pte unit 5
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
The Acute Care Setting
§ Immediate, short-term medical
treatment
§ Acute illness, injury, or surgery recovery
§ Often involve a multidisciplinary team
§ Protocols and standards of practice and
safety
admission and Stay Criteria
§ Admission through ER or direct from physician
§ Based on:
§ Doctor’s judgment
§ Patient’s need for medically necessary hospital care
§ Room for the patient
§ Patient (or the responsible party) must agree
§ 23-hour observation
§ Expected LOS: 3+ days
Health Conditions Encountered
§ Deconditioning – Hospital acquired disorders
§ Neuromuscular disorders
§ Neurological
§ Neurosurgical
§ Cardiopulmonary disorders
§ Cardiac dysfunction
§ Pulmonary dysfunction
§ Immune system and Infection disease
§ Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic disorders
§ Trauma
§ Elective surgery
§ Vascular and Hematology
§ Transplantation
§ Integumentary and Wound Care
§ Burns
§ Oncological
§ Gastrointestinal
§ Endocrine
§ Genitourinary
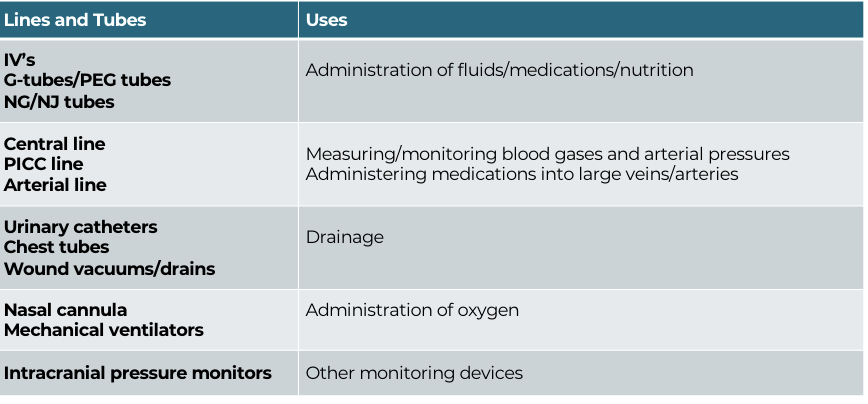
Lines and Tubes
Role of the PT
§ Assess patient and determine likely
discharge location
§ Make recommendations
§ Equipment
§ Discharge transportation
§ Optimize functional abilities
§ Safety and fall prevention
Patient safety is top priority
§ Keep patient safe at all times
§ Comply with hospital initiatives to maximize patient safety
§ Understand patient safety goals established by the
Department of Health Services.
§ Guidelines:
§ Reduce rate of infections
§ Confirm correct patient
§ Use equipment in good working order
§ Follow protocols for use of AD and equipment
Regulatory Agencies
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO)
§ Ensure patient safety
§ Monitors state and federal legislative and regulatory initiatives
§ Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
§ Health and safety of employees
§ Assess safety needs in hospital setting and enhances patient safe handling
§ Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
§ Aimed at protecting public health
§ Provides guidelines for contact and isolation precautions and personal protective
equipment (PPE)
Team Members Encountere
§ Physicians
§ Physician Assistant
§ Nurse practitioner
§ Nursing (RN, LPN, CRNA)
§ Psychologist/Neuropsych
§ Patient care managers (SW or RN)
§ Pharmacist
§ Therapists (OT, PT, SLP, RT)
§ Dietitian
§ Orthotist
§ Interpreter
Physician Hierarchy in Medical Centers
Attending
Fellow
Chief Resident
Resident
Intern
Medical Student
Interdisciplinary
Communication
§ Know the roles of the team members
§ Gather information
§ Be confident in your PT knowledge
§ Be clear, concise, confident, and objective
§ Show and expect respect
SBAR for Effective Communication
Situation
Background
Assessment
Recommendation
§ Standardized means for communicating in
patient care situations
§ Common and predictable structure
§ Can be used in any clinical domain
Introduction to SBAR
§ Situation: What is going on with the patient?
§ Background: What is the clinical background or
context?
§ Assessment: What do I think the problem is?
§ Recommendation: What do I think needs to be done
for the patient?
Current Challenges
in Acute Care
§ Sicker patients
§ Increased push for productivity
Chart Review
Alertness
Pain
Motivation
Preadmission screening (PAS) documentation
Physician notes from previous facility
Physical, Occupational, and Speech Therapy notes
must have had evaluations from at least two disciplines for admission
Functional Assessments
Recent labs
Recent imaging
Discharge plan from previous location
Preadmission Screening (PAS)
Patient's prior level of function (PLOF) before the event leading to rehabilitation need
Expected level of improvement
Evaluation of risk for clinical complications
Conditions requiring rehabilitation
Anticipated therapy needs (physical, occupational, speech)
Expected discharge destination
Physician Discharge Summary
Comprehensive summary of stay in previous setting
Medical history relevant to rehabilitation needs
Summary of labs, imaging, and course of care
Functional Assessments
Documentation of patient's functional abilities across domains like mobility, self-care,
communication, and cognitive function
Standardized assessment tools
i.e. Perme-ICU or AMPAC 6-clicks from acute care hospital
Cognitive assessments
ADL based assessments
Interdisciplinary
Team Notes
Communication between different
disciplines regarding patient progress and
care coordination
Documentation of team meetings and
collaborative decision-making
Documentation from case management
or social work for discharge planning
Discharge Planning
Discharge destination and anticipated post-
discharge needs
Patient and caregiver education regarding
discharge plan
Patient Interview
§ Communication with RN about patient status
§ HAND HYGIENE and infection control/PPE
§ Introduction to patient
§ Confirm patient identity
§ Explanation of your role
§ Description of session’s plan
§ Receipt of consent (if able)
§ Inquiry of patient experience and goals
Medical Record
§ General Demographics
§ Current Condition/Chief
Complaint
§ Medical/Surgical History
§ Family History
§ Medications
§ Other Clinical Tests
Patient / Caregiver Interview
§ Social History
§ Social/Health Habits
§ Employment/Work
§ Growth and Development
§ Living Environment
§ General Health Status
§ Functional Status and Activity
Level
Social History and Habits
§ Level of support:
§ Physical
§ Emotional
§ Financial
§ Identify roles and
responsibilities
§ Employment/work roles
§ School roles
§ Social roles
§ What IADLs do they
perform?
§ Cultural beliefs and
behaviors
Living Environment
Type of residence
§ Potential barriers associated with physical environment
§ Access and ownership of durable medical equipment
§ Who will be available to help?
§ Will the patient be returning to their primary residence?
§ Who will live with the patient upon discharge? What is their ability to assist
if needed?
§ If living alone, who will be available to assist if needed?
Functional Status and Activity Level
§ Abilities and need for assistance
§ Bed mobility
§ Transfers
§ ADLs
§ Ambulation
§ Endurance and activity tolerance
§ Ambulation distance
§ Prior exercise/activity regime
§ Fall history
§ Airway considerations
§ Use of AD
§ Use of other DME
Systems Review
§ Screening exams (brief systems review)
§ Discovering areas of deficit along with another
accurate knowledge of the condition
§ Cognition:
§ How did the patient respond when you
entered the room?
§ Alert? Aware? Oriented?
§ Cardiopulmonary:
§ Is there a monitor displaying values?
§ What equipment do you need to assess
vitals?
§ Are there parameters from the chart
indicating precautions/contraindications?
§ Integumentary:
§ What factors will influence your screening
of skin?
§ Health condition – sensation, motor
ability, cognition
§ LOS
§ Prior level of function and admission
with integrity issues
§ Observed positioning
Systems Review
Systems Review
§ Musculoskeletal:
§ What factors influence this screening?
§ Health Condition – motor function,
cognition, sensation
§ PLOF
§ Concurrent MSK conditions?
§ Risk of Contracture?
§ LOS- muscle atrophy
§ Neuromuscular:
§ What factors influence this screening?
§ Health condition – did it involve the CNS or
PNS causing primary impairments?
§ Age related changes
§ Impact of LOS- immobility
§ Multi-system exam for more complex
patients
Decision Making Time
§ Is this patient appropriate for a full PT
examination?
§ If NO…Now what?
§ Who do you communicate this with?
§ How do you document?
§ When will the patient be appropriate?
§ If YES….Then
§ Select appropriate test and measures
§ Select outcome measures as
appropriate
§ Begin formulating anticipation of
response to activity
§ Begin hypothesizing potential
discharge destination
Decision Making Time
Patient IS appropriate for PT exam:
§ Select appropriate test and measures
§ Select outcome measures as appropriate
§ Begin formulating anticipation of response to activity
§ Begin hypothesizing potential discharge destination
Examination
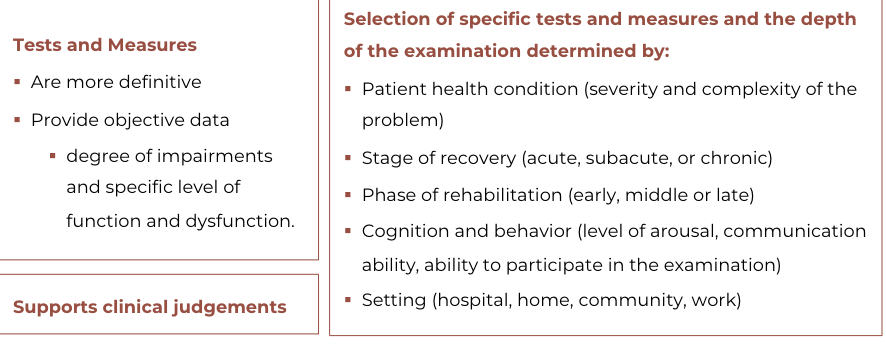
Examination : Selection of
Tests and Measures
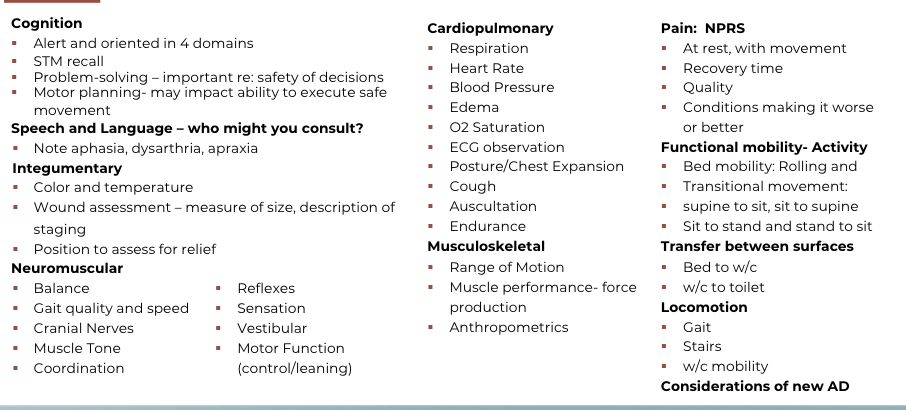
Cognition
§ Orientation:
§ Name
§ Current location
§ Month/day/year
§ Reason for admission
§ STM: Ask patient to repeat your name and discipline
§ Glasgow Coma Scale
§ Mini-Mental State Examination
Integumentary
§ Color and temperature
§ Positioning for relief
§ Wound assessment
§ location
§ size
§ classification
Neuromuscular
§ Cranial Nerves
§ Muscle Tone
§ Coordination
§ Reflexes
§ Sensation
§ Vestibular
§ Motor Function
Cardiopulmonary
§ Respiration
§ Heart rate
§ Blood pressure
§ Edema
§ O2 saturation
§ ECG observation
§ Posture/Chest expansion
§ Cough
§ Auscultation
Musculoskeletal
§ Range of motion
§ Muscle performance
§ Anthropometrics
Pain Assessment
§ Intensity
§ Quality
§ Location
§ Pain Scales
§ Numerical Rating Scale
§ Wong-Baker FACES
§ FLACC Pain Scale
FLACC Pain Scale
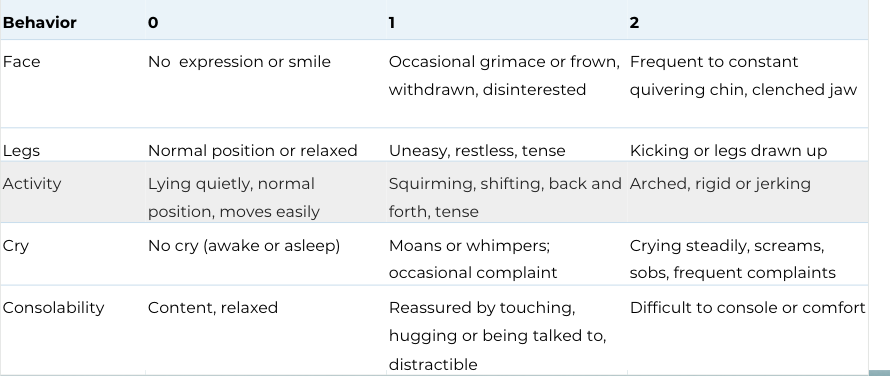
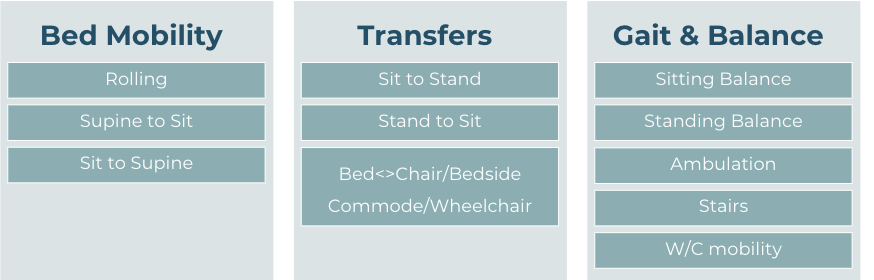
Functional Mobility Examination
Patient's Response
Constantly monitor the patient's response to
activity
§ Vital sign response
§ Emotional/behavioral response
§ Communication response
Guides progression of plan of care
Informs decisions about interventions
Documentation for patient NOT
appropriate for full exam
Patient evaluation attempted, however after reviewing medical chart,
communicating with nurse, and reviewing the patient’s systems, pt was displaying
uncontrolled heart rate and rhythm, effortful breathing, and complaint of dizziness
and headache. Pt did not appear medically stable therefore eval deferred at this
time. Plan to reattempt
Communication for patient NOT
appropriate for full exam
Verbally communicate with the RN
§ Uncontrolled heart rate and rhythm
§ Effortful breathing
§ Headache
§ Dizziness
Request pt status be assessed by RN and/or physician
Barriers to Implementation
Too time consuming for patients to complete
Too time consuming for therapists to analyze
Too difficult for patients to complete independently
Outcome Measures in
Acute Care
May only be performed at intake
Often concise
Used to assist with discharge planning
Acute Care Specific Outcome
Measures
Activity Measures for Post Acute Care (AM-PAC)
AM-PAC “6 clicks”
Acute Care Index of Function (ACIF)
Activity Measure for Post Acute
Care (AM-PAC)
Assesses activity limitations based on ICF framework
Measures three domains
Cognitive
Activities of Daily Living
Basic Mobility
Patient or clinician report
AM-PAC “6 clicks”
Shortened form of AM-PAC
Assesses 6 mobility domains
Bed mobility
Sit to stand
Supine to sit
Seated transfers
Ambulation
Ascending stairs
Helps predict discharge destinations
Acute Care Index of Function (ACIF)
Assesses basic mobility, metal status
impairments, and activity limitations
20-items
Score: 0 to 1
Assists in discharge planning
Outcome Measures: Balance and Fall Risk
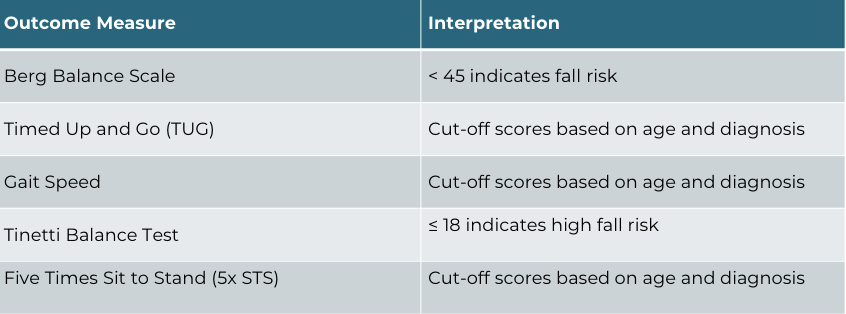
Outcome Measures: Cognition
Glasgow Coma Scale
Assesses
consciousness
3 items (eye response,
verbal response,
motor response)
Score 3 – 15
<9 indicates severe
brain injury and coma
states
Mini-Mental State
Examination
Assesses 5 cognition
functions (orientation,
registration,
attention, calculation,
recall, and language)
11 items; Score 0 - 30
<24 indicates
cognitive impairment
Evaluation
Organization and analysis of
data collected from the
initial examination
Leads to the
development of a
problem list
An accurate evaluation
supports the therapist’s
ability to determine a
diagnosis and prognosis and
develop a plan of care
Example Problem List for Acute Care
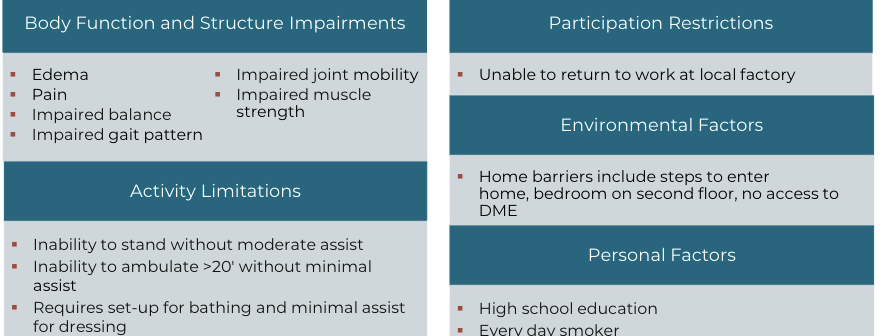
Goals of Acute Care Physical Therapy
Facilitation of transition to next level of care
Promotion of recovery
Minimize functional limitations and disability
Safety and fall prevention
Reduction of length of stay
Example Goals in Acute Care
STG:
In 3 days, patient will be able to perform sit to stand from EOB with min A or less while
maintaining sternal precautions to reduce risk of re-injury.
In 3 days, patient will be able to maintain static standing balance at EOB with no UE
support for 2 minutes with SBA to reduce risk of falls.
In 3 days, patient will be able to ambulate 50 ft across level ground with min A to improve
independence
discharge plan

successful d/c plnning

PT important role

entry level d/c planning
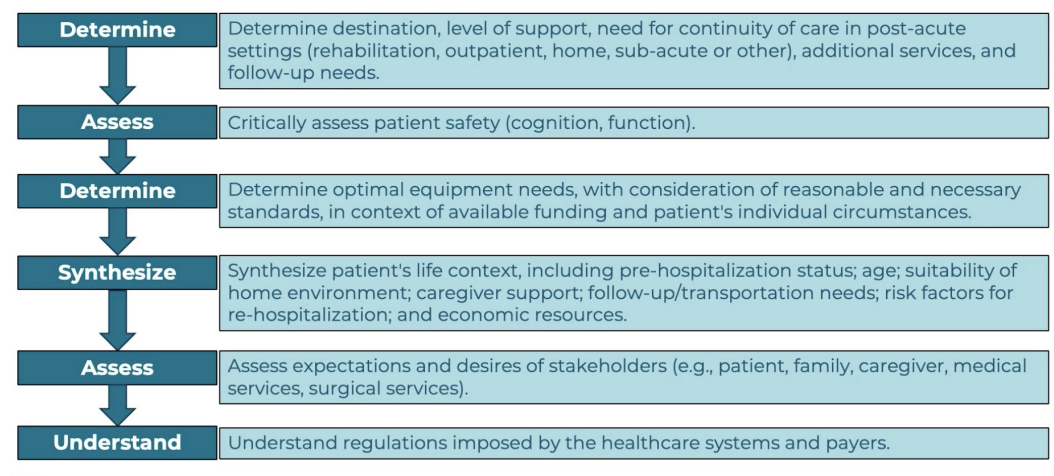
possible recommendations
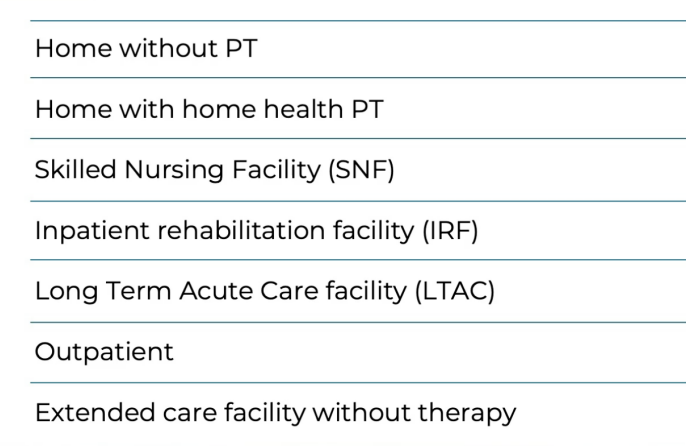
home health

homebound criteria
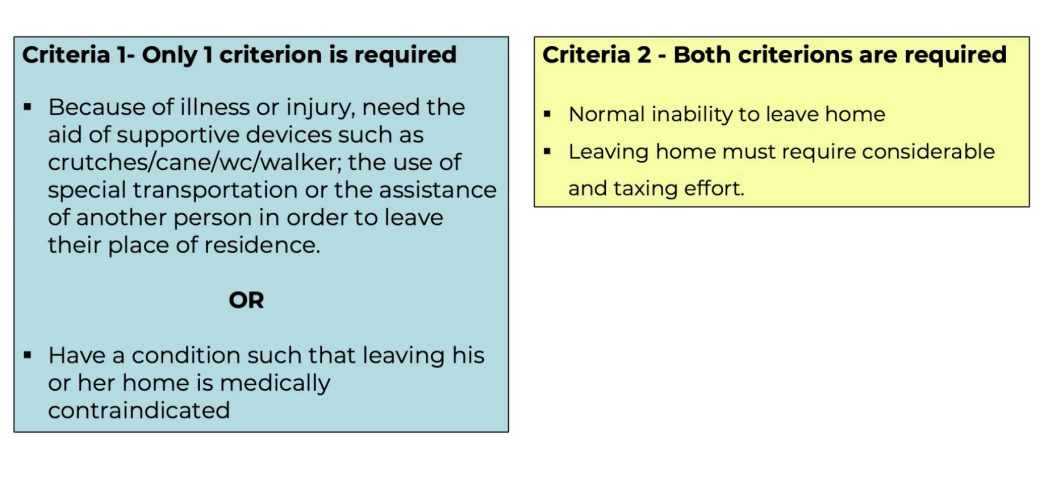
snf

homebound criteria from snf
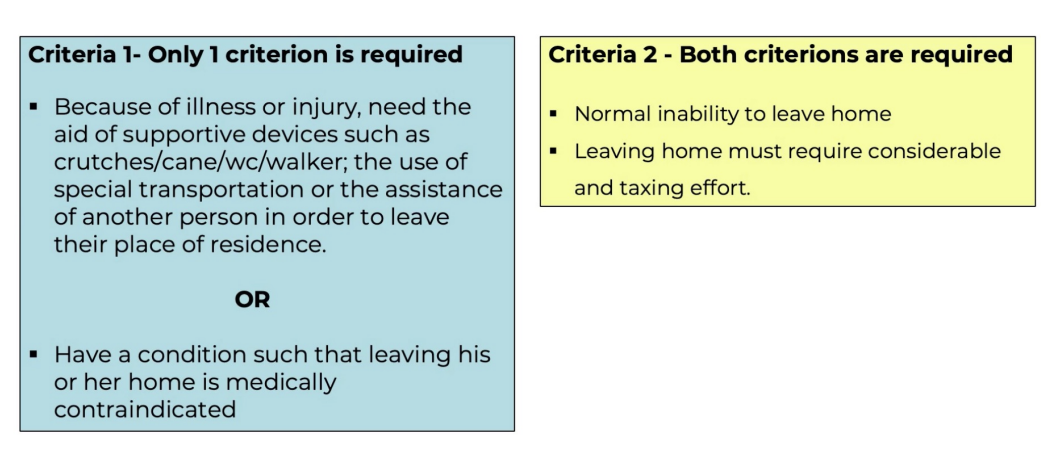
irf

ltac

op

other recs

Reviewing Medical Chart
§ Activity Orders
§ Precautions
§ Weight Bearing: LE/UE
§ Sternal
§ Spinal
§ Fall Risk
braces
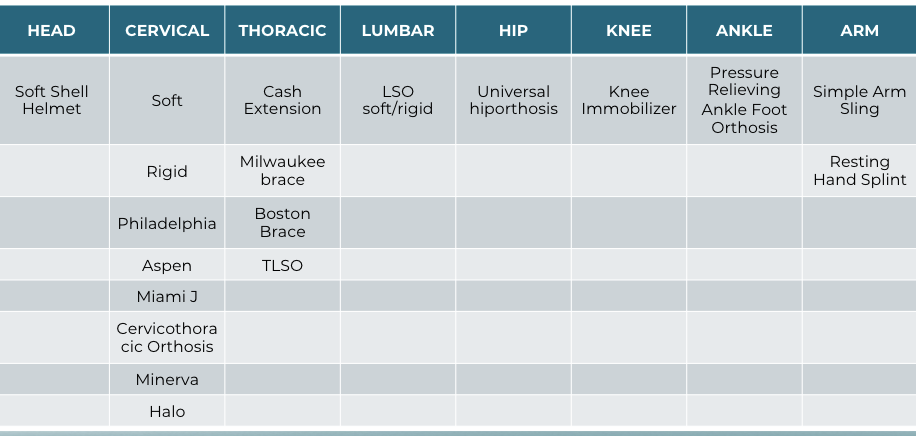
Cervical Orthoses: Minimal to Moderate Control
§ Soft Collar – whiplash, cervical weakness
§ Rigid SOMI collars (ex. Philadelphia, Aspen, Miami-J)
§ Stable cervical fractures; limits flex, ext, lateral flexion and rotation
Cervical Orthoses: Maximum Control
Halo
§ Fixed to skull with 4 screws
§ Donned following facet subluxations and dislocations
that have been reduced with traction
Minerva
§ Non invasive
§ Donned following cervical fractures
Thoracic Orthosis
Cash extension brace
§ Donned following a compression fracture
Jewett
§ Restricts flexion and encourages hyperextension
§ Limits rotation and SB to some degree
§ Improper adjustment could lead to pressure on throat or genitals in sitting
Knight-Taylor
§ Rigid frame worn posteriorly
Molded Thoraco-Lumbo-Sacral Orthoses (TLSO)
§ Maximal stability to trunk
§ Limits all planes of motion
§ Thigh extension (spica) for immobilization at and below L5
§ At or above C8- shoulder outriggers or cervical extension
Hip Abduction Orthosis
§ Used for total hip revisions or to ensure hip precautions (i.e. patient with dementia)
Characteristics of an Acute IRF
Intensive, round-the-clock care
Typically provided in a hospital-based rehabilitation facility
Licensed as a hospital
Nurse to patient ratio typically is 1:5 or 1:6
Physiatrist (DO/DM) sees patients daily
Therapy in two or more disciplines at minimum 15 hours per
week
Reasonable expectation of significant functional
improvement
Goals of IRF
Promote Independence
Prevent Complications
Patient Diagnoses: IRF
Severe injury
Post surgery
Post illness
Rehabilitation units include:
Stroke/CVA
Spinal cord injury (SCI)
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
Amputation/Medical complex
History After a Chart Review
Reconciliation of charts
Confirmation with patient and/or family
Focuses the review of systems with patients
Communication
Screening
Communication ability
Affect
Language
Cognitive ability
Learning preferences
Review of Systems –
Major Body Systems
Cardiopulmonary system
Endocrine system
Gastrointestinal system
Hematologic/lymphatic
system
Immune system
Nervous system
Musculoskeletal system
Integumentary system
Genitourinary
Patient Interview
Initial interview > shared decision making
Identify the nature and history of the current problems
Engage the patient in treatment planning
Identify desired outcomes in terms of functional activities
Identify environmental conditions where activities occur
Identify available social supports
Identify patient’s knowledge of current condition and
potential disablement risk factors
Systems Review
Cardiovascular: shortness of breath, chest pain or pressure, irregular heartbeat, leg cramps,
measures of heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, pedal pulses
Pulmonary: shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, cough, wheezing, breathing pattern,
respiratory rate, oxygen saturation
Integumentary: skin pallor/color, temperature, integrity, pliability, scar formation
Endocrine: fatigue, recent weight loss or gain, blood sugar anomalies
Neuromuscular: numbness, pins and needles, weakness, dizziness, problem with
balance/falls, headaches, loss of consciousness, visual changes, gross sensory or gross reflex
changes
CARE Tool
Inpatient Rehabilitation
Facility Admission
Administrative
Prior level of function
Pertinent discharge information
Hearing and speech
Cognition, mood, pain
Functional abilities and goals
Diagnosis
Bowel and Bladder function
Health conditions
Nutritional status
Skin conditions
Medications
CARE Tool Functional
Domains
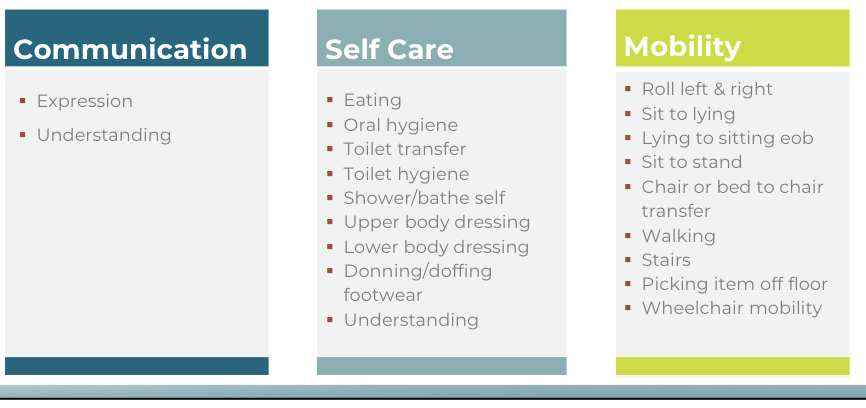
There are two sections for
health professionals to
complete
Prior level of function
Admission/goals/discharge
CARE Tool Scoring – Prior level
of function
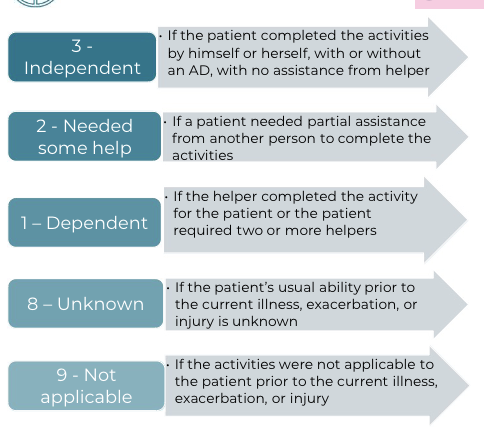
Mobility CARE Scoring
Admission/Goals/Discharge
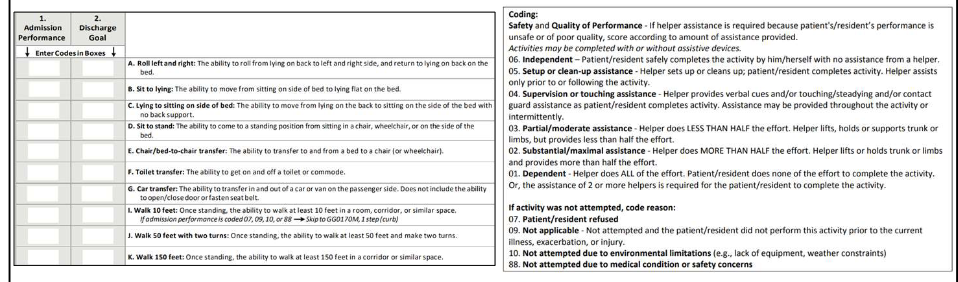
CARE Tool Scoring
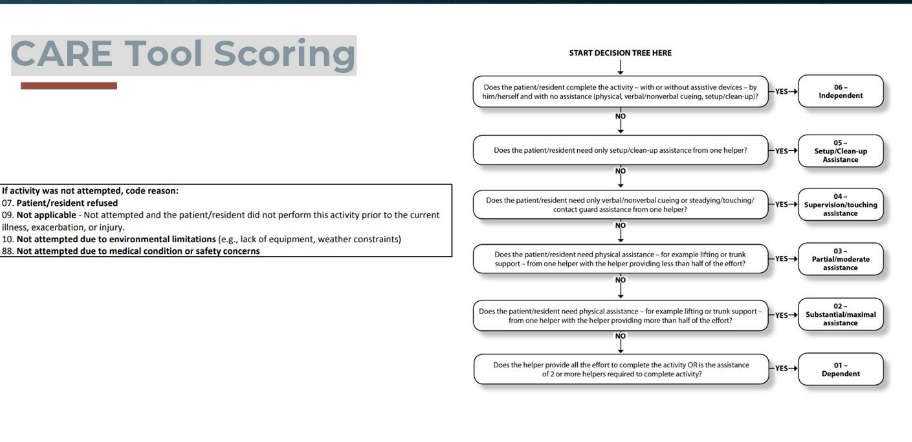
Examination Progression
PT Objective Examination
sensation, strength, range of motion
transfers
gait or wheelchair
All of Section GG: scored within three (3) days
of admission
Constantly evaluate patient safety, insight,
and judgment
Sensation, ROM, and Strength Testing
Review techniques from previous coursework
Overall muscle grade for major motions
i.e. hip flexion 4/5 or knee extension 3/5
Overall sensation grossly intact/impaired
Include level that sensation is impaired, i.e. stocking
glove pattern to popliteal space
Overall range of motion intact/impaired with estimation
i.e. knee flexion contracture ~10-15 degrees
Insight and Judgement

QRP and Section GG of the IRF PAI
Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Report Program Measure
(IRF QRP)
IRF Patient Assessment Instrument (IRF PAI)
Multi-page document for all disciplines to contribute to
Reported to Medicare
Influences payment/reimbursement and scores
Also Known As: The CARE tool or Quality Indicators (Qis, QI codes)
Section GG for Physical, Occupational, Speech Therapists as well
as nursing staff
Example of Section GG: Functional Abilities

Functional Independence Measure (FIM)
Measures level of disability
Administered by observation or interview
Determine functional status based on level of assistance required
18 items
13 motor tasks
5 cognitive tasks
Scoring
Minimum: 18
Maximum: 126
FIM Scoring Language
7 Complete Independence (no helper, timely and safely)
6 Modified Independence (uses a device with no helper, or needs a bit of extra time/safety)
5 Supervision (patient completes 100% physical burden of care, does require eyes on and verbal
cues, whether intermittent or constant)
4 Minimal Assistance (patient completes at least 75% of burden of care)
3 Moderate Assistance (patient completes at least 50% of the burden of care)
2 Maximal Assistance (patient completes at least 25% of the burden of care)
1 Total Assistance (patient completes less than 25% of the burden of care)
Also called not testable, or requires a second person
Section GG Scores

Section GG Items

Section GG Items Continued
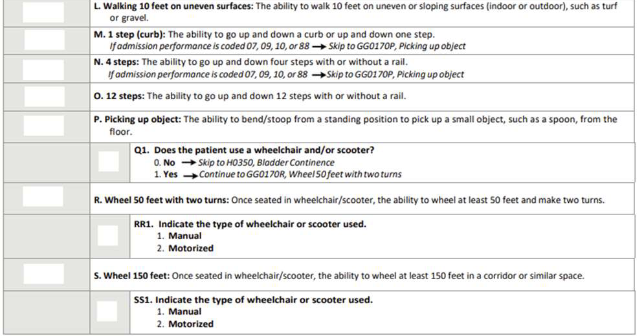
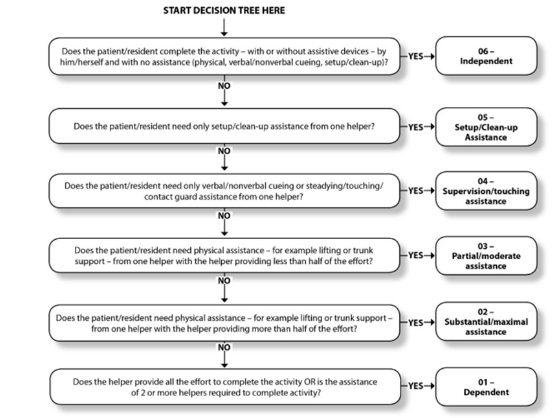
Decision Tree
Section GG