AP Biology - Unit 1: Hydrogen Bonds and Poperties of Water
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pg. 35 - 43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Polarity
The unequal sharing of electrons in a bond that create partial positive and negative charges.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Electrons are not shared equally betweens two atoms.
Nonpolar Covanelt Bonds
Electrons are shared equally.
Ionic Bonds
Bonds created by the transferring of electrons between atoms (cations and anions).
Hydrogen Bonds
The partial charges in molecules such as H2O, where hydrogen is bonded to an electronegative atom, cause attraction between the hydrogen atom in these mocelcules to electronegative atoms in other polar molecules.
What creates partial charges in hydrogen bonds?
Polarity within the molecules containing H+ that cause dipole moments, where the electrons are unequally shared and are more attracted to the electronegative atom.
Polarity
The unequal sharing of electrons within the molecule: directly responsible for other properties of water.
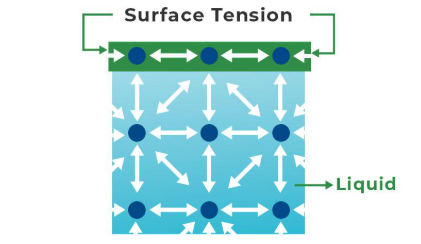
Cohesion
The attraction of H2O to other molecules of H2O (or of one molecule to another of the same kind) - allows water to go against gravity in plants and causes surface tension.
Adhesion
Attraction of H2O to other polar molecules (or of one polar molecule to another, different polar molecule) - allows water to cling to plant cell walls and other substances.
Capillary Action
Where adhesion is greater than cohesion (surface tension), causing the upward movement of water (and vice versa).
Temperature Control
Water has a high specific heat, meaning it resists dramatic changes in it's temperature - important for moderating air temp, stabilizing ocean temp, and organism's internal temps.
How does water have higher temperature control?
Heat must be absorbed to break hydrogen bonds (TTB), but heat is released when hydrogen bonds form (FTF). When heat is added, it must break these bonds before increasing it's kinetic energy (movement).
High Heat of Vaporization
Water requires lots of energy to evaporate due to it's strong intermolecular bonds.
Evaporative Cooling
As water molecules evaporate, the surface they evaporate from cools - important for moderating the climate, preventing terrestrial organisms from overheating, etc.
Density
As water solidifies it also expands and becomes less dense - this is why ice floats on top of liquid water.
Solvent
Water is a “universal solvent” (able to dissolve an array of molecules) due to it's polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds - can dissolve polar and covalent molec. by attracting the separate ions and effectively surrounding them with water.
Acids and Bases
Acids will donate H+ (hydrogen) ions and bases will receive them or release OH- (hydroxide) ions - water can dissociate into both.
pH
The measure of how acidic or basic (alkaline) a solution is.
Buffer
A solution that resists changes in pH with the addition of acids or bases - aids in maintaining pH stability in biological systems.