Lecture 10.1
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Conduct Disorder and Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
poverty
violence
→ reaction
Both CD and ODD are influenced by culture/context and are:
Strongly associated with _______
Strongly associated with exposure to ______
→ This is why diagnosis of these disorders should only be applied when the behaviour is not a ______ to the immediate social context
Social causation: stress associated with poverty → increased childhood psychopathology
Social selection: families with genetic predispositions to psychopathology → drift down towards poverty
How do social causation and social selection theories explain CD and ODD links with poverty?
Study details:
Longitudinal study of Indigenous children living on a reservation and their disruptive problems
Opened a casino on the reservation and gave families money
Findings:
Youth whose families were no longer poor due to the money received from the casino reported decreases in disruptive behaviours
The variable that mediated the relationship was improved parental supervision
Theoretical support:
Supports the social causation theory (poverty stress → disruptive behaviours)
What was the Great Smoky Mountains study, its findings, and theoretical support?
male
10
2
Conduct problems (symptoms + behaviours) are 2-4 times more common in _______ children
Early-onset persistent CD→ ___ male: 1 female ratio
Adolescent-limited CD → ___ male: 1 female or no gender difference
more, small
Girls engage in slightly ______ relational aggression than do boys, but the difference is ______ and not meaningful
50, 35
50
CD and ODD comorbidities:
ADHD → more than ___% of children with CD also have ADHD, ___% of children with ODD also have ADHD
Depression and anxiety → ___% of children with CD and ODD also have depression and anxiety
verbal
academic
family
peers
risks (30)
Impacts of CD and ODD on children:
Cognitive and _______ challenges, not associated with intellectual impairment
Impaired ________ functioning
Impaired ________ functioning
Problems with ______
Significant health _______ (boys with conduct problems are 3 to 4 times more likely to die before the age of ___)
40
Up to ___% of children with CD develop Antisocial Personality Disorder as adults
The diagnostic criteria are more geared towards older children
→ The symptoms or behaviours are impossible/improbable (ex: staying out all night) at this age
What are the diagnostic challenges for CD or ODD in preschoolers?
decrease
dysregulation
For preschoolers:
Some misbehavior is normative and will ______ as they grow older
Some misbehavior is an indicator of significant behavioral and emotional ______ that will escalate with time if left untreated
We can use:
Frequency
Severity
Flexibility → can the behaviour be modified?
Expectability → can we predict the behaviour?
Pervasiveness → across number of settings
On what can we base ourselves to distinguish typical misbehaviour from significant and problematic misbehaviour?
Early-onset/life-course consistent pathway | Late-onset/adolescent-limited pathway |
Aggression | extreme |
delinquency | violent |
forms | persist |
high | peaks |
Differences between the early-onset and late-onset pathways:
Early-onset/life-course consistent pathway | Late-onset/adolescent-limited pathway |
_______ in childhood | Less _____ antisocial behaviour |
More serious ______ in adolescence | Less likely to commit ______ offenses |
Diversification → adding new _____ of disruptive behaviours over time | Less likely to ______ over time |
Linear → starts high and stays ______ | Curvilinear → starts low, _____ in adolescence, declines |
50
___% or more of the variance in antisocial behavior is hereditary
weight
protein
poisoning
substances
alcohol
Some pregnancy and birth factors:
Low birth ______
Malnutrition (possible _____ deficiency) during pregnancy
Lead _____
Mother’s use of nicotine, marijuana, and other ______ during pregnancy
Maternal _____ use during pregnancy
maltreatment
Childhood _______ is a universal risk factor for antisocial behavior
conditional, MAOA
Vulnerability to adversities may be ______ and depending on genetic factors such as ______, an enzyme linked to a gene
For people with low MAOA activity, the relationship between maltreatment and antisocial behaviour was stronger
What was the finding for the interaction/moderation of MAOA and antisocial behaviour?
parenting
Negative ______ behaviours that do not constitute abuse are also associated with disruptive behavior problems
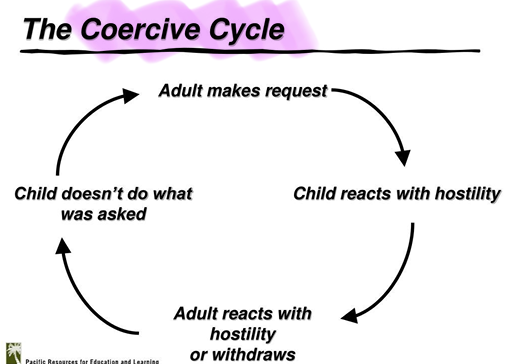
Demands from parent → child uses delay ans escape strategies + reacts with hostility → inconsistent responses and explosions from parent → reinforces disruptive behaviours
→ It’s also a key target for interventions
What’s the coercive cycle in relation to parenting?
cognitive
processing
Social information processing:
Is a series of _____ steps taken by a person from situation to action
Multiple _____ mechanisms such as encoding, interpretation, response search, response decision, enactment
There is robust evidence linking this bias to aggressive behaviour
Children with aggressive behaviour problems are more likely to think the other child did it on purpose
How does the hostile attribution bias relate to aggressive behaviour?
fewer
effective
able
aggressive
Social information processing in aggressive people:
Response search
Think of ______ possible responses
Response decision
Think that aggressive strategies are more _______
Perceive themselves as being _____ to carry out those aggressive strategies
Finally pick _______ strategies
Parents | Peers |
|
|
How do these aggressive cognitive patterns develop through parents or peers?