L3: SDS-PAGE, Isoelectric Focusing, 2D gel electrophoresis, Probe
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What type of technique can be conducted to reveal how much protein was in an original sample from a mixed protein sample
Protein Assay
What type of protein gel can be done on a sample of different proteins in cells?
SDS-PAGE
more proteins = more bands in gel
What is done to prepare a protein sample?
cells are ground up to release proteins
Using Fluorescent Revealers or a Tag to bring the protein of interest to the surface and hide the other proteins we are not interested in.
How is a protein of interest identified?
Antibody is required to detect the specific protein, revealed using a Western Blot
What does an SDS-PAGE protein gel do?
Separates proteins based on size/molecular weight
What type of gel is used in SDS-PAGE?
Polyacrylamide Gel
What is Isoelectric Focusing?
Technique that separates proteins based on differences in their Isoelectric Point (pI), which is related to charge
What is the Isoelectric point (pI)?
The pH at which a protein or amino acid has NO NET Electrical Charge and is least soluble
allowing it to precipitate out of solution
What type of gel is used in Isoelectric focusing?
Polyacrylamide Gel
What happens to an amino acid when it is dissolved in water
The amino acid takes an ionic form as water breaks covalent bonds, creating H+ and OH- ions
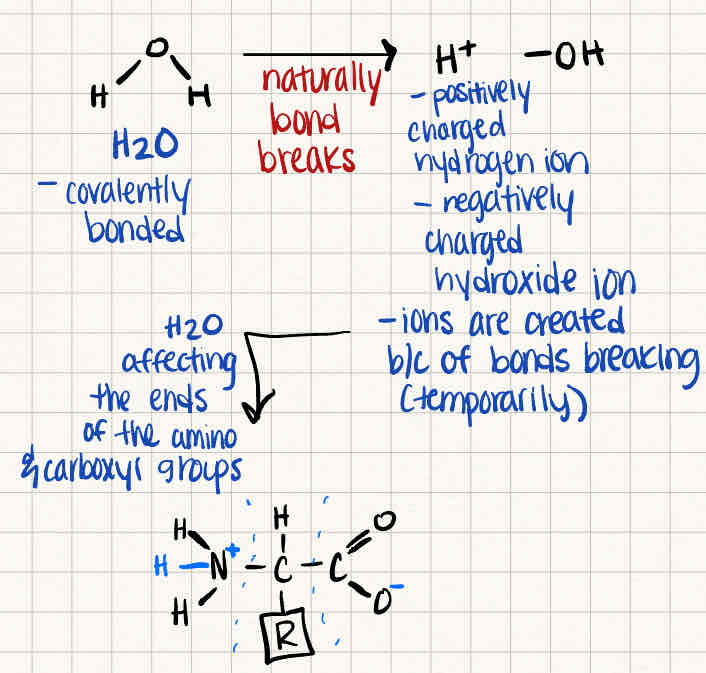
Draw a generic amino acid
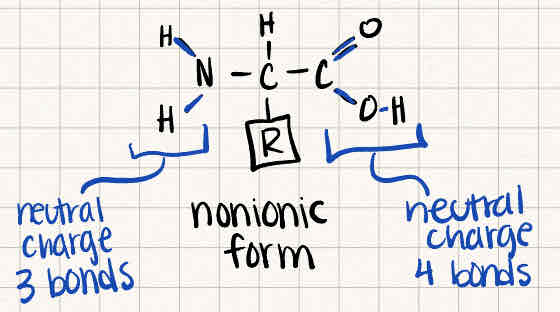
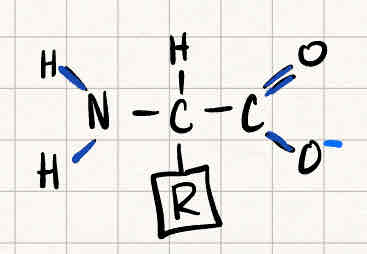
What happens to amino acids in BASIC conditions? (NaOH)
The amino group stays the same, while the carboxyl group loses H+ to form water, leaving oxygen negatively charged.
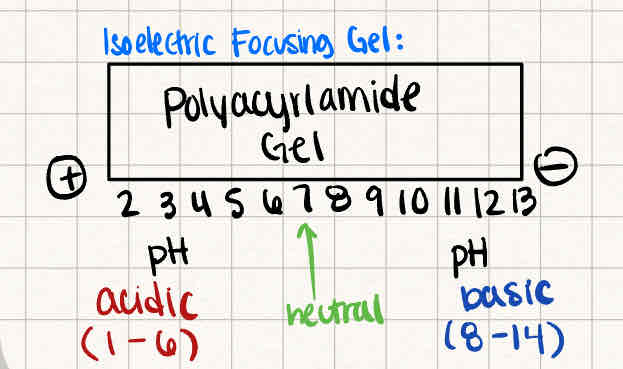
What are the charges in a Polyacrylamide gel during Isoelectric focusing?
Acidic pH (1-6) near the positive electrode
Basic pH (8-14) near the negative electrode
How are two amino acids linked together
Peptide bond
releasing H2O as a byproduct
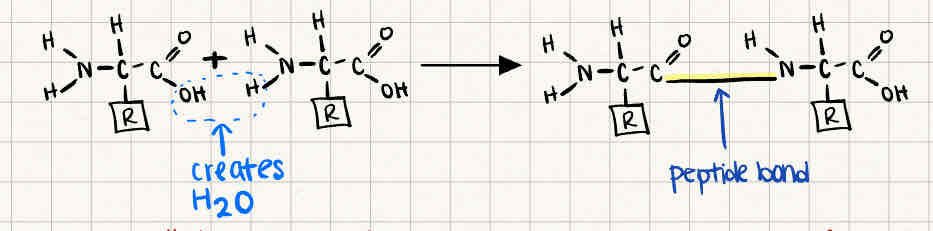
What happens if an amino acid that is basic is loaded at the pH 7 well in the Polyacrylamide gel and is NOT at its Isoelectric point?
It will migrate toward the negative electrode because of a positive charge on the nitrogen
there would be OH- groups floating around more than H+ because of the solution migrating to basic above pH 7
When pH increases, OH- increases resulting in a H+ leaving the nitrogen to make it a neutral charge
What happens to a protein when it reaches its Isoelectric point in a gel?
It becomes electrically NEUTRAL and stops migrating
How does the Isoelectric point technology help separate proteins
Based on where they achieve a neutral charge, by adding or removing protons
If 3 bands appear at pH 4, 5, and 9 on a Polyacrylamide gel, how many proteins are in the sample?
3 proteins, each sharing the same pI value.
What is SDS-PAGE used for after Isoelectric focusing?
To separate proteins based on molecular weight
a single band can contain proteins with the same pi but different molecular weight
What are the steps of 2D gel electrophoresis
Run Isoelectric focusing gel (IEF) with Polyacrylamide gel
Soak the IEF gel into SDS
Load the IEF gel as a source of proteins for an SDS-PAGE
Run SDS-PAGE
Why is IEF run with a Polyacrylamide gel during 2D gel electrophoresis?
To allow the proteins to separate based on pI
In an SDS-PAGE how do proteins migrate on the gel?
Based on molecular weight
How do proteins migrate on an SDS-PAGE gel with the Polyacrylamide gel strip ?
Based on Isoelectric points (pI)
How is data represented in 2D gel electrophoresis
Each protein is represented by a spot, not a band
What does a spot on the SDS-PAGE gel indicate
Proteins with the same pI but different Molecular Weight will form separate sport
What is the purpose of a kDa ladder in SDS-PAGE
It helps estimate the molecular weight of proteins
True/false: a single band can have multiple proteins that share the same molecular weight
True
A 2D gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate proteins based on what two things?
Molecular weight (MW)
Isoelectric point (pI)
How is molecular weight separated on a 2D gel electrophoresis
Separated by SDS-PAGE based on size
How is pI separated on 2D gel electrophoresis?
By Isoelectric focusing gel which separated proteins based on their pI
What is a way you can study ONE PROTEIN you are specifically interested in from a mixture?
Using a Probe
What is a Probe?
Tool used to help identify, tag, or highlight a protein of interest
What are the two functions of a Probe
Bind specifically to your interest
Way to reveal itself by using chemical reactions such as:
fluorescent signal
Radioactive activity
Enzymatic reaction
How can a probe tag your protein of interest
By obtaining a chemical that can identify its specific shape
What can create a good foundation of creating a good probe to identify a protein?
Antibodies
When you get sick or injured, your body defends itself by sparking your immune system to create what 3 things?
Antibodies
T-cell activity
Inflammation
What are antibodies (immunoglobulins)?
Y-shaped proteins made of 4 polypeptides (2 long chains, 2 short chains) held together by disulfide bridges
They have a quaternary structure
Can be cell bound or free floating
What are the two regions of an antibody?
Hyper variable regions
Constant regions
What are the constant regions on an antibody
Similar across antibodies of the same class
How are antibodies made?
Made by B-cells
How are B-cells made?
Produced in the bone marrow
What do B-cells create?
Antibodies with unique hyper variable regions to target specific antigens
How do B cells differ?
Each B cell makes identical antibodies, with a specific hyper variable regions that differs from other B cells
What determines the effectiveness of B cells?
The more diverse the hyper variable regions, the broader spectrum of antigens the immune system can detect
What holds antibody chains together
Disulfide bridges connect the long and short chains
When a foreign protein is present from a virus or bacteria, the hyper variable region of it can interact with other epitopes of a foreign protein. What happens with the B cells when this interaction occurs?
The B cells will replicate (clonal expansion)
there are chemical and genetic signals that undergo mitosis to create many identical cells of the same type of antibody to fight the foreign protein
What is an advantage of the immune system
We can use animals that create immune cells to create antibodies of a particular protein
What happens when a rat is injected with your protein of interest?
It will create antibodies and B-cells
a booster shot is then added to make more B cells to create antibodies that will specifically bind to the protein of interest at a particular epitope