The Skull
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Which bones make up the cranium?
frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid, parietal, and temporal
which bones of the cranium are paired (2 on each side)?
parietal and temporal
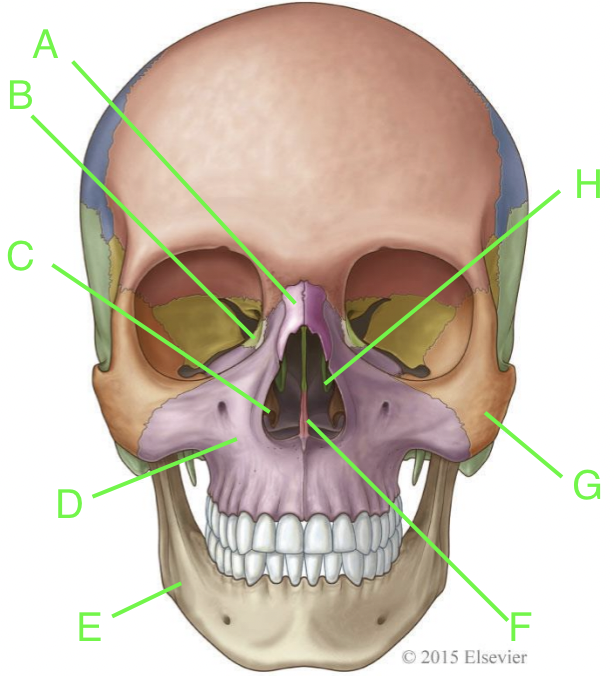
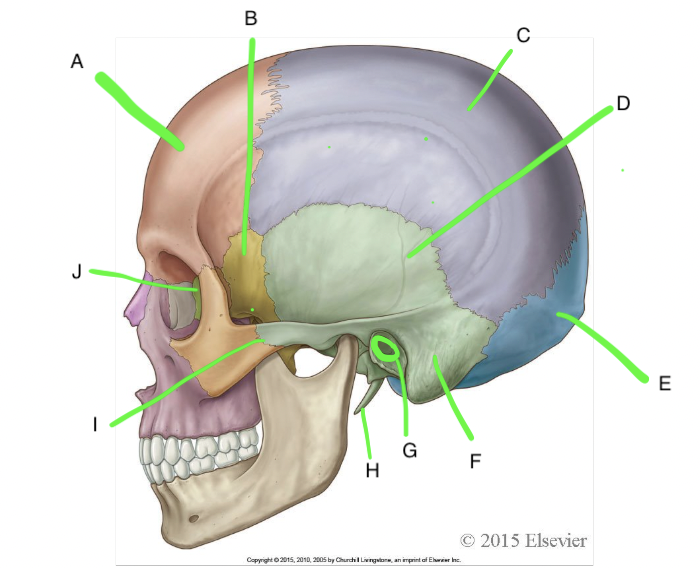
A
nasal
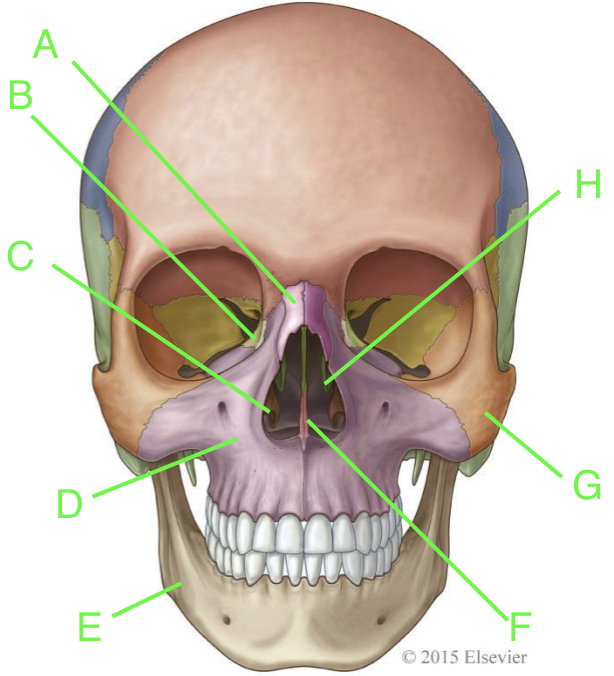
B
lacrimal
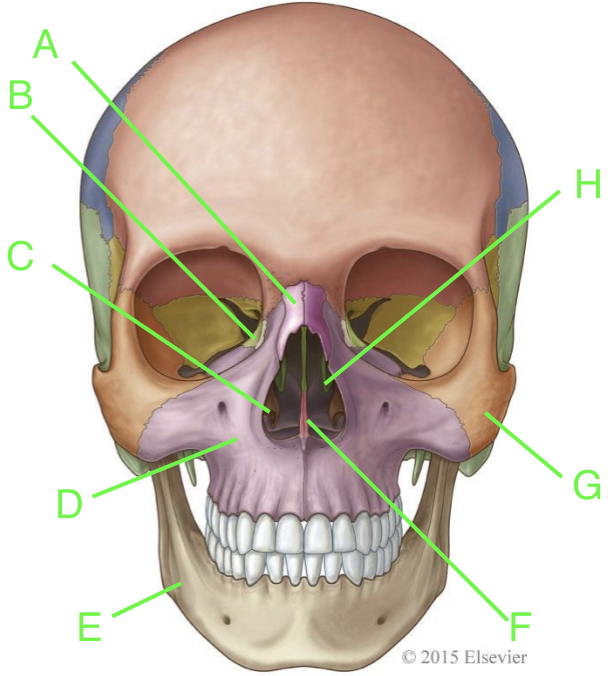
C
inferior nasal conchae
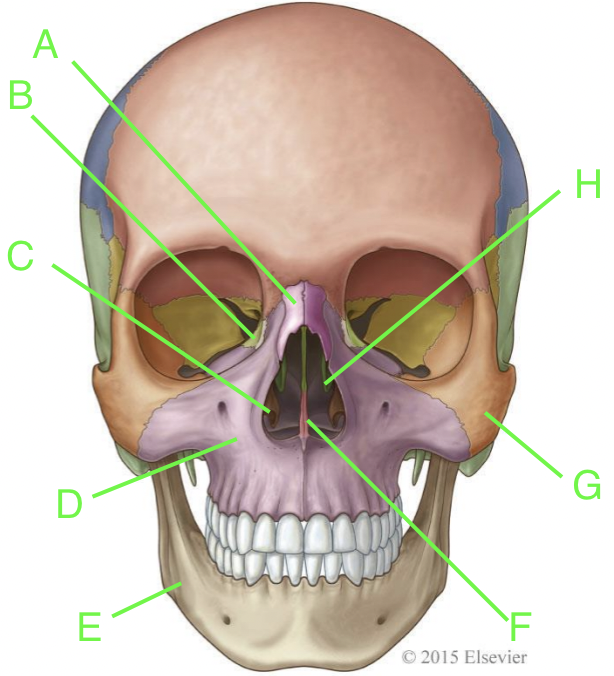
D
maxilla
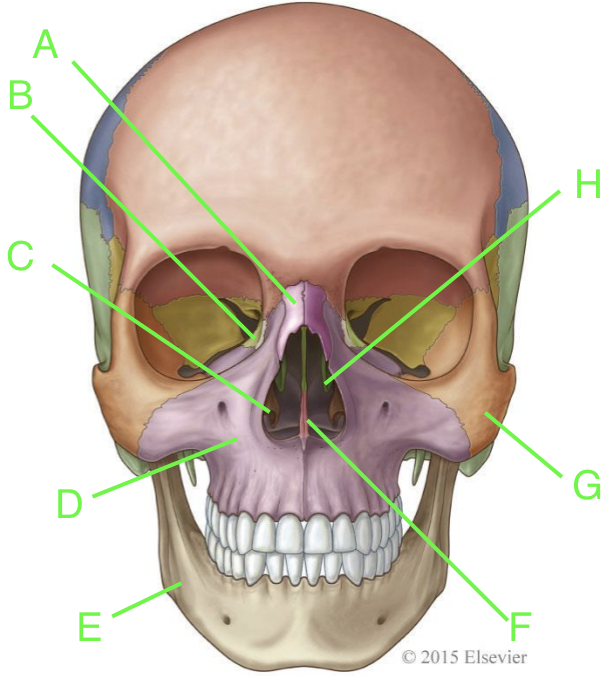
E
mandible
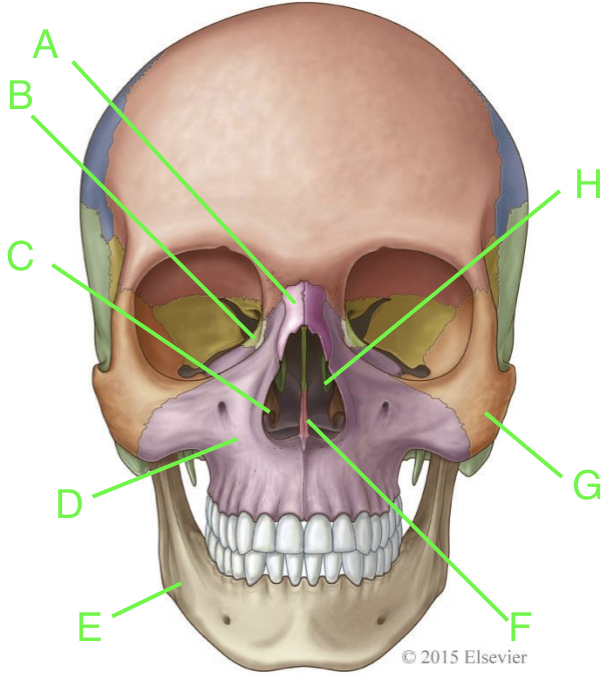
F
vomer
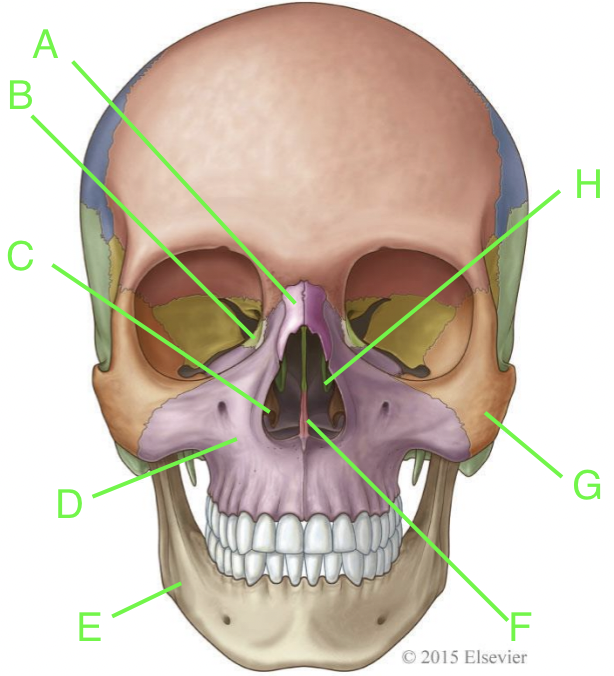
G
zygomatic
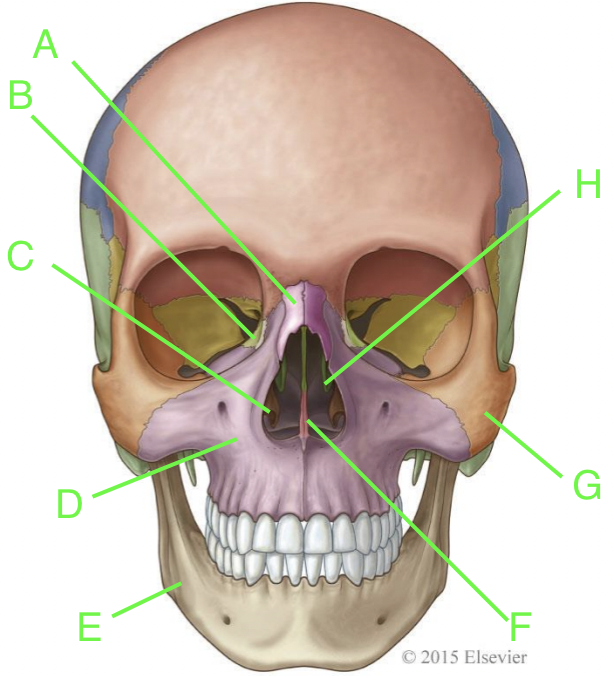
H
palatine
the unpaired bones of face include:
vomer and mandible
What are the bones of the face?
nasal, maxillae, zygomatic, lacrimal, palatine, inferior nasal conchae, vomer, and mandible
how many bones associated w/ the face?
14
how many bones form the cranium
8
how many total bones of the skull?
22
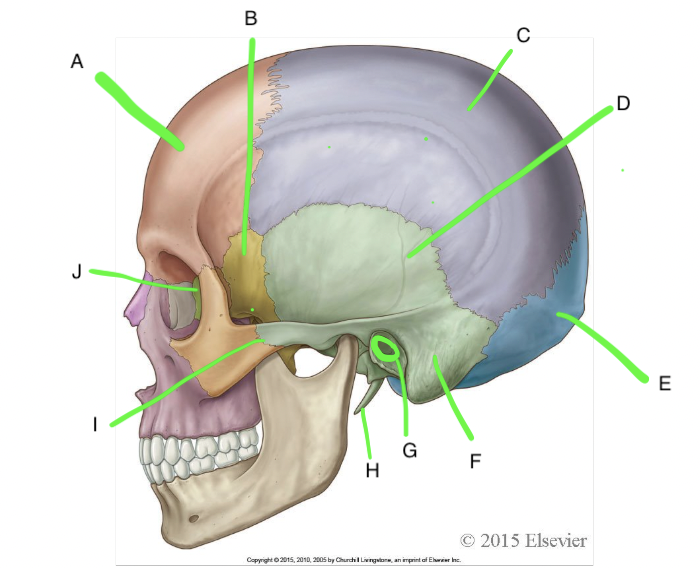
A
frontal
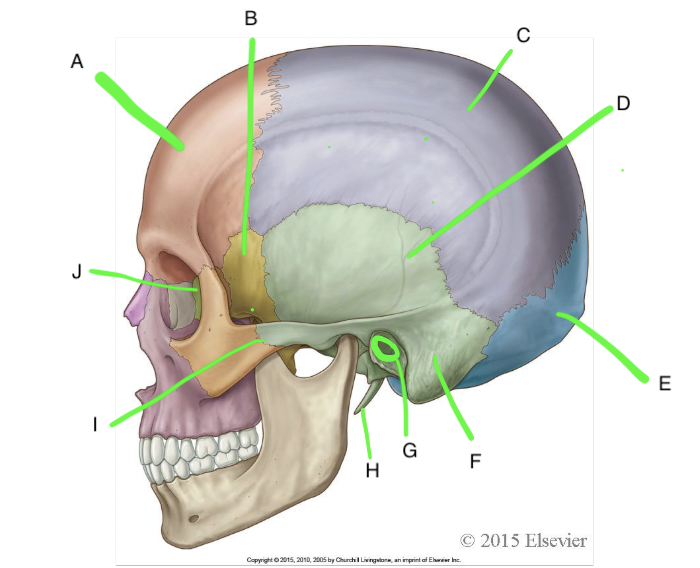
B
sphenoid
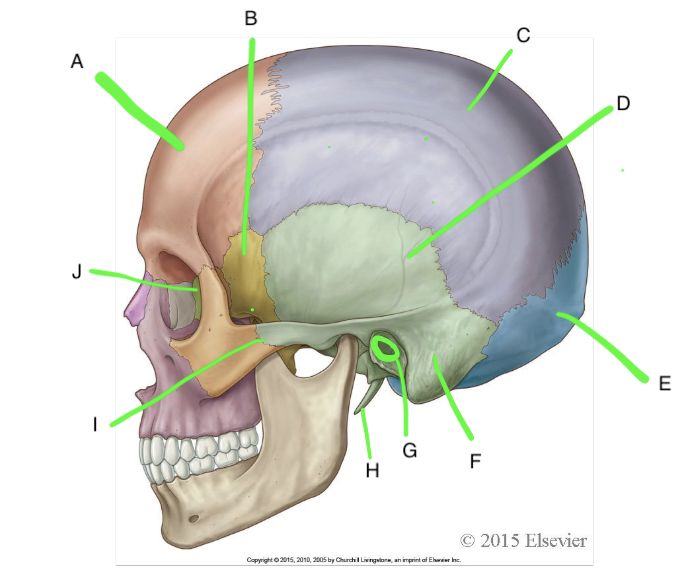
C
parietal
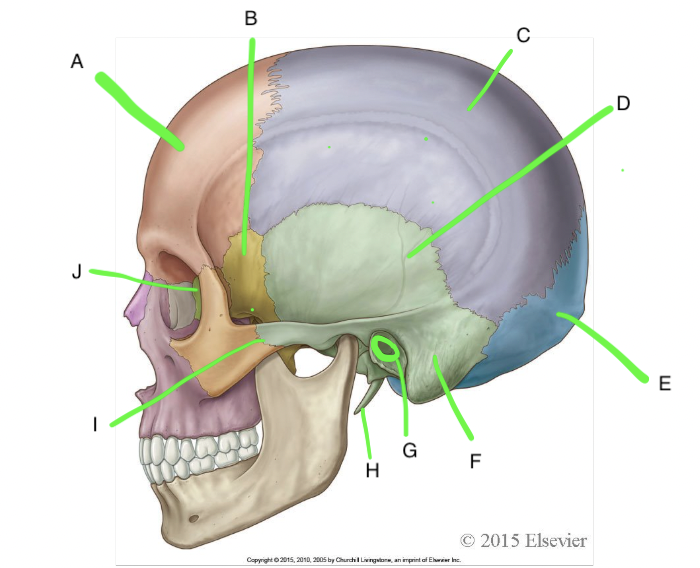
D
temporal
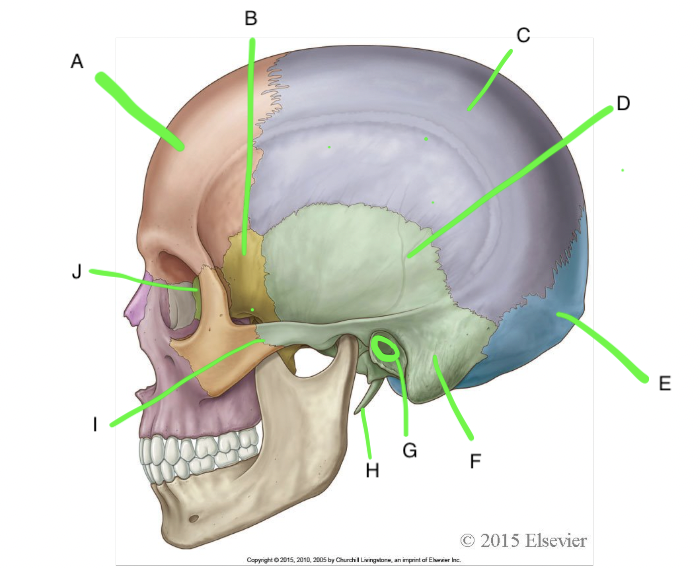
E
occipital
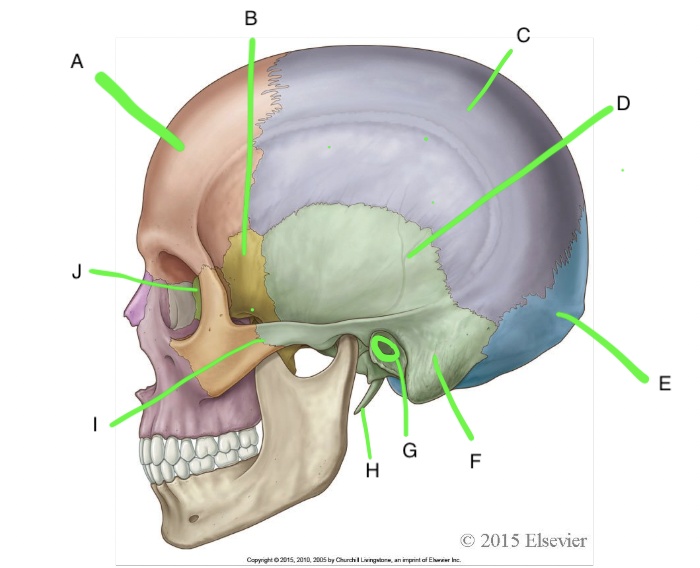
F
mastoid process
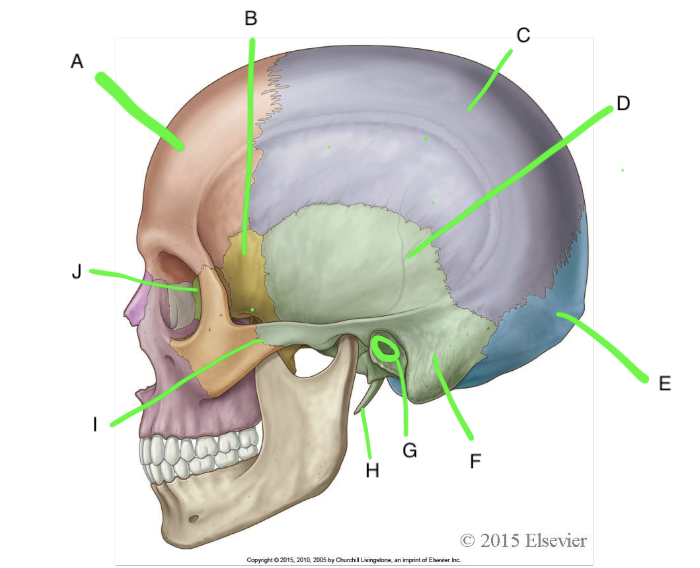
G
external acoustic meatus
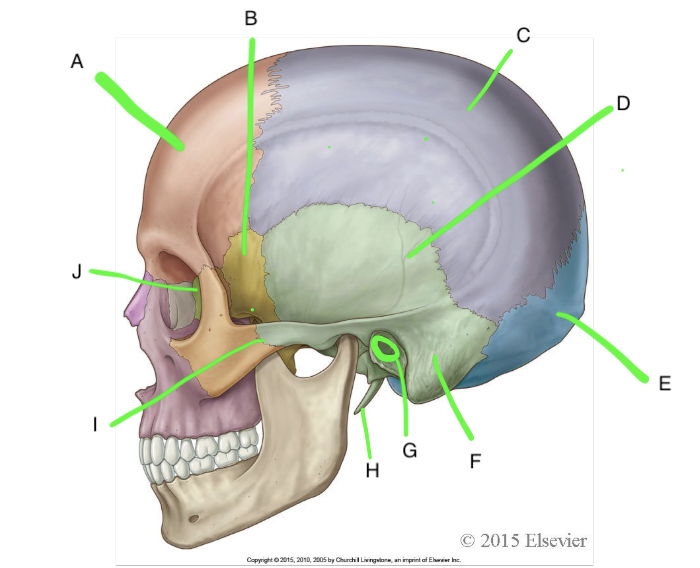
H
styloid process
I
zygomatic process of temporal bone
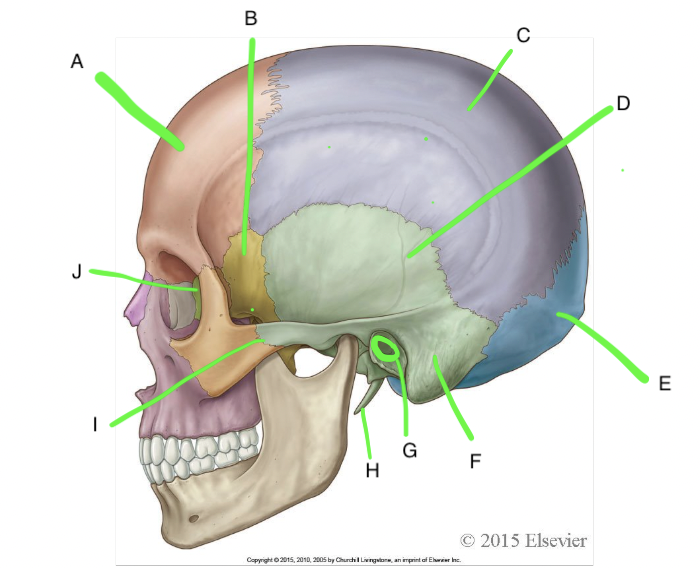
J
ethmoid
4 major sutures of the skull include:
coronal, sagittal, squamosal, and lamboidal
the coronal suture separates which two bones
frontal and parietal (2)
the squamosal suture separates which bones
parietal (2) and temporal
the sagittal suture separates which bones
the parietal bones
the lamboidal suture separates which bones
occipital and parietal (2)
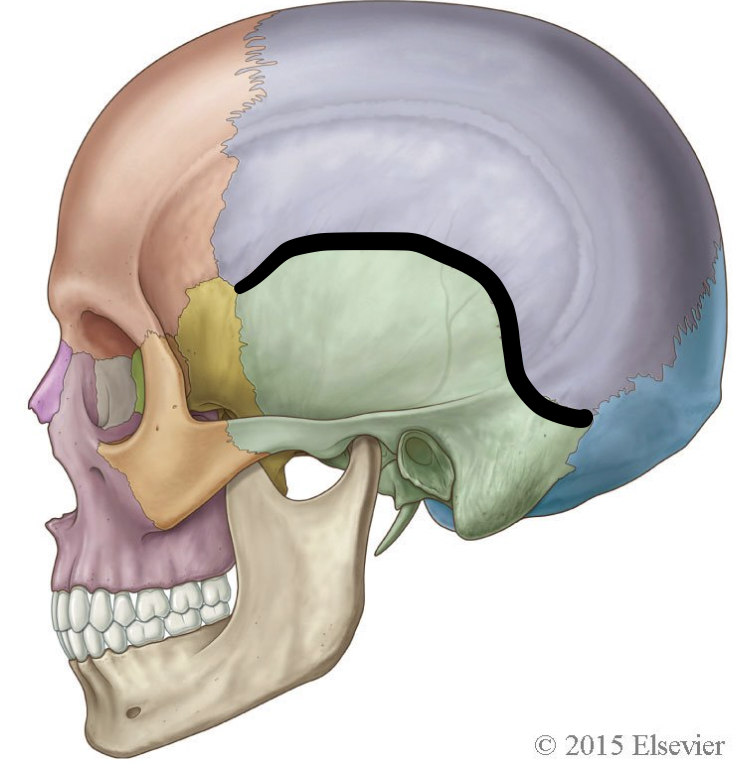
which suture is highlighted here
squamosal
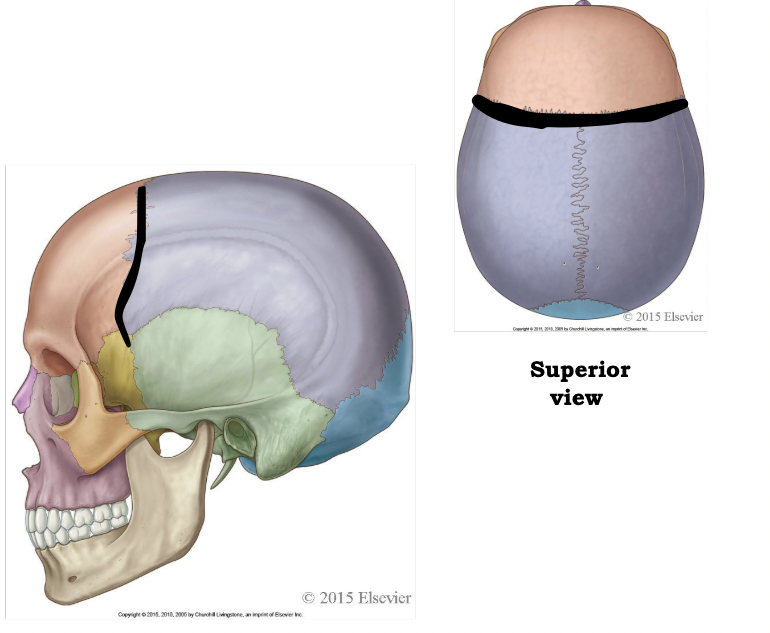
which suture is highlighted here
coronal
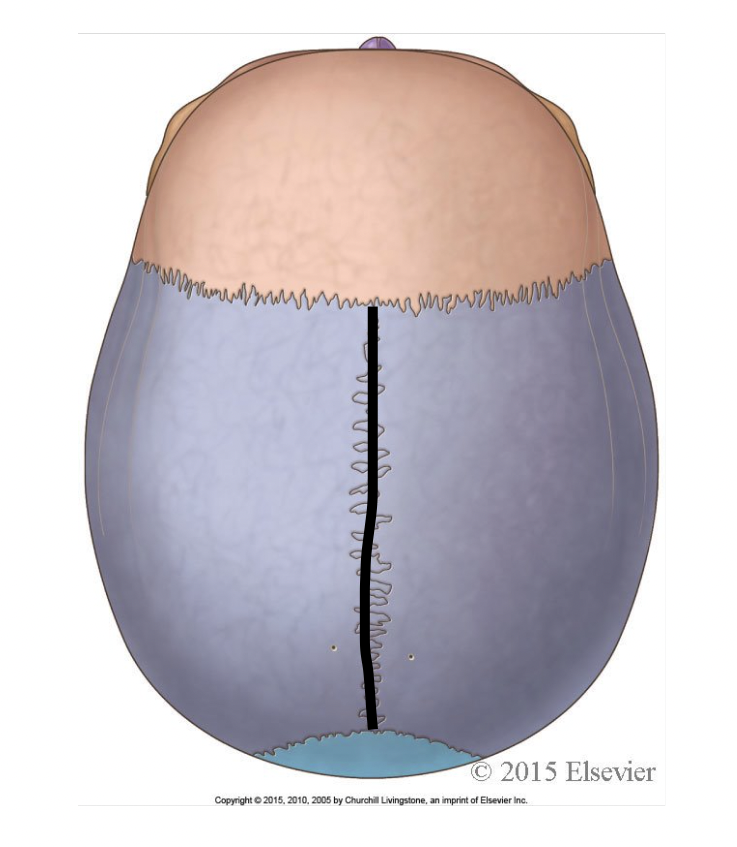

which suture is highlighted here
sagittal
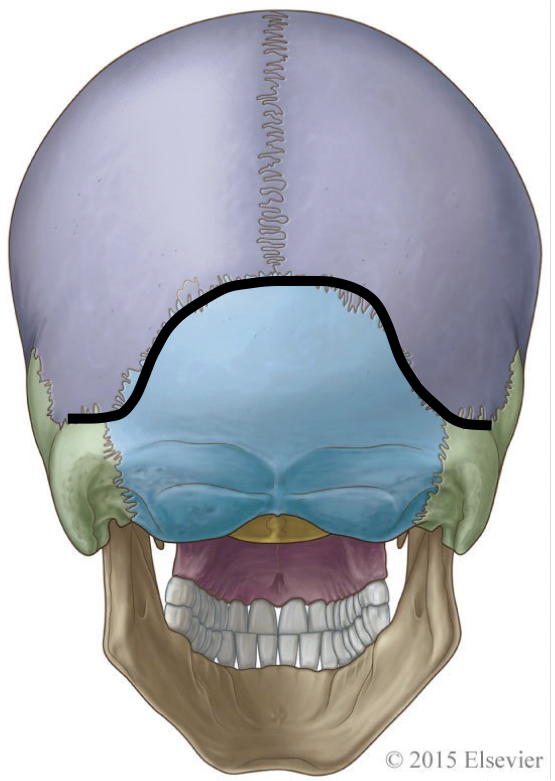
which suture is highlighted here
lamboidal
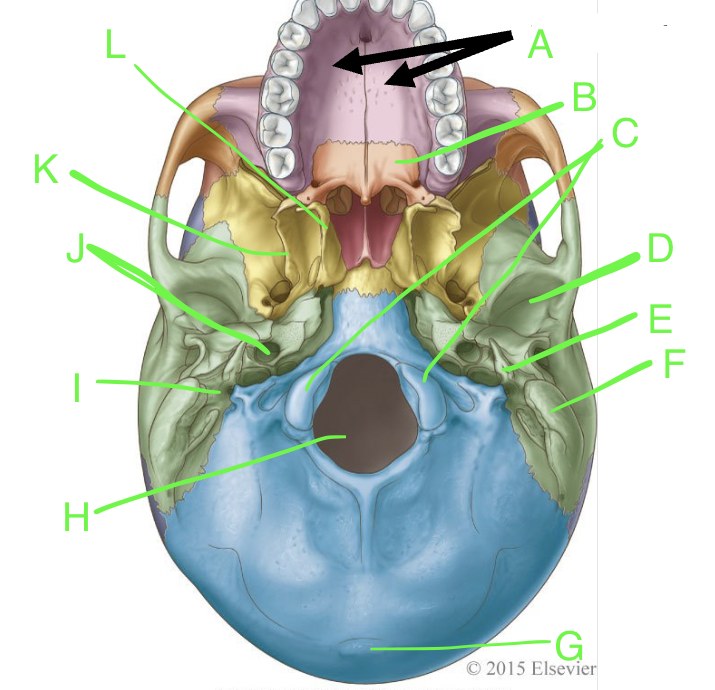
A
palatine processes
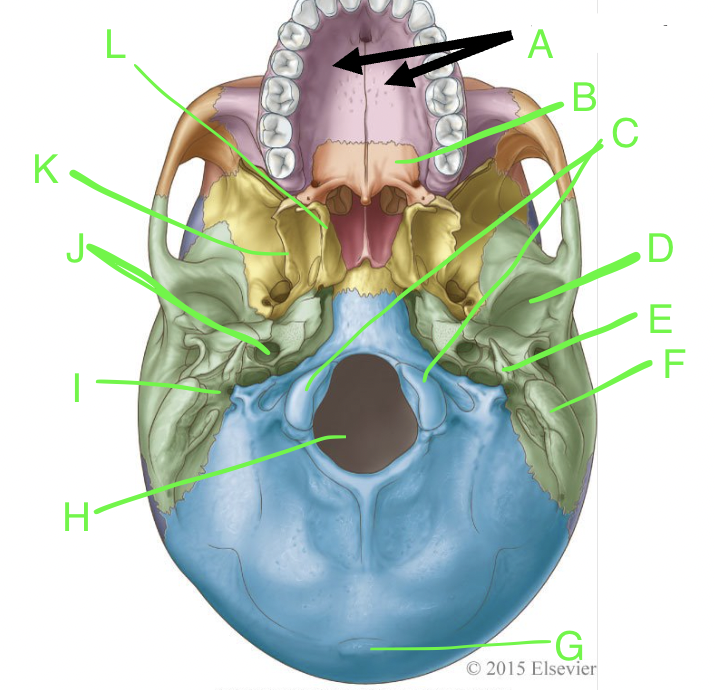
B
horizontal plate
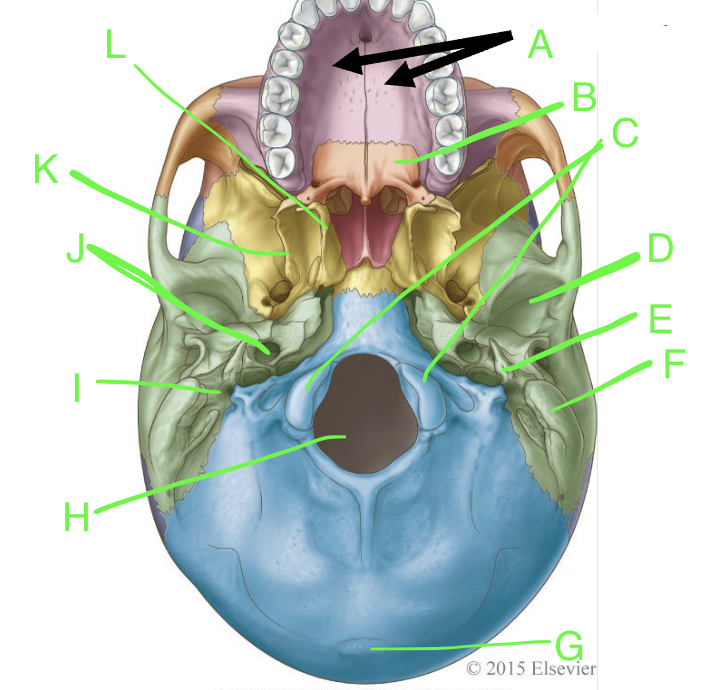
C
occipital condyles
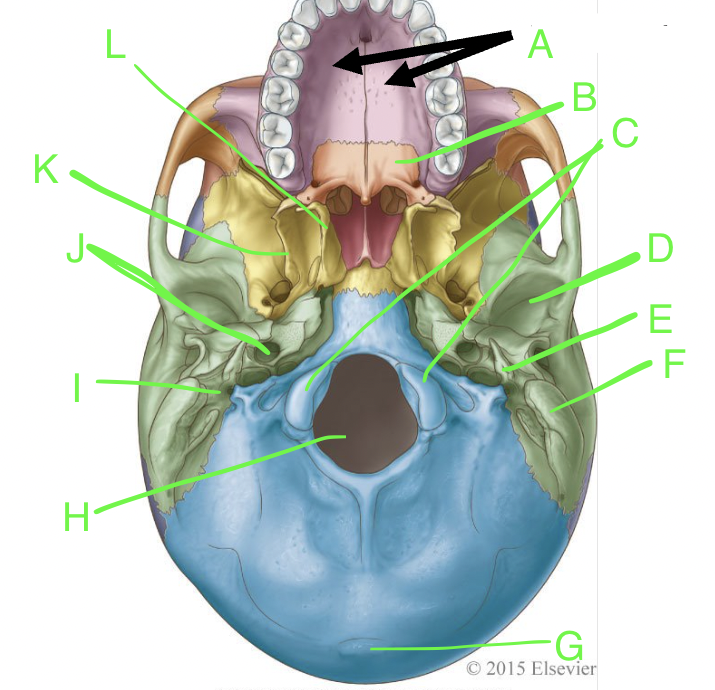
D
mandibular fossa
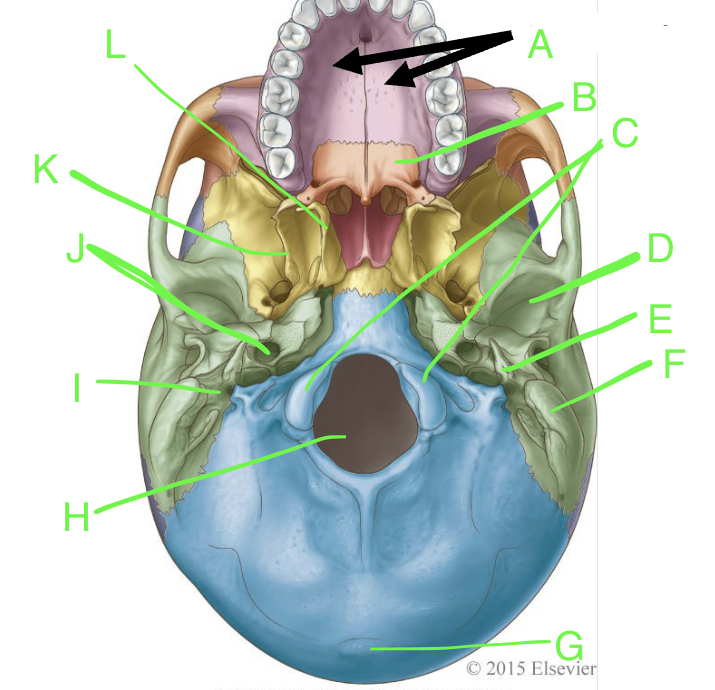
E
styloid process
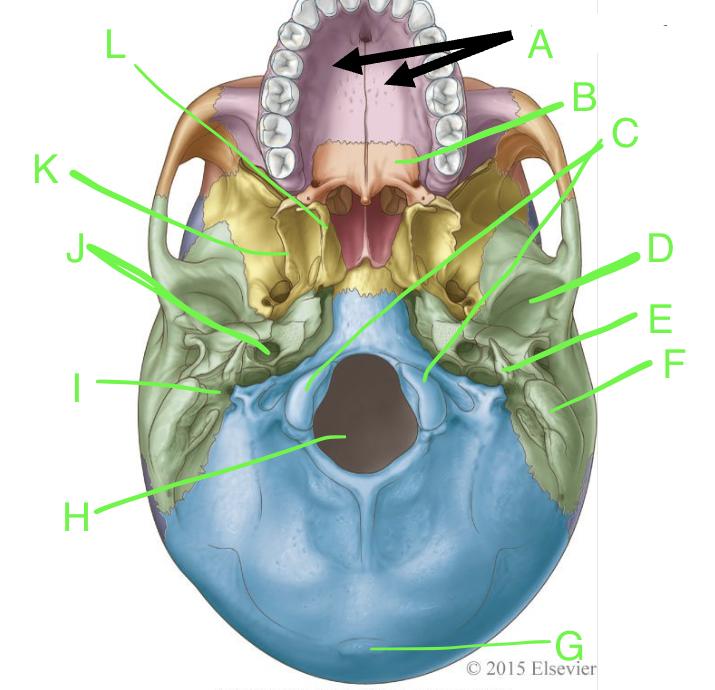
F
mastoid process
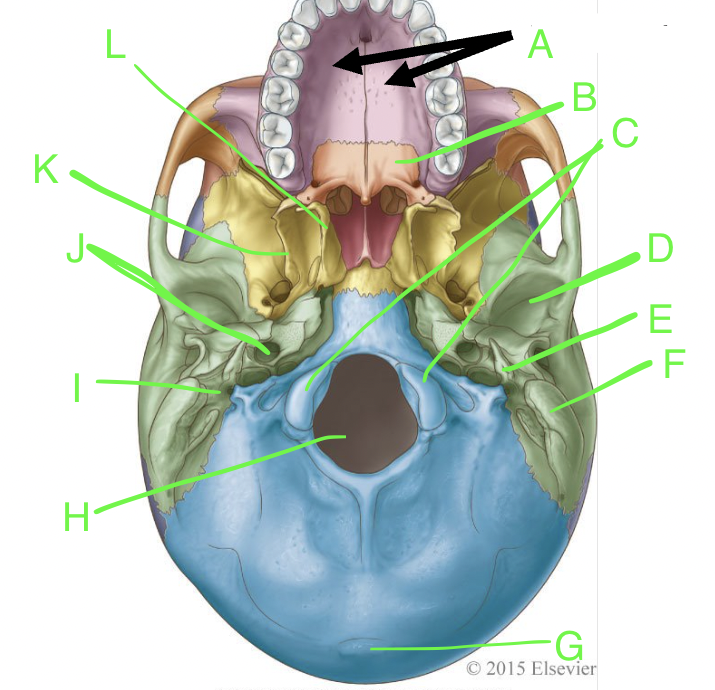
G
external occipital protuberence
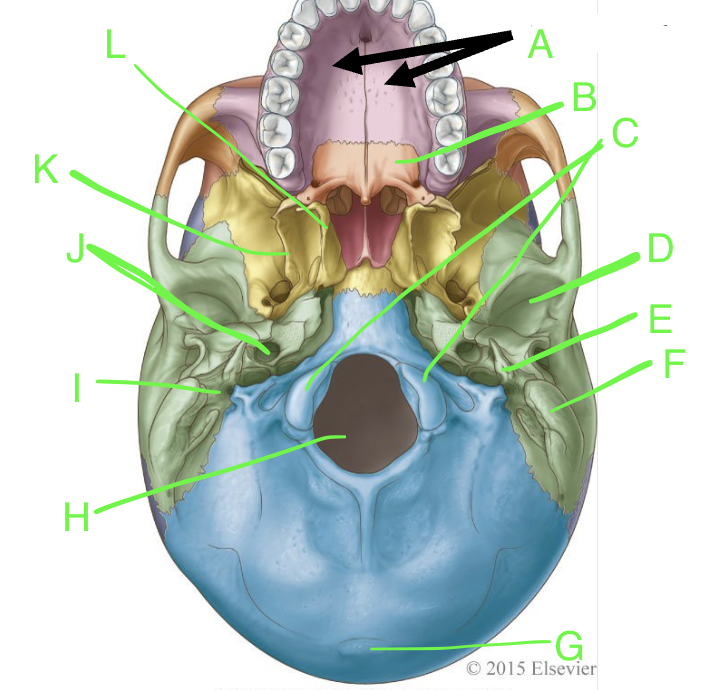
H
foramen magnum
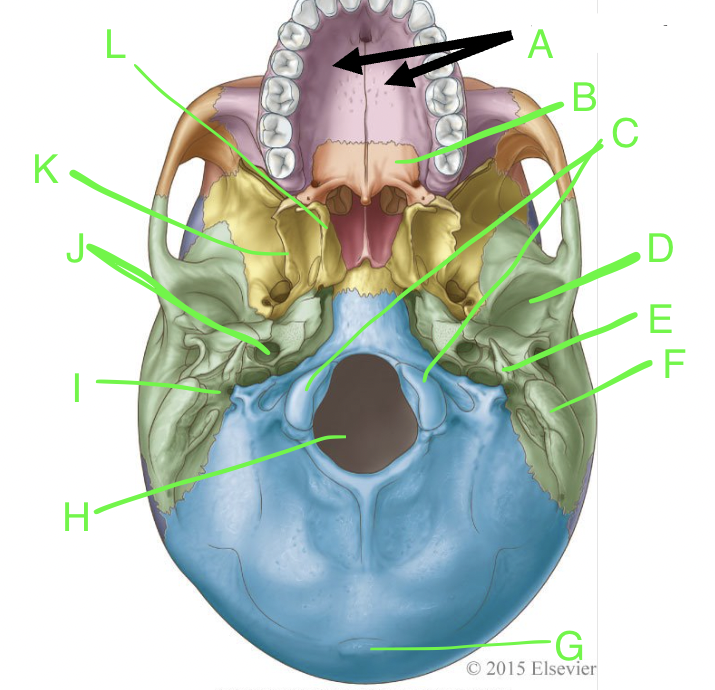
I
stylomastoid foramen
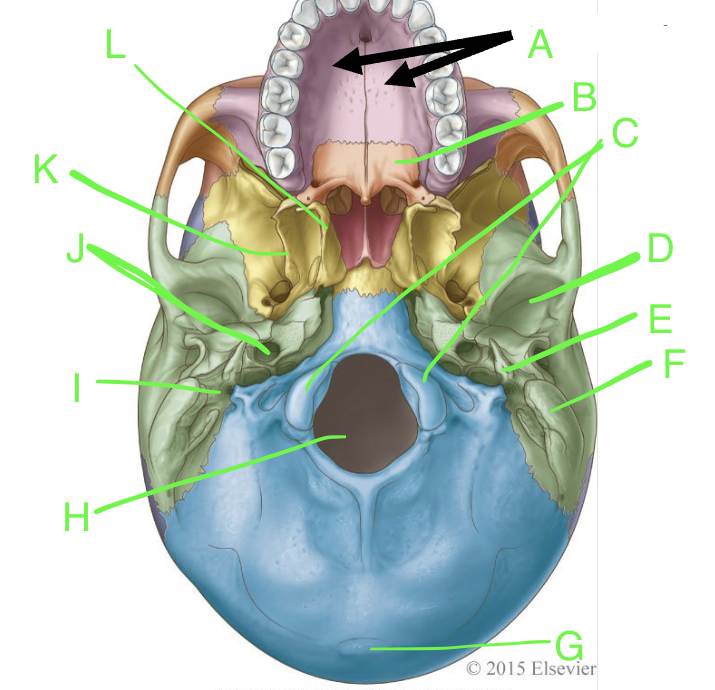
J
carotid canal
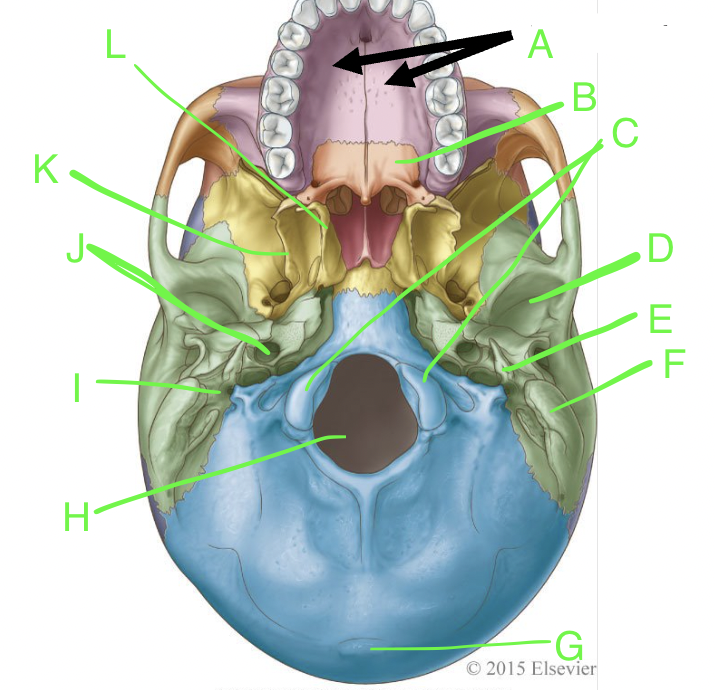
K
lateral pterygoid plate
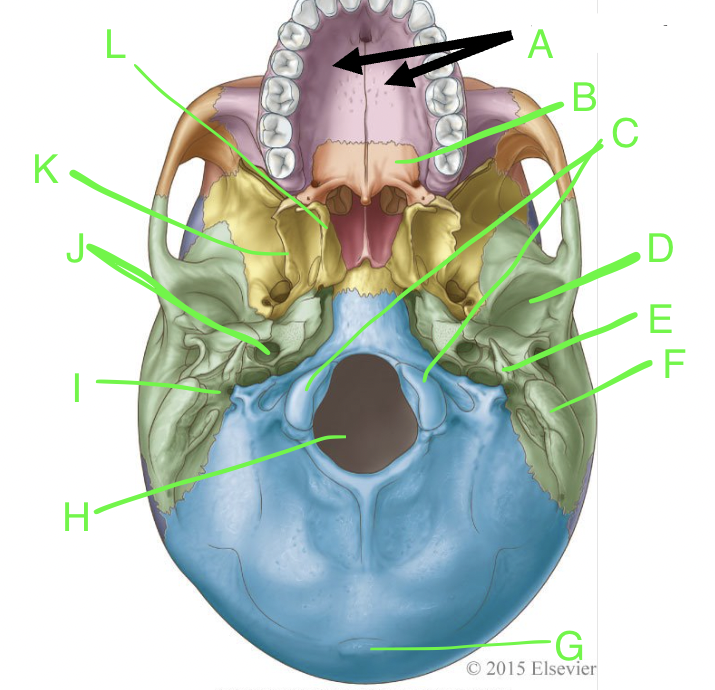
L
medial pterygoid plate
soft fibrous areas where several sutures unite
fontanelles
fontanelles are important aspect of infant skulls b/c they allow for
molding and bone modeling
the only non-fused mobile bone of the skull is the
mandible
the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone make up the
zygomatic arch
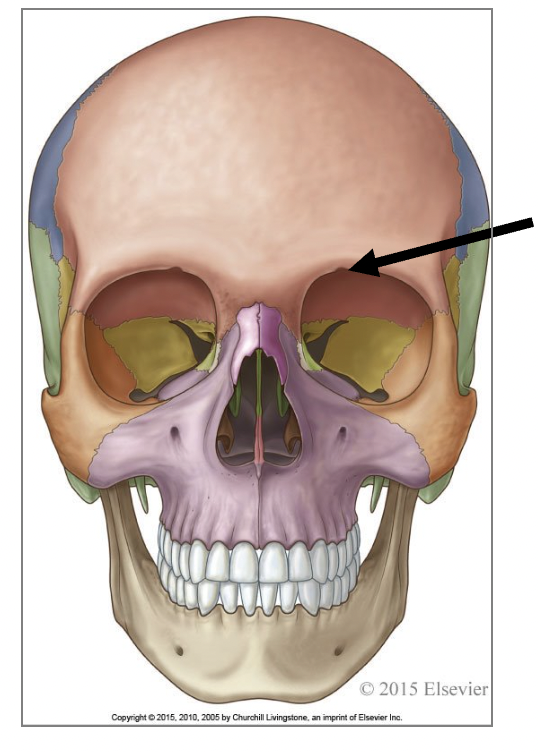
the arrow is pointing to what feature
supra-orbital notch (foramen)
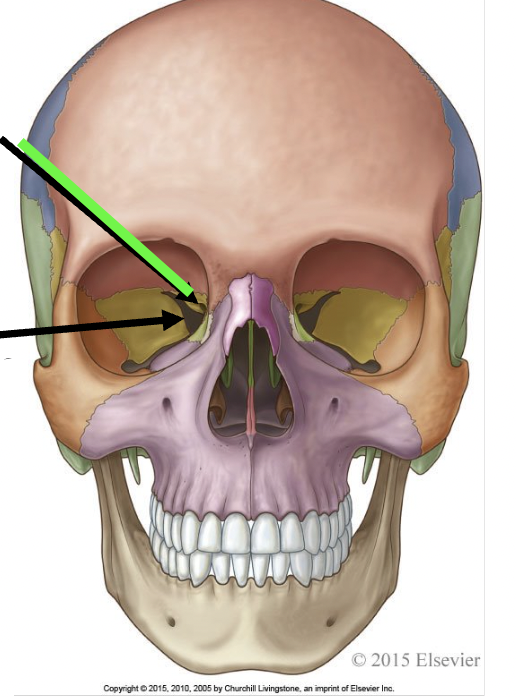
what does the green line point to
optic canal
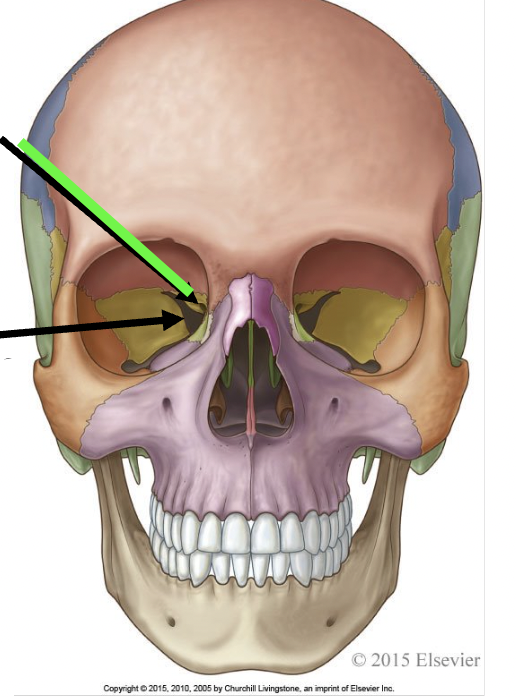
what does the black arrow point to
superior orbital fissure
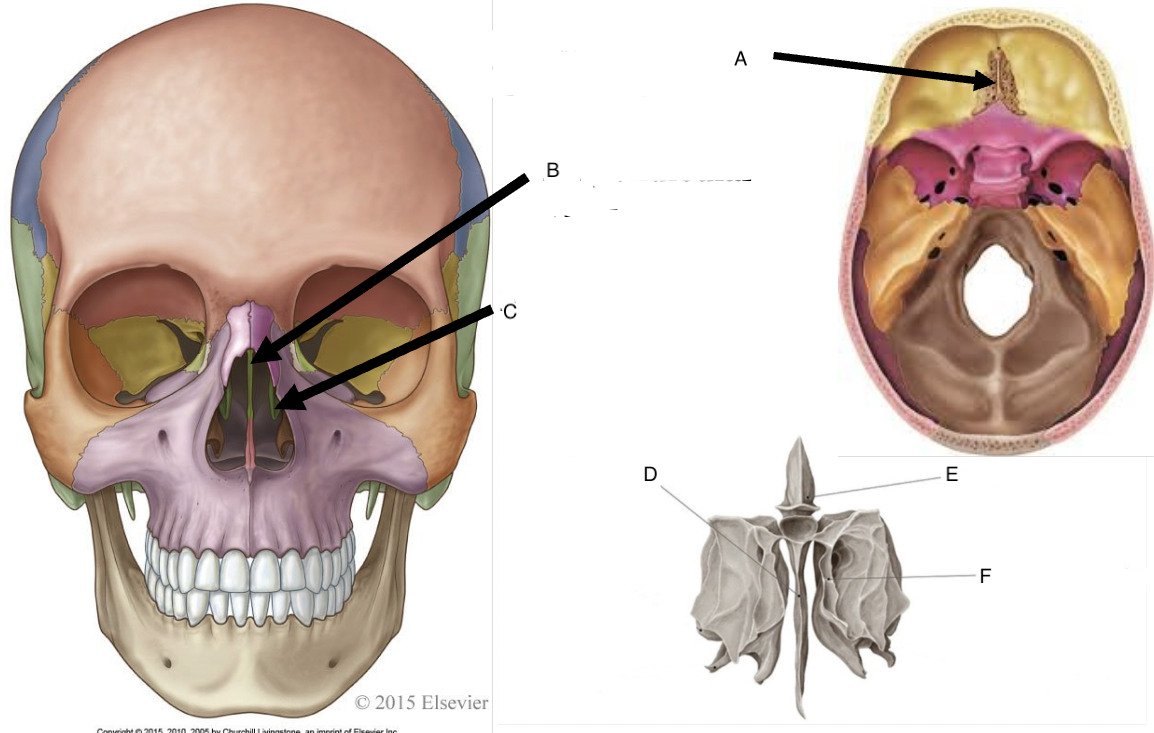
A
cribriform foramina of the cribriform plate
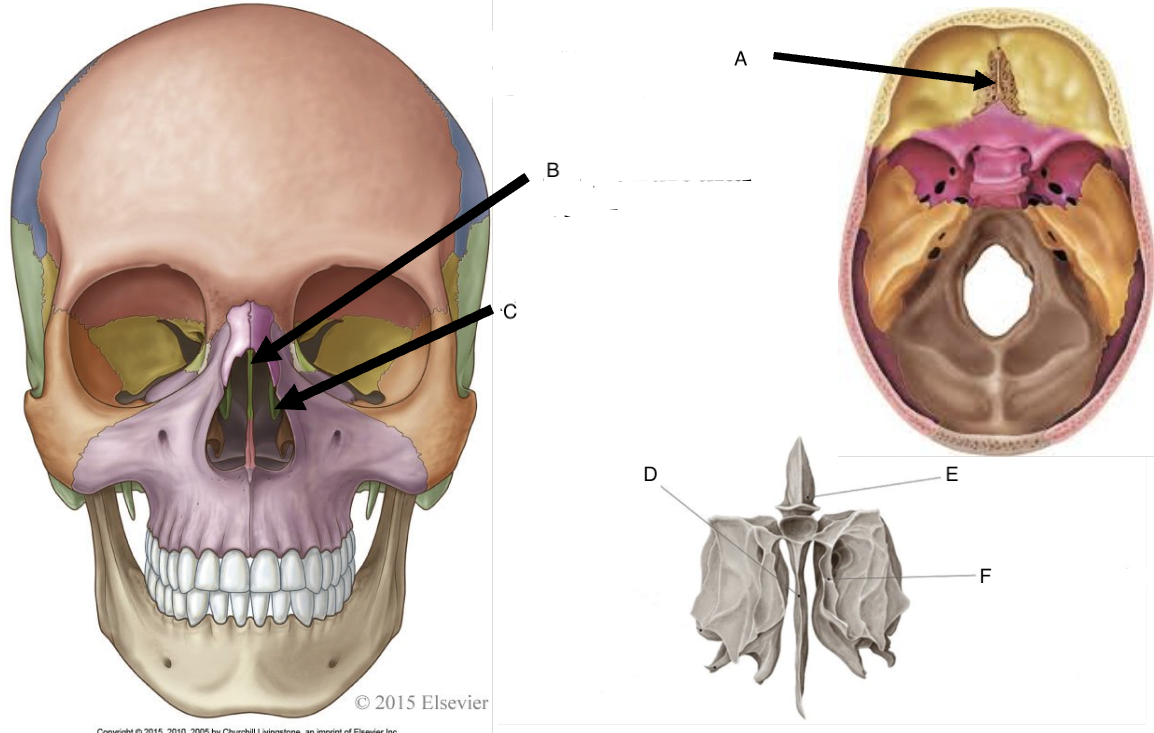
B
perpendicular plate
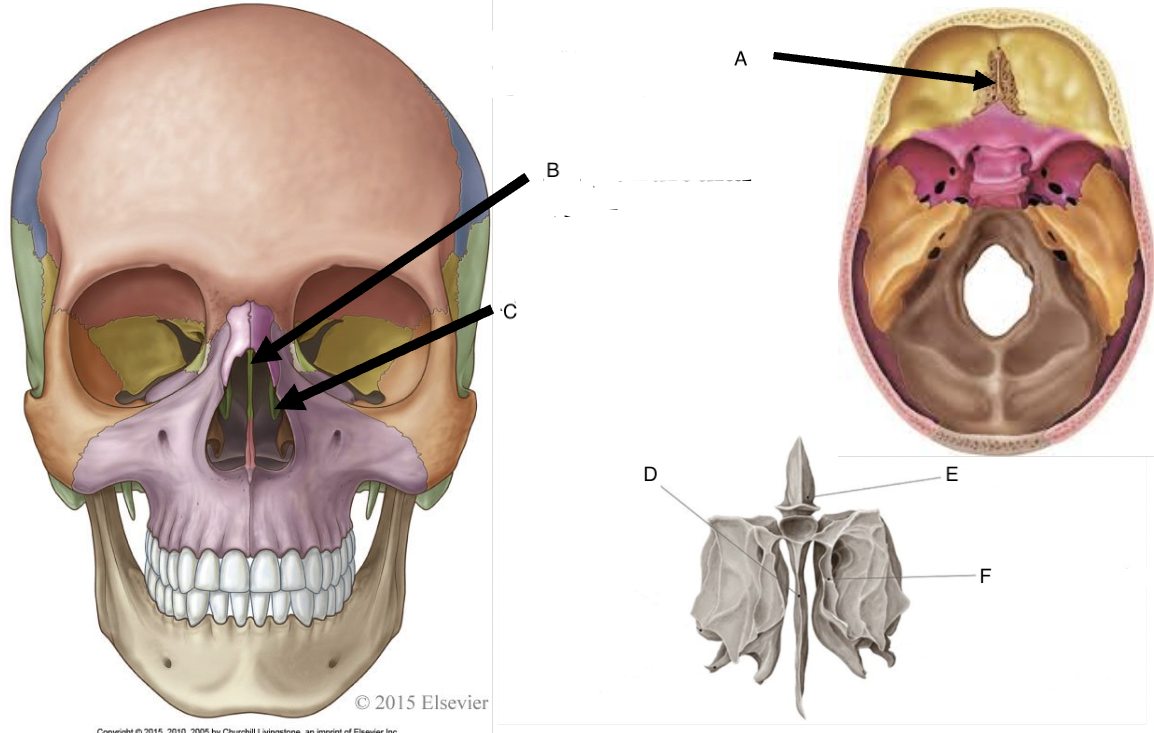
C
middle nasal concha
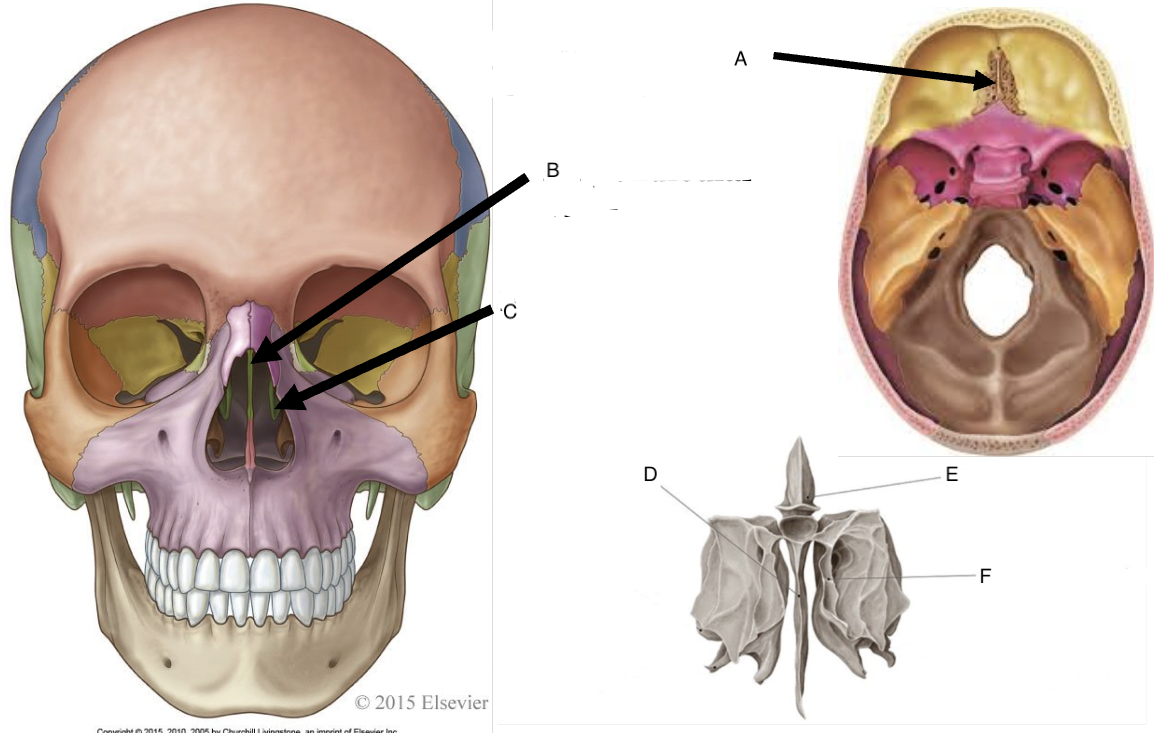
D
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
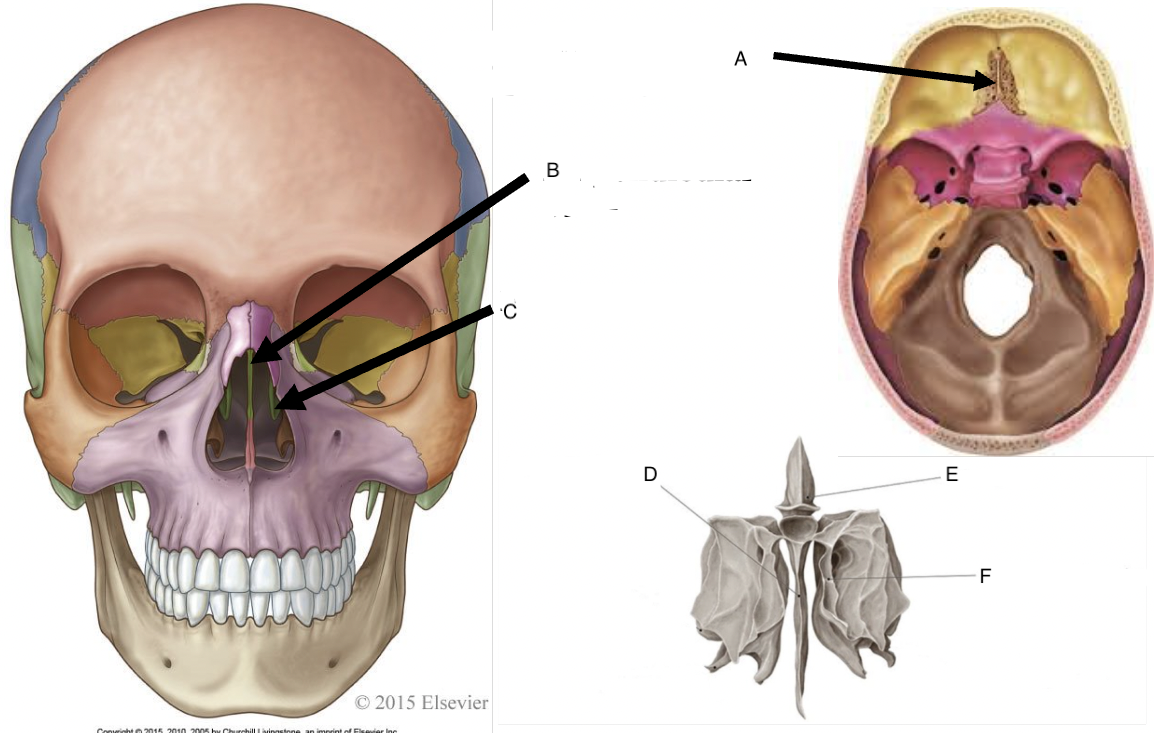
E
crista galli
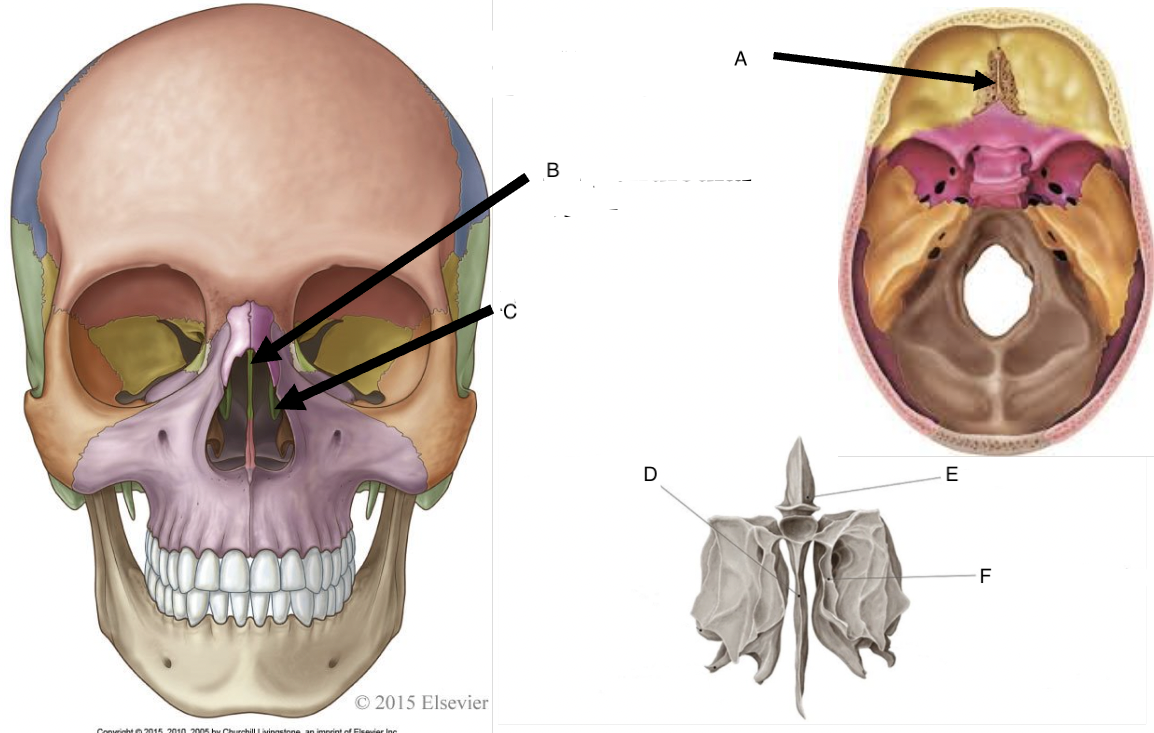
F
superior nasal concha
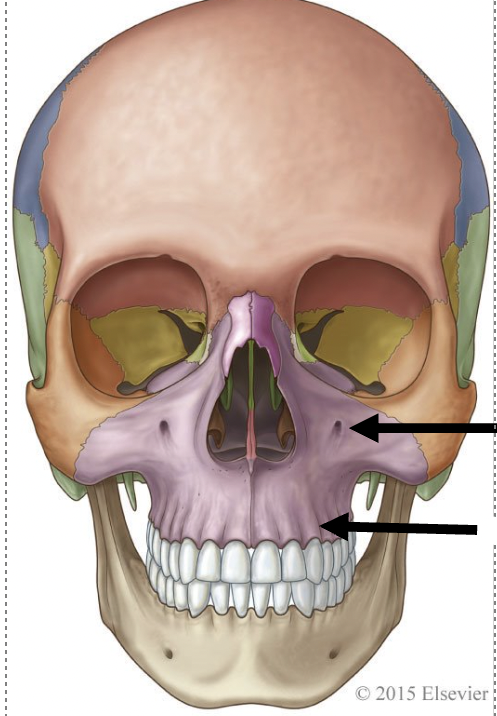
the top arrow points to
infra-orbital foramen
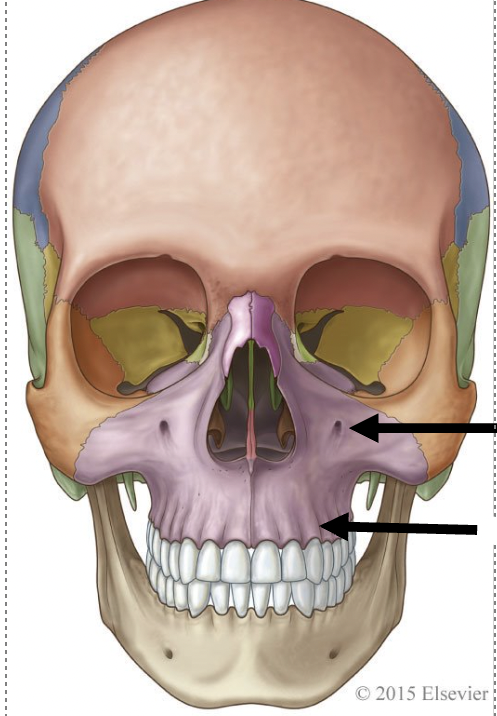
the bottom arrow points to
alveolar process
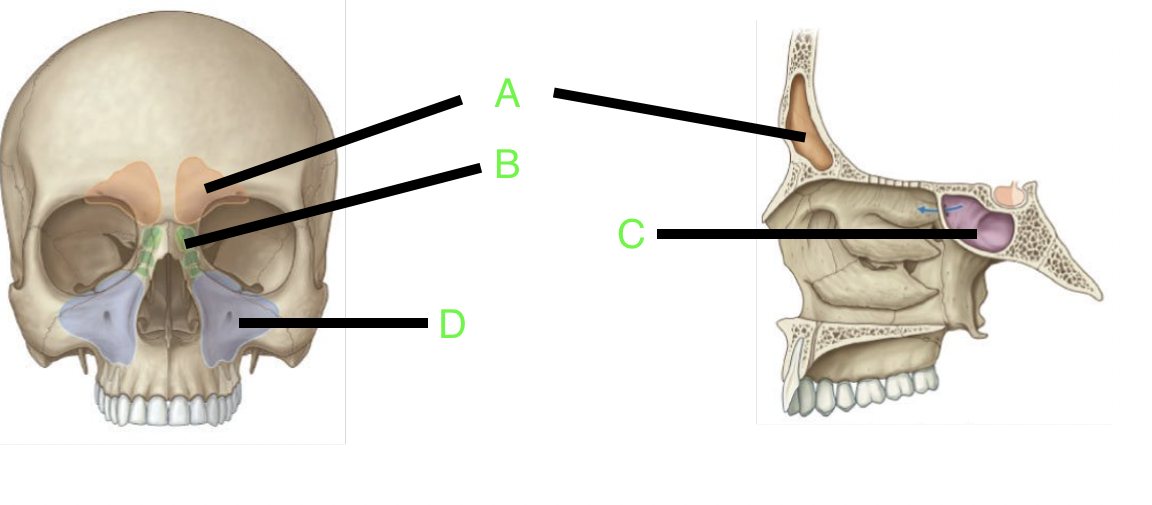
A
frontal sinus
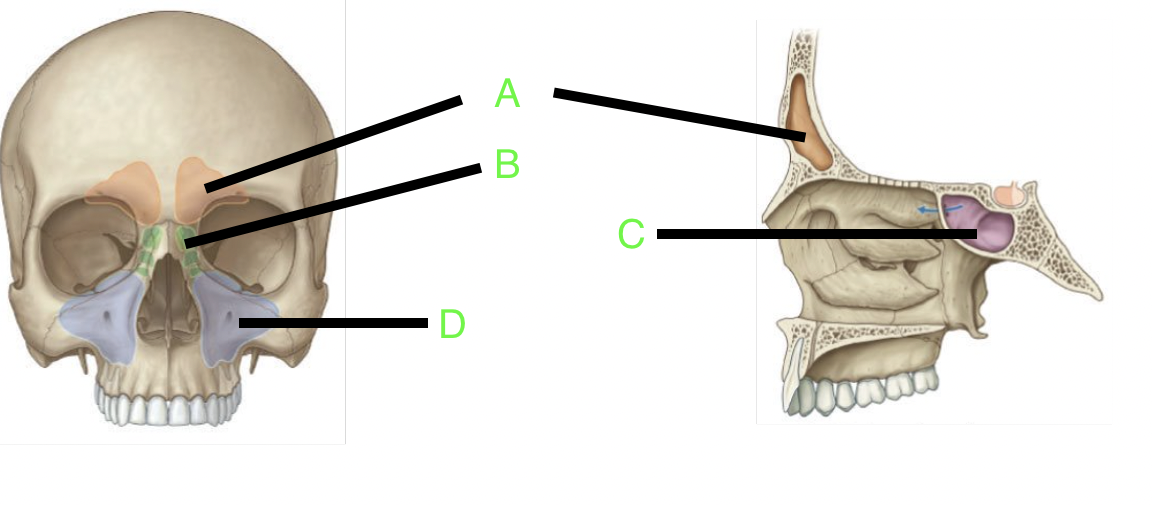
B
ethmoid sinus
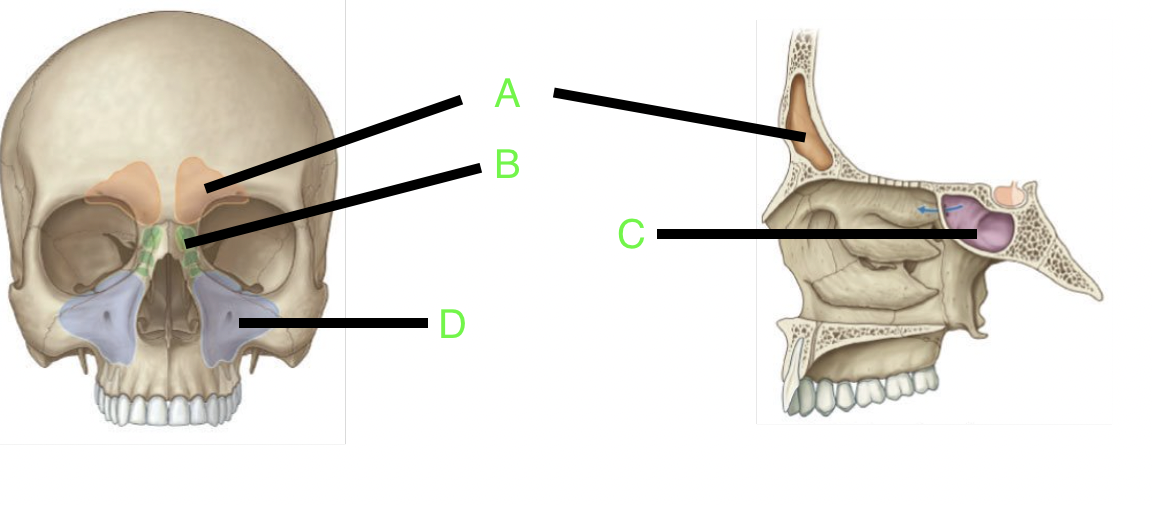
C
sphenoid sinus
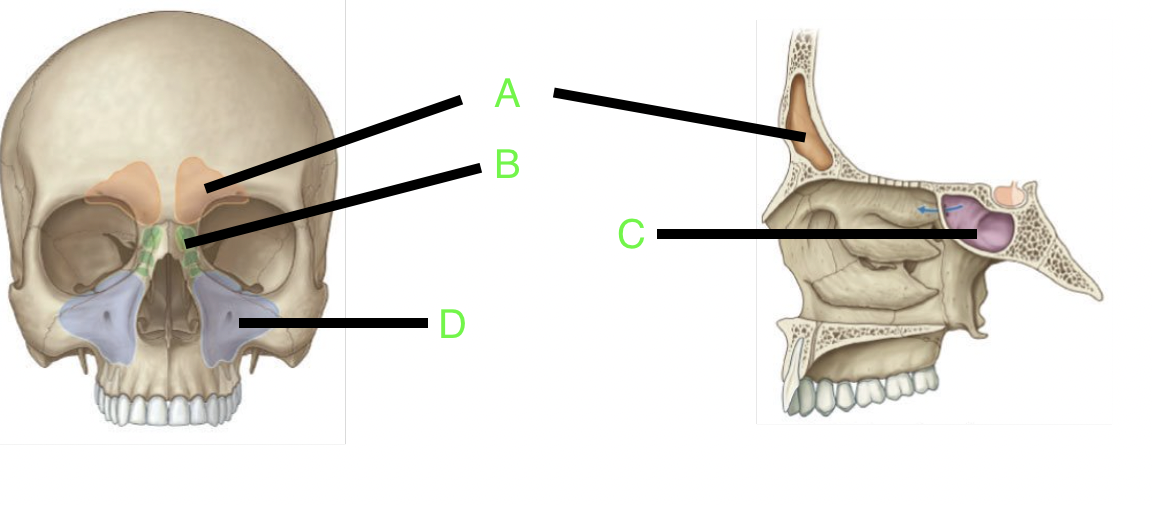
D
maxillary sinus
how many paranasal sinuses are there?
4
what are the four paranasal sinuses?
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary
the hard palate of the mouth is formed by:
palatine process of the maxillae and horizontal plates of the palatine bones
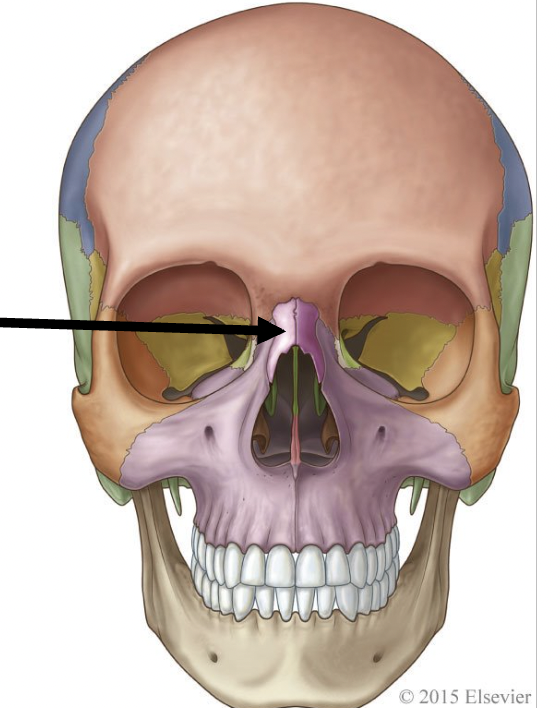
what bone is being pointed to?
nasal
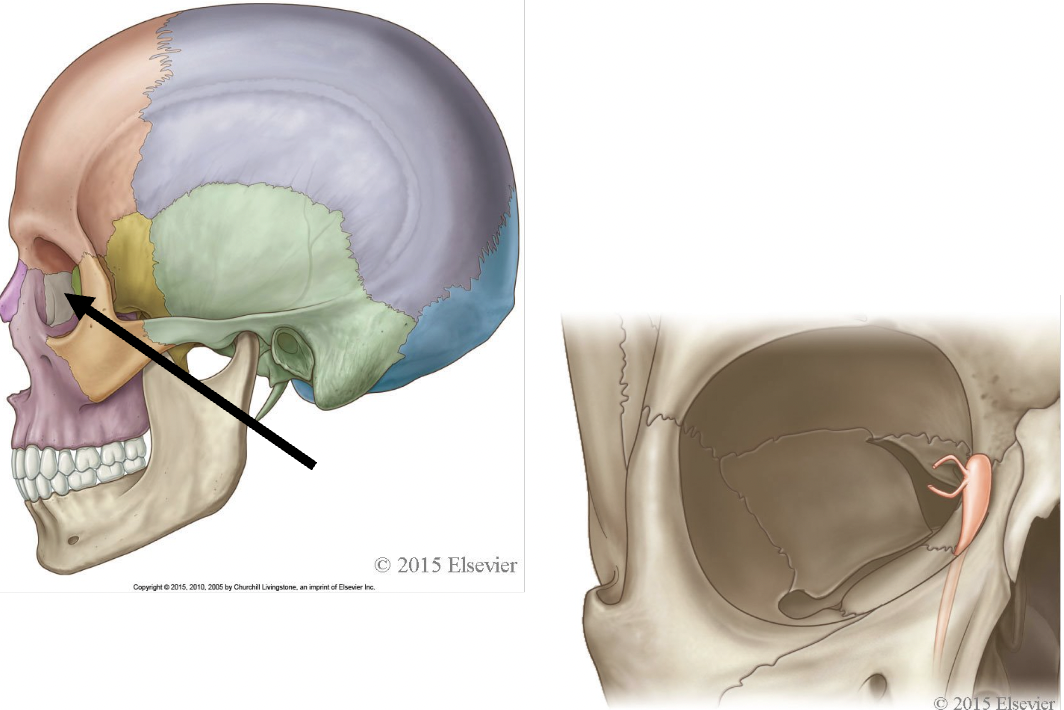
what bone is this
lacrimal
how many bones make up the orbit
7
the orbit is aka
eye socket
Many Friendly Zebras Enjoy Lazy Summer Picnics (orbit)
maxillary, frontal, zygomatic, ethmoid, lacrimal, sphenoid, palatine
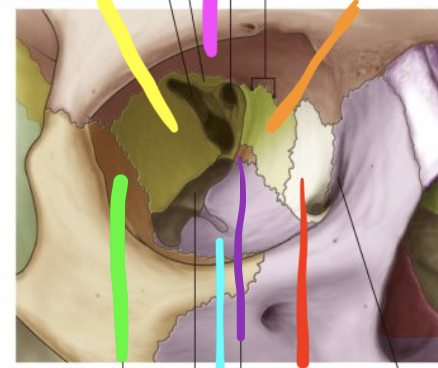
pink
frontal bone
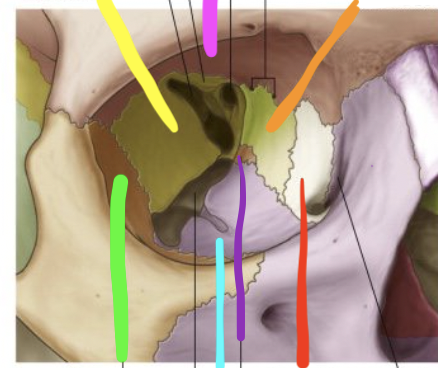
orange
ethmoid bone
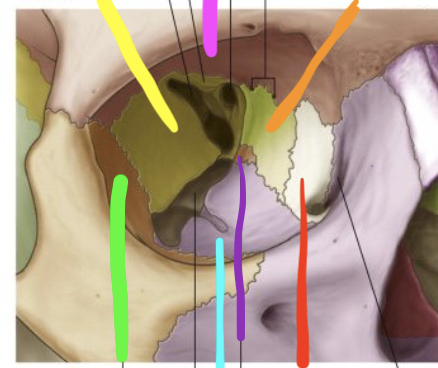
red
lacrimal bone
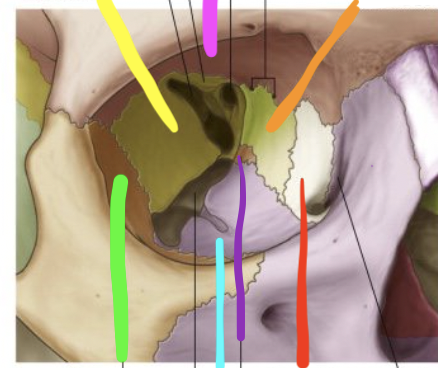
purple
palatine bone
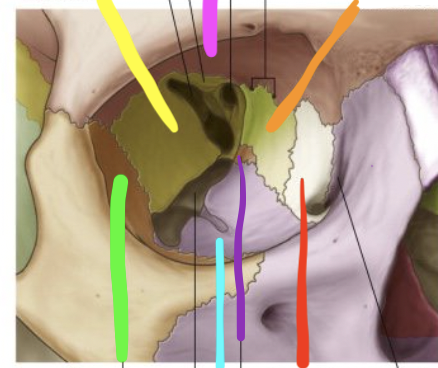
blue
maxilla
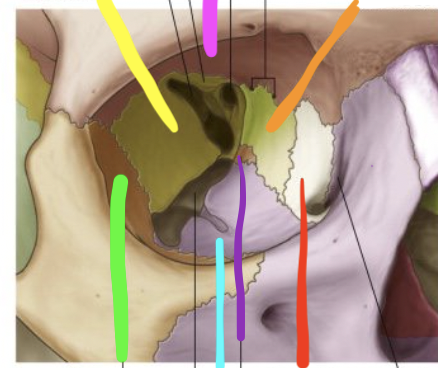
green
zygomatic
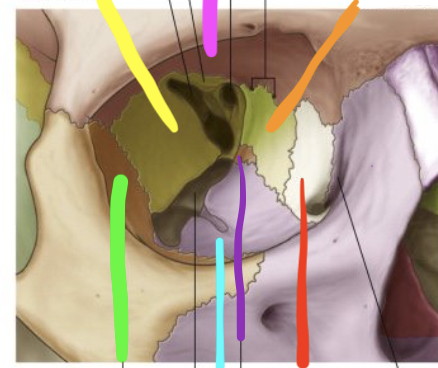
yellow
sphenoid
what is this arrow pointing to?
inferior nasal concha
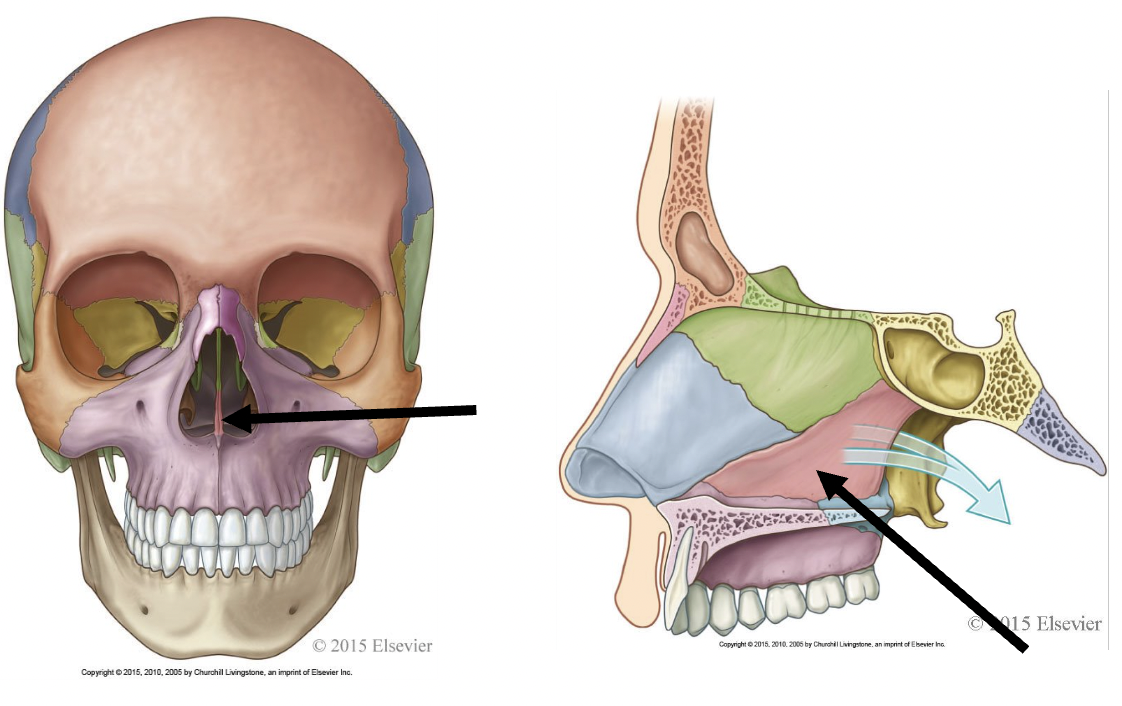
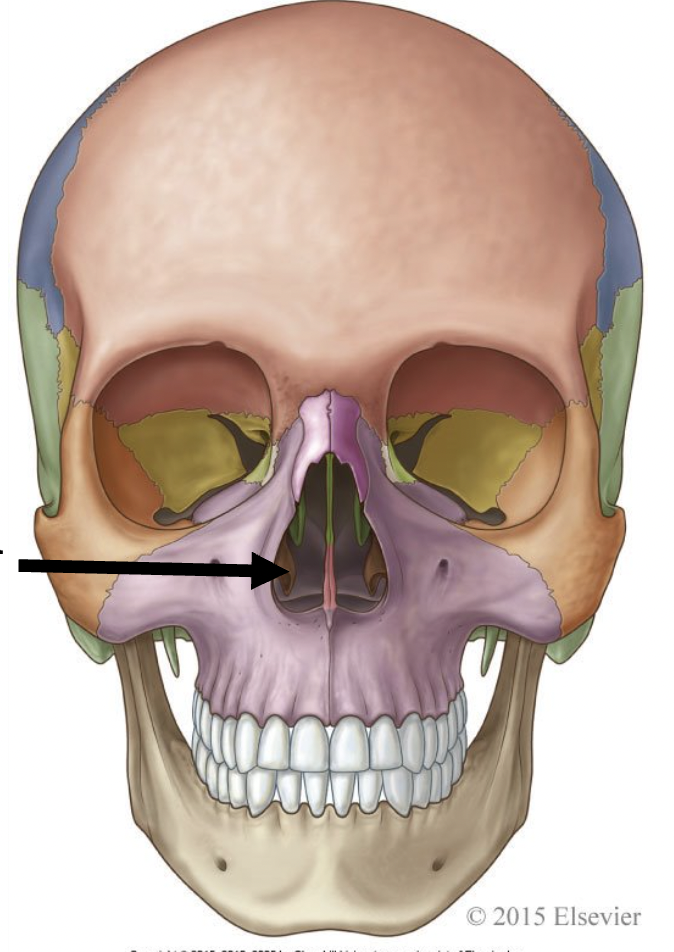
what is the arrow pointing to?
vomer
the nasal septum is composed of
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, vomer bone, septal cartilage
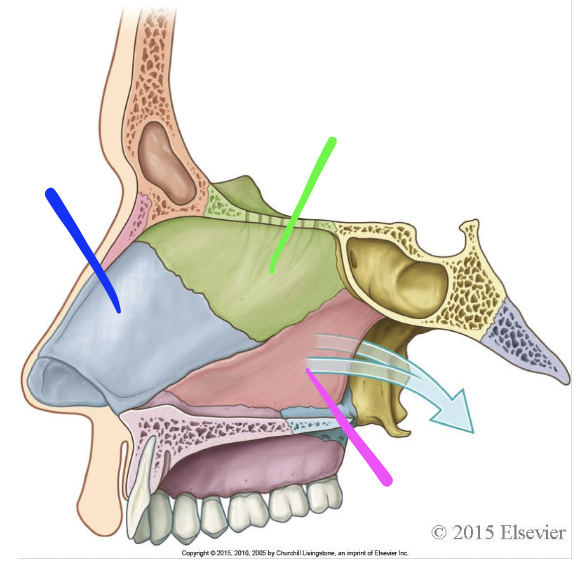
blue
septal cartilage
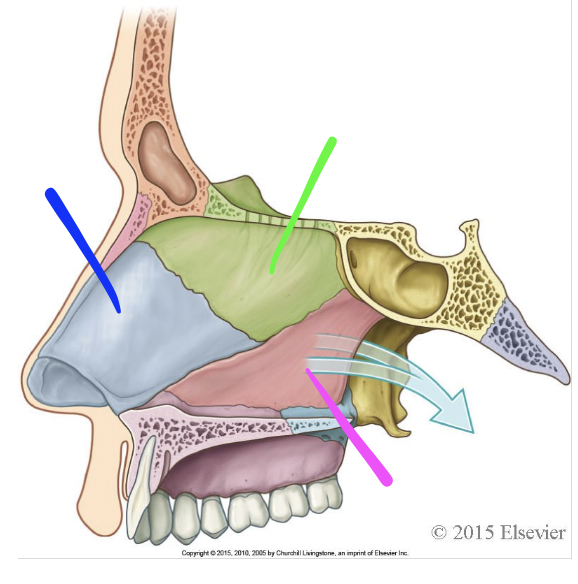
green
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
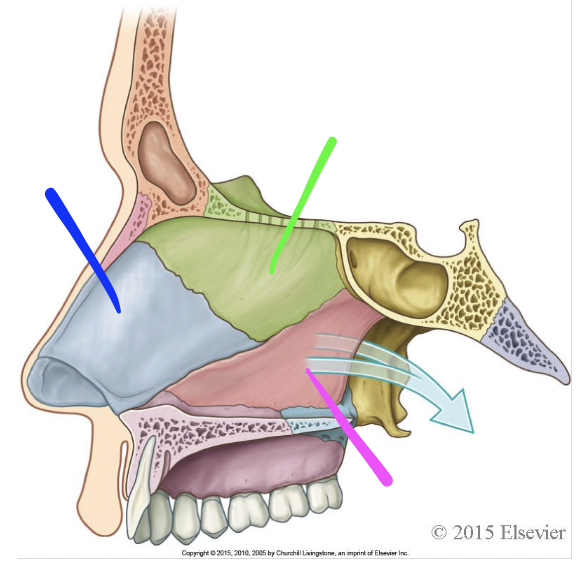
pink
vomer
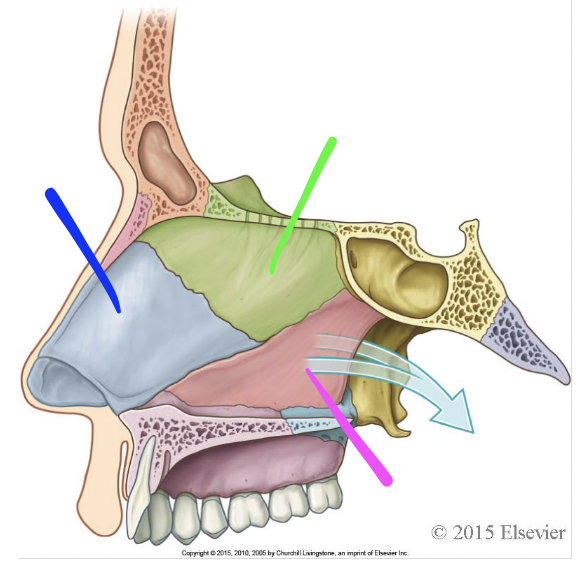
what is this structure
nasal septum
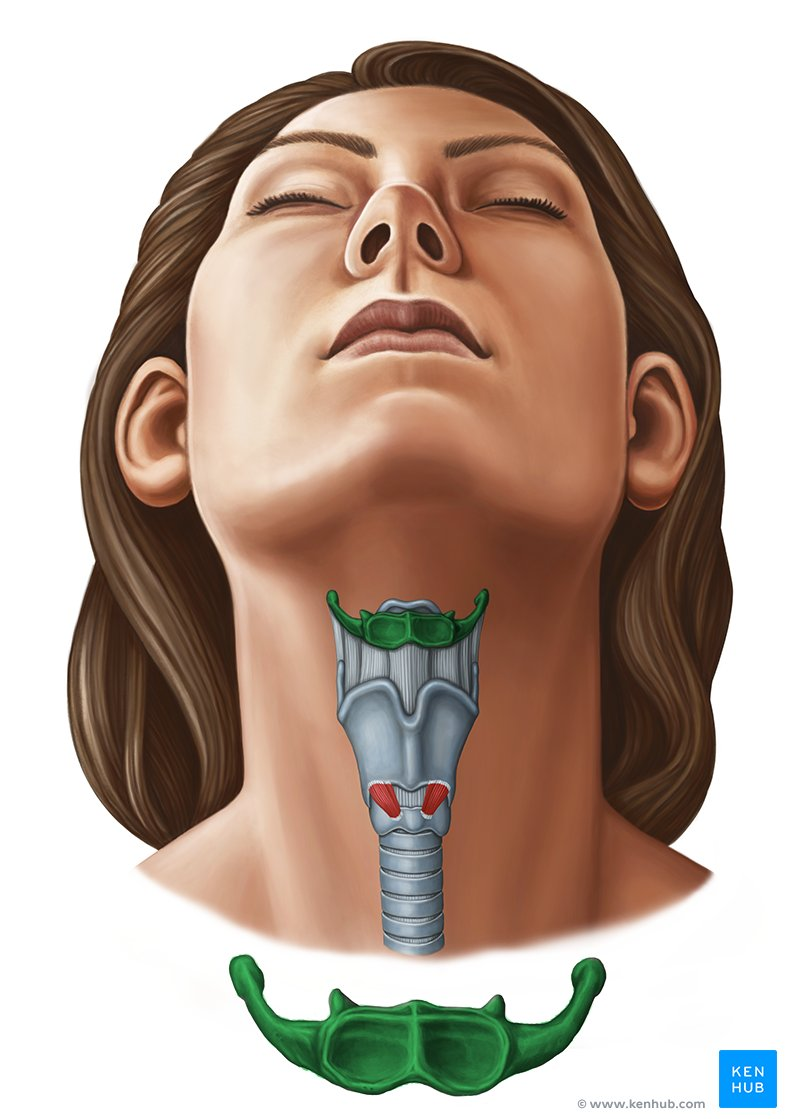
which bone is highlighted
hyoid
the hyoid bone has a greater and lesser
horn
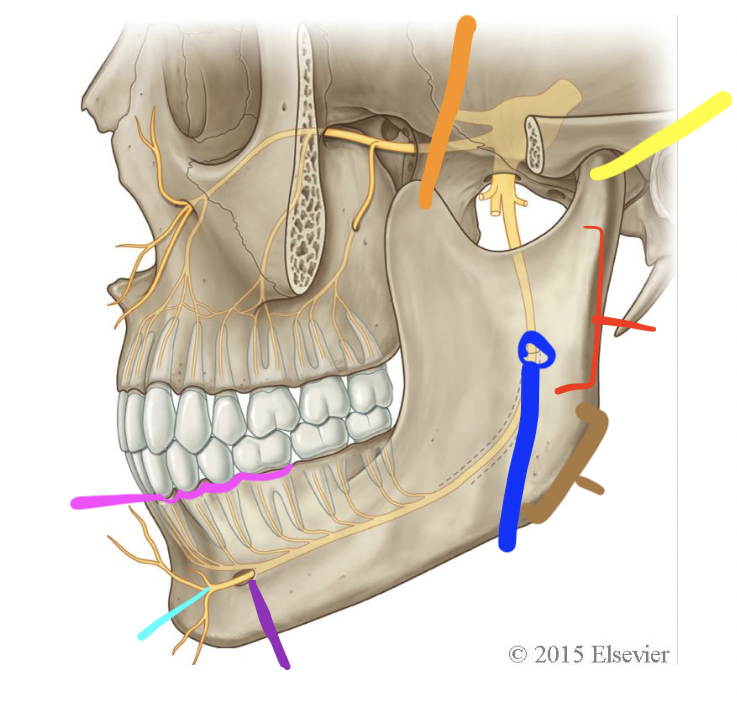
orange
coronoid process
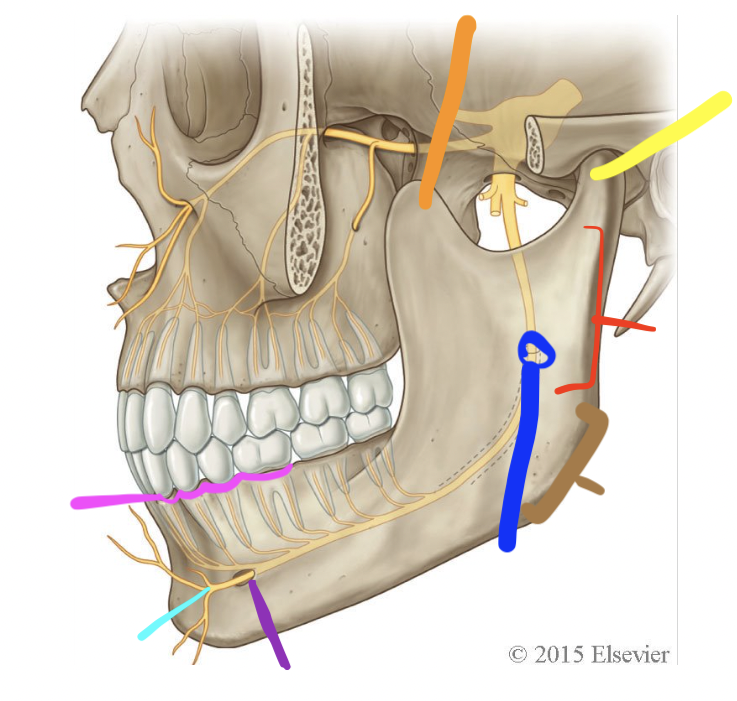
yellow
condylar process (TMJ)
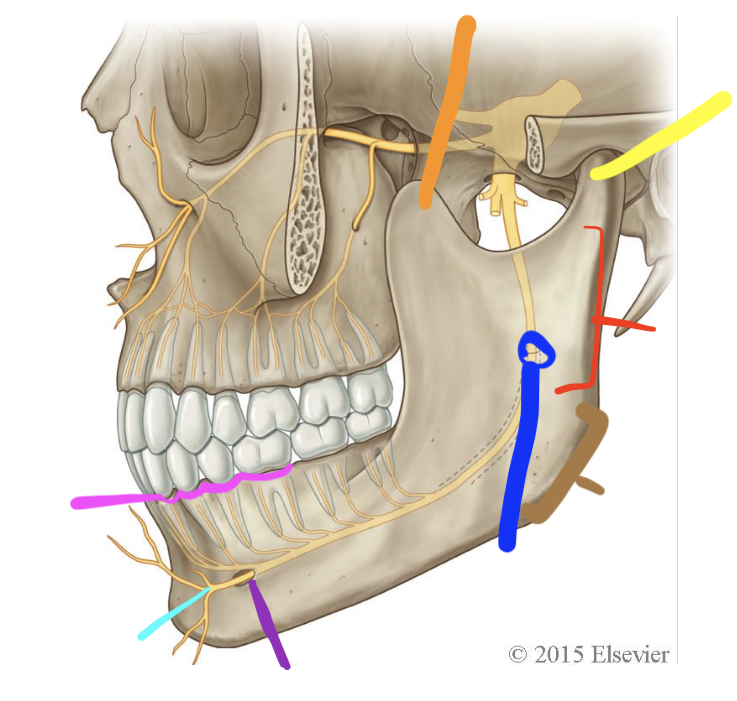
red
ramus
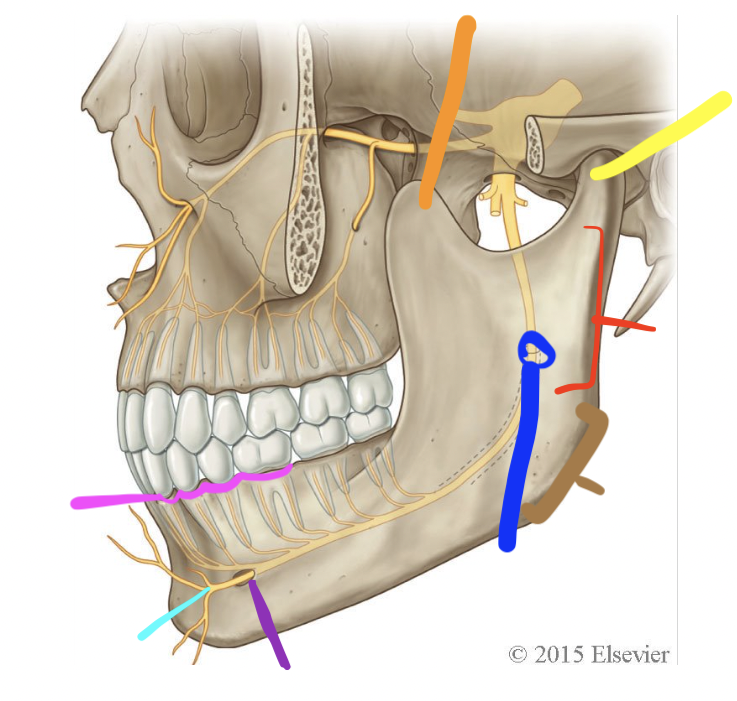
brown
angle
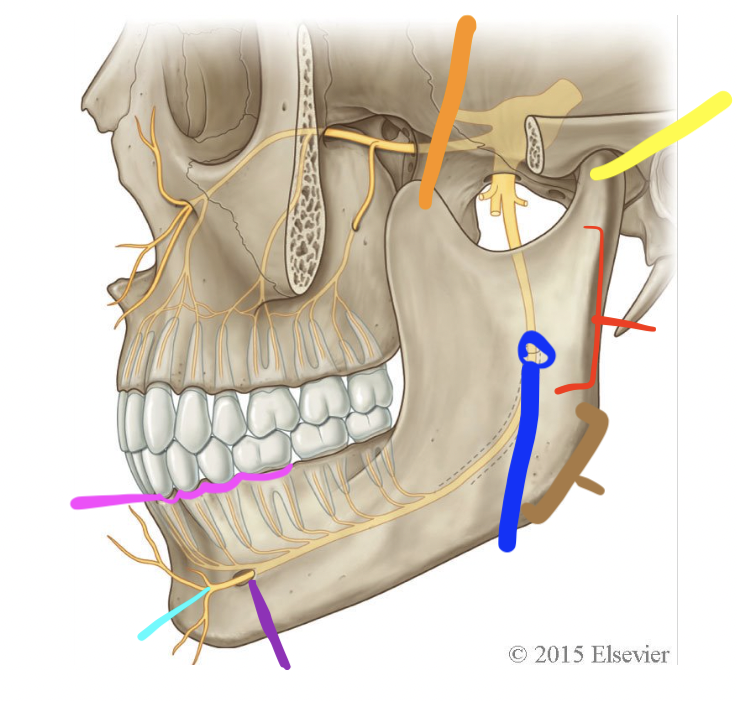
dark blue
mandibular foramen
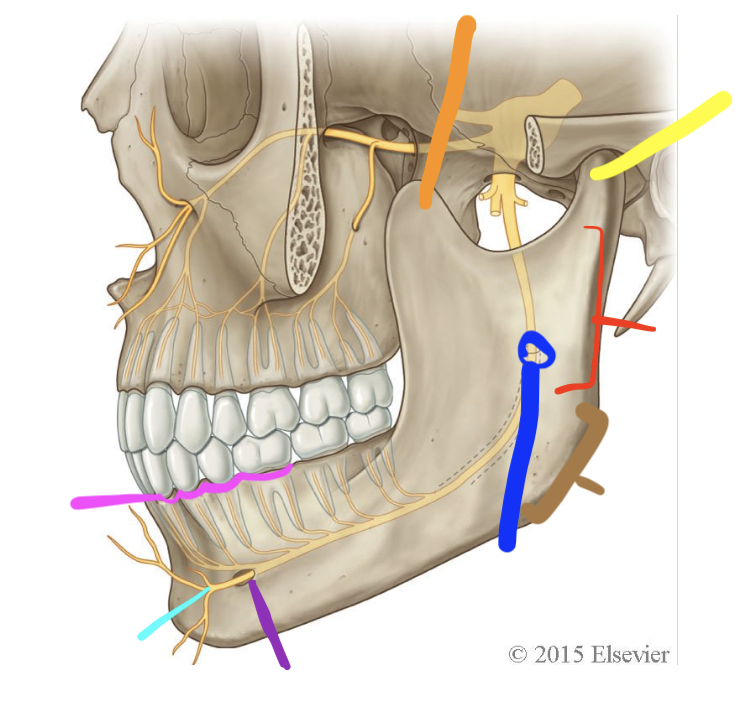
purple
mental foramen
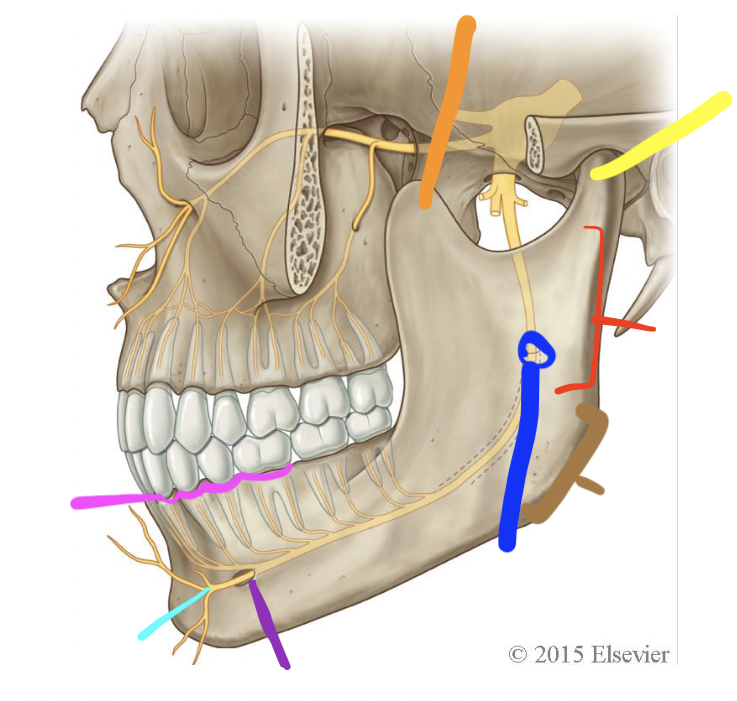
light blue
mental n.
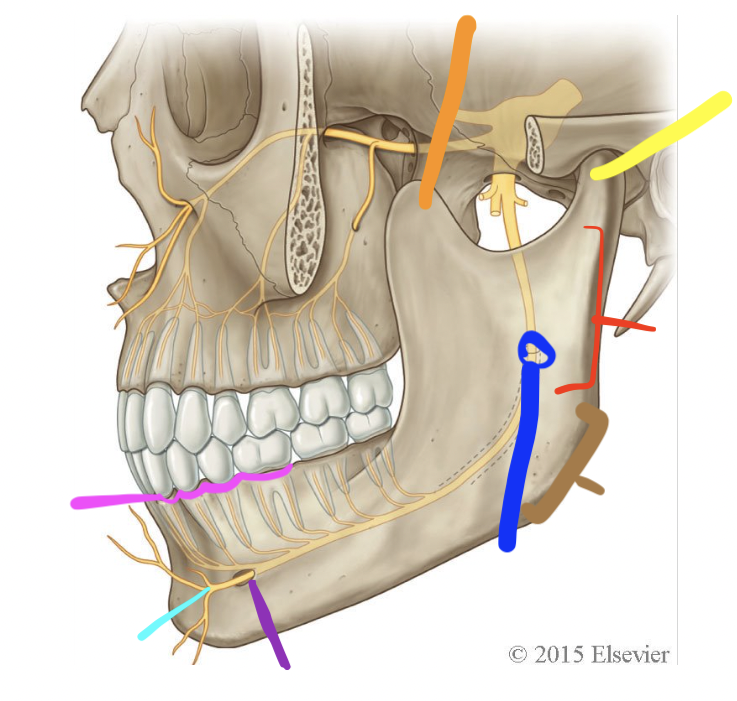
pink
alveolar processes
defining features on the medial side of the mandible are called the
mylohyoid line and submandibular fossa