HBS 2 Final Exam Review
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Heart Diagram
Cardiac Output Calculations
heart rate (beats/min) x stroke volume (mL/beat) = CO (mL/min)
ABI (ankle-brachial index) Calculation
dividing the highest systolic blood pressure measured at the ankle by the highest systolic blood pressure measured at the arm
Stroke Volume
amount of blood being pumped out of heart with each heartbeat (avg. = 75 mL/beat)
Pulse
rhythmic expansion and recoil of arteries resulting from heart contraction
Heart Rate
measure of cardiac activity; usually expressed in number of beats per minutes
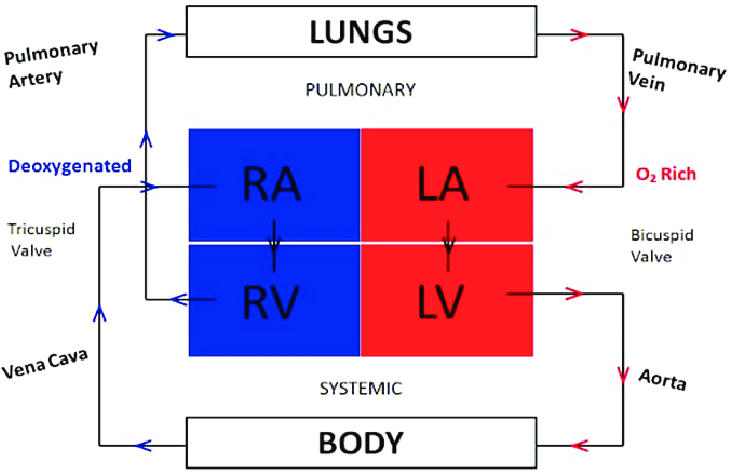
Atria
the two upper chambers of the heart, receiving blood from the body and lungs
Ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart, responsible for pumping blood out to the body and lungs
Pulmonary Artery
carries blood from your heart to your lungs; they're the ONLY arteries in the body that carry deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary Vein
carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs back to the heart, specifically the left atrium
Artery
carries blood AWAY from the heart; has thick, muscular walls for high blood pressure
Vein
carries blood TOWARDS the heart; have valves to ensure that blood only flows in one direction and has large lumens because they carry blood at low pressure so they need wide space
EKG Diagram
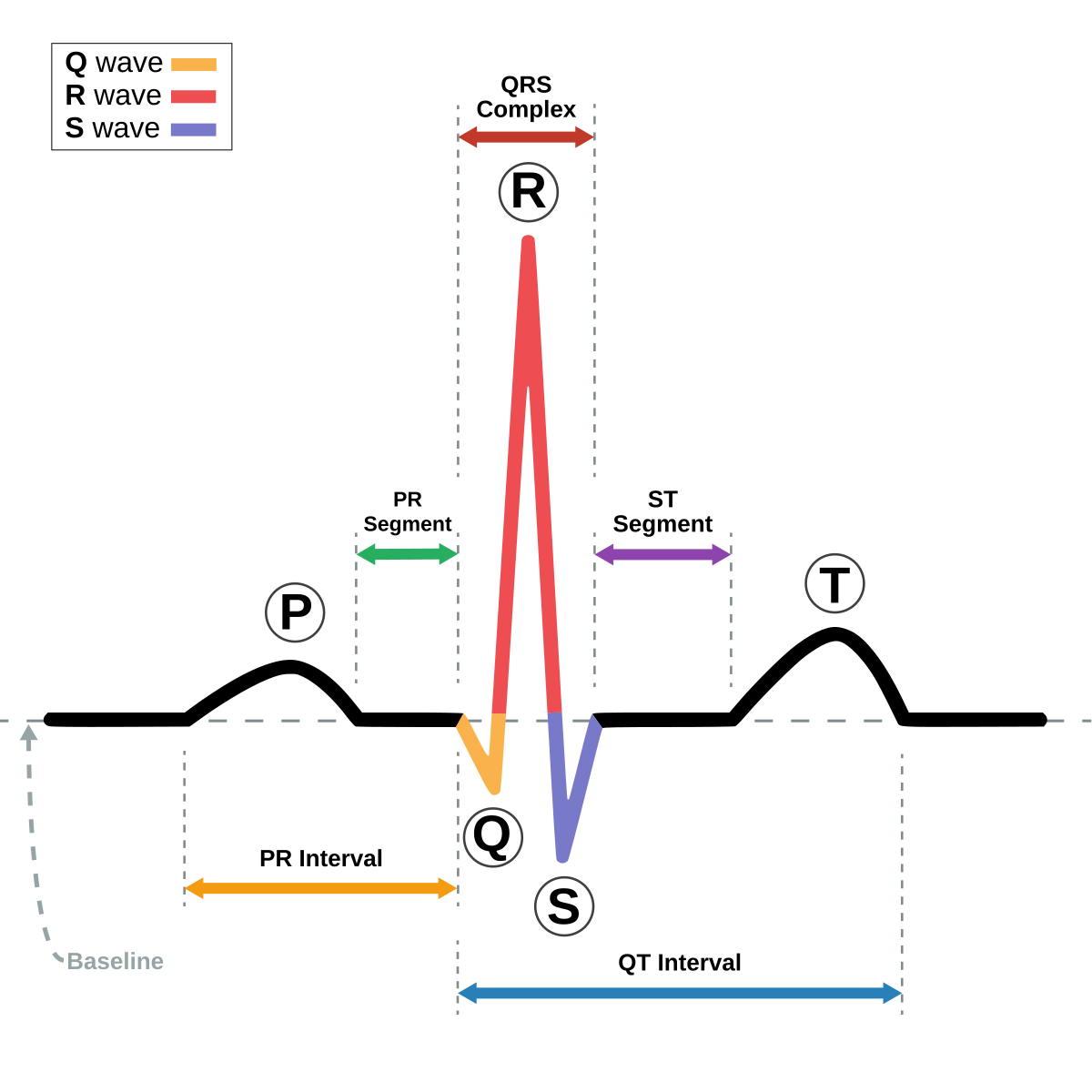
P Wave
SA node - signals atrial depolarization when filled with blood
QRS Complex
bundle of His - bundle of His fibers; ventricular depolarization (contract)
T Wave
ventricular repolarization; stimulates relaxation of ventricles
Location of Bundle of His
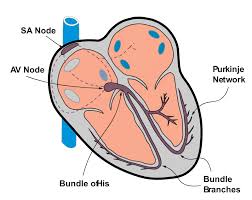
Location of Purkinjie Fibers
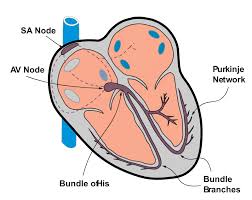
SA Node
signals atrial depolarization when filled with blood
AV Node
signals atrial contraction; start of atrial repolarization
Some EKG Notes
depolarization leads to contraction
repolarization leads to relaxation
hyperpolarization is the refractory period (no signals can come in)
order = SA BPT
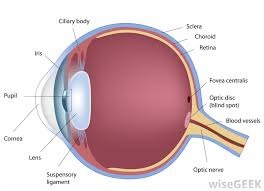
Eye Diagram
Blind Spot
an area in the visual field where a person cannot see; it occurs when light cannot reach the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye
Optic Nerve
bundle of nerve fibers that carry information form the retina to the brain
Vitreous Humor
maintain the eye's shape, allowing light to pass through unimpeded to reach the retina
Aqueous Humor
a clear fluid in the anterior part of the eye that help the cornea keep its rounded shape
Iris
muscle that controls how much light enters the eye
Retina
sheet of nervous tissue in the back portion of the eye that receives light images and converts them to nervous signals
Lens
a clear, flexible structure that makes an image on the eye's retina
Cornea
bends light as it passes through; a tough clear covering over the iris and the pupil that helps protect the eye
Pulmonary Diagram
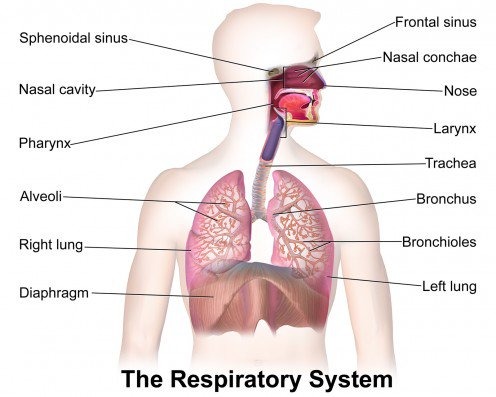
Flow of Oxygen
external environment
nose or mouth
pharynx
larynx
trachea
bronchi
bronchioles
alveoli
capillaries
bloodstream
Diaphragm
muscle; contracts = lungs expand pulling in air; relaxes = air is pushed out
Total Lung Capacity
the total volume of the lungs: sum of the vital capacity and residual volume (VC + RC)
Pulmonary Circulation vs. Systemic Circulation
pulmonary circulation moves blood between the heart and the lungs, while systemic circulation moves blood between the heart and the rest of the body
Pharynx & Trachea
both passageways that air travels through; air moves from nose to pharynx and down the trachea towards the lungs
Bronchi
bring air from the trachea into the lungs
Bronchioles
bronchi branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles
Nose/Mouth
self explanatory…?
Flow of Carbon Dioxide
bloodstream
capillaries
alveoli
bronchioles
bronchi
trachea
larynx
pharynx
oral/nasal cavity
external environment
Larynx
voice box, sits on top of the trachea; also called Adam’s Apple
Alveoli
thin-walled air sacs that extend from the bronchioles and are wrapped in capillaries; oxygen from lungs enters the bloodstream through the alveoli and capillaries
Capillary
delicate blood vessels that deliver nutrients and oxygen to cells throughout the body; thin walls allow fluids and gases to pass through easily; connects arteries and veins and helps organs function
Spirometry Graph
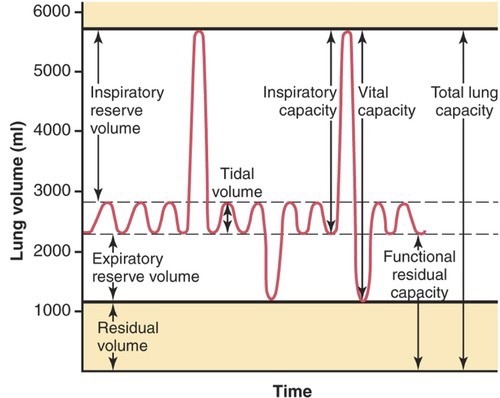
Vital Capacity Calculation
Tidal Volume + Inspiratory Reserve Volume + Expiratory Reserve Volume
Total Lung Capacity Calculation
Vital Capacity + Residual Volume
Residual Volume
the volume of air that remains in the lungs after max exhalation
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
the additional volume of air that can be inhaled with maximum effort after normal respiration
Expiratory Reserve Volume
the additional volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after normal respiration
Tidal Volume
the volume of air breathed in and out without conscious effort
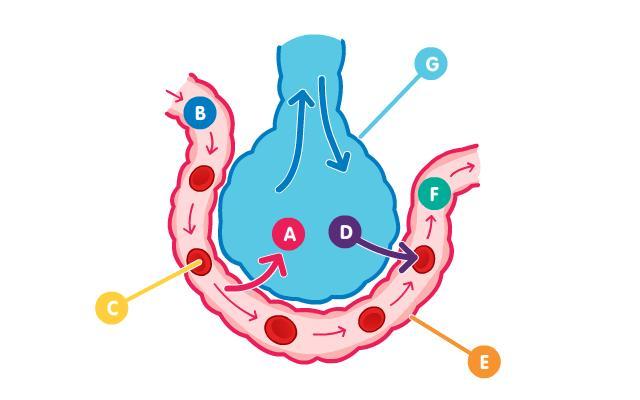
A (waste gas) = Carbon Dioxide
B (blood, before gas exchange) = Deoxygenated Blood
C (cell) = Red Blood Cell
D (gas) = Oxygen
E (vessel) = Capillary
F (blood, after gas exchange) = Oxygenated Blood
G (respiratory structure) = Alveolus
Nephron Diagram
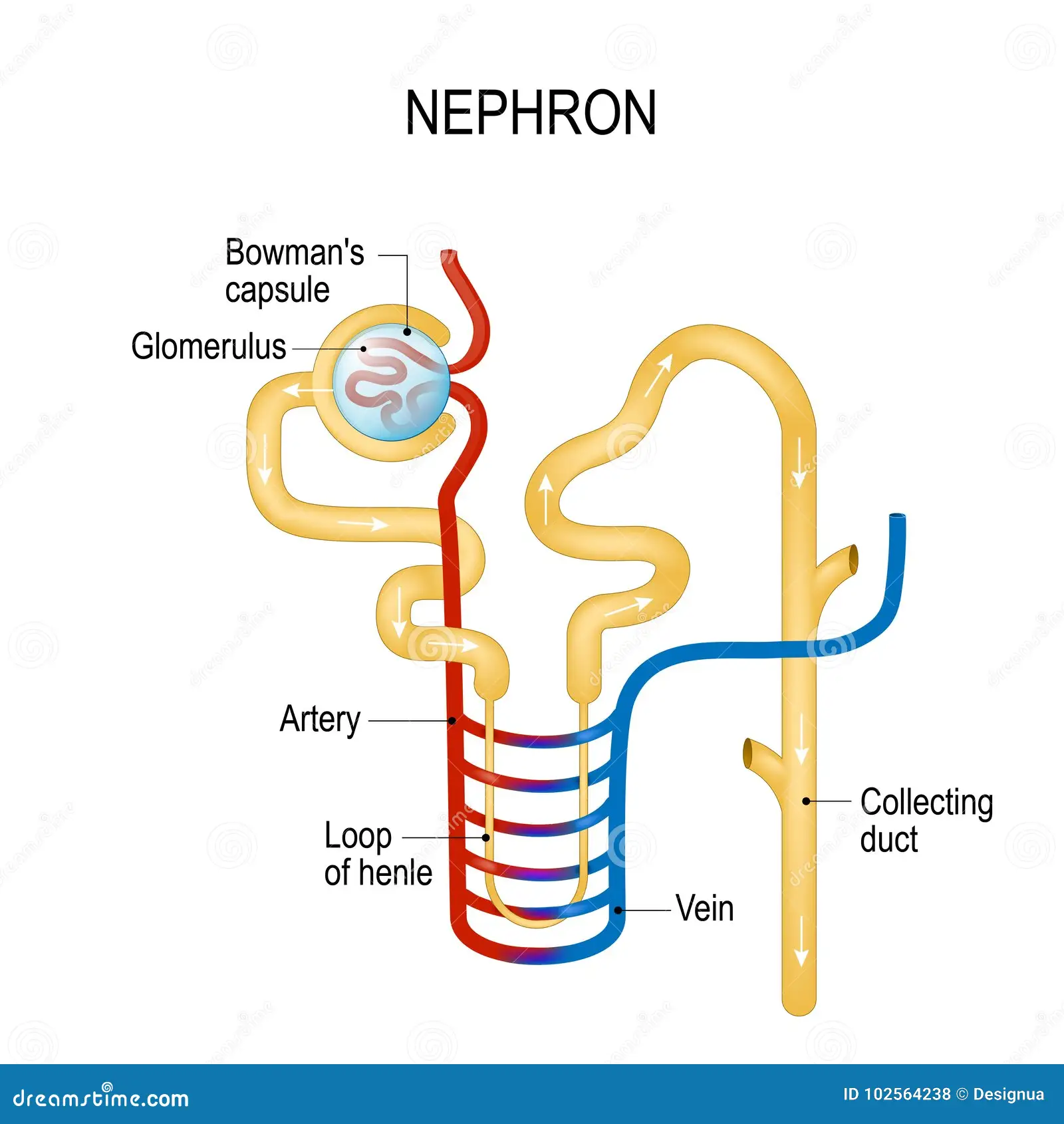
Afferent Arterioles
into Bowman’s Capsule
Efferent Arterioles
from Bowman’s Capsule
Reabsorption
moving a substance from the tubes of the nephron back into the bloodstream
Secretion
moving a substance from blood vessels into the tubes of the nephron; leave the body
Filtration
the specific process of moving and separating waste from the glomerulus into the nephron; occurs in Bowman’s Capsule; filtering, etc.
Site of reabsorption of glucose/water
in the proximal convoluted tubule/in the descending Loop of Henle
Site of filtration in the nephron
in Bowman’s Capsule
Flow of Urine
nephron
glomerulus
proximal convoluted tubule
descending loop of Henle
ascending loop of Henle
distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct
minor calyx
major calyx
renal pelvis
ureter
bladder
urethra
Renal Medulla/Pyramid
filters blood; no blood vessels/tissue that filters
Flow of Digestion
oral cavity
pharynx
upper esophageal sphincter
esophagus
lower esophageal sphincter
stomach
small intestine
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
large intestine
cecum
ascending colon
transverse colon
descending colon
sigmoid colon
rectum
anus