ur heart: “amaccana bhie” \**sinapak**)
(defib to ur heart: “amaccana bhie” \**sinapak**)
TRUE or FALSE: The defibrillator helps the heart to start beating
85
New cards
▪ Stenosis (narrowing)
▪ Regurgitation (backflow)
▪ Prolapse (displacement; can cause regurgitation)
▪ Regurgitation (backflow)
▪ Prolapse (displacement; can cause regurgitation)
What are the different valvular problems?
86
New cards
1. Surgery: Valvuloplasty, valve replacement
2. Management of heart failure
How do you manage valvular problems?
87
New cards
Mechanical and Tissue (mostly from a pig) valves
What are the two types of valve replacement?
88
New cards
Endocarditis
What do you call the inflammation of the inner lining of the heart due to bacterial infection?
89
New cards
• Antimicrobial therapy (penicillin, meropenem, vancomycin \[IV route\])
• Oral hygiene
• Prevention of URTI (untreated strep infections can cause endocarditis)
• Oral hygiene
• Prevention of URTI (untreated strep infections can cause endocarditis)
How do you manage endocarditis?
90
New cards
• Antimicrobials
• Anti-inflammatory (steroids)
• Proper position (tripod, orthopneic)
• Pericardiocentesis, if needed (can cause tamponade if heart is perforated)
• Anti-inflammatory (steroids)
• Proper position (tripod, orthopneic)
• Pericardiocentesis, if needed (can cause tamponade if heart is perforated)
How do you manage pericarditis?
91
New cards
Heart Failure
The end of all heart diseases
92
New cards
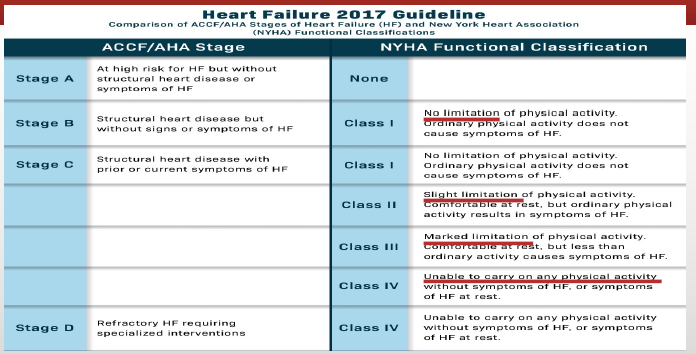
Slight Limitation
What is class II of the NYHA Functional classification of heart failure?
93
New cards
1\. Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion (forward failure)
2\. Excess fluid volume (backward failure)
3\. Activity intolerance and fatigue
4\. Anxiety, Powerlessness, Noncompliance
5\. CP: Cardiogenic shock, edema, dysrhythmia, thromboembolism (stasis)
2\. Excess fluid volume (backward failure)
3\. Activity intolerance and fatigue
4\. Anxiety, Powerlessness, Noncompliance
5\. CP: Cardiogenic shock, edema, dysrhythmia, thromboembolism (stasis)
What are the different nursing and collaborative problems secondary to heart failure?
94
New cards
Decrease the workload of the heart by REDUCING PRELOAD AND AFTERLOAD
What is the main goal/intervention for a pt. with heart failure? (RPA)
95
New cards
1\. Prevention of exacerbations
2\. Stress management
3\. Fluid restrictions
4\. Medications: Diuretics\**, Digitalis* \*\*, ACE-I, ARB, Beta Blockers
\
\*An example is furosemide (potassium-wasting)
increased CO → increased kidney perfusion → increased urine output → increased potassium wasting
THERE IS RISK FOR HYPOKALEMIA
\
\*\* Only given once a day or once every other day
2\. Stress management
3\. Fluid restrictions
4\. Medications: Diuretics\**, Digitalis* \*\*, ACE-I, ARB, Beta Blockers
\
\*An example is furosemide (potassium-wasting)
increased CO → increased kidney perfusion → increased urine output → increased potassium wasting
THERE IS RISK FOR HYPOKALEMIA
\
\*\* Only given once a day or once every other day
How do you primarily manage heart failure (how do you reduce the preload and afterload)?
96
New cards
Blood pressure (should not administer if 90/60 or below)
What should you assess before giving furosemide to the patient?
97
New cards
Apical pulse (should not be 60 or below)
What should you assess before giving digitalis/digoxin to a patient?
98
New cards
1\. Monitoring for symptoms of fluid overload
2\. Daily weight; I&O
3\. Diuretic therapy; timing of meds
4\. Fluid intake; fluid restriction
5\. Maintenance of sodium restriction
2\. Daily weight; I&O
3\. Diuretic therapy; timing of meds
4\. Fluid intake; fluid restriction
5\. Maintenance of sodium restriction
How do you intervene with fluid volume excess in heart failure?
99
New cards
1\. Bed rest for acute exacerbations
2\. Regular physical activity; 30-45 minutes daily
3\. Pacing of activities: Wait 2 hours after eating before physical activity
4\. Avoid activities in extremely hot, cold, or humid weather
5\. Modify activities to conserve energy.
6\. Positioning; elevation of HOB to facilitate breathing and rest, support of arms
2\. Regular physical activity; 30-45 minutes daily
3\. Pacing of activities: Wait 2 hours after eating before physical activity
4\. Avoid activities in extremely hot, cold, or humid weather
5\. Modify activities to conserve energy.
6\. Positioning; elevation of HOB to facilitate breathing and rest, support of arms
How do you intervene with activity intolerance in heart failure?
100
New cards
Exercise counseling and training
Education for healthy-heart living
Counseling to reduce stress
Education for healthy-heart living
Counseling to reduce stress
What are done in cardiac rehabilitation?