Human Body Systems Final Exam Review
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
anterior
front
posterior
back
superior
higher
inferior
lower
medial
midline
lateral
away from the midline
proximal
close
distal
far
superficial
skin level/close to skin level
deep
further within than skin level
dorsal
spinal (back)
ventral
abdominal (front)
axial
main axis of the body (head, neck, and trunk)
appendicular
all appendages, which are attached to the axis
connective tissue
supports and connects all tissue types. includes adipose tissue (fat)
epithelial tissue
made of epithelial cells, aligned in sheets. lines outer surface of all organs, blood vessels, and human skin.
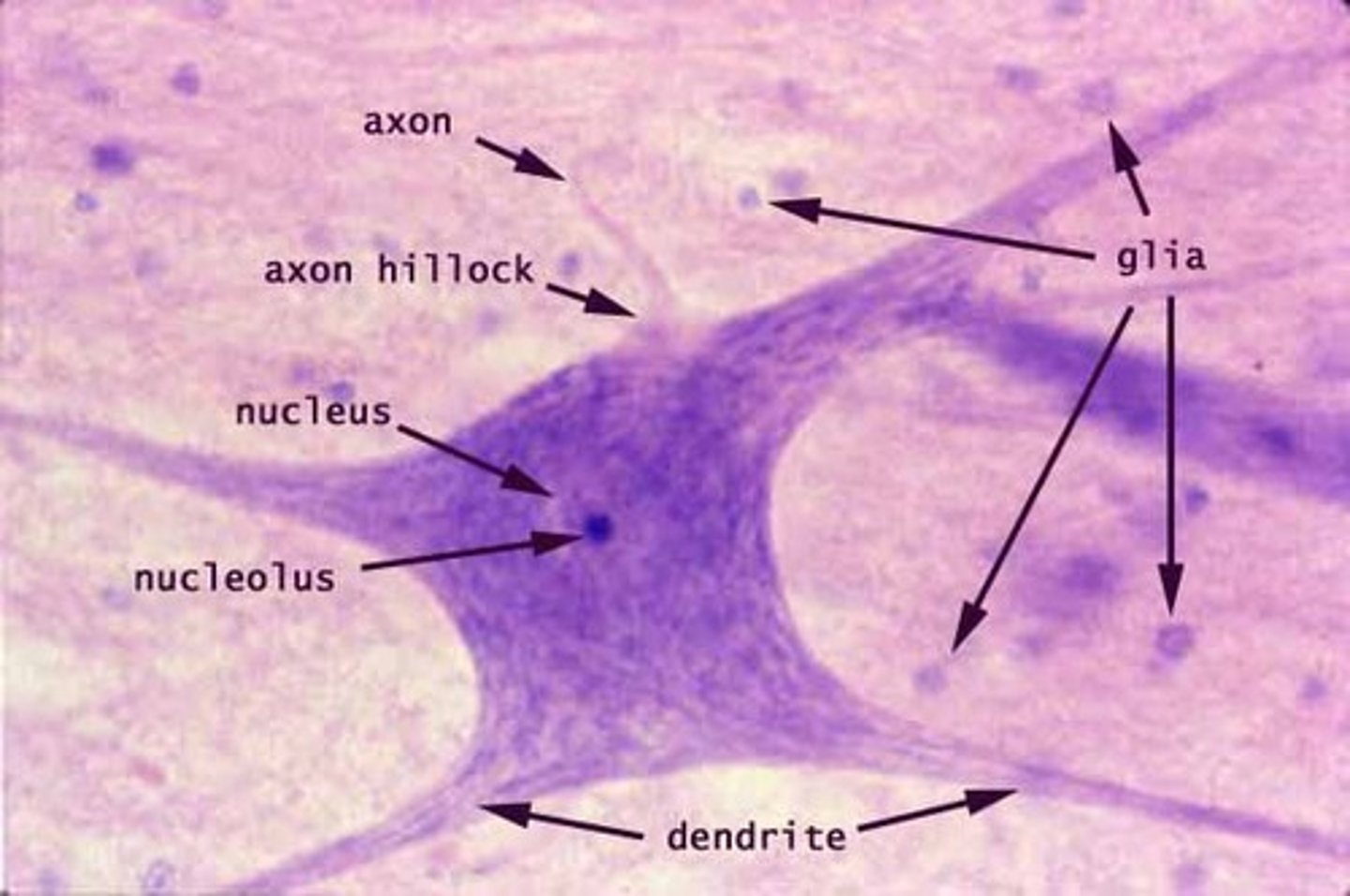
nervous tissue
makes nerves, spinal cord, and brain. made of neuron cells that receive, interpret, and respond to signals
muscular tissue
skeletal (voluntary), smooth (involuntary), and cardiac (involuntary) based on muscle.
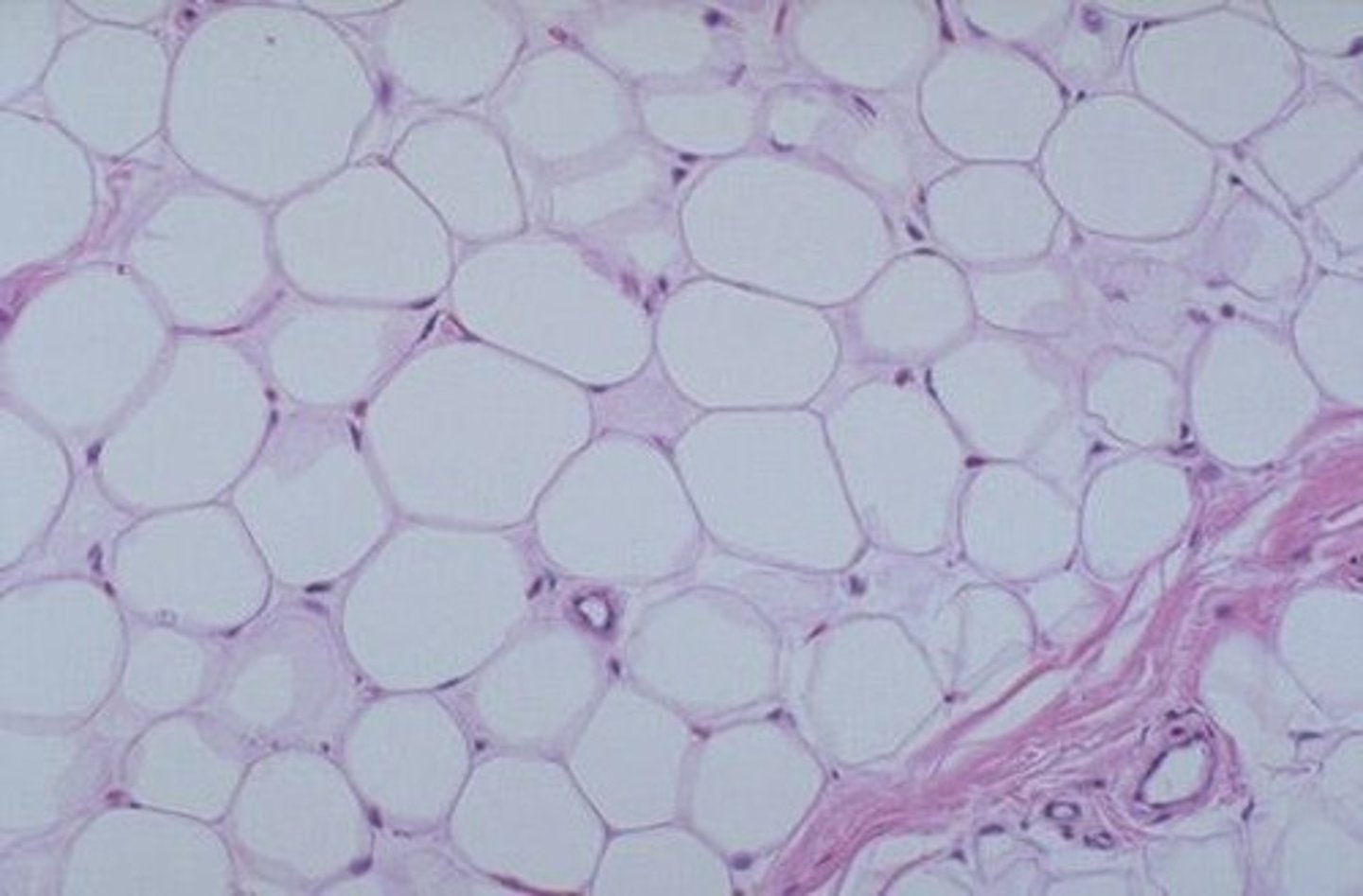
adipose tissue
stores body fat w/ adipocytes (fat cells)
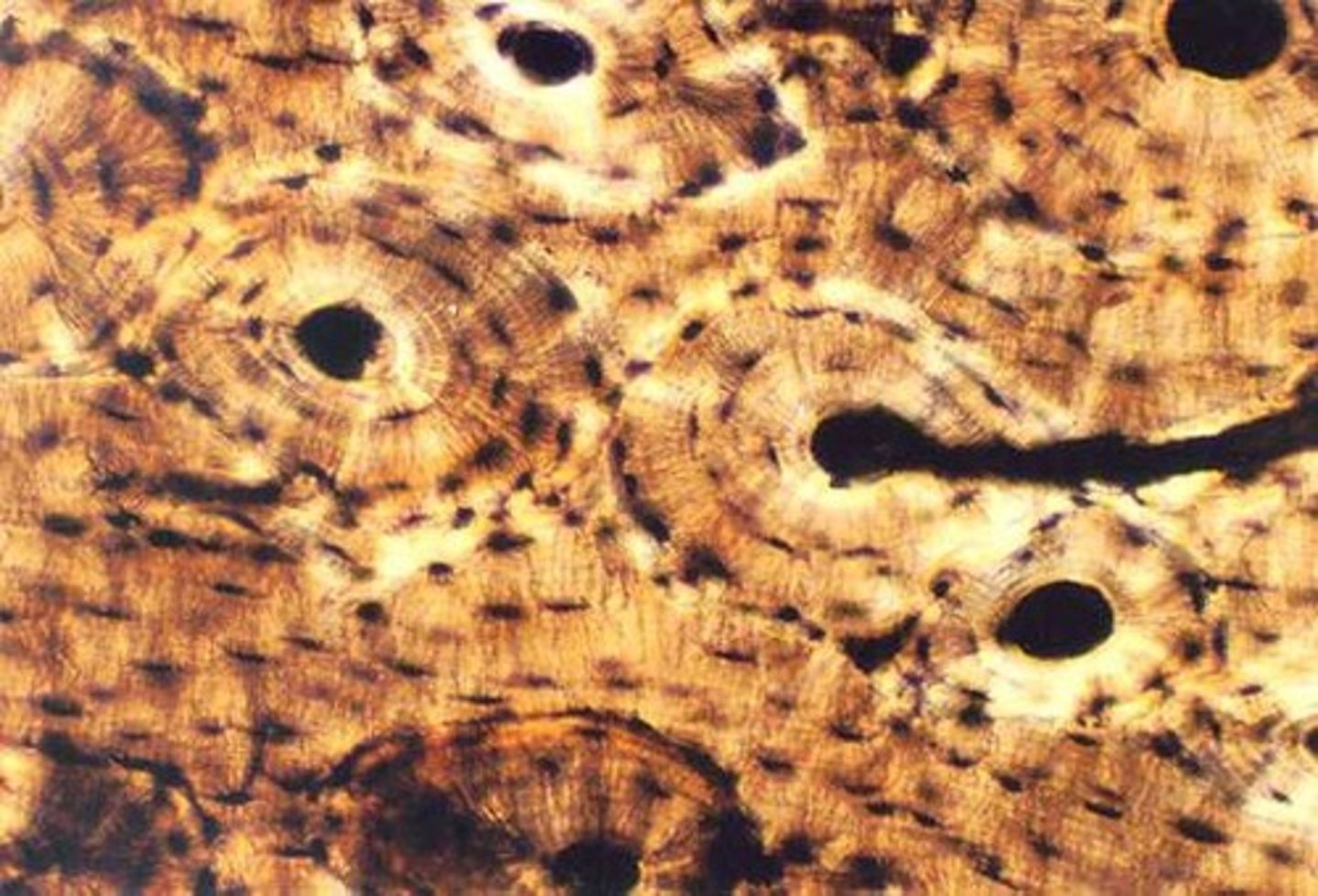
compact bone tissue
dense bone structure that provides strength and support
flat bone
layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone, marrow w/o a marrow cavity. ex: left parietal and sternum
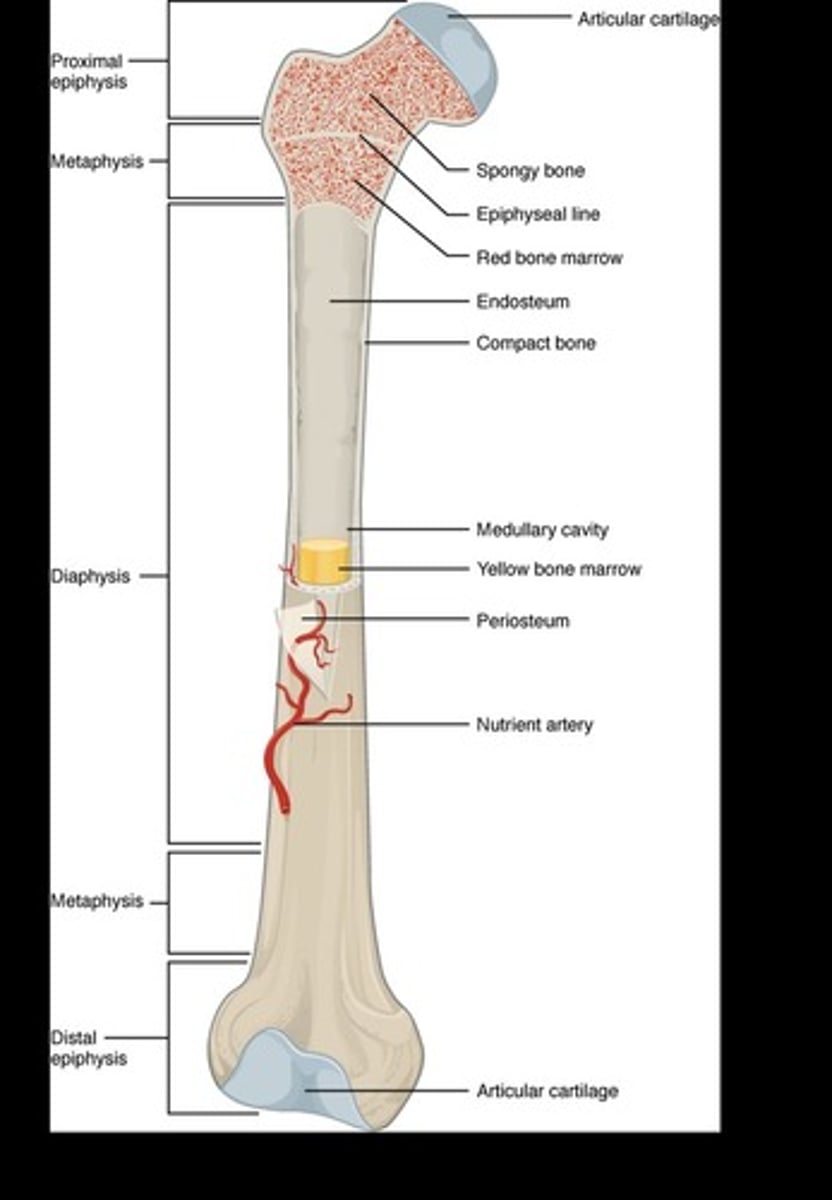
long bone
shaft and two ends. thick outside layer w/ marrow cavity. ends are spongy. ex: humerus and femur
irregular bones
thin layers of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone. ex: thoracic vertebrae and mandible
short bones
cube shaped w/ equal horizontal & vertical measurements, mostly spongy w/ thin outside layer of compact bone. ex: carpal and patellae
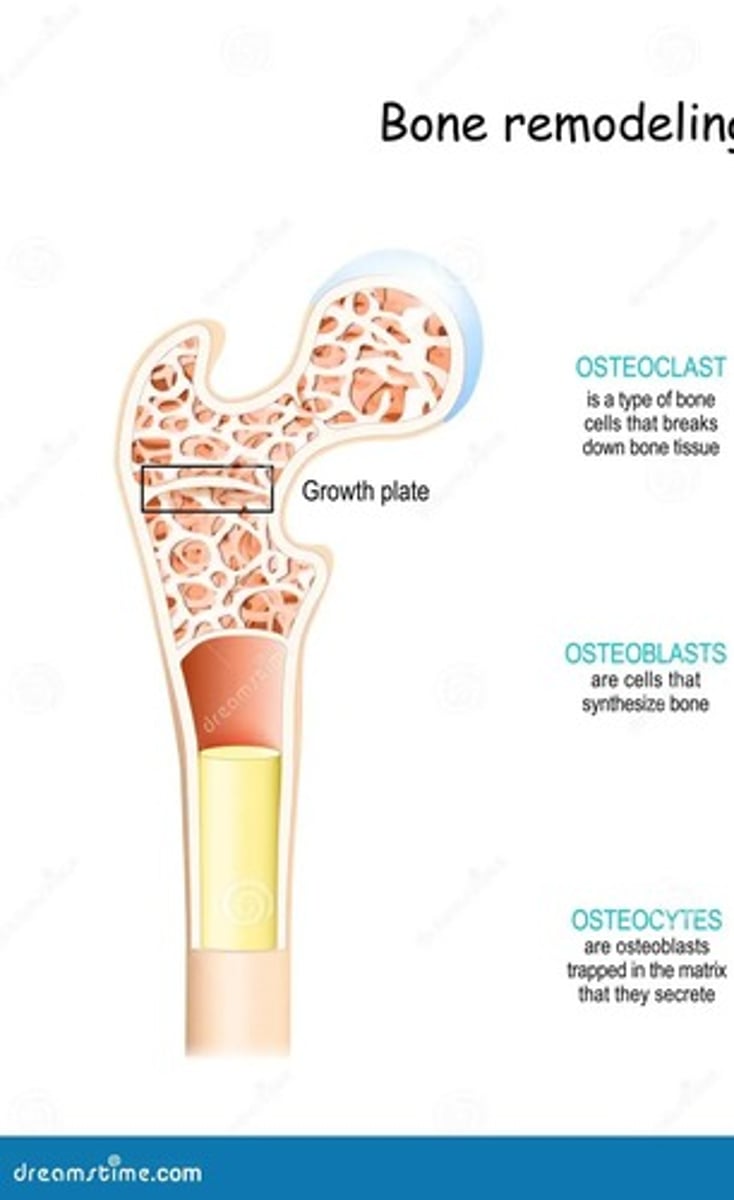
osteoblasts
cells that help build bones
osteoclasts
cells that break down bones
bony callus formation
fibrocartilage callus is gradually replaced with a spongy bone callus. osteoclasts and osteoblasts appear
hematoma formation
broken blood vessels swell to form a mass (hematoma) between broken pieces. kills injured cells by reducing blood supply
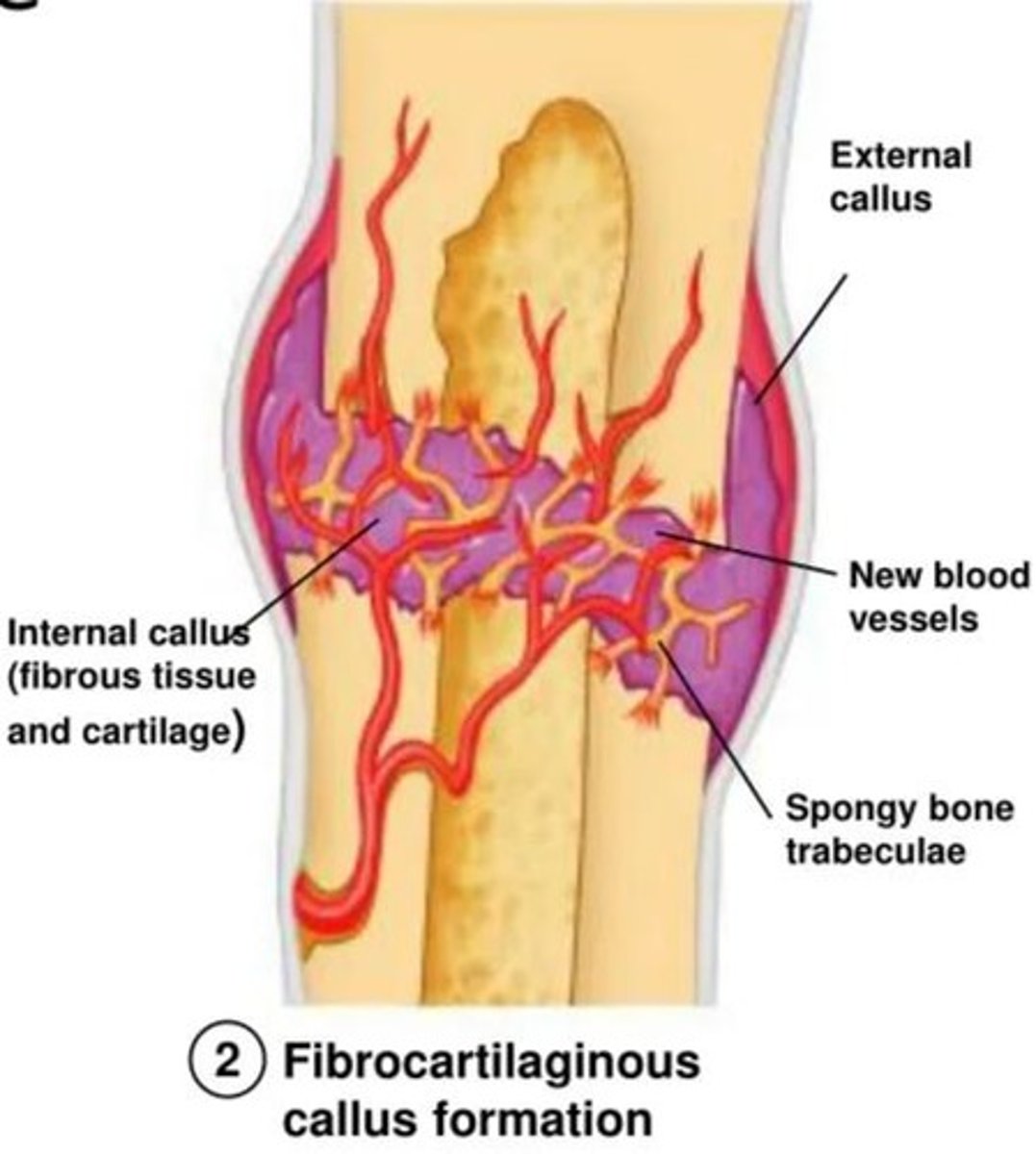
fibrocartilage callus formation
new capillaries form in clotted blood in damaged area. fibrocartilage callus forms to close gap
bone remodeling
callus remodeled with osteoblasts and osteoclasts, bone heals over next few weeks/months
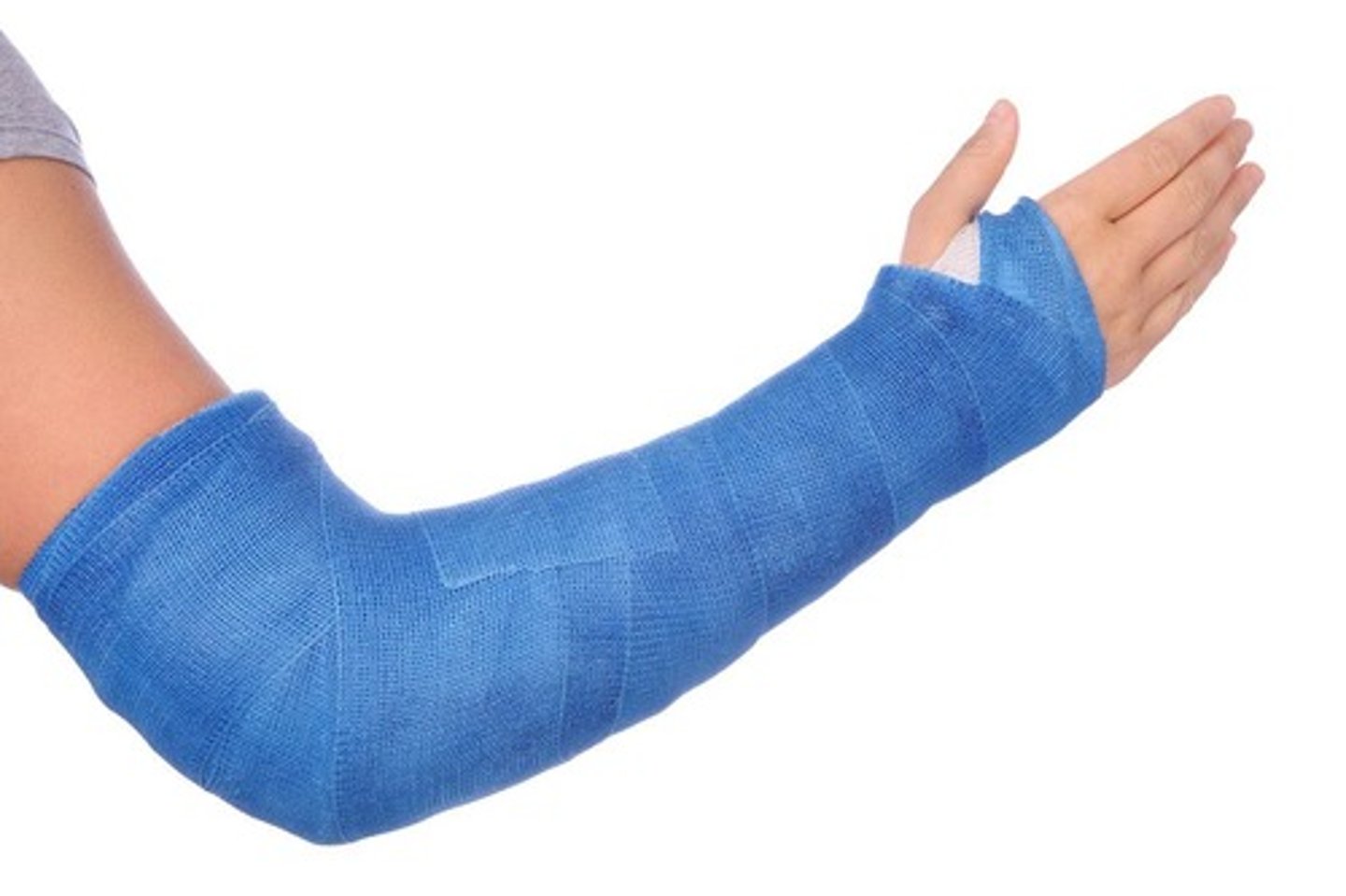
cast
external brace to support bone remodeling, usually only for children or minor adult fractures
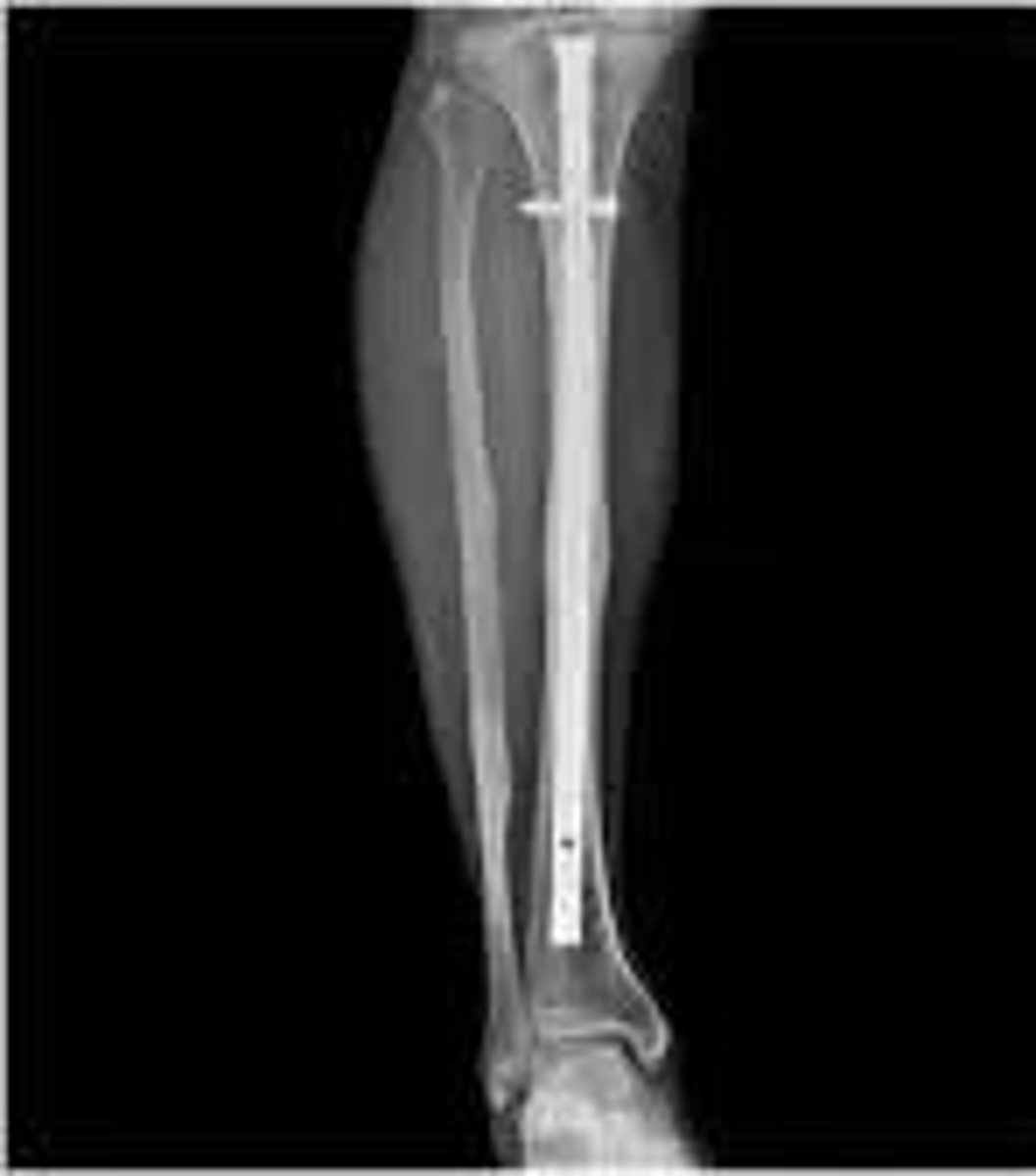
intramedullary nailing
bone marrow removed from medullary canal, common in broken long bones where medullary canal is easy to navigate
external fixation
minimally invasive short-term fixation during emergency situation, likely to lead to infection
intramedullary plating
relatively large opening used to align metal plate with broken bone
spiral fracture
cockscrew-esque appearance fracturing all the way around the bone ("complete fracture")
impact/comminuted fracture
multiple fractures
transverse fracture
straight across the bone
oblique fracture
diagonal
greenstick
occurs when the bone bends so that only one side fractures, occurs in children who have more flexible bones
compression fracture
spinal
tendon
attaches skeletal muscle tissue to bones
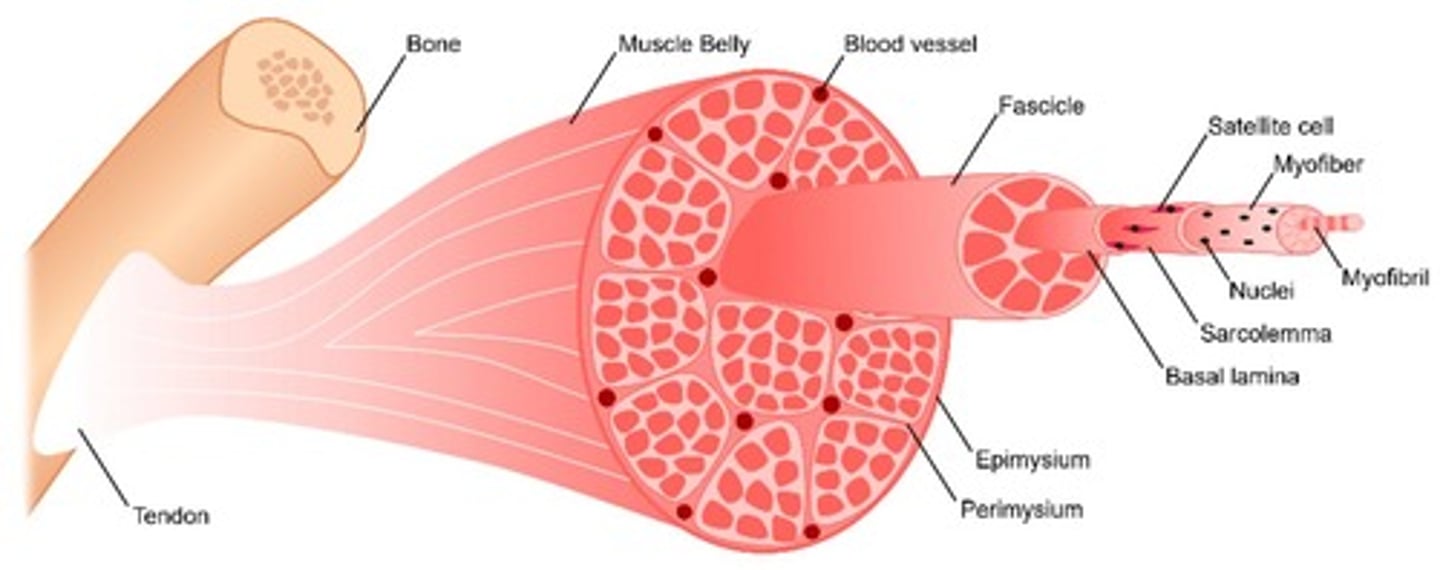
epimysium
outermost layer of connective tissue surrounding skeletal muscle
perimysium
connective tissue surrounding bundles of fascicles
endomysium
separates single cell fibers from one another
fascicle
individual bundles of muscle fibers
myofibril
basic contracting units within muscle fibers
muscle rules
1. must have two attachments and must cross at at least 1 joint; 2. muscles always pull and get shorter
Insertion
The attachment that moves.
Origin
The stationary attachment.
Flexors
Muscles that decrease the angle between ventral surfaces of the body.
Extensors
Muscles that increase the angle between ventral surfaces of the body.
Opposing pairs
Muscles that work in pairs to perform opposite actions.
Muscle striations
Point to the attachments and show the direction of the motion.
Central nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral nervous system
Nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebrum
Contains all four brain lobes.
Frontal lobe
Responsible for behavior, personality, voluntary muscle movements, planning, mood, emotions, social interaction, and attention.
Parietal lobe
Involved in sensing touch, temperature, pressure, pain, spatial processing, language, and long-term memory.
Occipital lobe
Responsible for visual perception and some forms of visual short-term memory.
Temporal lobe
Processes smell and sound, linguistic recognition, and visual memories.
Cerebellum
Area of the brain underneath the cerebrum, responsible for muscle control and balance.
Brain stem
Includes the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain; responsible for breathing, blood pressure regulation, sleeping, and waking.
Hypothalamus
Coordinates nervous system, pituitary gland activity, body temperature, thirst, hunger, homeostasis, sleep, and emotion.
Thalamus
Relays sensory information and is the center for pain perception.
Corpus callosum
Bundle of nerve fibers that communicates between the hemispheres.
Pituitary gland
Produces hormones and activates hormone production in other glands.
Dendrites
Branching protoplasmic processes that conduct impulses toward the cell body.
Cell membrane
Membrane surrounding cytoplasms of all cells.
Nucleus
Contains genetic material (chromosomes) for cell development and protein synthesis.
Cell body (soma)
Central part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and is the main component of gray matter.
Sensory neurons
Send signals to the brain.
Interneurons
Send signals within the brain.
Motor neurons
Send signals to muscles.
Axon
Long nerve cell process conducting impulses away from the cell body.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin sheaths on the axon of the neuron, allowing ions to diffuse.
Myelin sheath
Insulating layer around nerves, made of protein and fatty substances, allowing for electrical signal transmission.
Schwann cells
Cells that produce myelin sheaths.
Axon terminals
Endings of axons that change electrical impulses into chemical messages in the form of neurotransmitters.
Pineal gland
Regulates sleep and secretes melatonin (sleep hormone).
Thyroid gland
Major role in growth, development of the body, and metabolism.
Thymus
Makes white blood cells until puberty and releases hormones.
Adrenal glands
Releases hormones that help to regulate the body's response to stress, metabolism, blood pressure, and immune system.
Pancreas
Creates enzymes to break down sugars and fats, and hormones that regulate blood sugar, appetite, stomach acid, and stomach emptying.
testis
produces sperm, testosterone, which helps in the development of muscle, deep voices, and body hair
insulin
secreted by pancreas, essential to metabolism of carbs and glucose regulation
ovaries
produces estrogen and progesterone, to regulate reproduction and menstruation
liver
stores glucose from food as glycogen
glucagon
secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells to raise blood glucose levels, antagonistic to insulin
type 1 diabetes
pancreas doesn't produce insulin, due to immune system attacking cells in pancreas
type 2 diabetes
pancreatic insulin output decreases and body becomes resistant to insulin
pulmonary veins
vessels that bring oxygenated blood to the heart
left coronary artery
supplies blood to left side of heart
right coronary artery
supplies blood to right ventricle, atrium
sinoatrial node
generates an electrical signal that causes upper heart chambers (atria) to contract
atrioventricular node
controls passage of electrical signal from atria to ventricles
bundle of His
extends from AV node, receives electric signal from AV node to carry to the purkinje fibers
purkinje fibers
carry electrical impulses to ventricles, runs through the intraventricular system
capillaries
facilitate exchange of blood and oxygen with tissue
veins
carries oxygen-depleted blood to heart
arteries
distributes oxygen rich blood throughout body