Translation and protein turnover
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
( ) is the “output” of genetic code
gene expression
the “flow of genetic information” in biology/life is called the?
The central dogma of molecular and cellular biology
RNA synthesis aka
transcription
protein synthesis aka
translation
( ) and ( ) are processes driven by direct base pairing
RNA synthesis (transcription)
protein synthesis (translation))
The ( ) is a triplet code of nucleotides= ( )
“genetic code”
codon
( ) these are specifically recognized by tRNAs
codons
What are the three stop codon?
UAA
UAG
UGA
multiple codons code for most ( )
amino acids
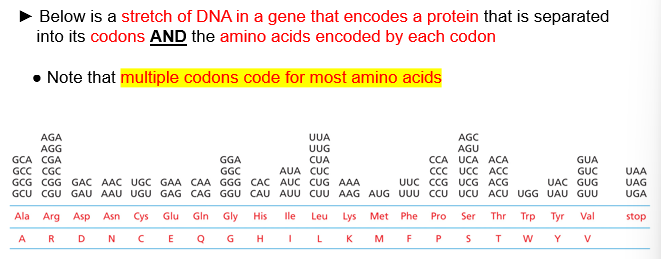
look
kk
an mRNA sequence could be “read” by the translation machinery in ( ), actual ( ) reading frame for a given polypeptide is set by the start codon ( ) , but one correct reading frame is “set” by ( )
three different reading frames
ONE
ATG
start codon
Th process of translation of the genetic code- a “sub-outline”
1) ( )
2) ( )
3) ( )
4) ( )
1) charging the tRNA- done by tRNA synthetases- one for each codon for each a.a.- and codon-anticodon pairing
2) initiation
3) elongation
a.transfer of growing polypeptide to next amino acid on the tRNA in position A
b.reset-move the tRNA with the growing polypeptide to the P position
c.Bring in nect charged tRNA
d.repeat 4a.-4c. over and over…
4)… until ribosome reaches a stop codon- then translation stops= termination
Cells “( )“ RNA information into proteins (nucleotides translated into amino acids)
translate
( ) molecules bring the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis (translation) on mRNA/ribosome complexes
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
amino acids attach to the ( ) end of tRNA
3’
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) match ( ) to mRNA ( ), anticodons of tRNAs ( ) with ( ) of the mRNA and bring in correct amino acid
amino acids
codons
base pair
codons
Aminoacyl-tRNA “charging” is done by ( )
tRNA synthetase
Specific binding between tRNA synthetase and anticodon of tRNA ensures that ( ) is attached to ( ) , so just as critical as codon to ( )
correct amino acid
correct tRNA
anticodon pairing
tRNAs are “charged” with ( )- done by tRNA synthetases, one for each ( ) for each ( )
amino acids
codon
amino acid
tRNA “charging” requires ( )- amino acids first linked to ( ) initially, so charged molecule
energy input
AMP
tRNAs get amino acids ( ) attached (aka “charged”)- by ( ) called tRNA synthetases
covalently attached
enzymes
tRNA synthetase recognizes this ( ) in the tRNA
specific anticodon
look at slide 19
ikay
Incorrect charging is corrected by ( )
tRNA synthetase proofreading
UGG codon in mRNA codes for
Trp
The ribosome has ( ) tRNA binding sites- called ( )
three
E P A
look at slide 27 now
okay
initiation is regulated by the ( )
G-protein elF2
elongation is driven by ( ) that are also ( ), namely ( ) and ( )
GTPases
elongation factors (EF)
EF-Tu
and EF-G
GTPases ( ) the elongation phase of translation and they provide some ( )- only if proper codon-anticodon base pairing is GTP hydrolyzed
regulate
fidelity/proofreading
Termination:
1)binding of ( ) to an ( ) site bearing a ( )
2) ( )
3) ( )
4) ( )
release factor (that does NOT have an amino acid attached)
A
stop codon
GTP hydrolysis by GTPase
ribosome conformation change
dissociation
To initiate translation, it really important to recognize two concepts what are they?
1) that translation NEVER starts at the very end of the mRNA but at the internal start codon
2) the orientation of the START CODON: 5’-AUG-3’
the ribosome:
-very complex ( )
-site of:
( )
ribozyme (enzyme that uses RNA for catalysis)
1)tRNA anticodon- codon pairing
2) catalyzes the transfer (covalent bonding) of growing polypeptide to the next amino acid (so peptide bond formation)
Ribosomes are ( )- have RNA ( ) in them, catalyze peptide bond formation using rRNA (so are ( ))
ribonucleoproteins (RNPs)
rRNA
ribozymes
ribosomes are made of ( )
large subunit, small subunit and rRNA
Ribosomes are the same among prokaryotes and eukaryotes
false l
look at slide 39
okay
The ribosome is a ribozyme- bound rRNA participates in ( )
enzyme activity
( ) are the target of several antibiotics, because they are necessary and differ from the eukaryotic host’s ribosomes
bacterial ribosomes
Ribosomes may be ( ) or ( ) to the rough ER
free
bound
look at slide 43
okay
Ribosomes may be ( ) to rough ER or free
membrane-bound
Potential steps in post-translation modifications to create a functional protein,:
nascent (newly formed) polypeptides can begin ( ) as they emerge from a ribosome, assisted by
folding
chaperone proteins
look at slide 48
mkat