Honors bio evolution
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
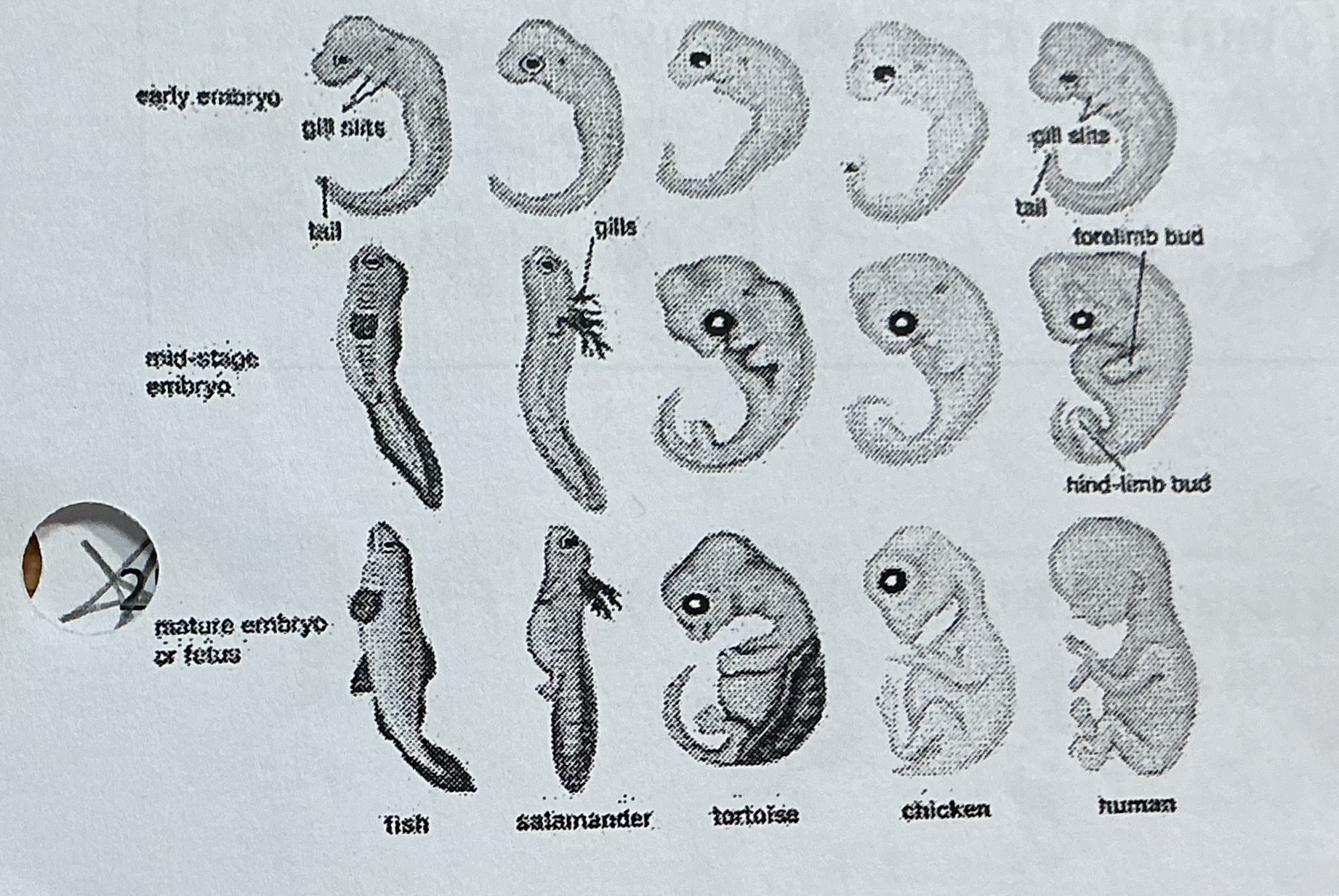
Explain the evolutionary significance
Embryological similarities - this shows that from a developmental standpoints there is evidence for living things common ancestry
Homologous structures
Similar features of 2 diff. Organisms that share an evolutionary past
Analogous structures
Similar features that evolved independently
Vestigial structures
Used to serve a role, but serve no purpose now
Fitness
An organisms relative ability to survive and reproduce
Population
A group of organisms within an area that reproduce
Gene pool
The total of all the diff. Alleles in a given pop.
Allele frequency
Of times an allele occurs in a gene pool
Migration
Movement of organisms into or out of pop.
Genetic drift
When allele frequencies are changed by random events
Micro evolution
Evolutionary change in a small group over a short period of time
Founder effect
When a small pop. Starts an entirely new isolated pop.
Genetic bottleneck
When a pop. Is driven nearly extinct, then recovers
What did Lamarck believe
Organisms acquired traits through life experiences
What did both Lamarck and Darwin believe
Traits are passed onto generations (offspring)
What did Darwin believe
There was natural variation in pop. Of organisms & that the environment naturally those organisms with the greatest fitness
How did geologists influence Darwins thinking
Darwin started to view the world as much older than other biologists, and then he just assumed that slow, steady changes added up over time
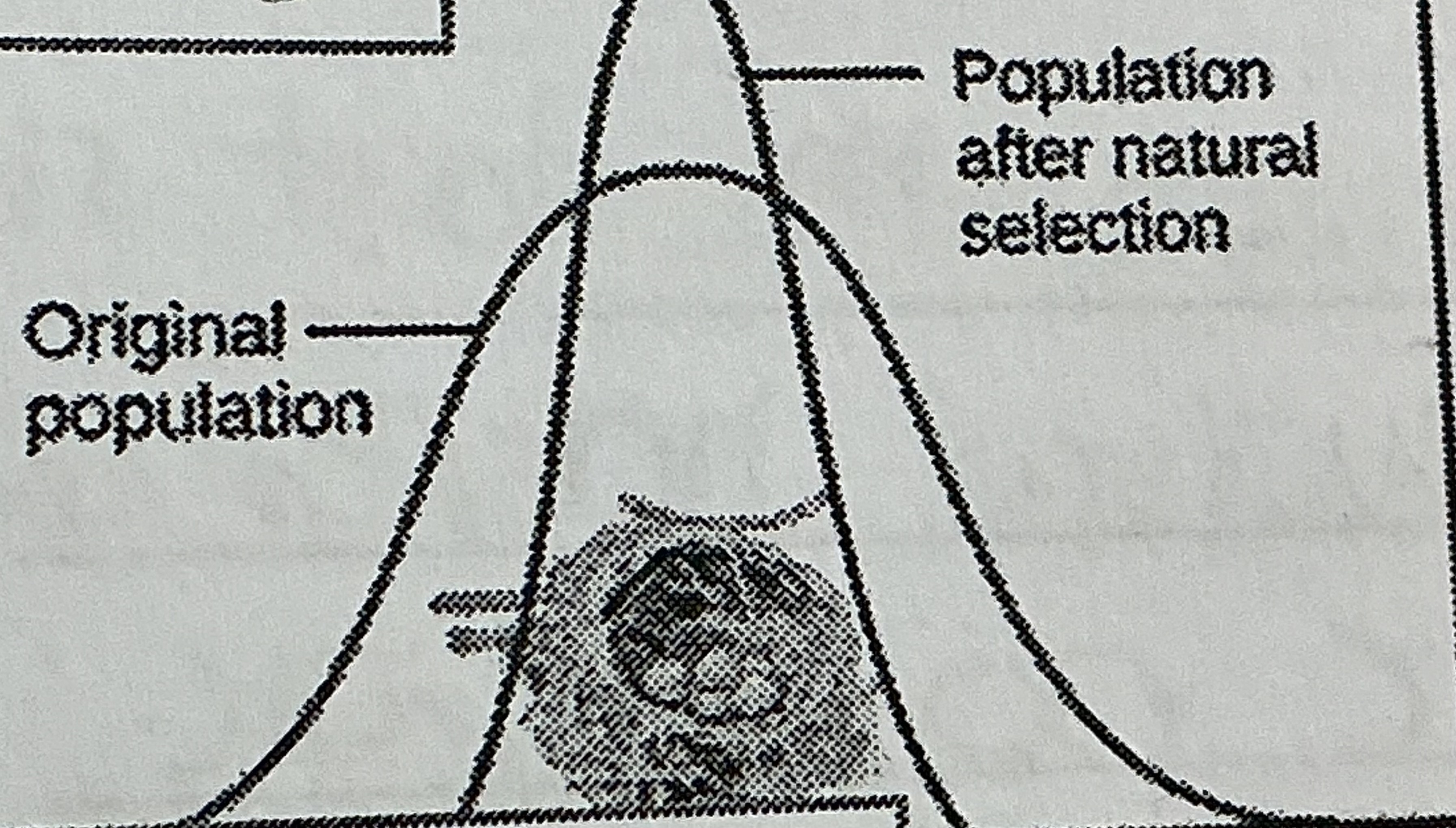
Label the type of selection & explain
Stabilizing - the extremes selected against
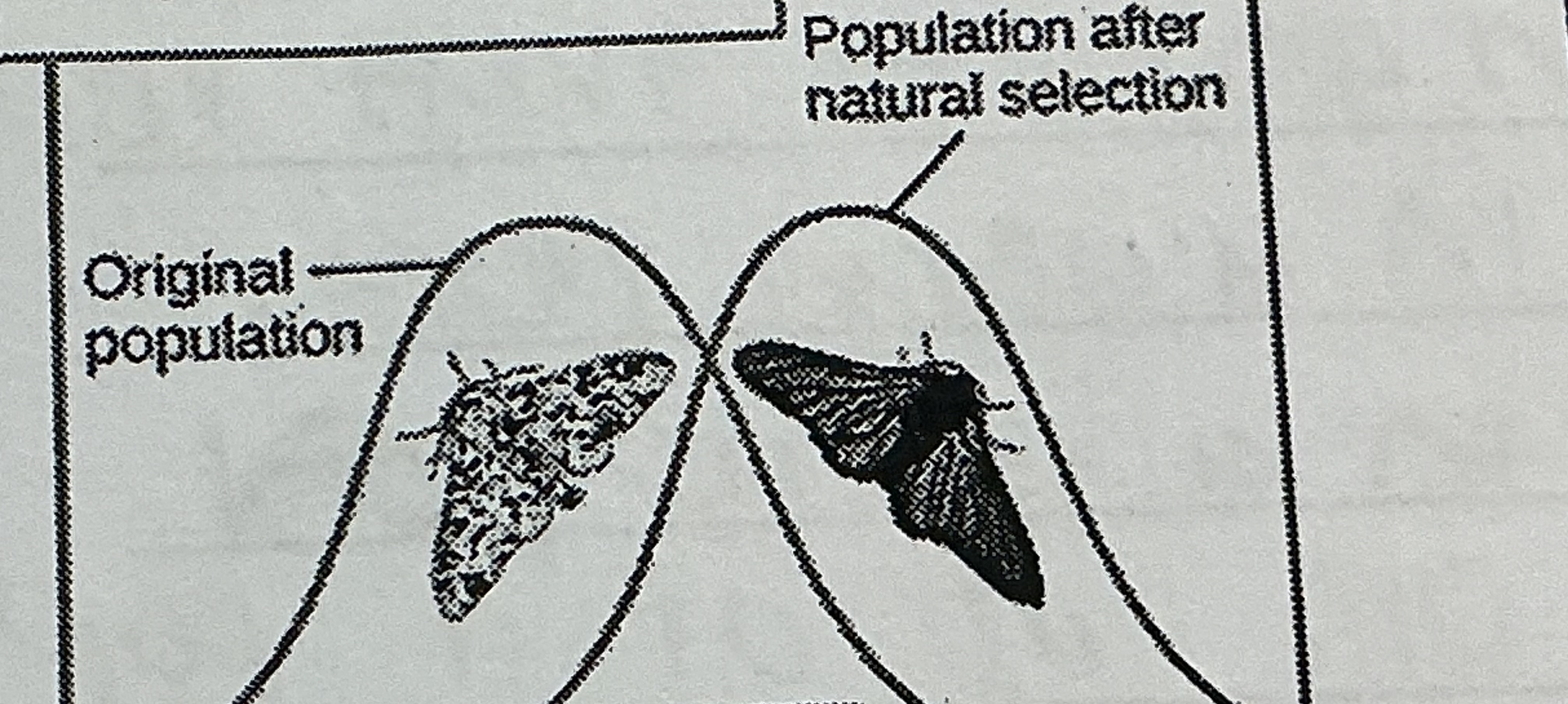
Label the type of selection & explain
Directional-only one phenotype is selected against

Label the type of selection & explain
Disruptive - the average phenotype is selected against
List & describe the 3 causes of variation within a species
Mutation - random changes in the genetic code can alter proteins
Recombination(chromosomal changes can cause speciation)
Sex(reduction division increases variability)
List & describe the five mechanisms of microevolution
natural selection -environment selects for or against a trait
Norandom mating-sexual selection can quickly affect gene pools
Gene flow(migration)-movement of members into or out of a pop. Changes gene pools
Mutation-changed to DNA can affect proteins which influence traits
Genetic drift-random chance can shape evolution
Differentiate between the 2 types of genetic drift
Founder- when a small group from an oringinal pop. Starts a new pop.
Bottleneck - after a pop.Has been brought to near extinction, then recovers
What 5 criteria must be met for Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium
No natural selection, no mutation, no migration , large pop. , random mating
Describe the biological species concept
A species is defined as any organism that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring
Describe prezygotic& postzygotic barriers
Prezygotic - these preventa viable offspring from reproducing .
Postzygotic: these prevent living organisms from passing their genes to the next generation
classify the types of isolating mechanisms that fit into them
Prezygotic = geographical, temporal, behavioral, mechanical isolation
Postzygotic: hybrid sterility
What is adaptive radiation? Hows it possible?
Process by which a single species rapidly evolves into numerous diff. Species in short period of time. it occurs because there is a niche within an ecosystem that is unified ( ex. Galapagos islands )