metabolism- fatty acids
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
how are FA activated
joined to CoA via Acyl CoA synthetase (uses ATP→AMP), THIOESTER BOND
irreversible via hydrolysis PPi
how is Acyl CoA shuttled into mitochondrial matrix?
adds acyl to carnitine via CPT-1, transported across via CAT, acyl-carnitine is converted back via CPT-2
what happens when carnitine transferases (particularly in pharoh isles) non functional? how is it treated
can’t breakdown FA, during sleep blood glucose plummets, neurological→ floppy, must wake up throughout night & give small feeds
what is the 4 steps of FA synthesis?
condensation, reduction, dehydration, reduction
how do FA synthesis and break down differ?
whilst they mirror processes, diff enzymes and diff locations used
how are FA oxidised?
Acyl CoA dehydrogenase (uses FAD)
how are FAs hydrated?
enoyl CoA hydratase
how are FAs 2nd oxidised?
L-3 hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (uses NAD)
what finally lyses FAs?
B-ketothiolase (only snaps off 2C)
how would you figure the no. ATP produced from a e.g 14C FA?
what types of enzymes do you need to deal with unsaturated FA?
isomerase, reductase
what if breaking down a odd chain FA?
need carboxylation, isomerisation
which cells prefer ketones to glucose
heart, renal medulla in kidneys, also useful to brain in fasting (can pass through BBB)
what is the most important site for ketone production?
liver
what are the 3 ketones produced from ketone synthesis?
hydroxybutyrate (more stable), acetone (a mistake), acetoacetate, via B-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
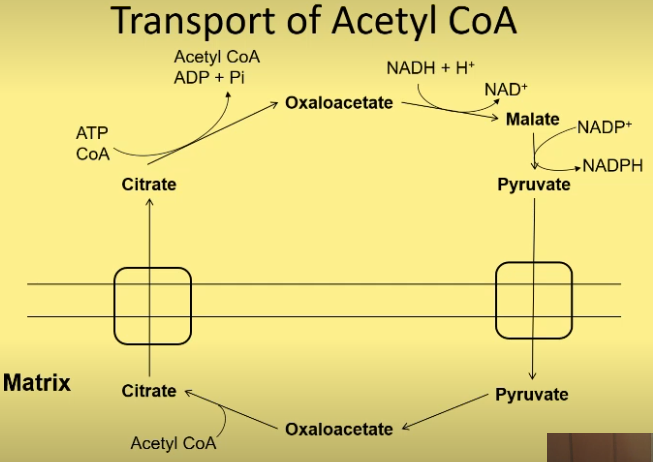
what shuttle does FA synthesis need to get Acetyl CoA out of mitochondria into cytoplasm?
convert oxaloacetate + acetyl CoA→ citrate, which moves across
→ oxaloacetate (uses ATP) + Acetyl CoA
then oxaloacetate → malate (uses NADH),
then → pyruvate (reduces NADP+), pyruvate transported across
converted back to oxaloacetate
what does acetyl CoA carboxylase do? (FA synthesis)
adds C to make 2C→3C (malonyl CoA), uses ATP
how is acetyl CoA carboxylase regulated
insulin activated (phosphatase dephosphorylates), glucagon, epinephrine deactivated (phosphate kinase phosphorylates)
what does acyl carrier protein do?
takes acyl off acetyl CoA, and malonyl off Malonyl CoA
what does Acyl-malonyl ACP condensing enzyme do
joins Acetyl ACP + Malonyl ACP and also condense (3+2=5-1=4) to produce acetoacetyl ACP
what does B-ketoacyl ACP reductase do?
uses NADPH, forms D-isomer from reduction of acetoacetyl ACP
what does 3-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase do?
dehydration, aims for saturated FA
what does Enoyl ACP reductase do?
reduction (uses NADPH)
how are fats transported?
albumin
how are FA that you produce? digested transported?
lipoproteins, names: chylomicrons (from intestine & r largest), VLDL (very low density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), HDL (high-density lipoprotein, smallest)
once FA are transported to peripheral tissues, where do chylo remnants, cholesterol etc. go?
liver to be recycled (cholesterol→ bile salts/ other)
what are the ‘good’ fats? bad?
none r good/bad, but high ration of LDLs and VLDLs compared to HDL is one of many risk factors for cardiac disease
what massive molecule is acyl carrier protein part of?
fatty acid synthase