Human Evolution Midterm (copy) (copy)
1/499
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
500 Terms
Evolution
A change in the allele frequencies in a population over time.
Natural Selection
An evolutionary process that occurs when certain phenotypes confer an advantage or disadvantage in survival and/or reproductive success. This is one of the forces of evolution.
Non-Random
Natural Selection: Random or Non-Random?
Mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence of the genetic code. This is one of the forces of evolution.
Random
Mutation: Random or Non-Random?
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies within a population from one generation to the next. This is one of the forces of evolution.
Random
Genetic Drift: Random or Non-Random?
Gene Flow
The movement of alleles from one population to another. This is one of the forces of evolution.
Random
Gene Flow: Random or Non-Random?
Sexual Selection
An aspect of natural selection in which the selective pressure specifically affects reproductive success (the ability to successfully breed and raise offspring).
Non-Random
Sexual Selection: Random or Non-Random?
Artificial Selection (i.e., domestication)
Human-directed assortative mating among domestic animals, such as pets and livestock, designed to increase the chances of offspring having certain desirable traits.
Non-Random
Artificial Selection (i.e., domestication): Random or Non-Random?
Variation in a trait, inheritance of the trait, variants of the trait cause differential reproductive success
Three necessary & sufficient conditions of selection
Species change over time, evolution is gradual, the primary mechanism of evolution is natural selection, evolution results in speciation, all organisms are related by descent from a common ancestor
Darwin’s Five Theories of Evolution
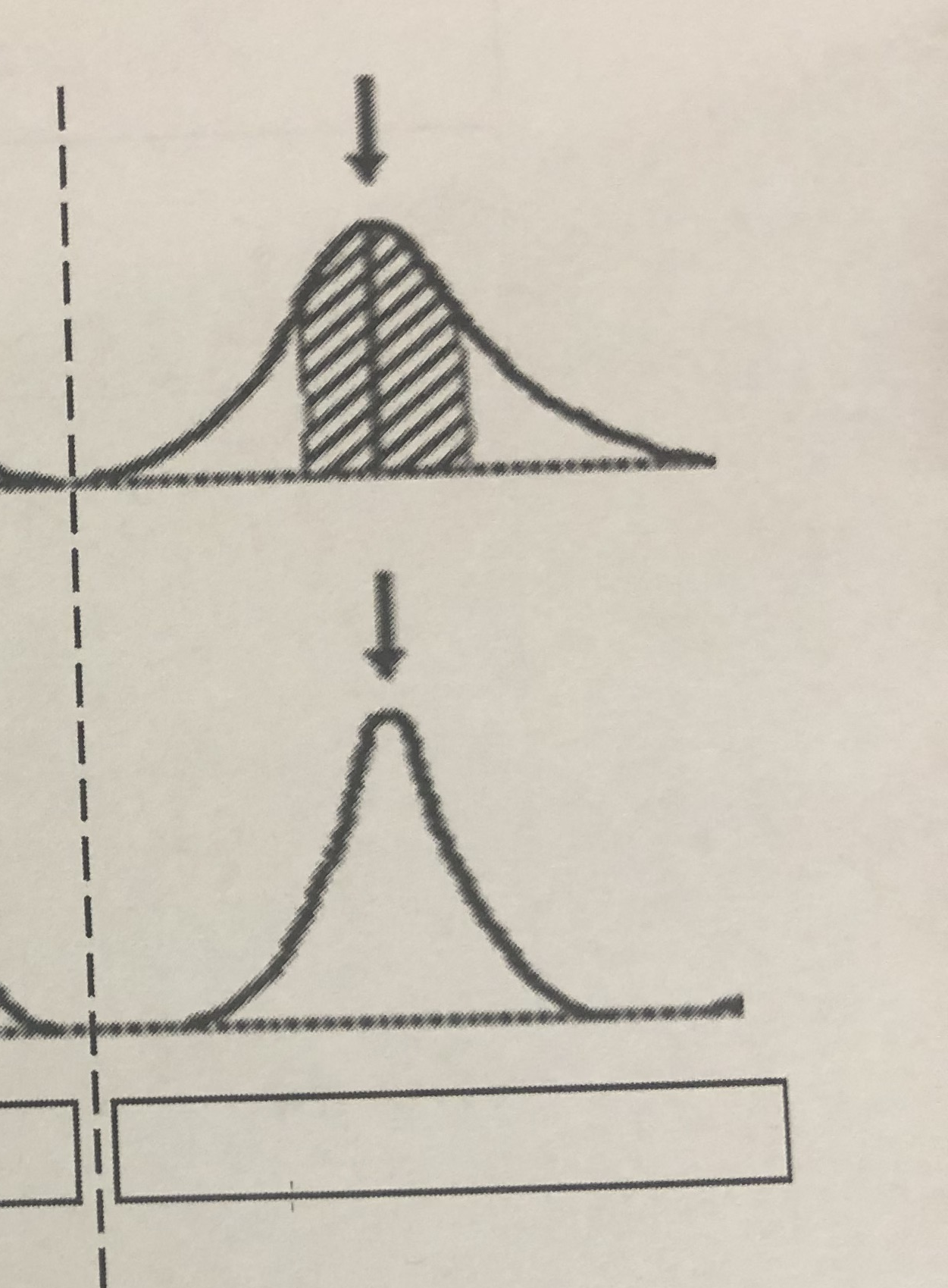
The average
Stabilizing selection: Selected for
Both extremes
Stabilizing selection: Selected against
Both extremes
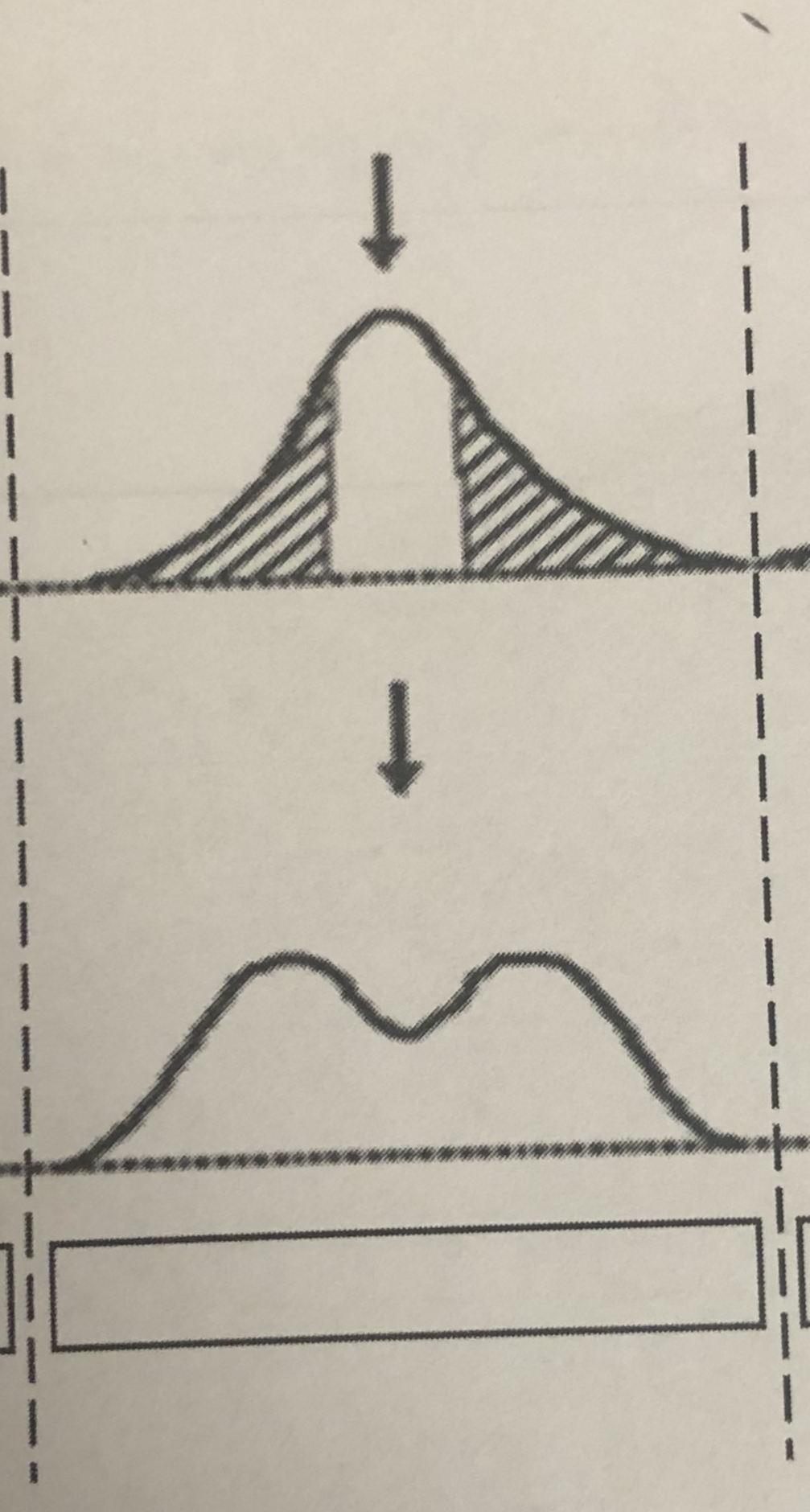
Disruptive selection: Selected for
The average
Disruptive selection: Selected against
One extreme
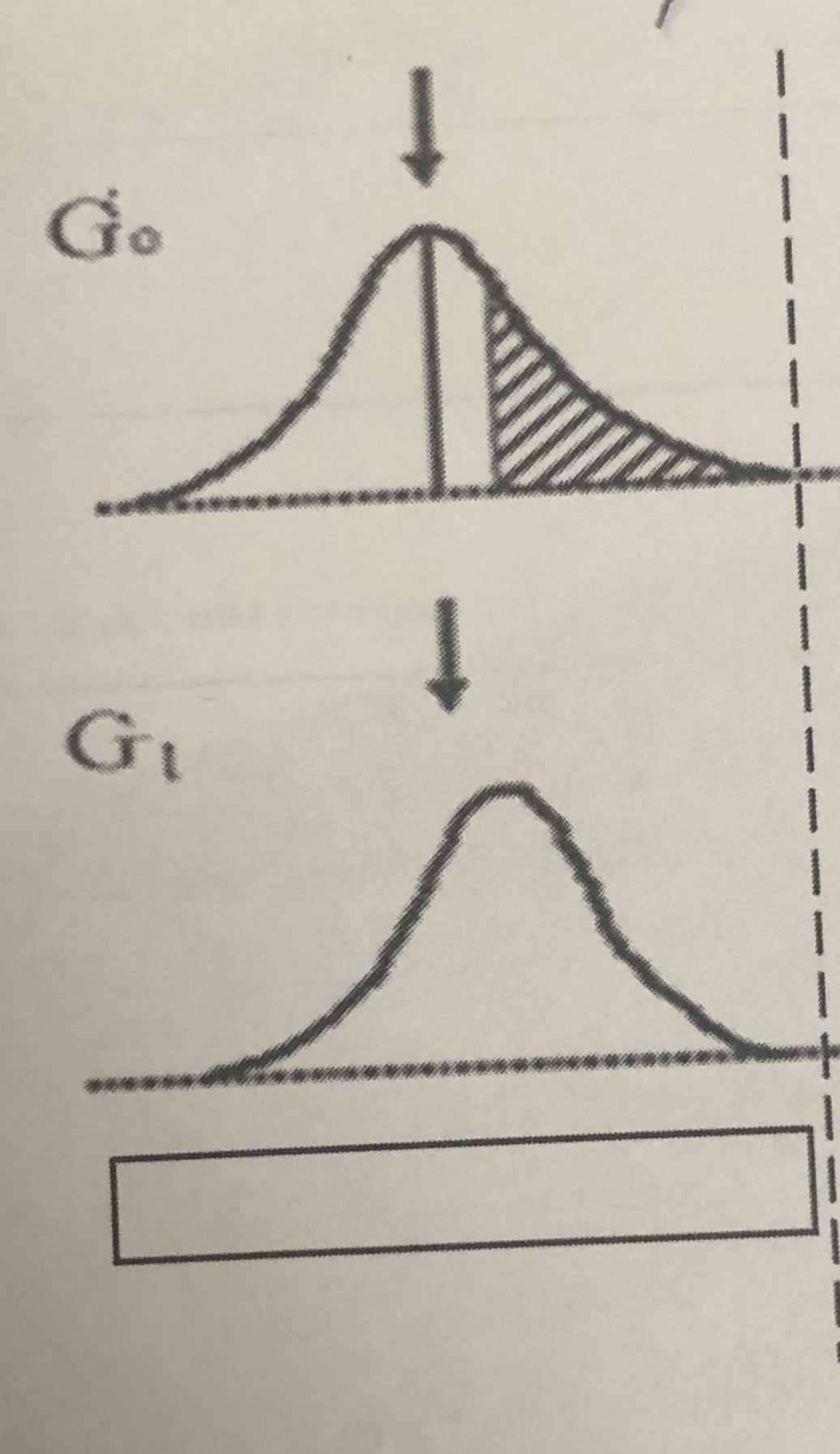
Directional selection: Selected for
One extreme
Directional selection: Selected against
Directional selection
Fill in the blank
Disruptive selection
Fill in the blank
Stabilizing selection
Fill in the blank
Grade
Reptiles represent a(n) ___ because this grouping does not include the ancestor and all of its descendants.
Clade
Mammals represent a(n) ___ because this grouping includes the last common ancestor and all of its descendants.
Homology
Whales, bats, and humans all possess mammary glands due to ___, a trait shared due to common ancestry.
Convergence
Humans, kangaroos, and penguins are all bipedal due to ___, a trait shared due to common function.
Unique derived
The blow hole represents a(n) ___ trait in whales, which is not useful for reconstructing evolutionary relationships.
Ancestral
Egg laying represents a(n) ___ trait in vertebrates.
Shared, derived
Mammary glands represent a(n) ___ trait within vertebrates, allowing us to separate out grade.
Bergmann’s Rule
For a broadly distributed monophyletic group, species and populations of smaller size tend to be found in environments with warmer climates and those of larger size tend to be found in ones that are colder.
Allen’s Rule
Due to thermal adaptation, homeothermic animals have body volume-to-surface ratios that vary inversely with the average temperature of their environment. In cold climates, the anticipated ratio is high, and it is low in warm climates.
Bergmann’s Rule
Ungulates from cooler environments (moose) have more body weight and less surface area than ungulates from warmer environments (gazelle). What rule is this an example of?
Allen’s Rule
Rabbits in the Arctic have shorter limbs and ears than rabbits in the desert. What rule is this an example of?
Adaptation
Alteration in population-level gene frequencies related to environmentally induced selective pressures; leads to a greater level of fitness for a population related to a specific environment.
No mutation, no gene flow, infinite population size, random mating, no selection
Five Assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
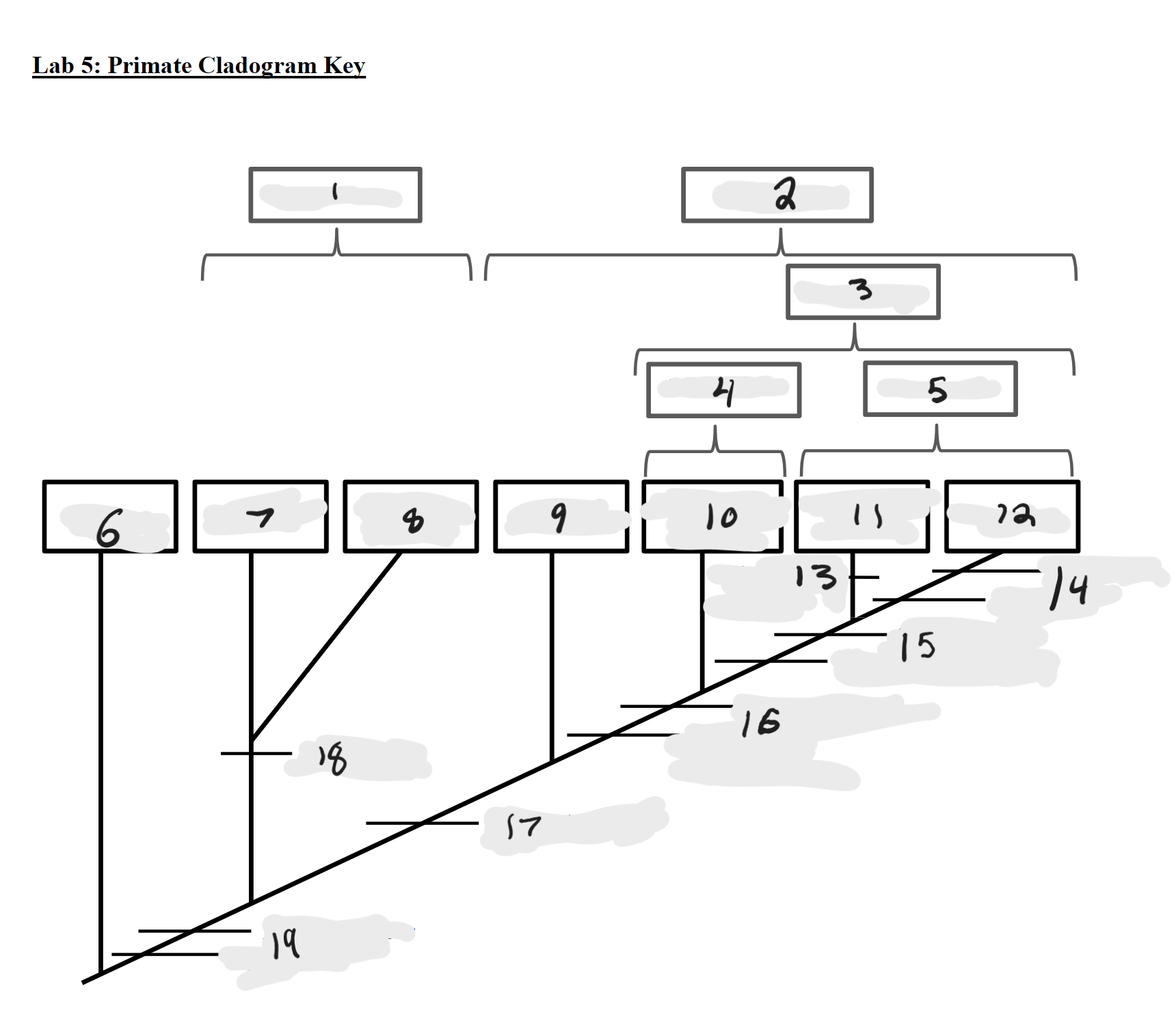
Strepsirrhines
1
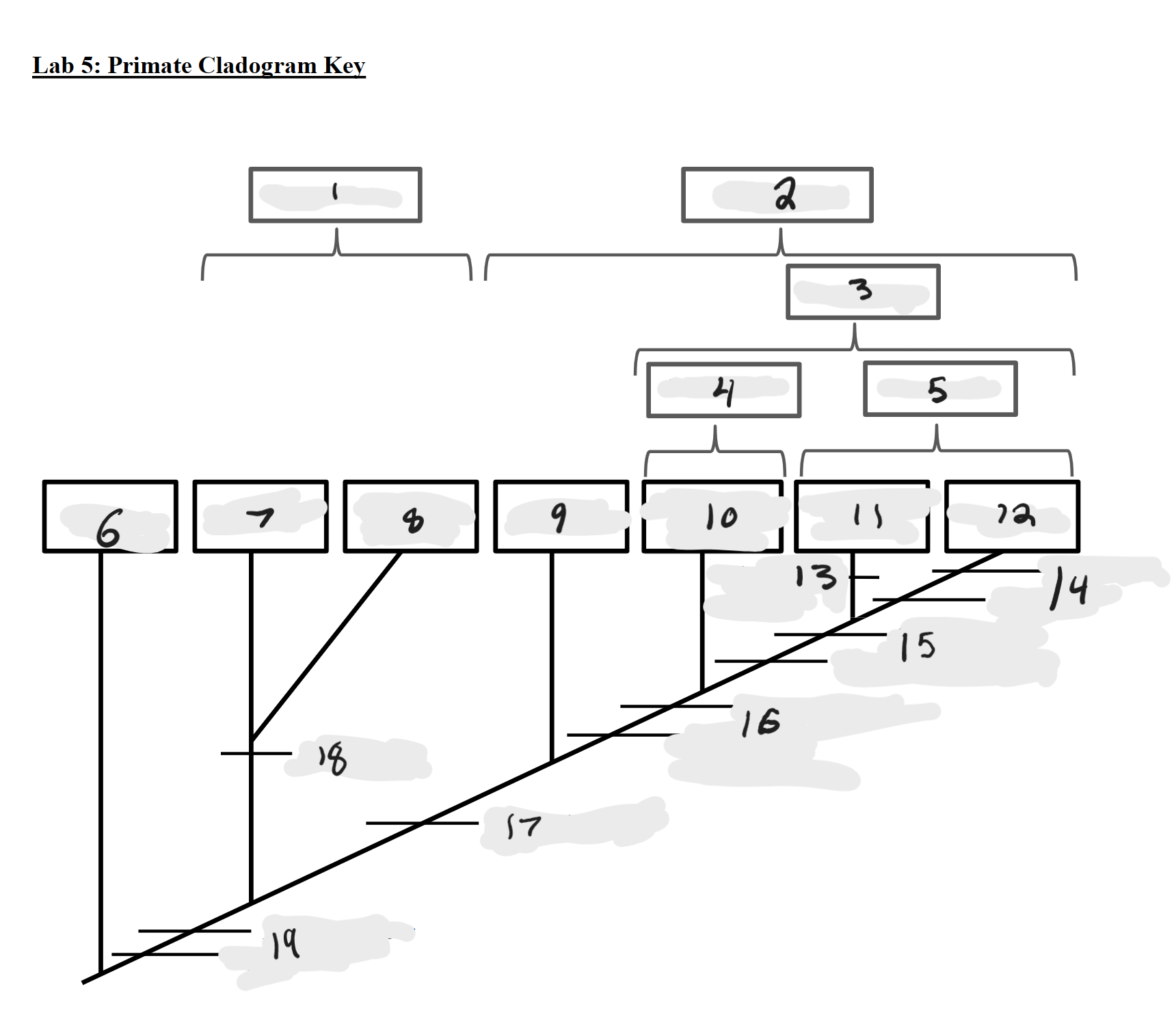
Haplorrhines
2
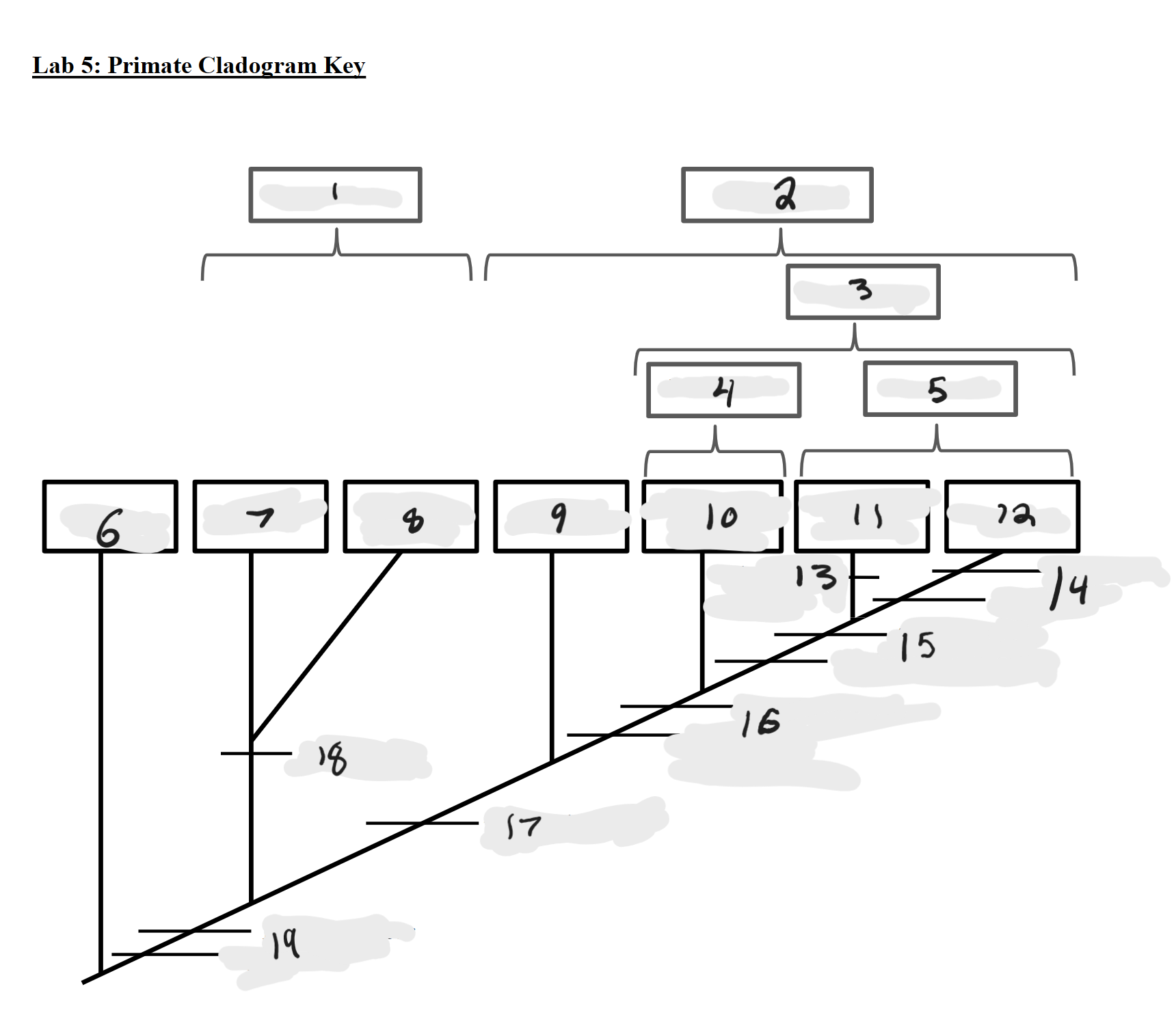
Anthropoids
3
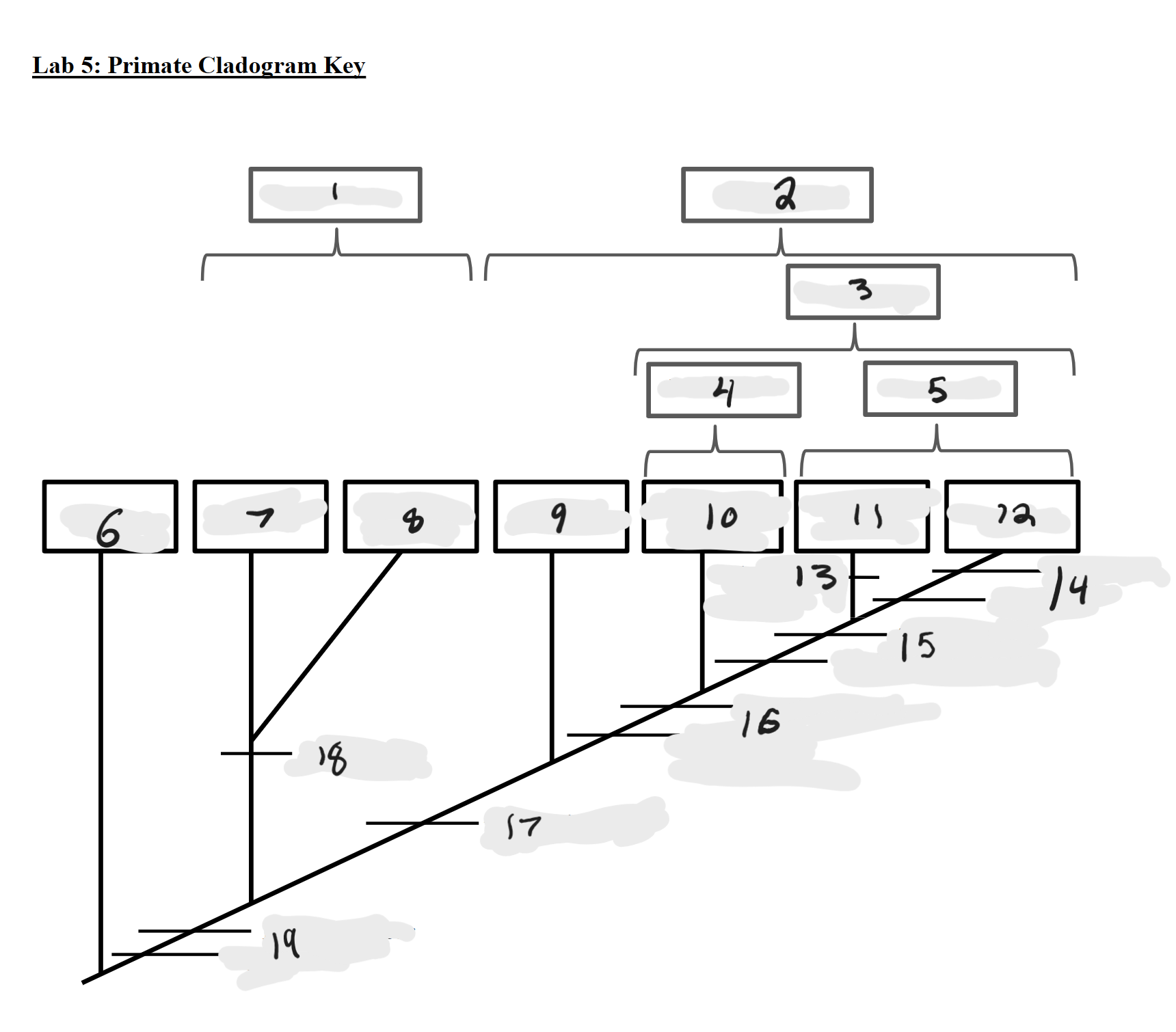
Platyrrhines
4
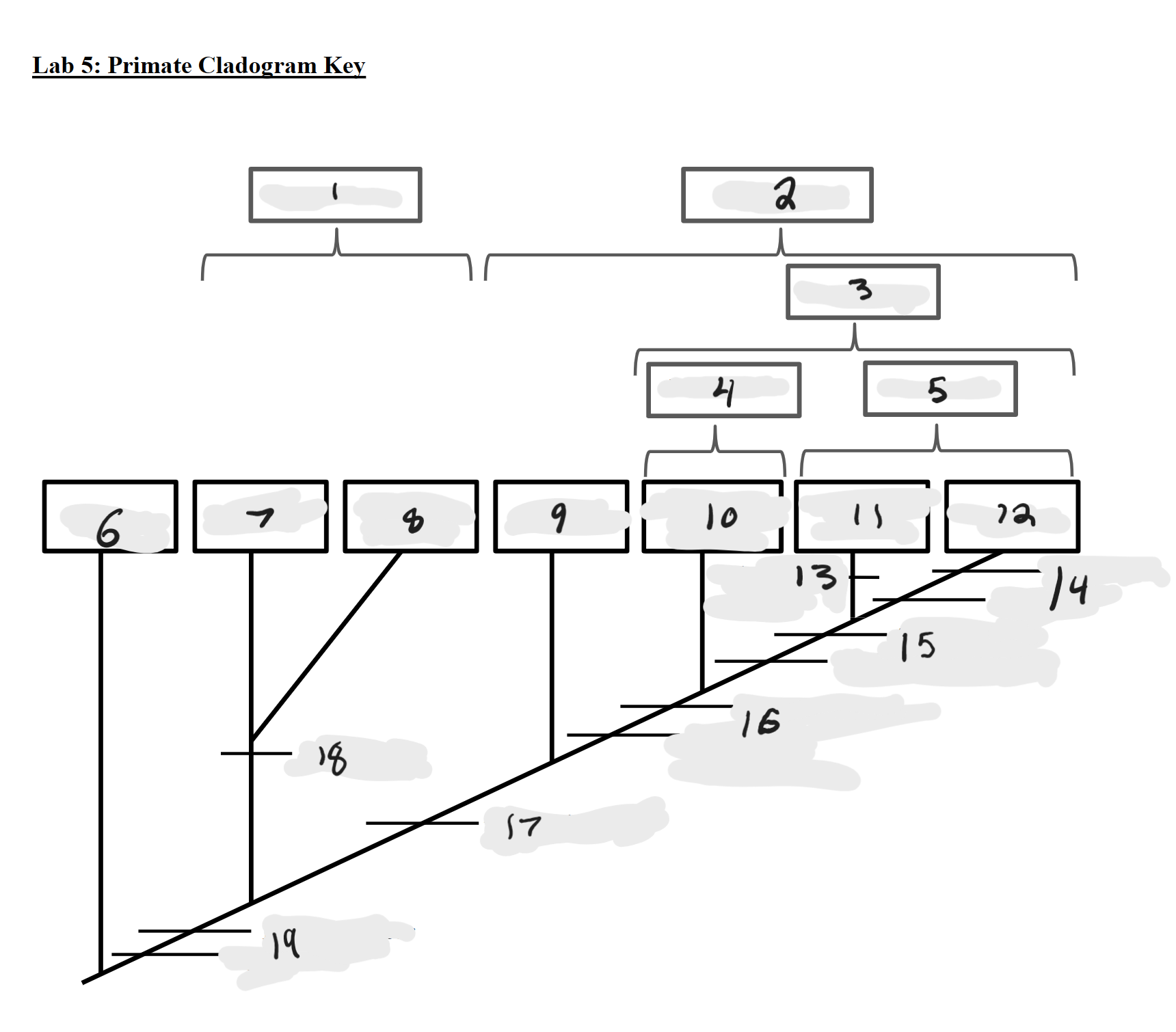
Catarrhines
5
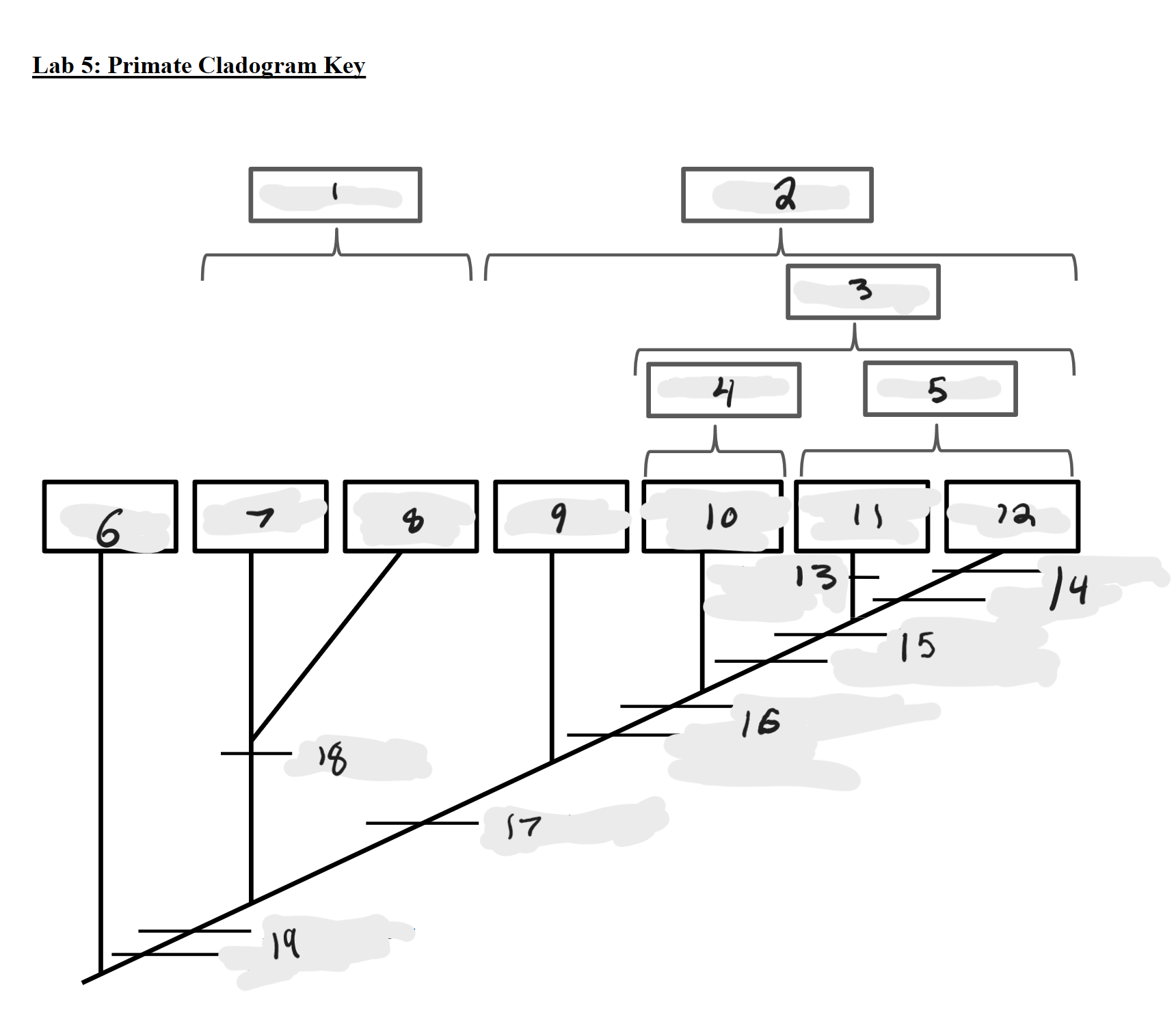
Outgroup
6
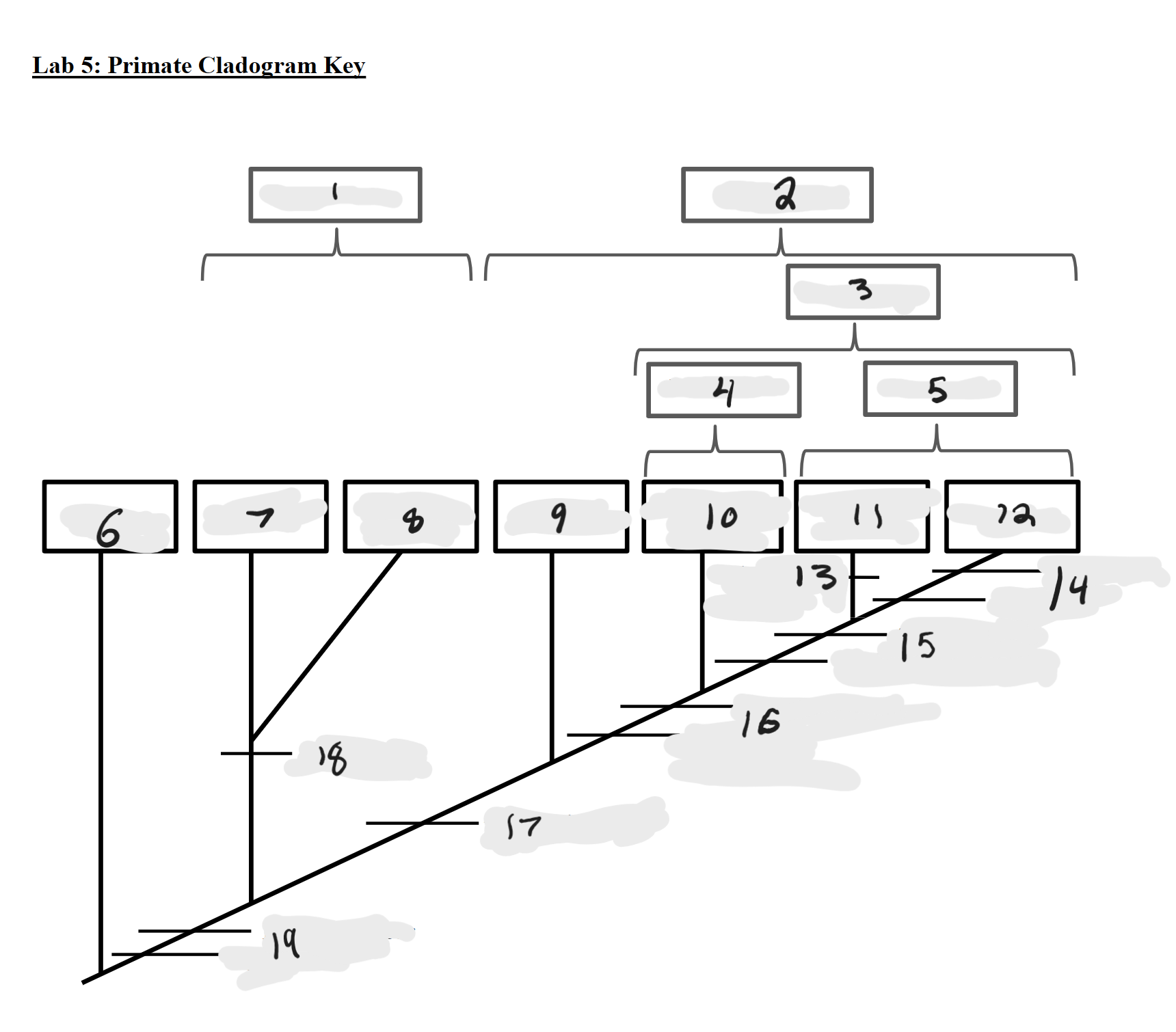
Lemurs
7
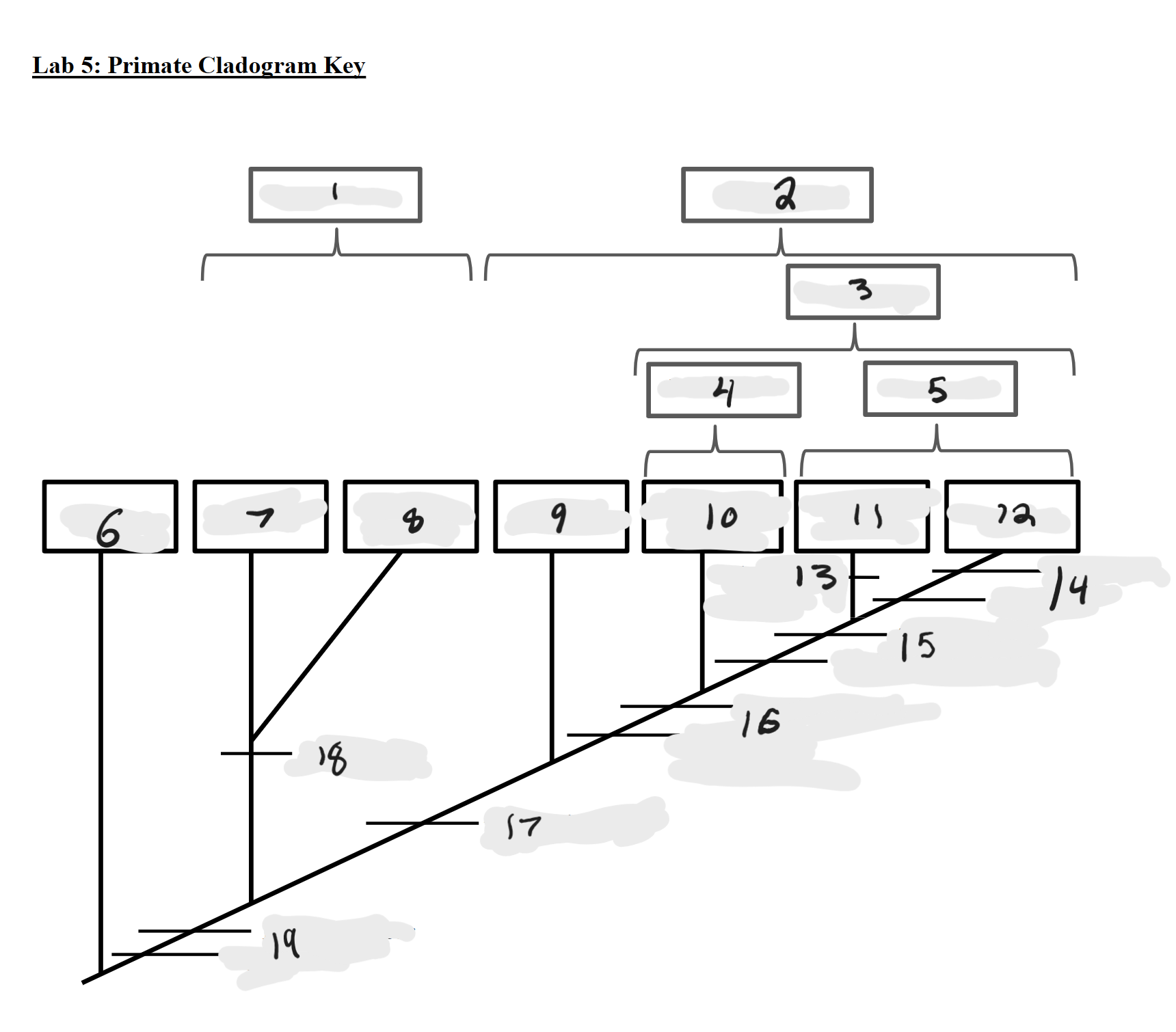
Lorises and Galagos
8
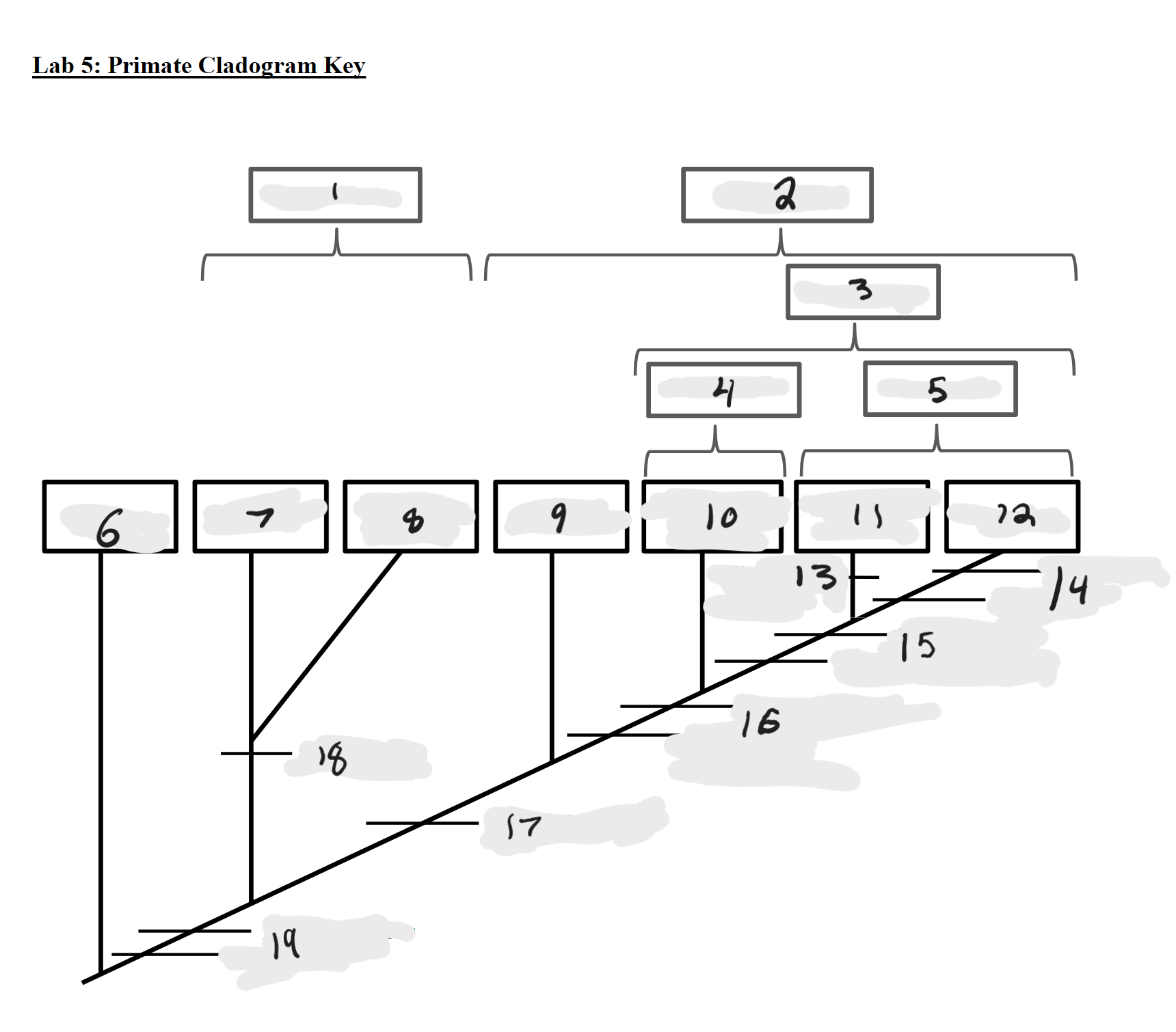
Tarsiers
9
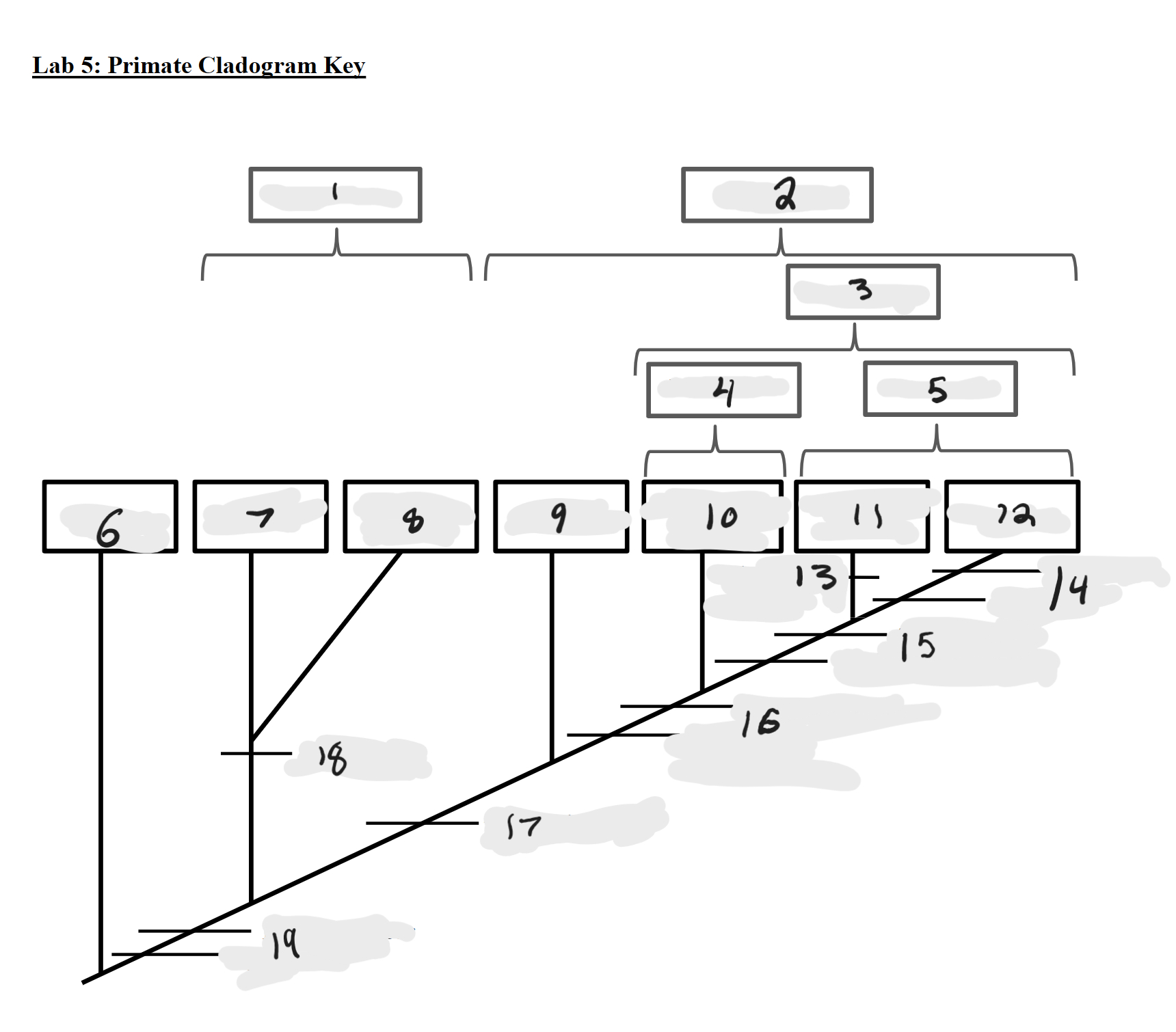
New World Monkeys
10
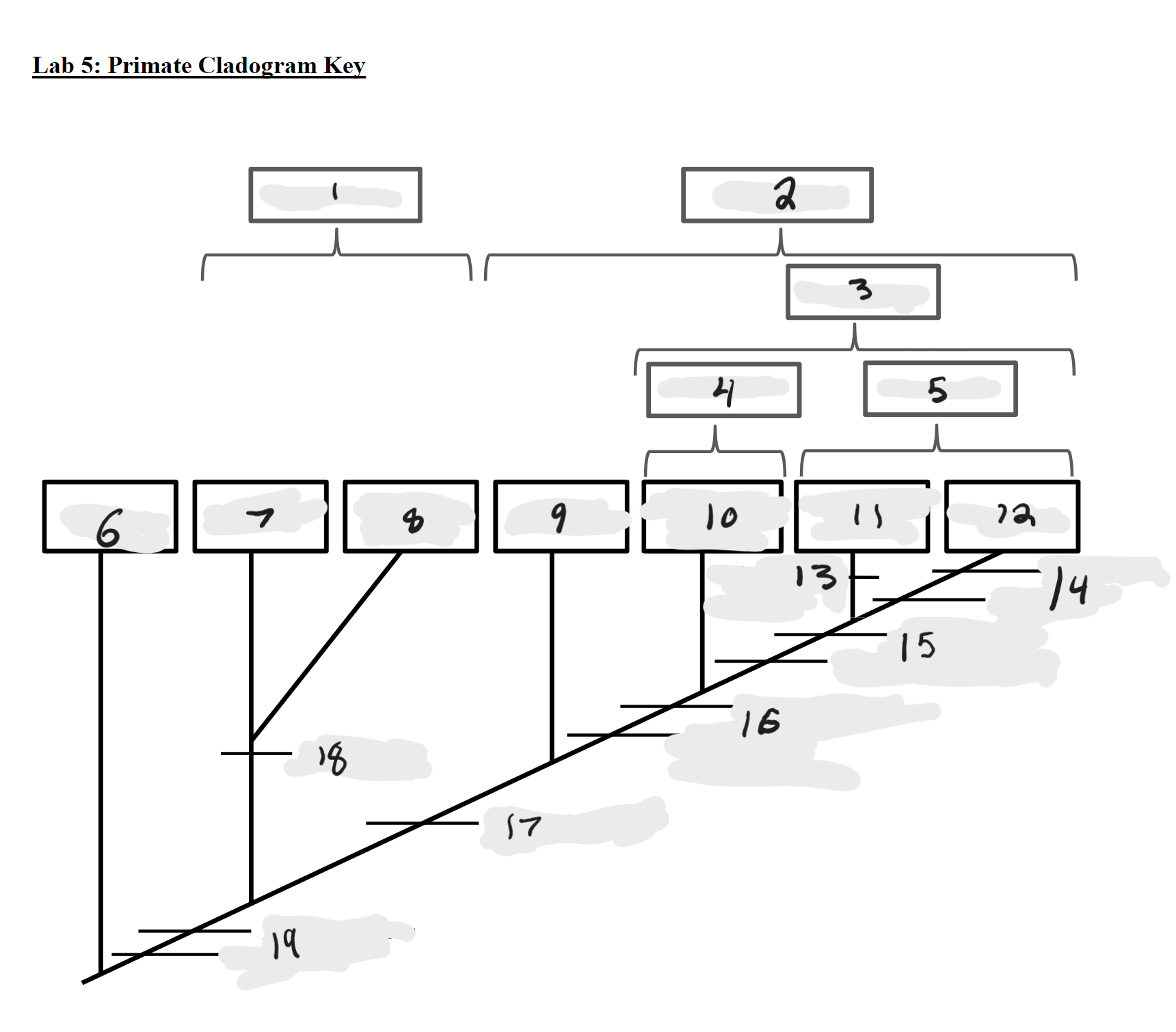
Old World Monkeys
11
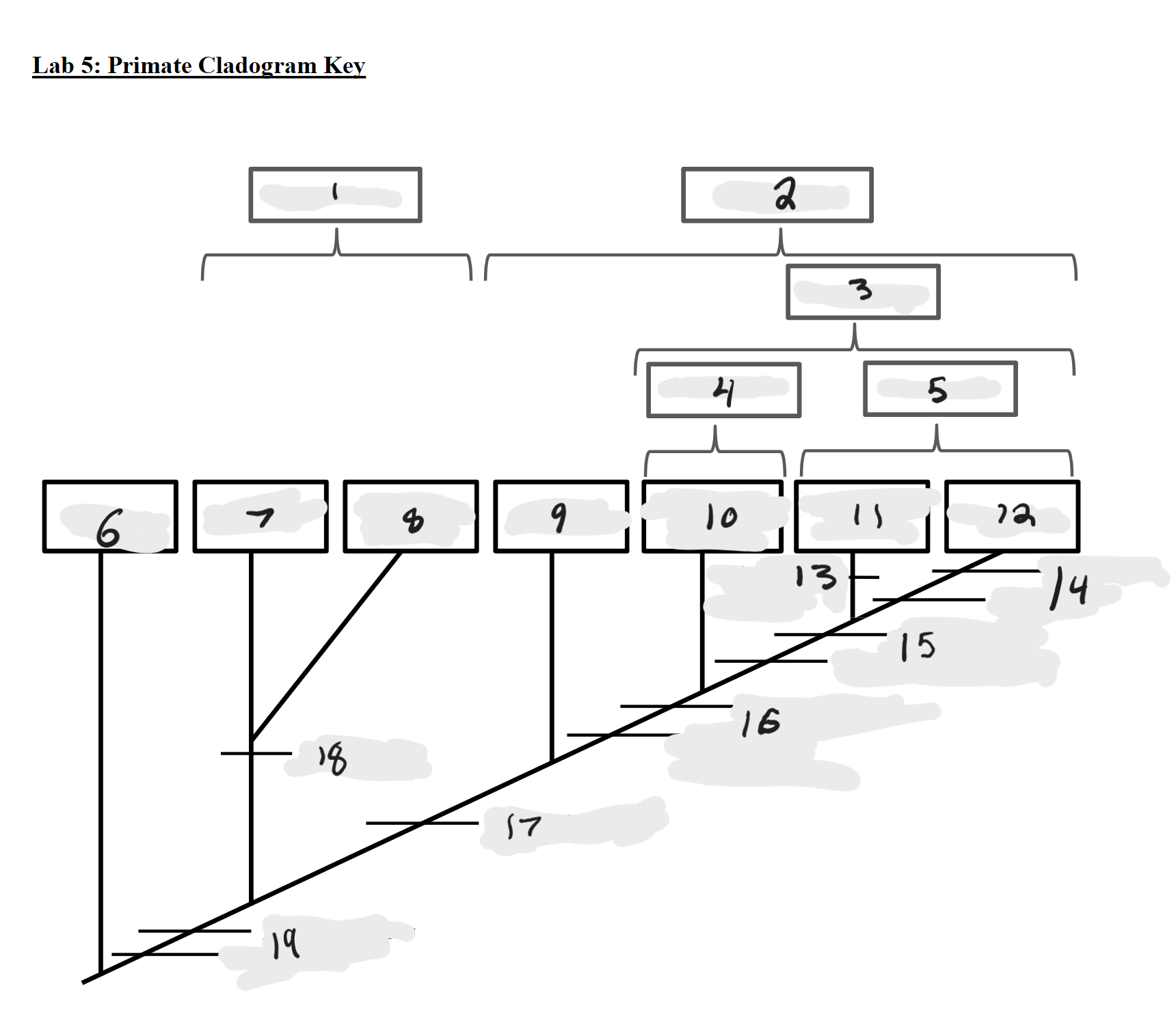
Apes
12
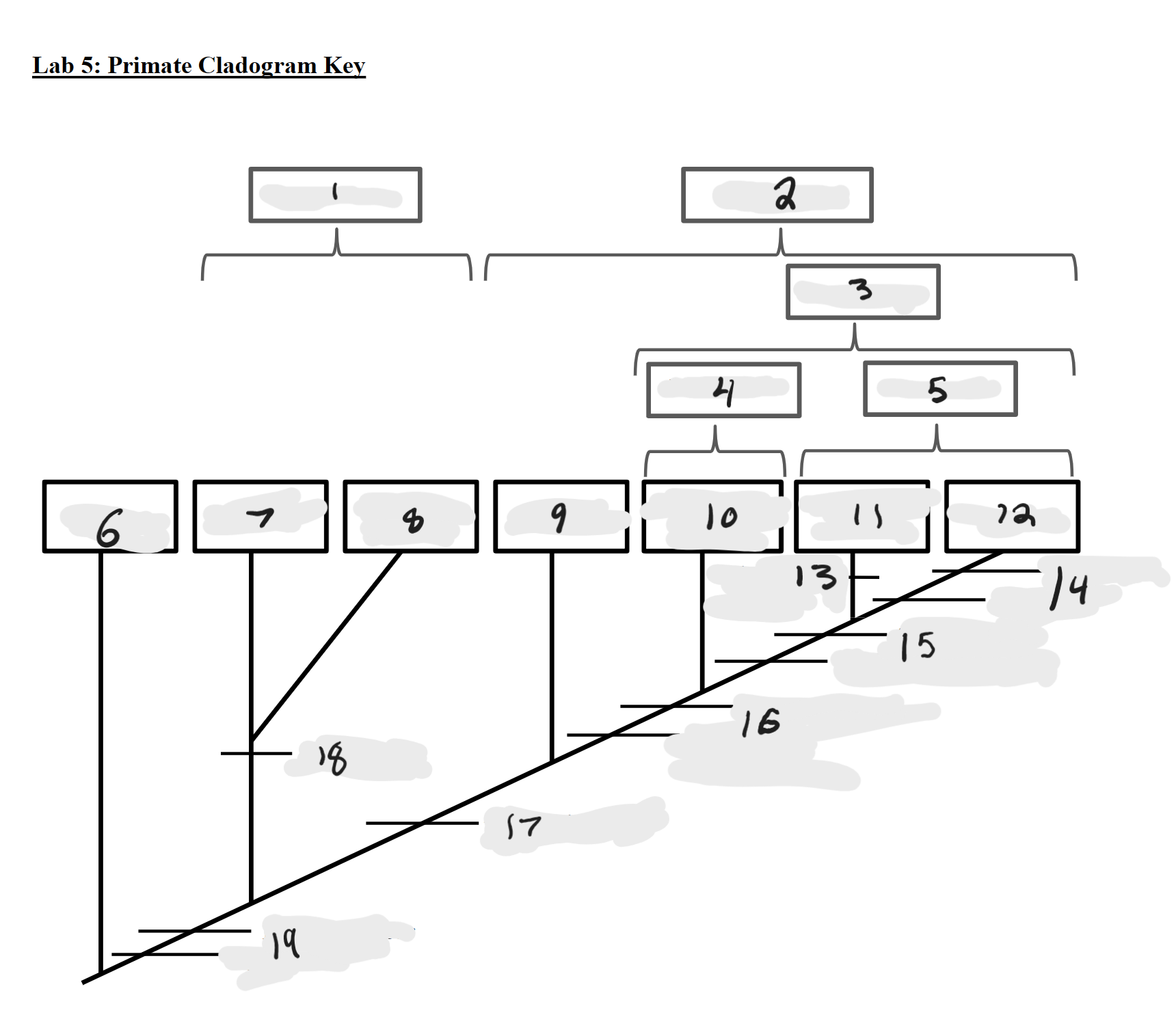
Bilophodont molars
13
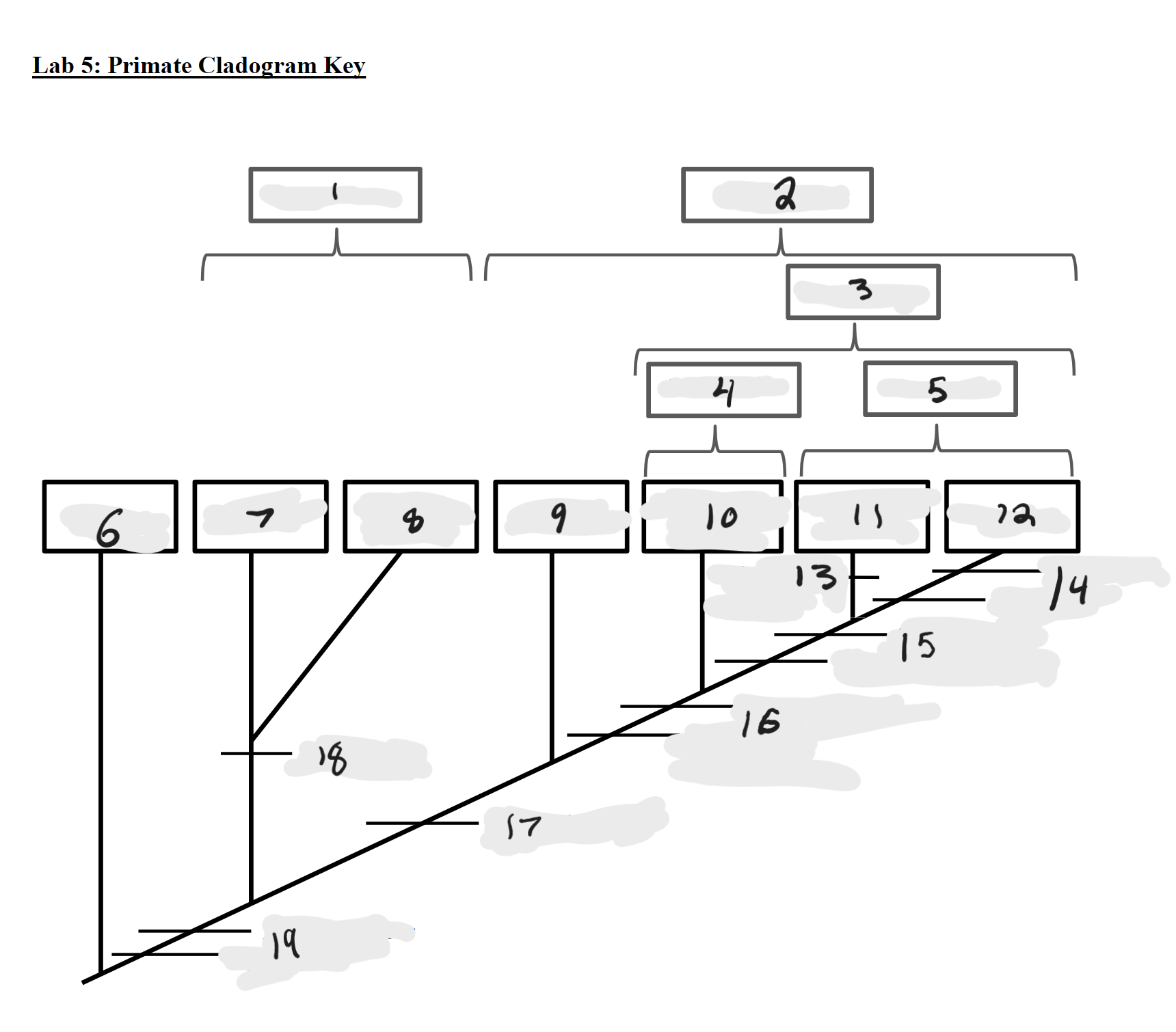
Loss of tail, Orthogrady
14
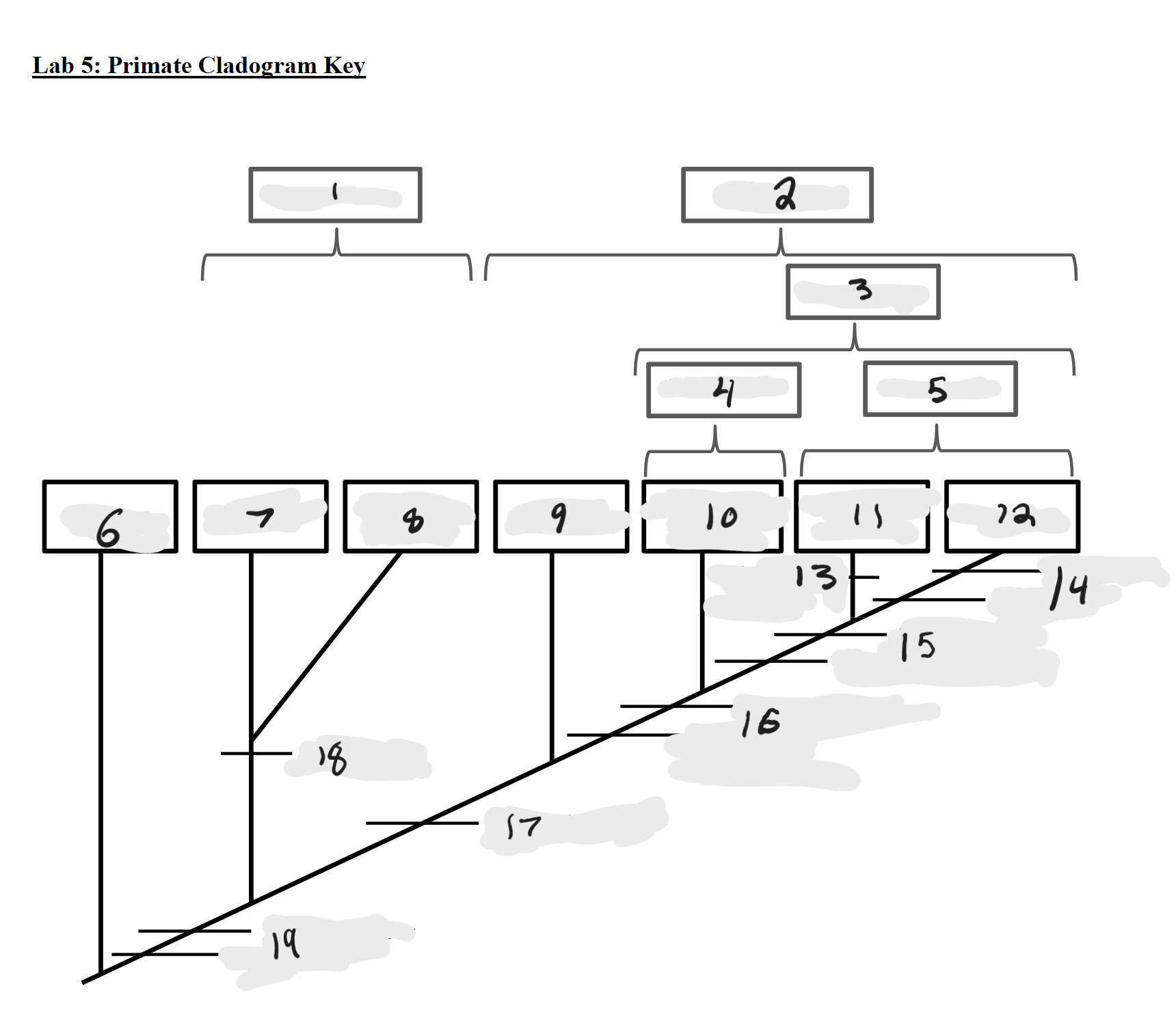
Tympanic tube, 2:1:2:3 dental formula
15
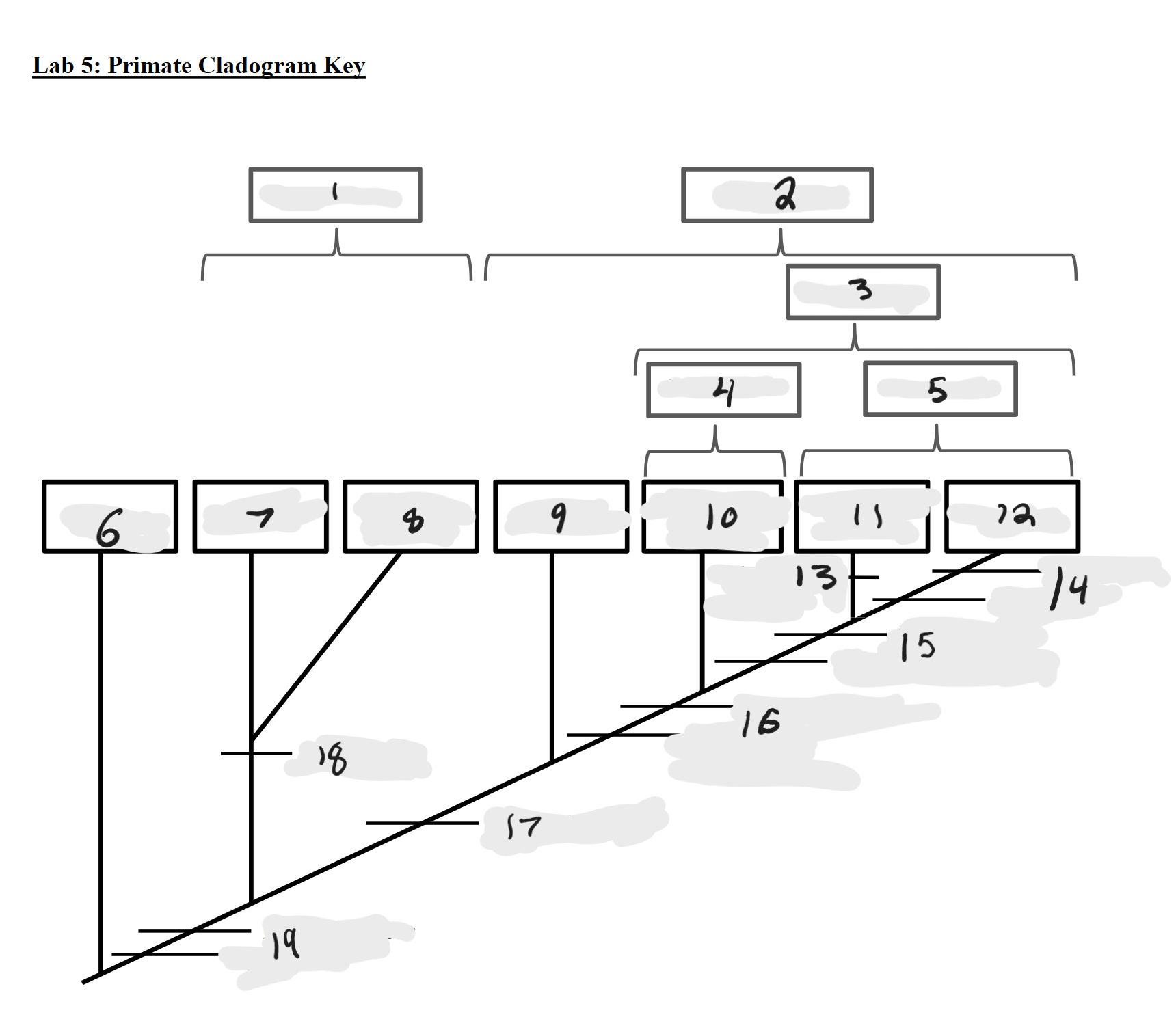
Fused mandible, Full orbital convergence
16
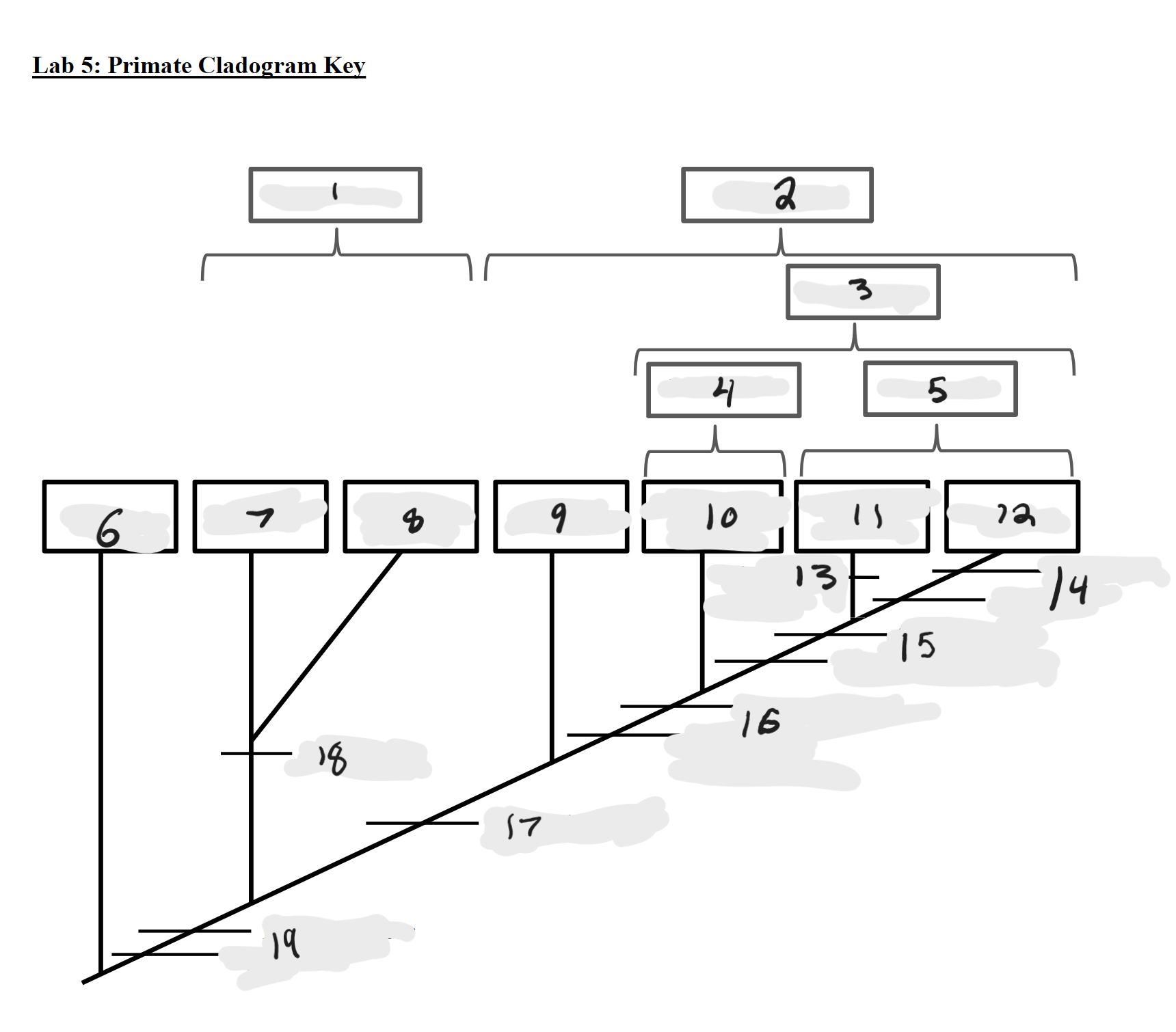
Post-orbital wall
17
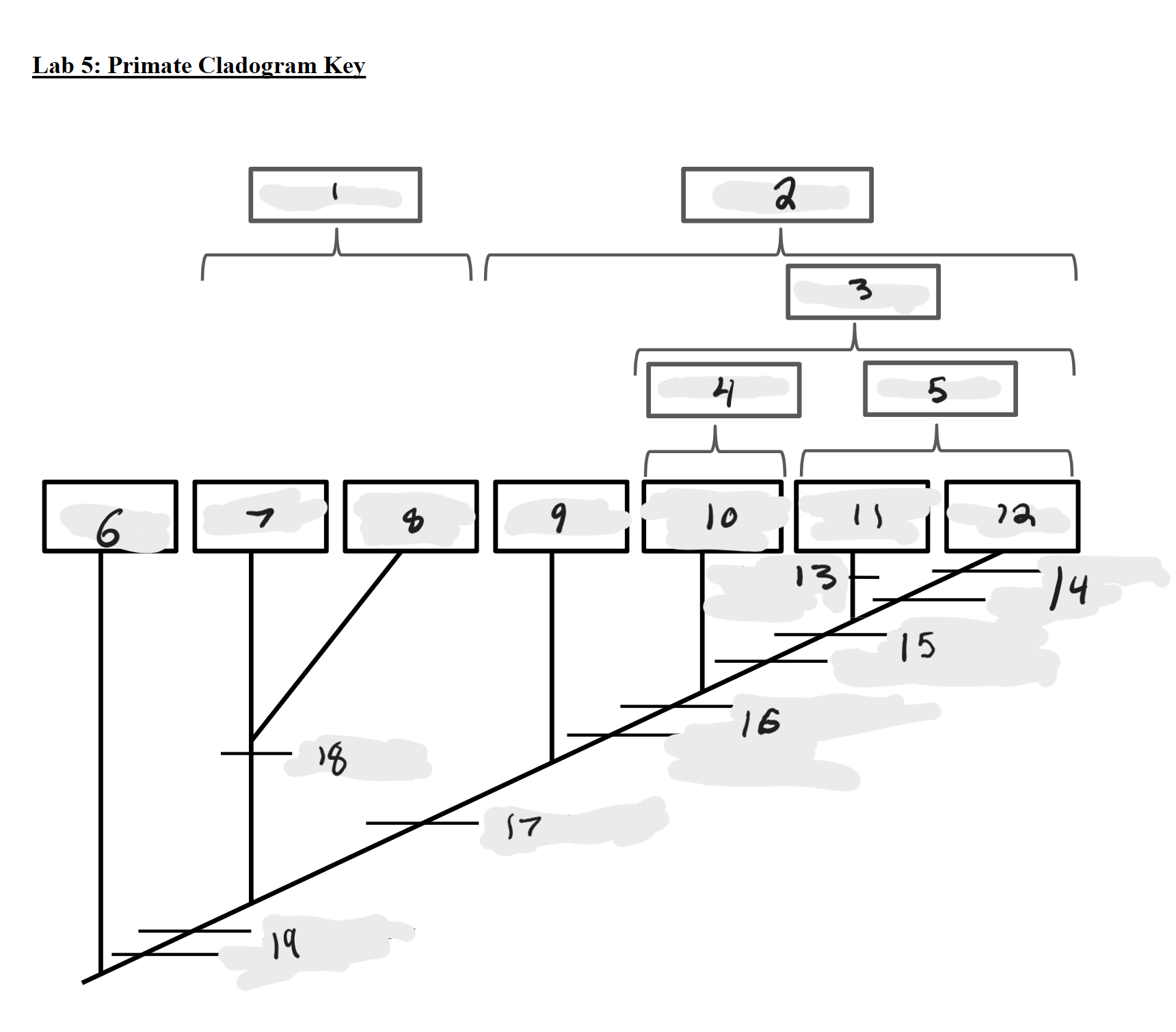
Toothcomb
18
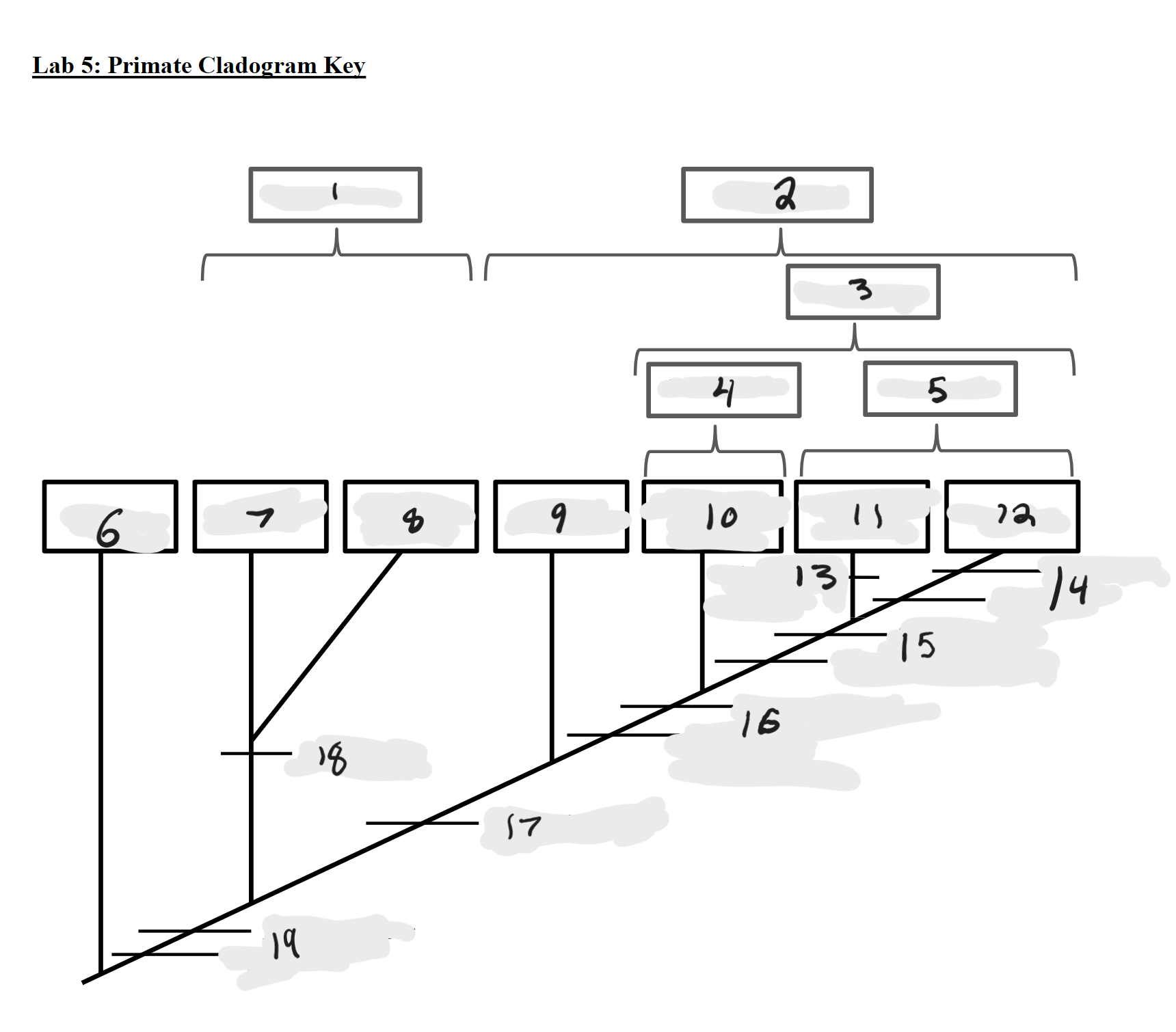
Post-orbital bar, 3 premolars
19
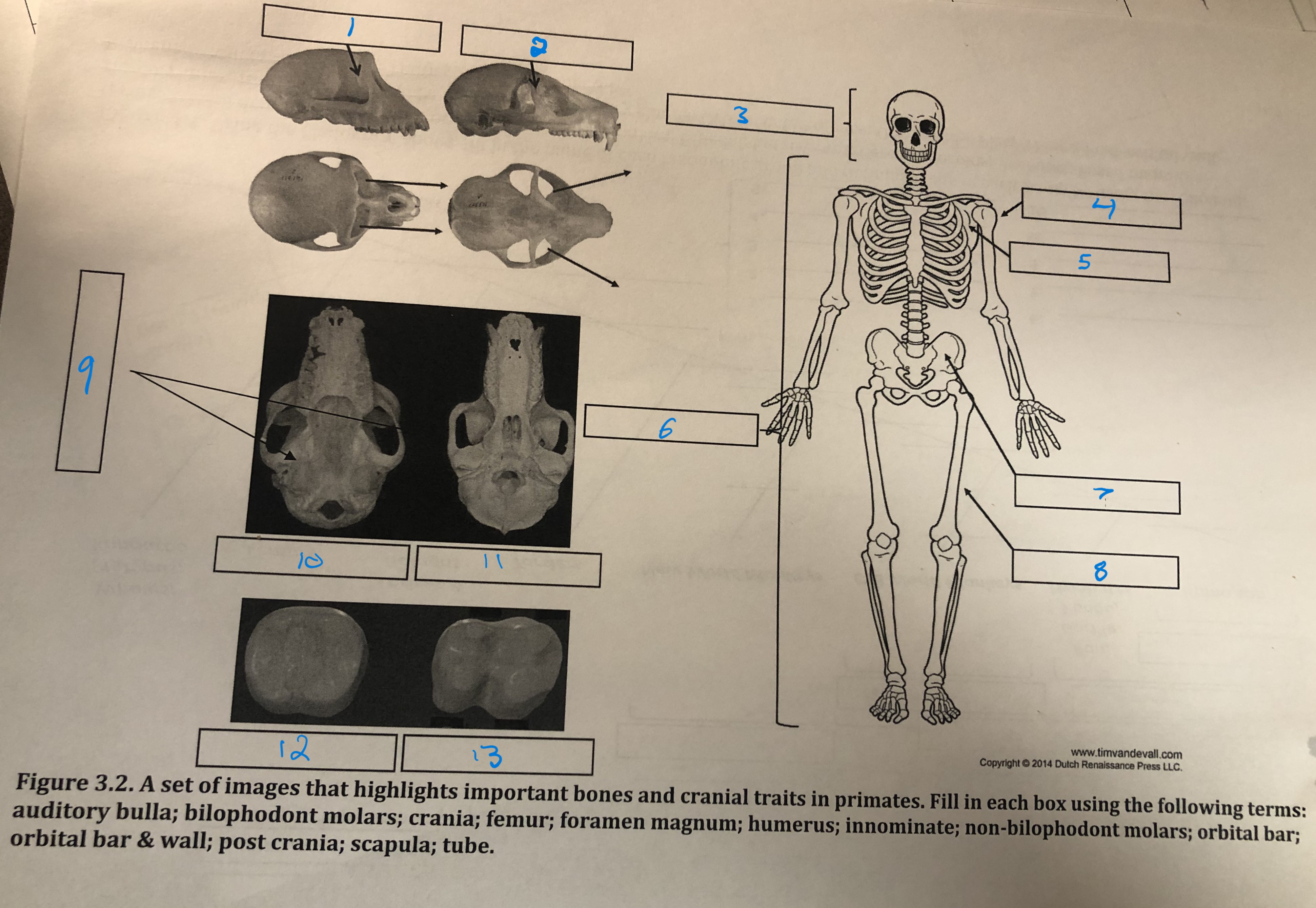
Orbital bar and wall
1
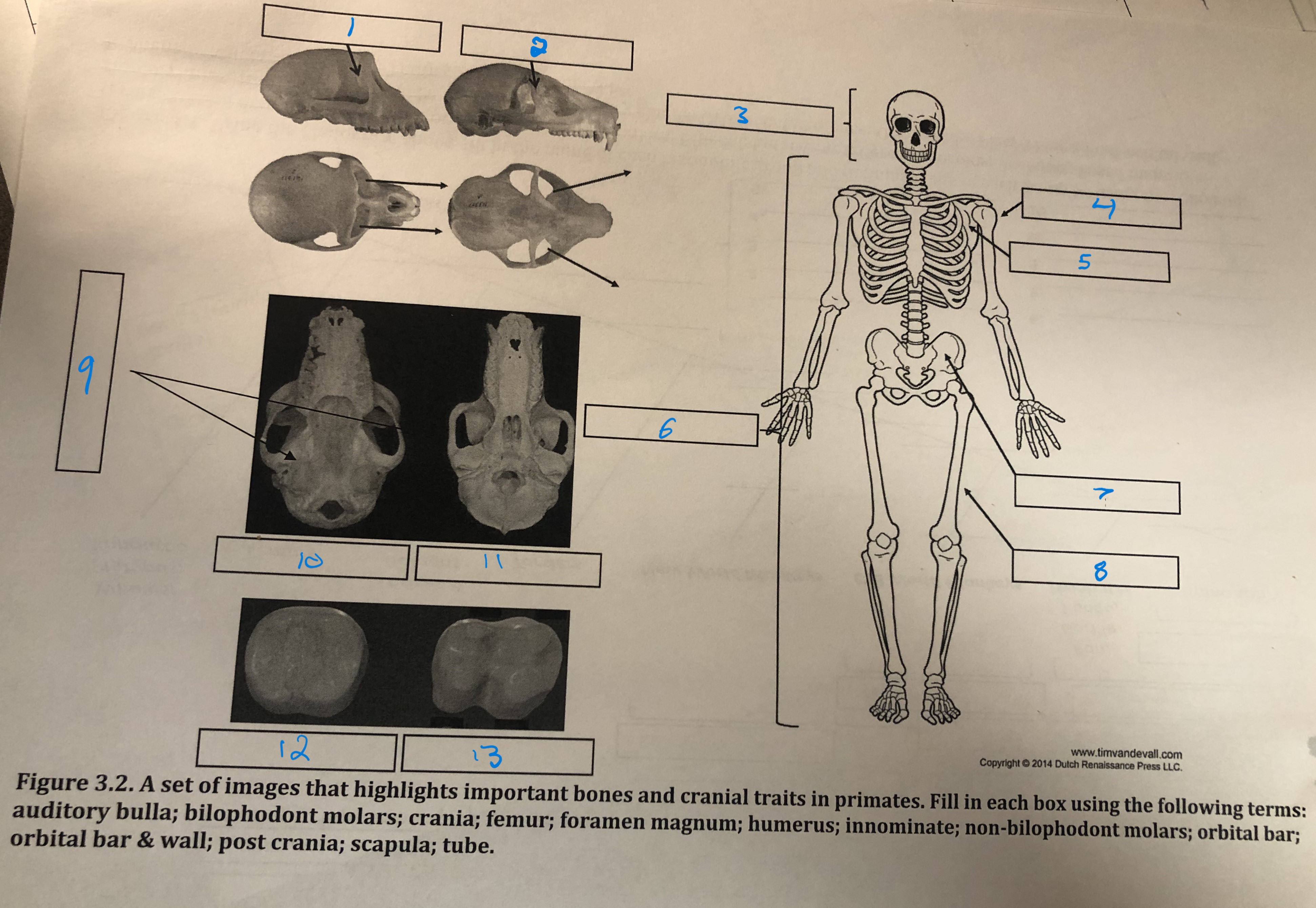
Orbital bar
2
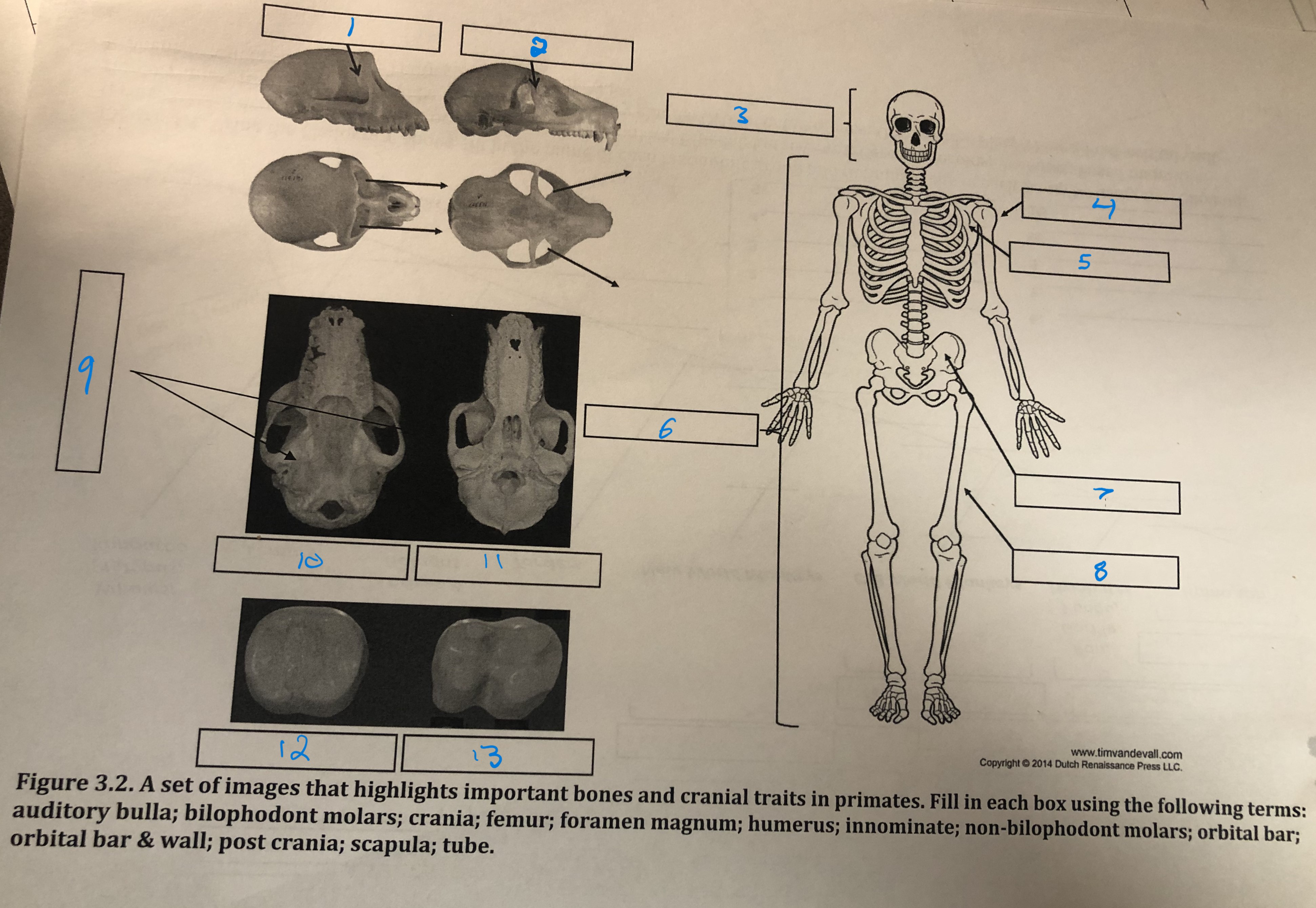
Crania
3
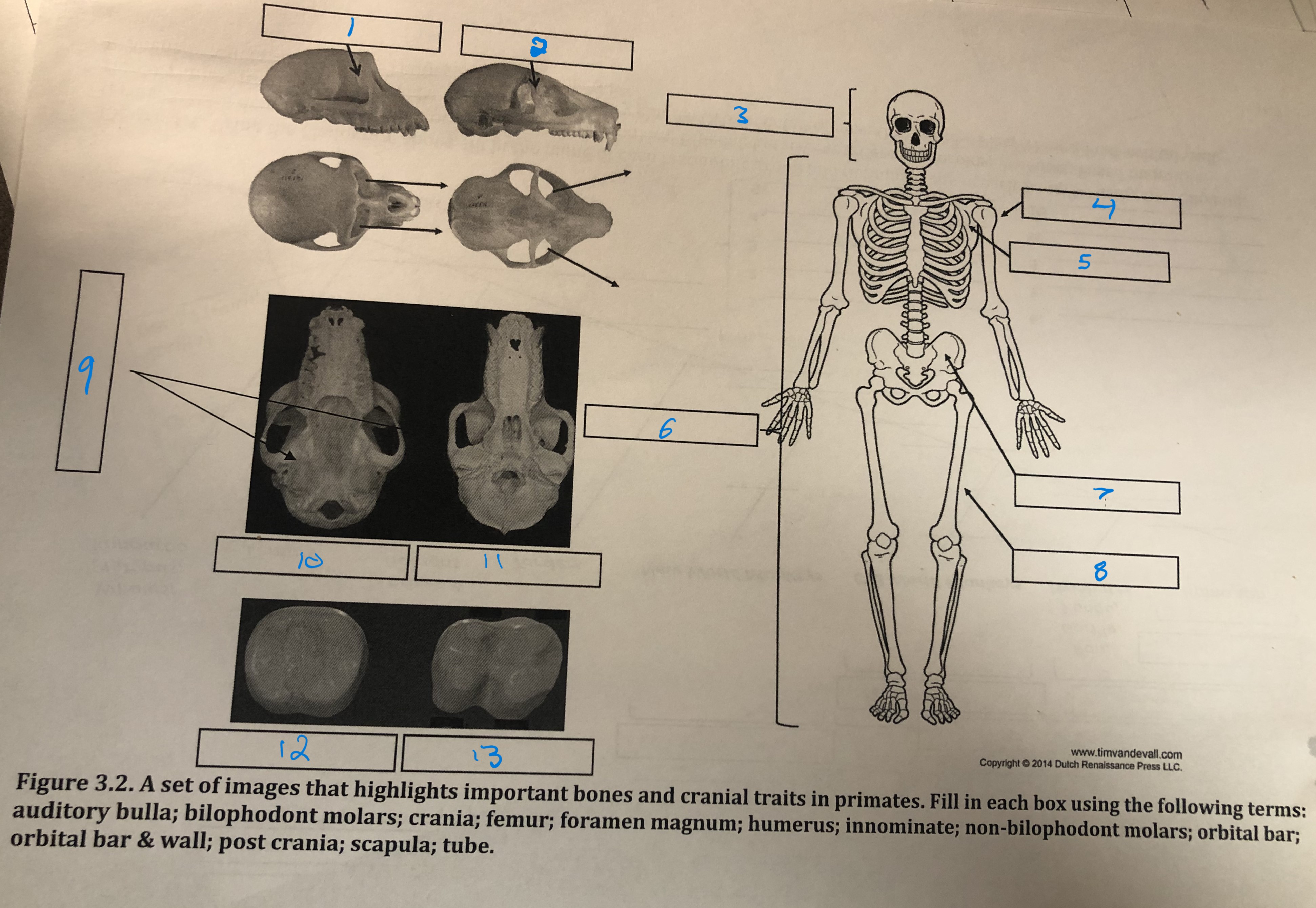
Humerus
4
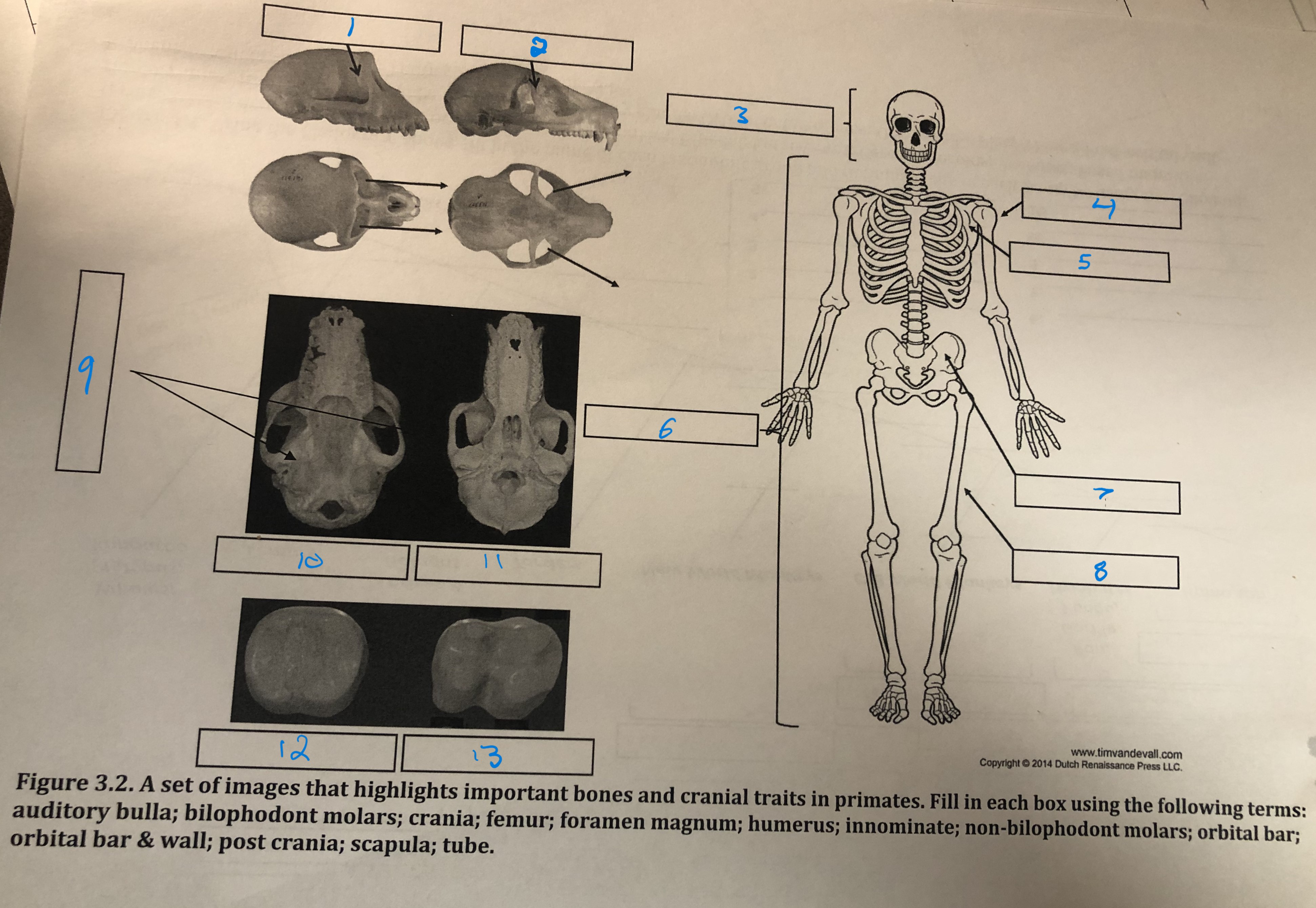
Scapula
5
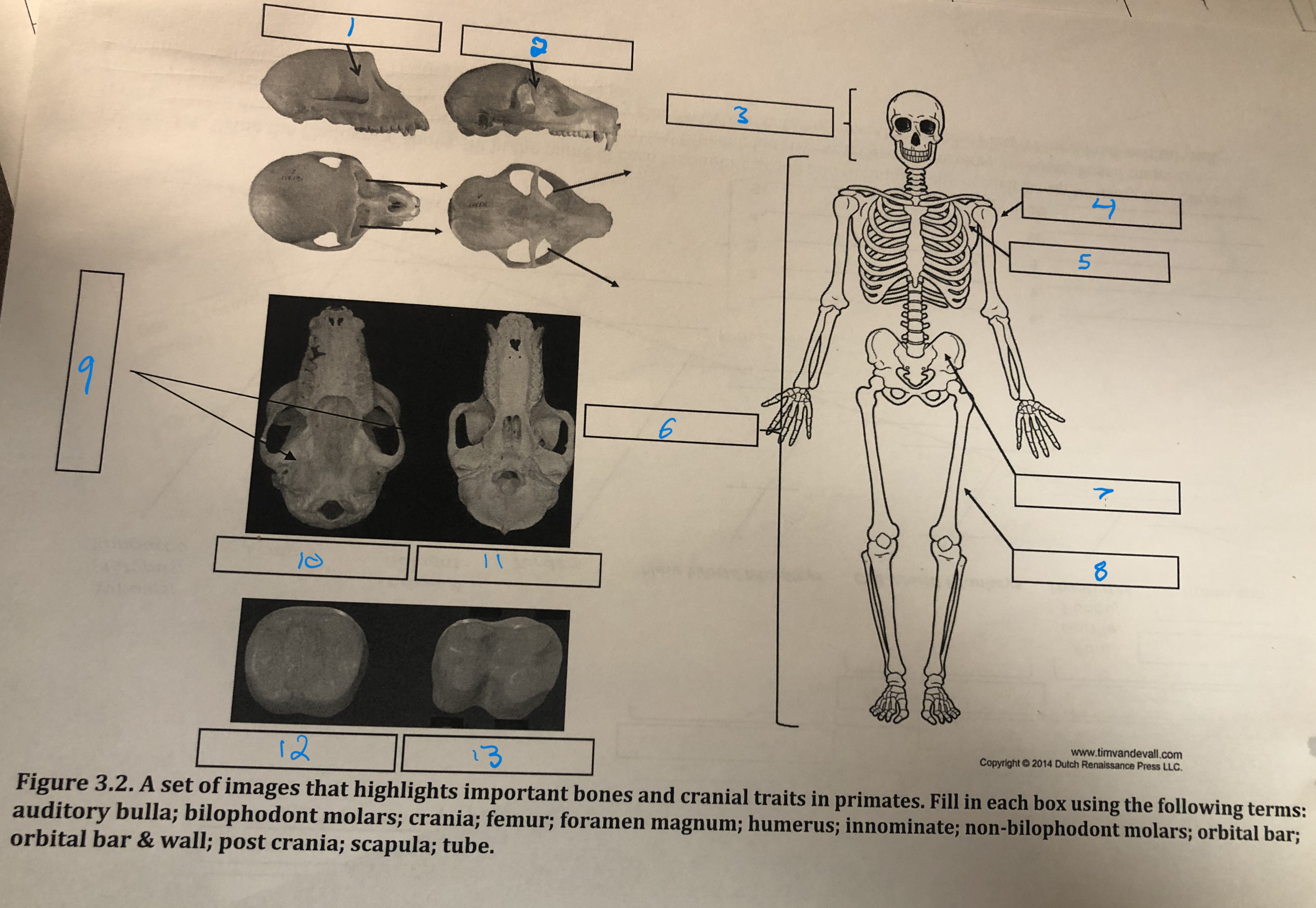
Post crania
6
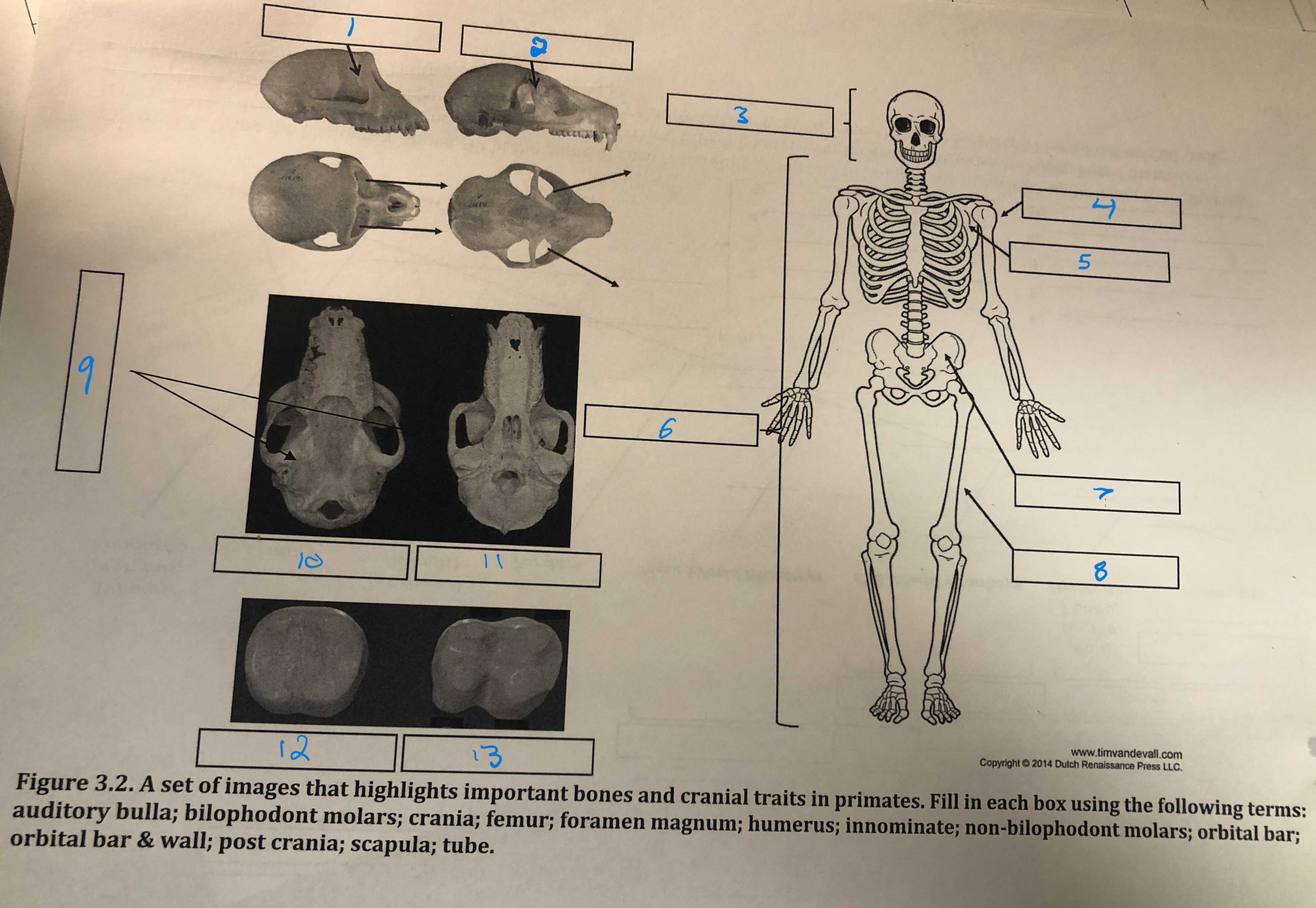
Innominate
7
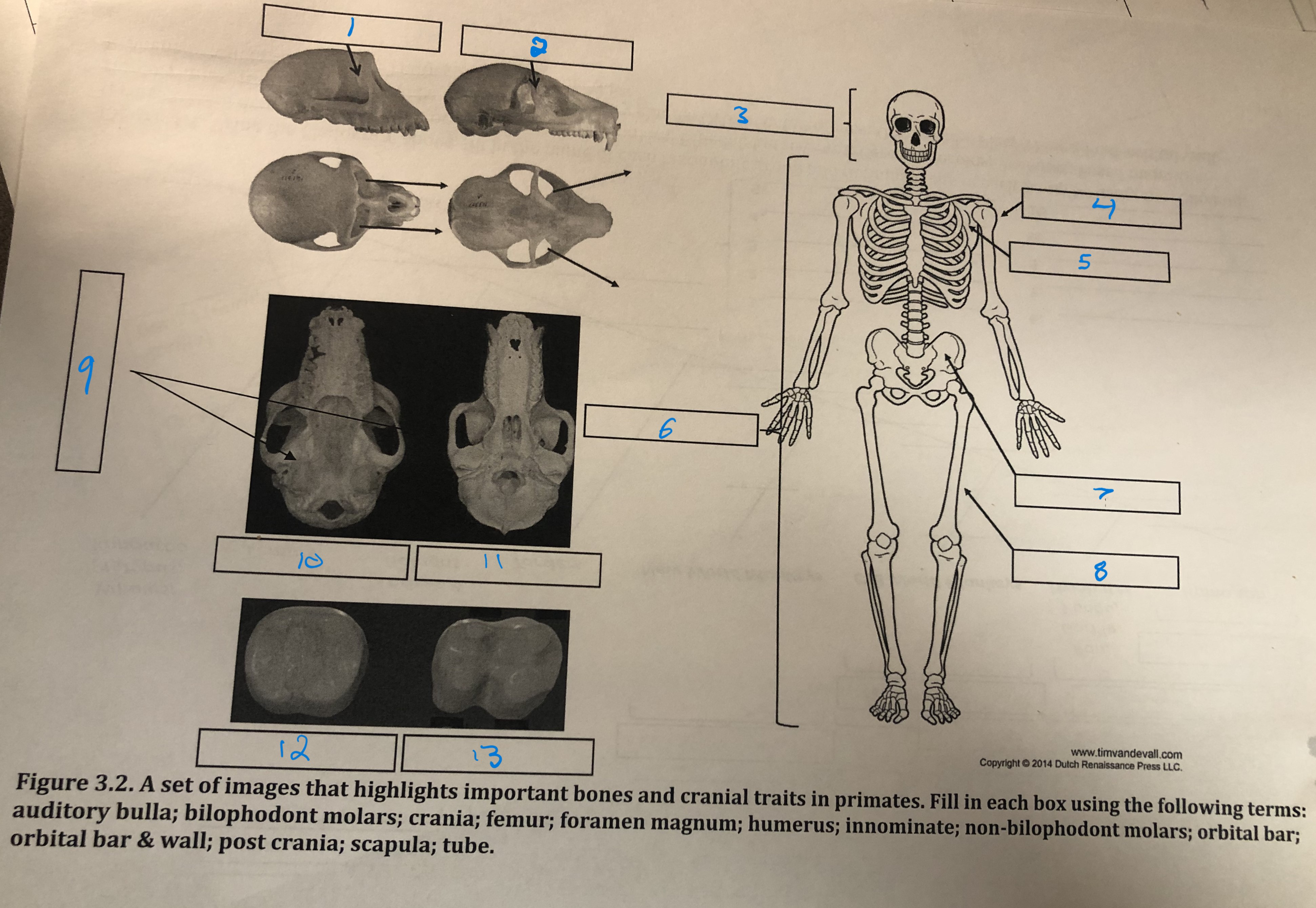
Femur
8
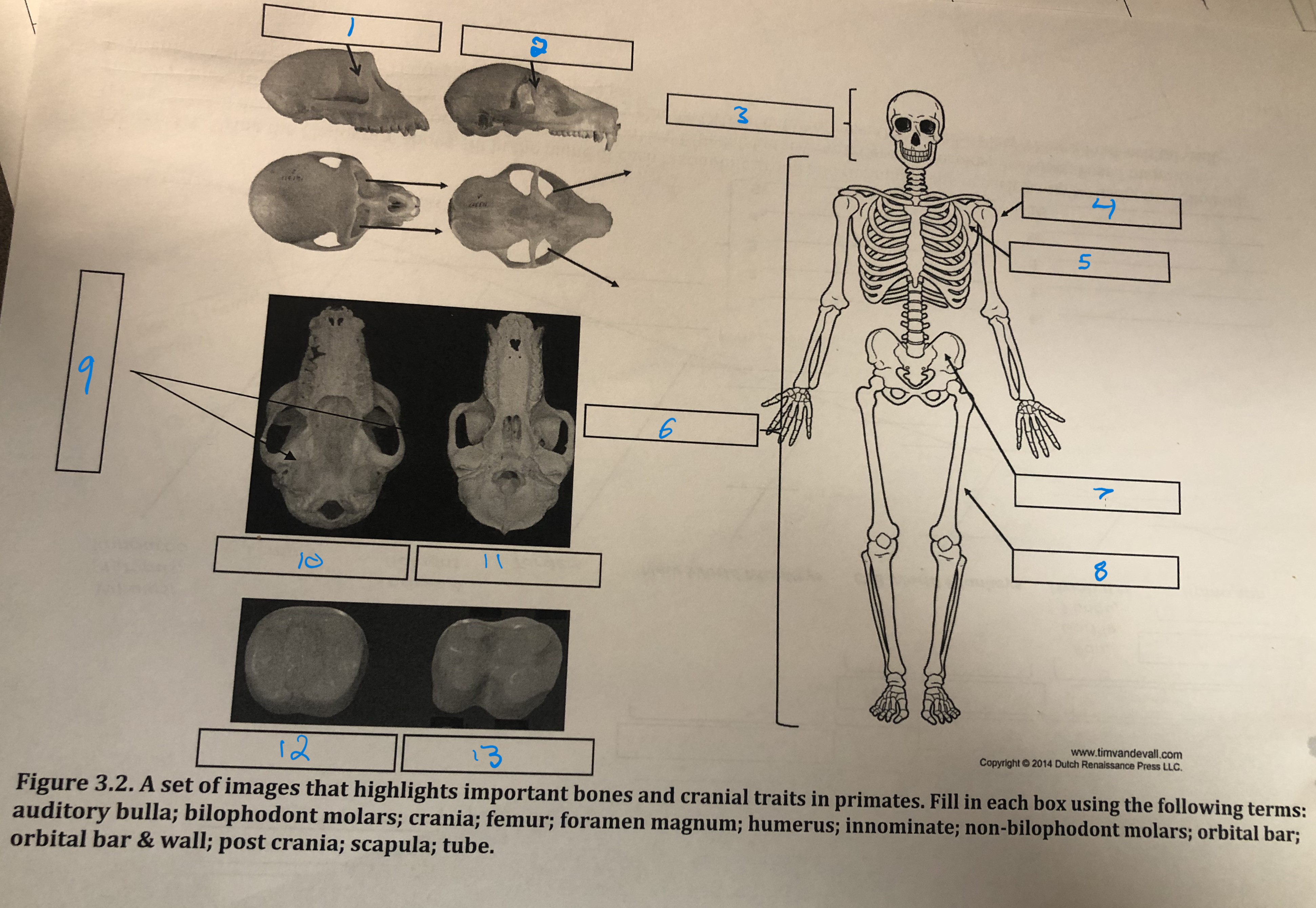
Foramen magnum
9
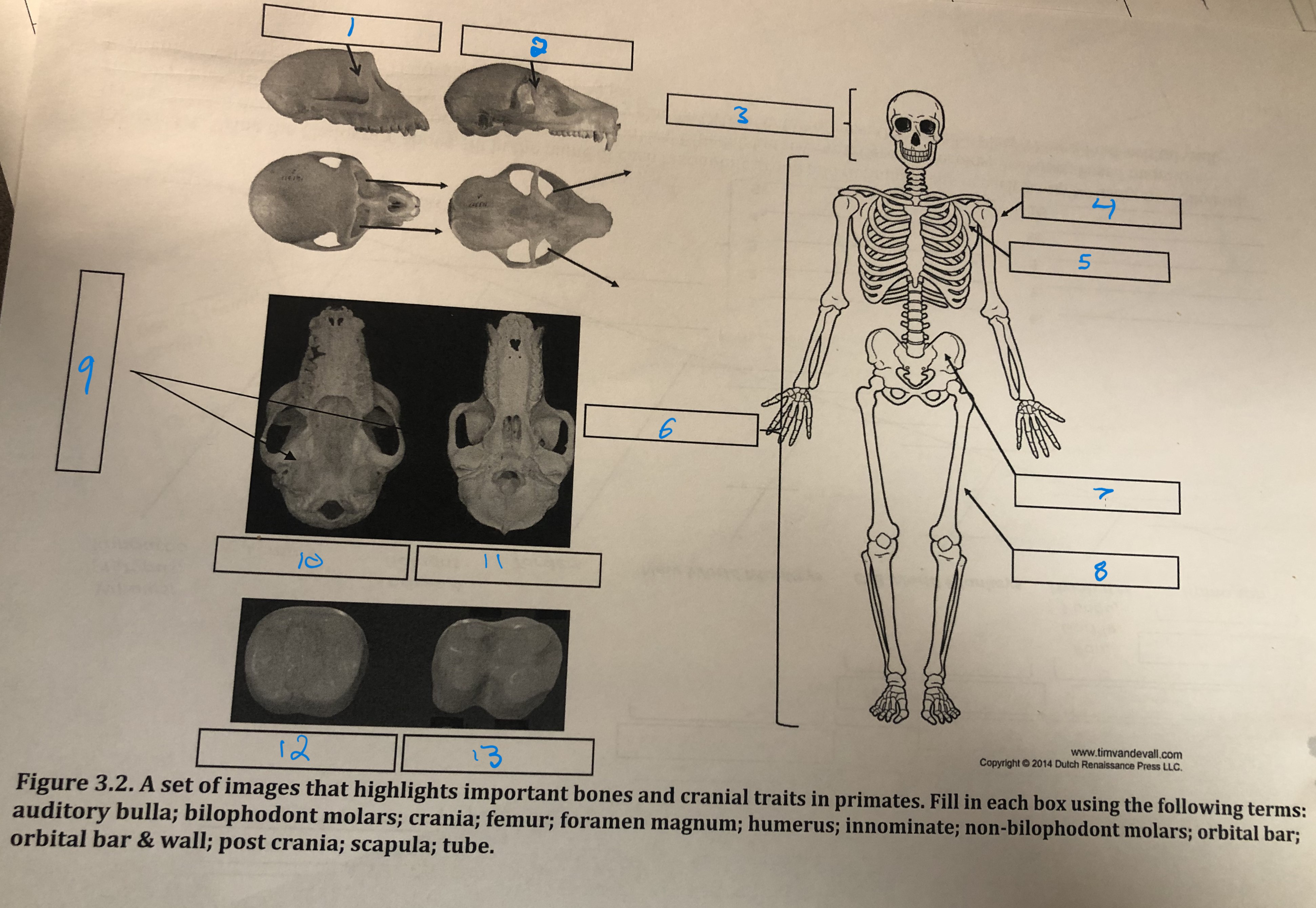
Auditory bulla
10
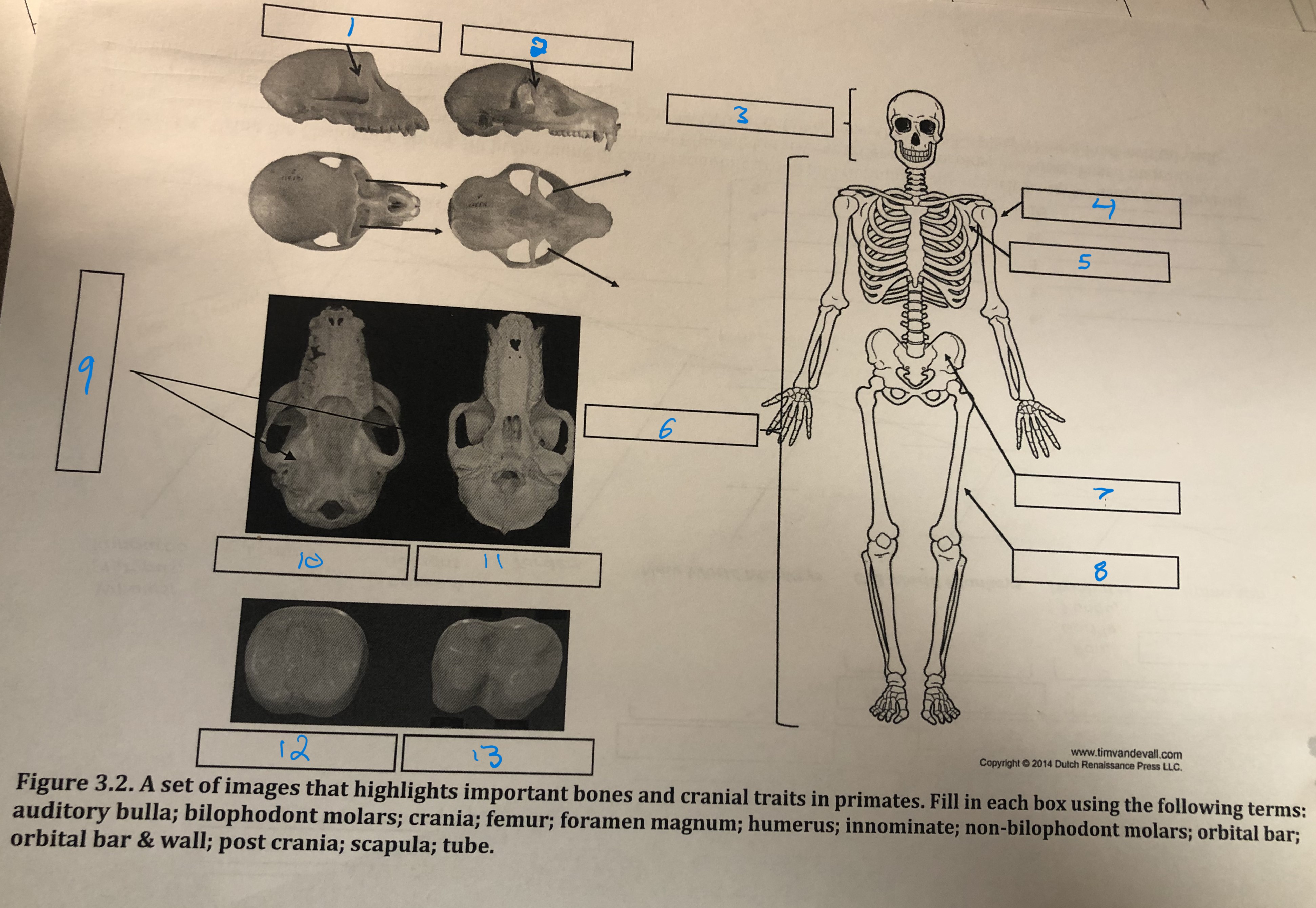
Tube
11
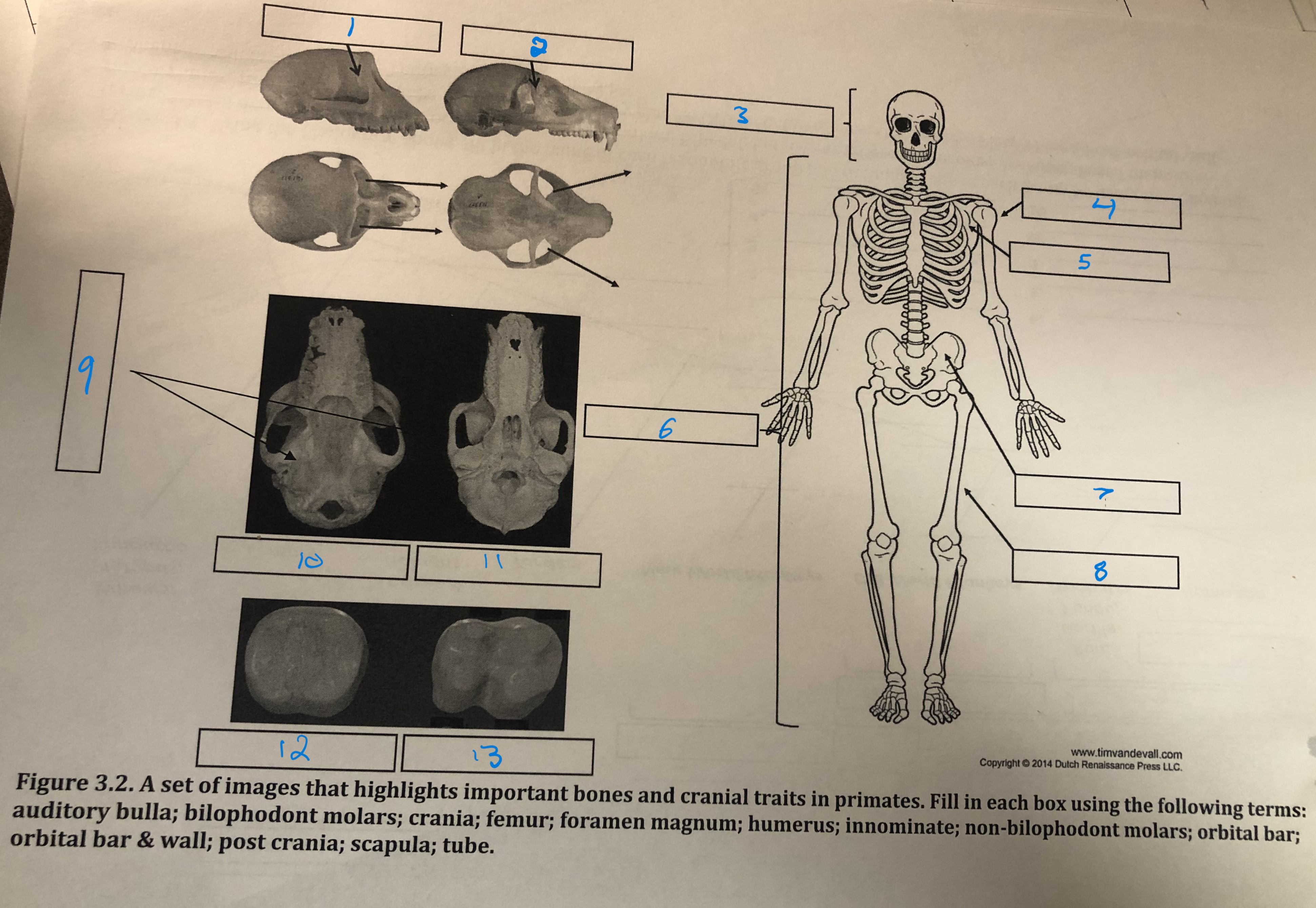
Non-bilophodont molars
12
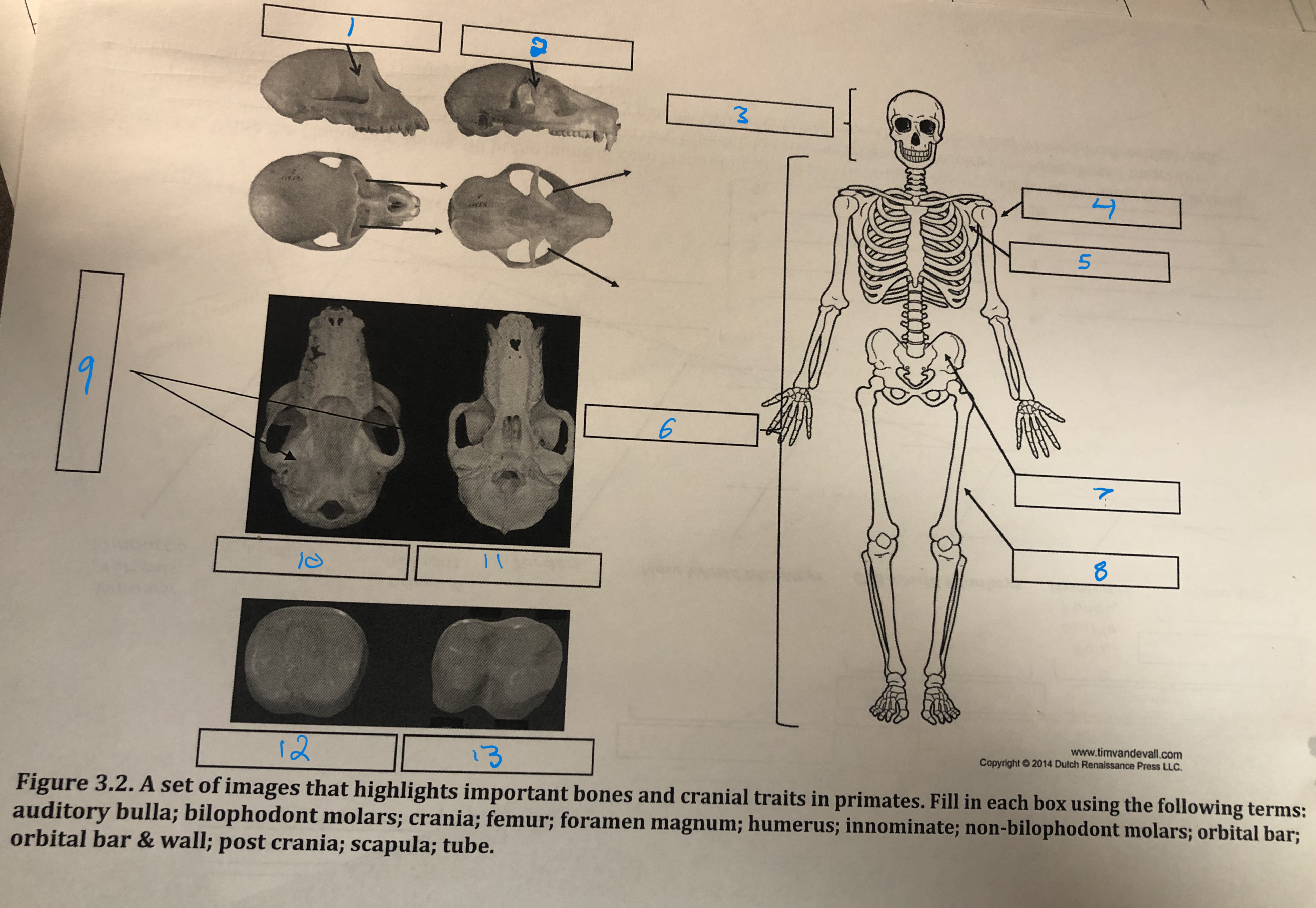
Bilophodont molars
13
Terrestrial (knuckle-walking), some arboreal
Chimpanzee (pan troglodytes) locomotion
Africa (outside Congo river)
Chimpanzee (pan troglodytes) geographic location
Fruit
Chimpanzee (pan troglodytes) diet
Polygyandrous
Chimpanzee (pan troglodytes) mating system
Moderate
Chimpanzee (pan troglodytes) sexual dimorphism (yes, no, moderate)
Africa (inside Congo river)
Bonobo (Pan paniscus) geographic location
Terrestrial (knuckle-walking), some arboreal
Bonobo (Pan paniscus) locomotion
Leaves, fruit, insects
Bonobo (Pan paniscus) diet
Polygyandrous
Bonobo (Pan paniscus) mating system
Moderate
Bonobo (Pan paniscus) sexual dimorphism (yes, no, moderate)
Africa (outside Congo river)
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) geographic location
Terrestrial (knuckle-walking), some arboreal
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) locomotion
Foliage, fruit
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) diet
Polygynous
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) mating system
Yes
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) sexual dimorphism (yes, no, moderate)
Female defense
Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) method of mating competition
Southeast Asia
Orangutan (Pongo) geographic location
Arboreal
Orangutan (Pongo) locomotion
Fruit, leaves, bark
Orangutan (Pongo) diet
Polygynous
Orangutan (Pongo) mating system
Yes
Orangutan (Pongo) sexual dimorphism (yes, no, moderate)
Resource defense
Orangutan (Pongo) method of mating competition
Southeast Asia
Gibbon (Hylobates) geographic location
Arboreal, brachiation
Gibbon (Hylobates) locomotion
Fruit
Gibbon (Hylobates) diet
Monogamous
Gibbon (Hylobates) mating system
No
Gibbon (Hylobates) sexual dimorphism (yes, no, moderate)
Low male-male competition
Gibbon (Hylobates) method of mating competition
Africa
Olive baboon (Papio anubis) geographic location
Arboreal
Olive baboon (Papio anubis) locomotion
Omnivore
Olive baboon (Papio anubis) diet