DPT 744 Week 4 Lecture Notes Pt. 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
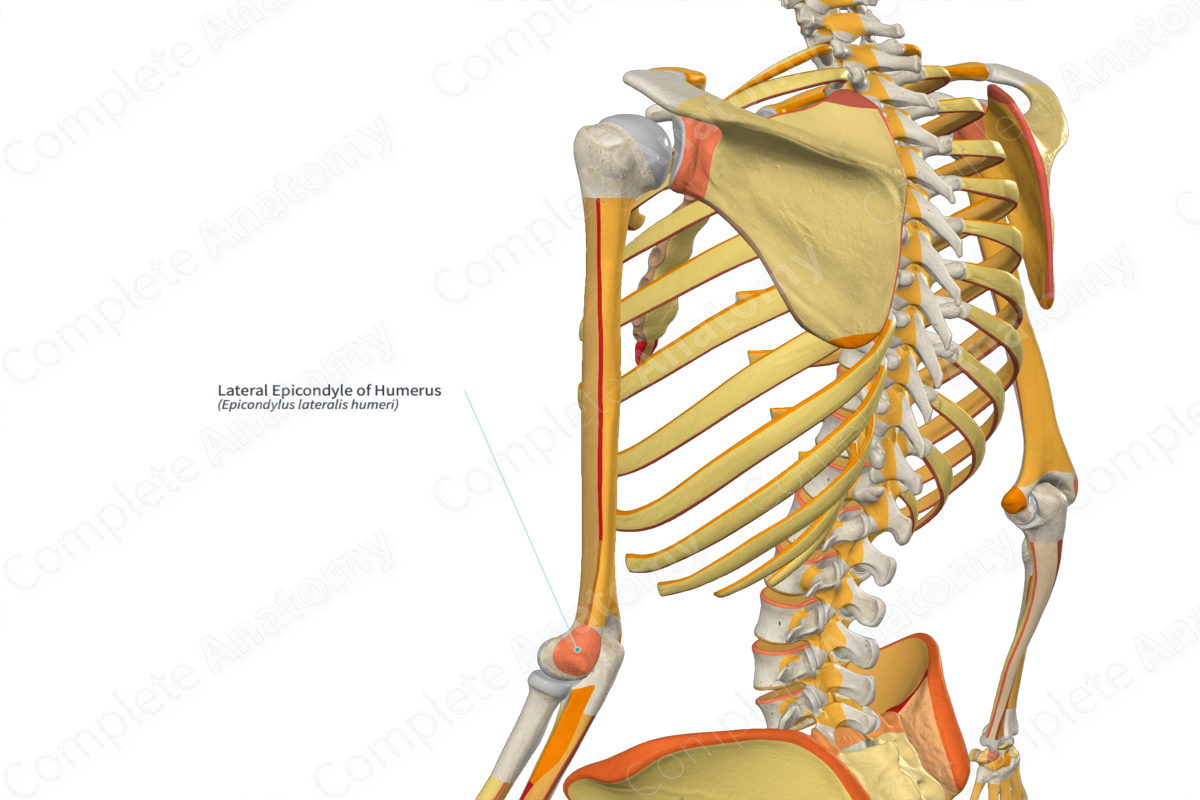
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
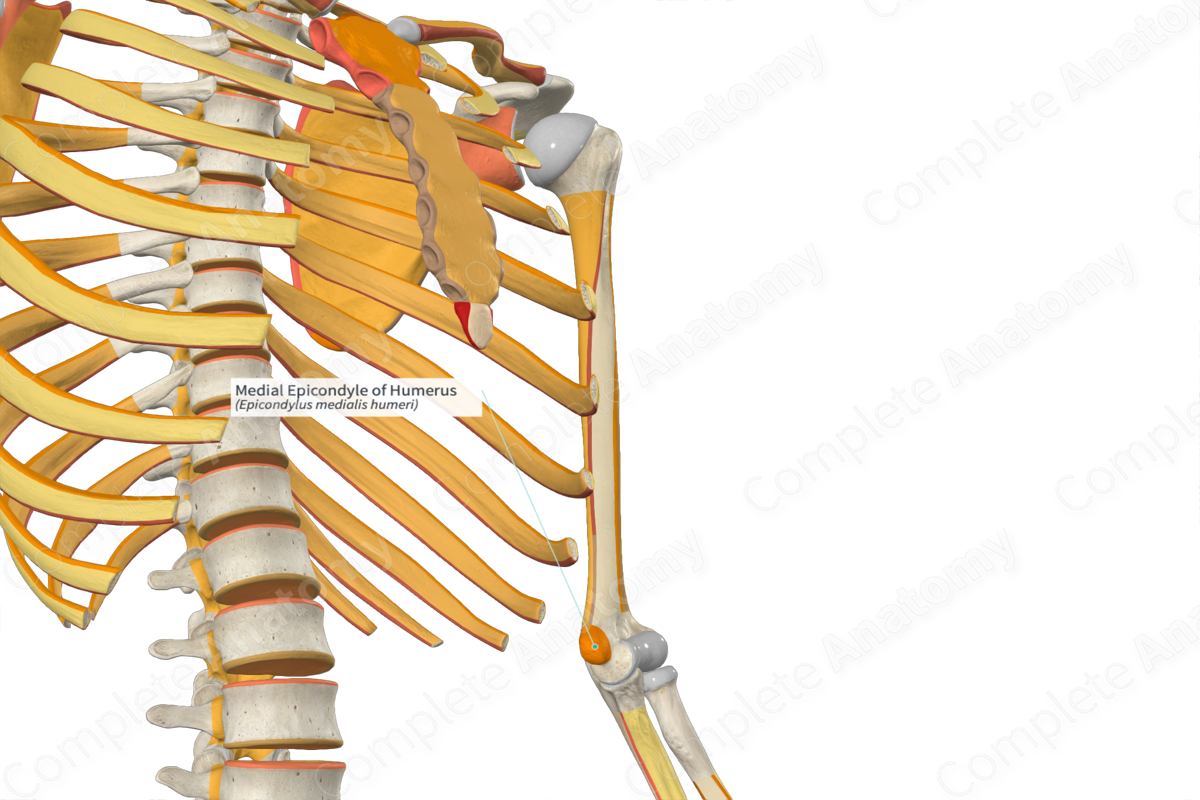
Medial epicondyle of humerus
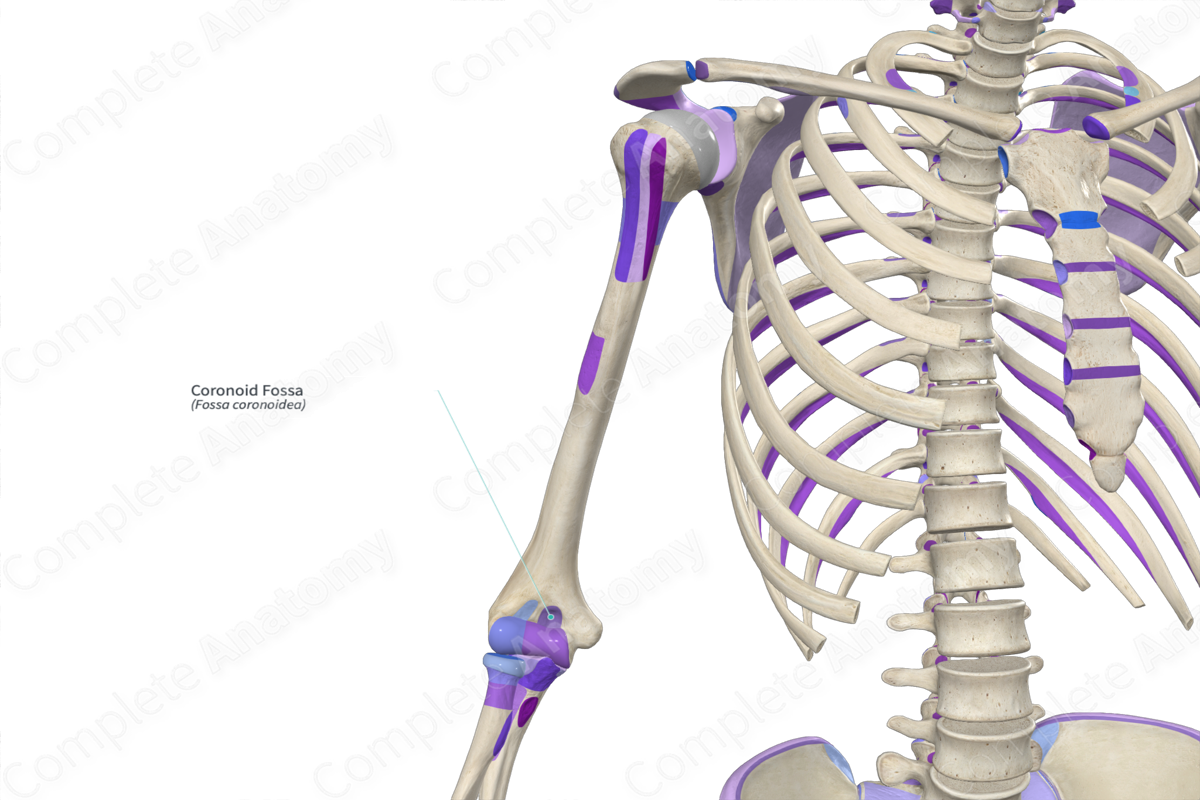
Coronoid fossa
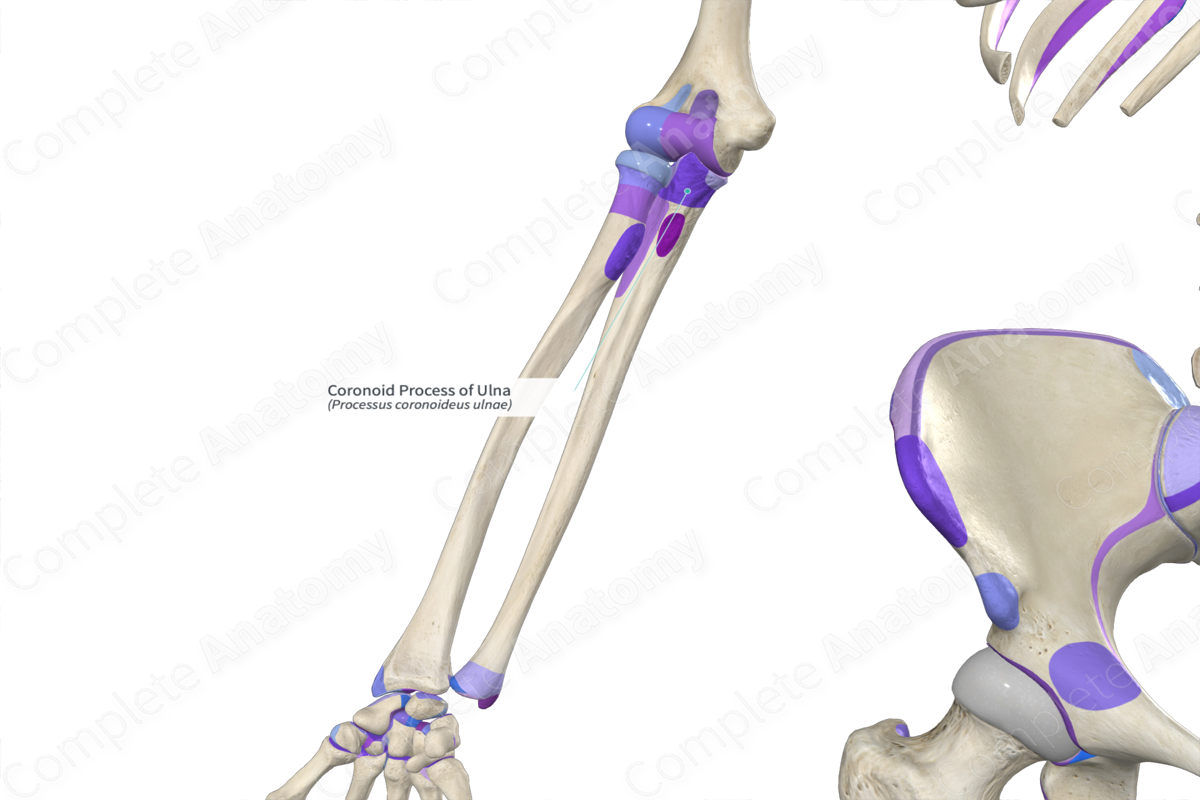
Coronoid process
Metacarpals
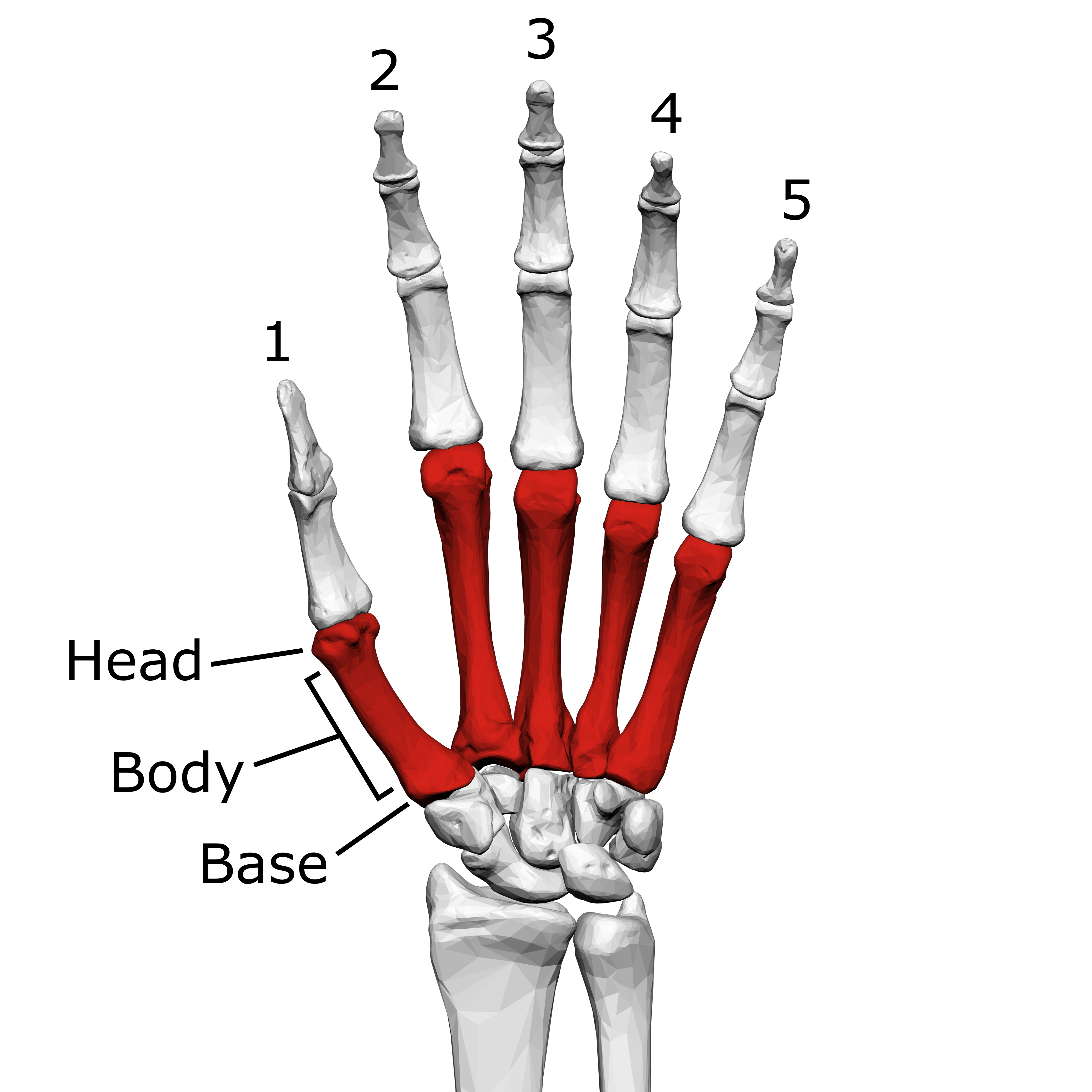
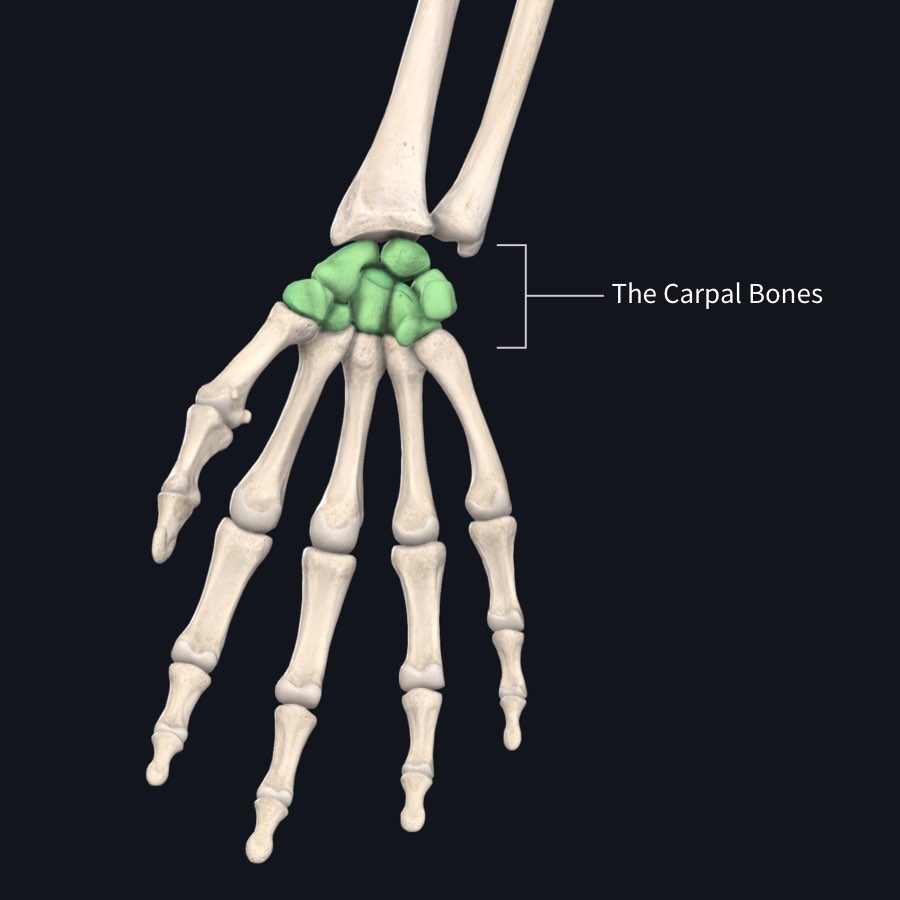
Carpals
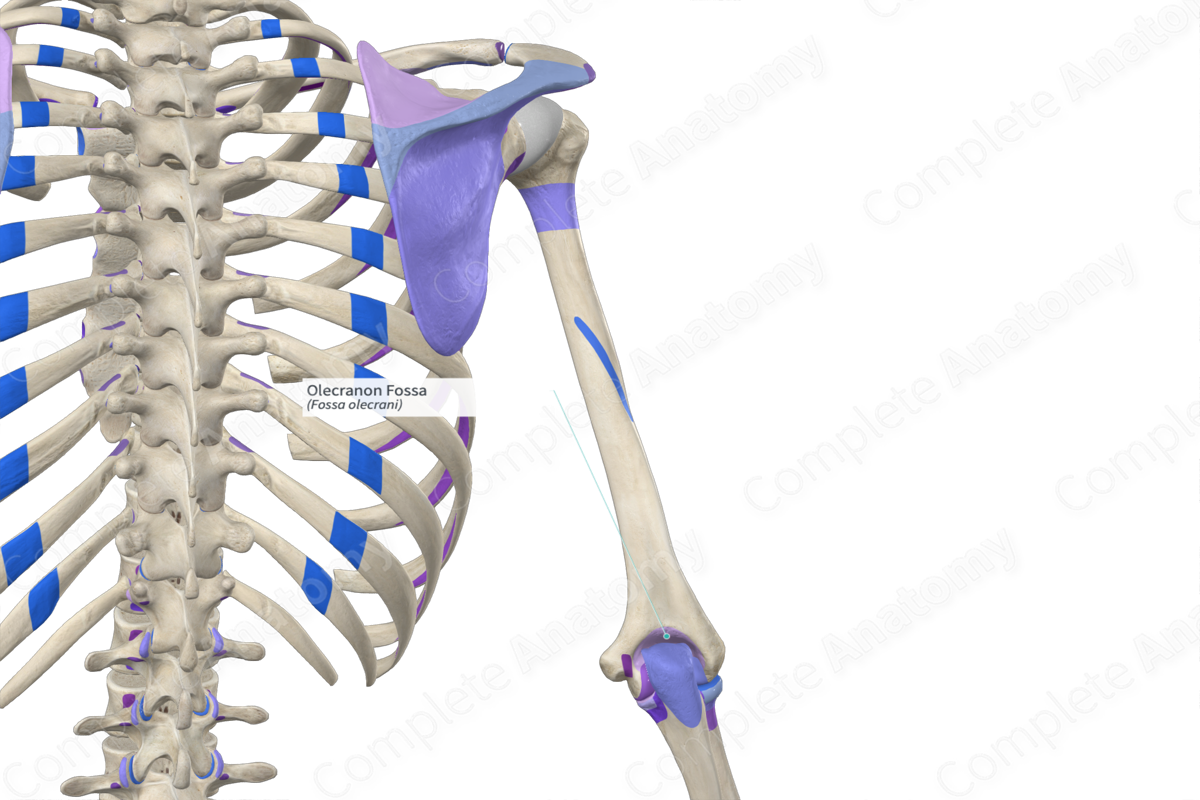
Olecranon fossa
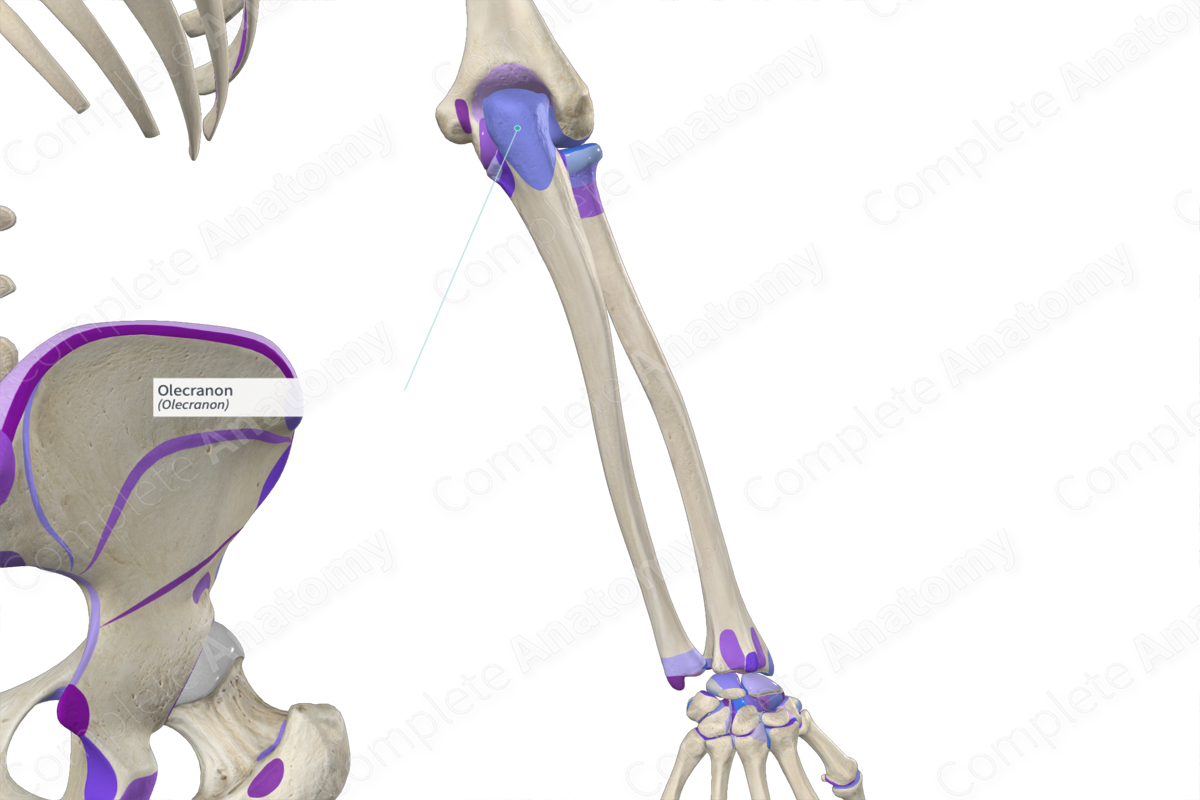
Olecranon
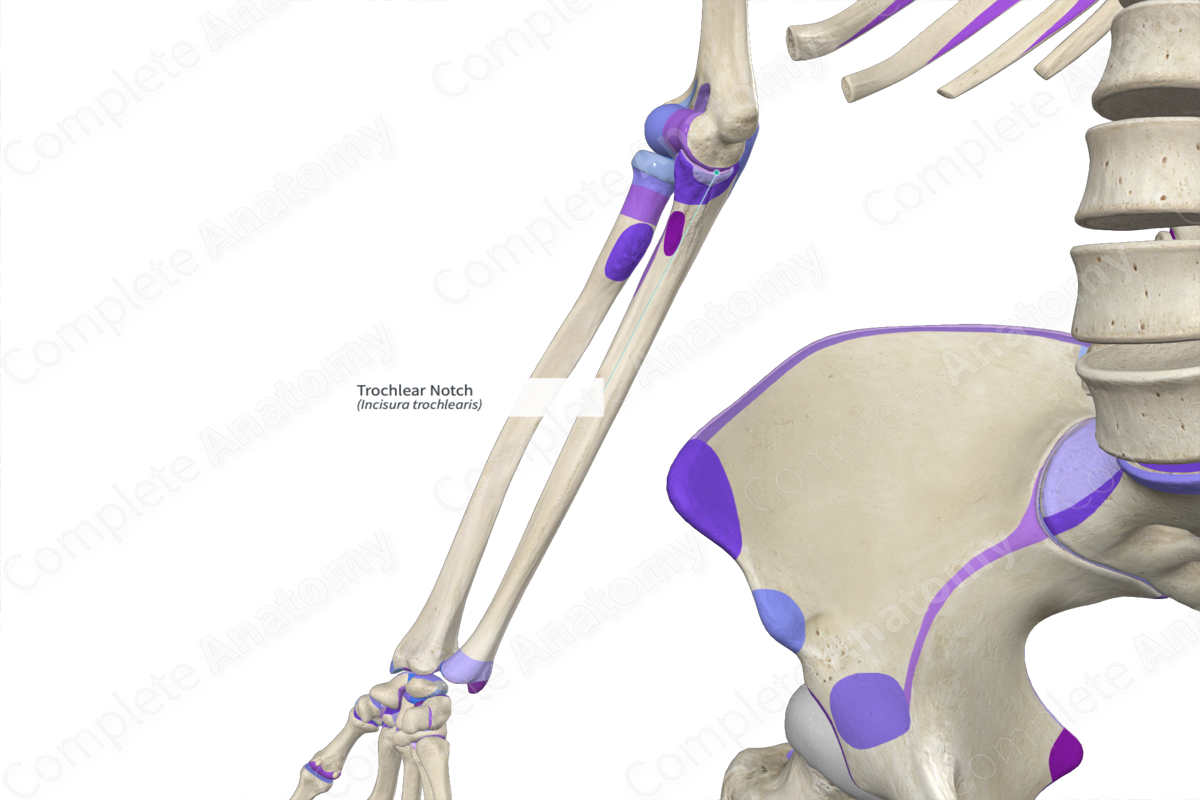
Trochlear notch
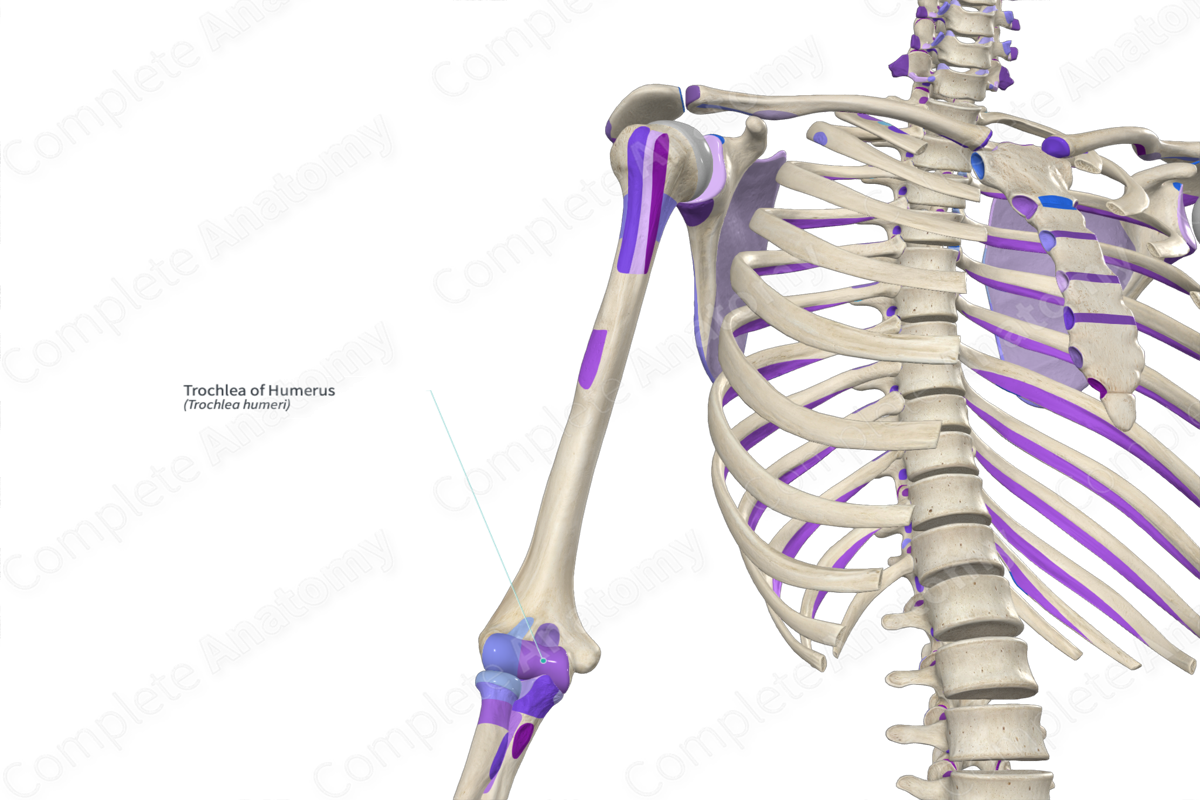
Trochlea
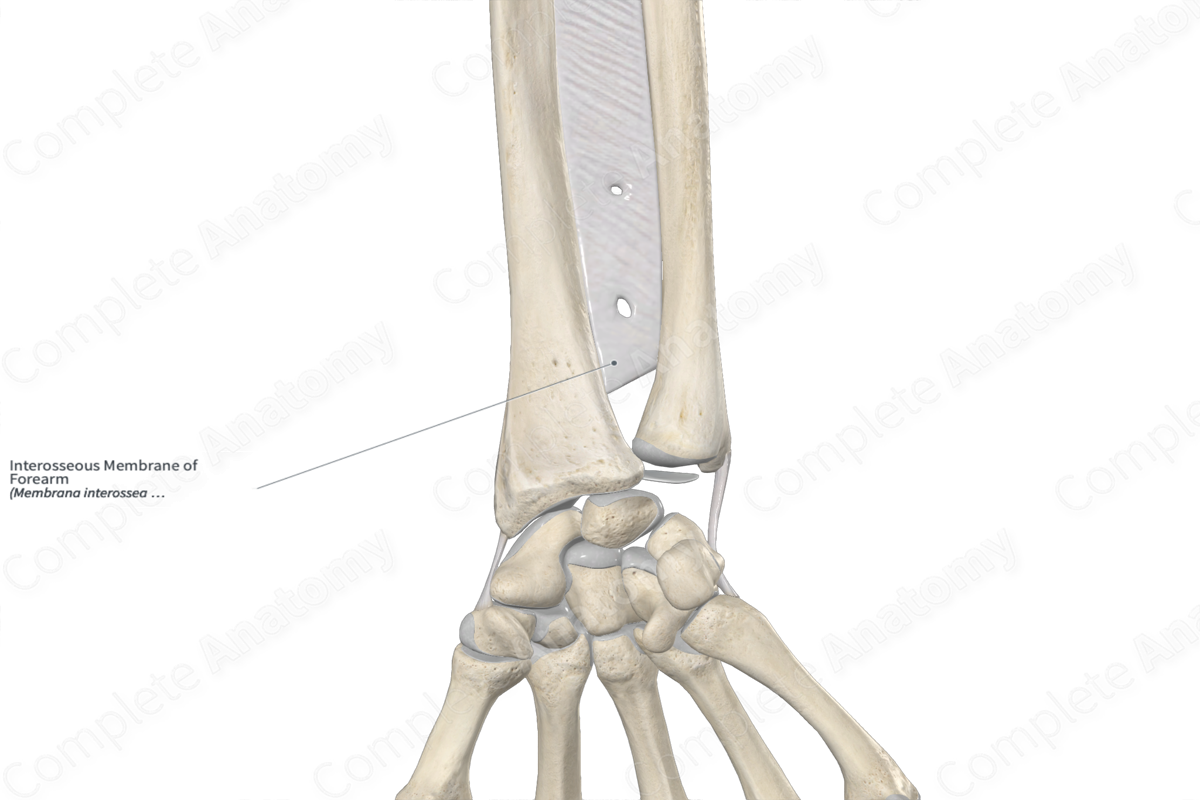
Interosseous membrane
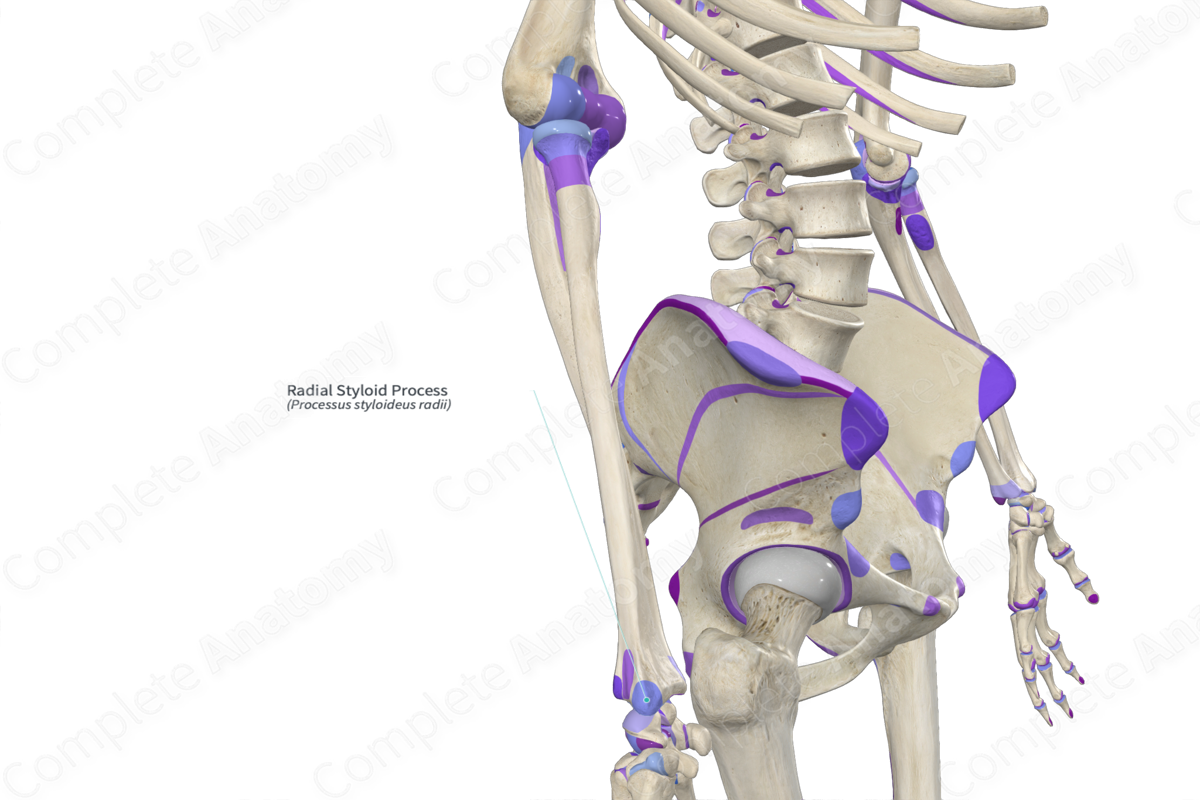
Radial styloid process
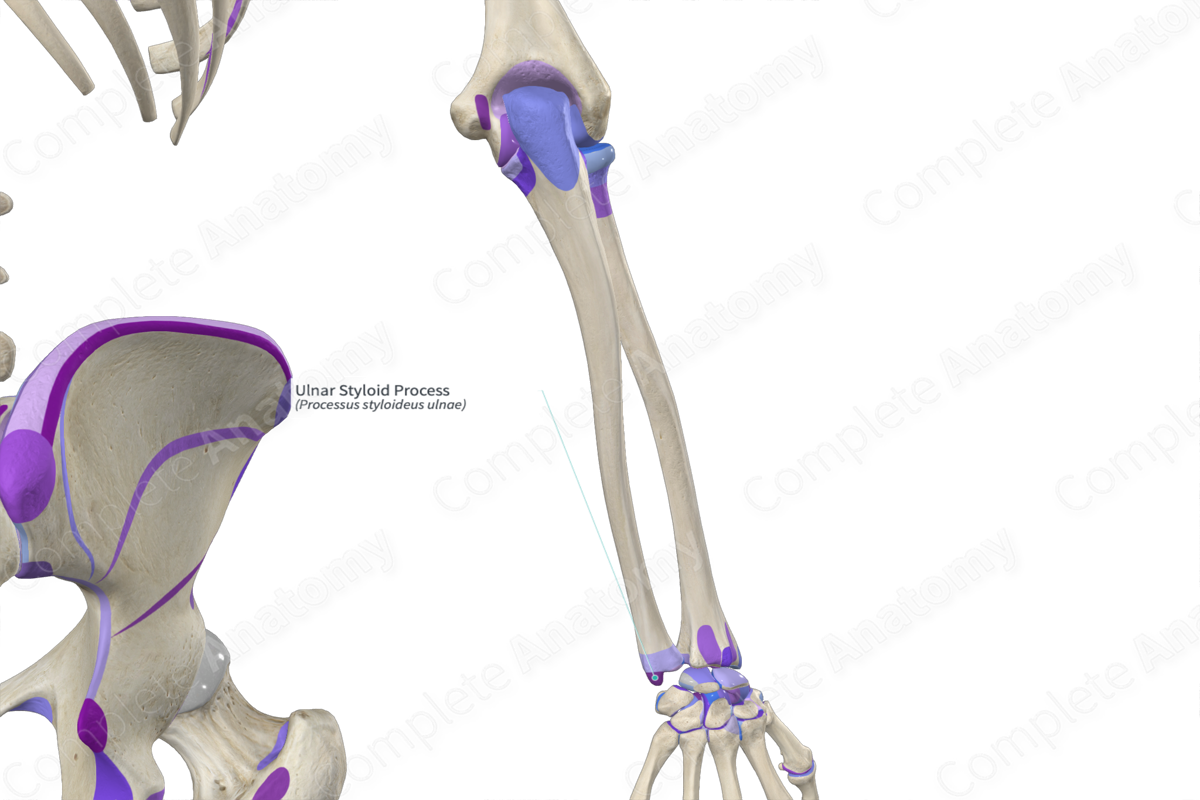
Ulnar styloid process
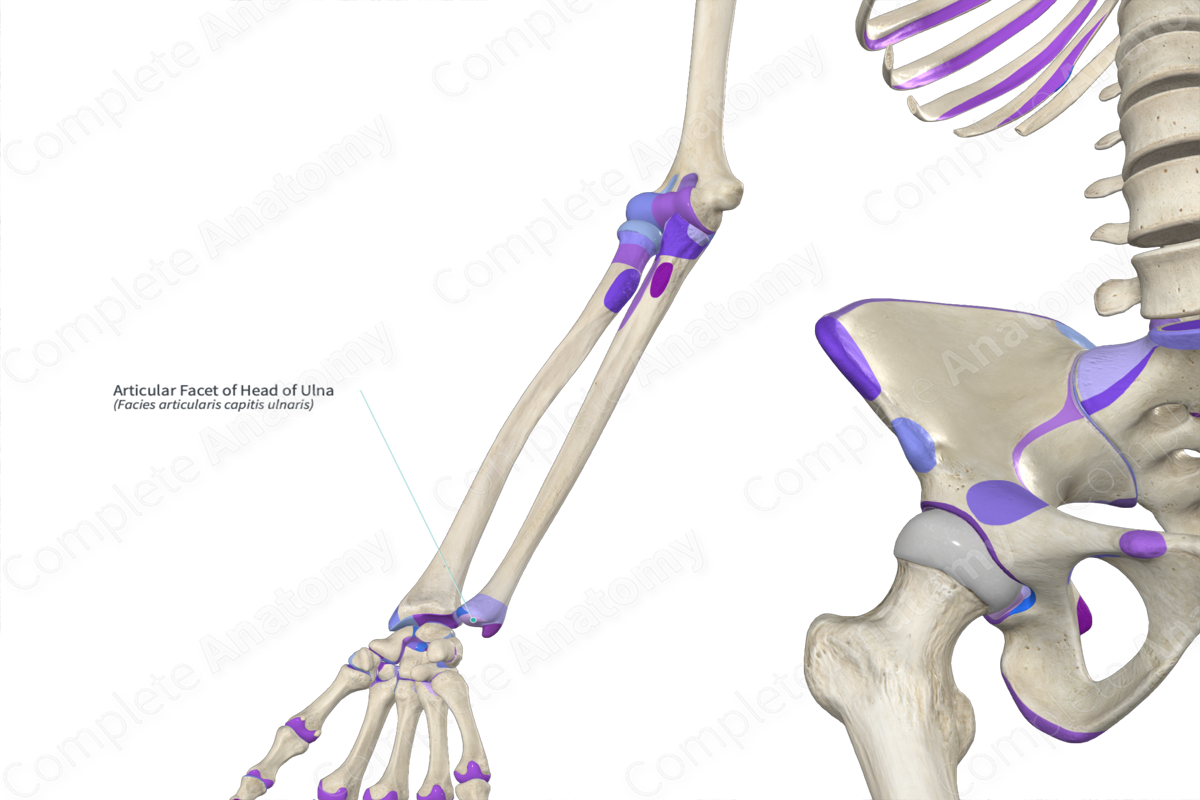
Articular facet of ulna
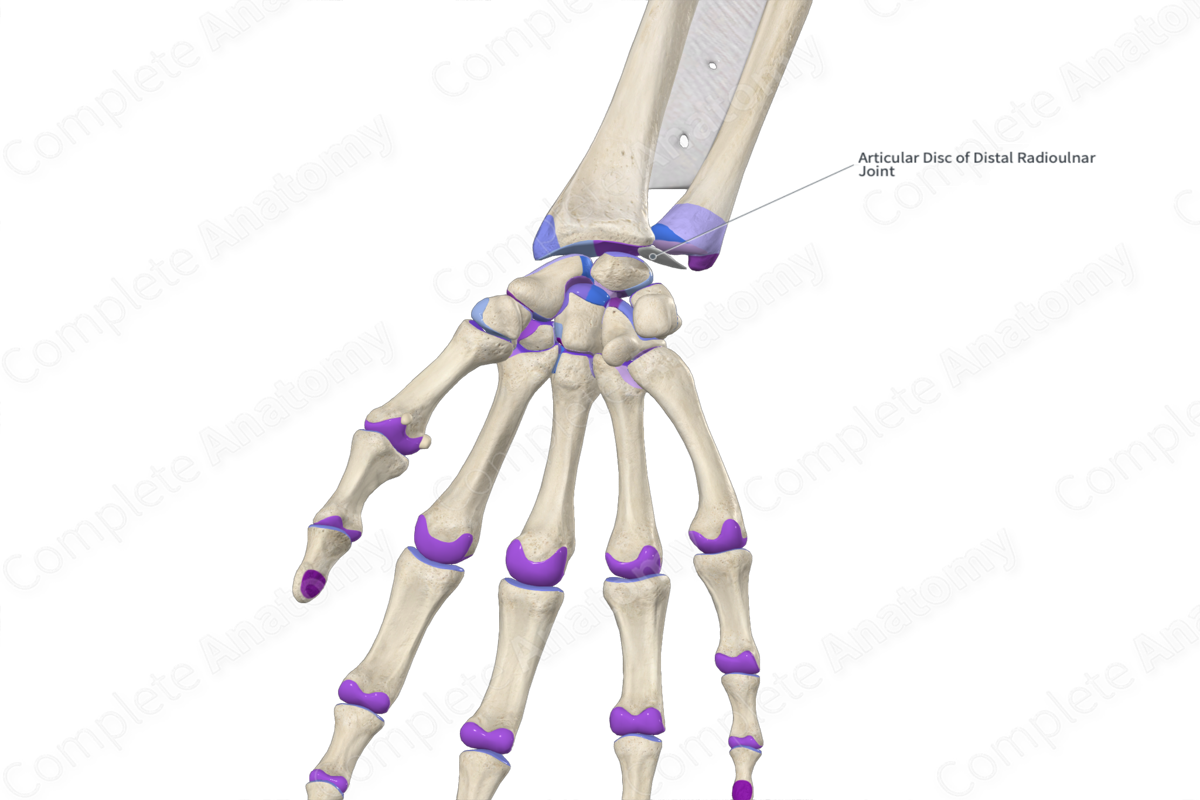
Articular disc of radioulnar joint
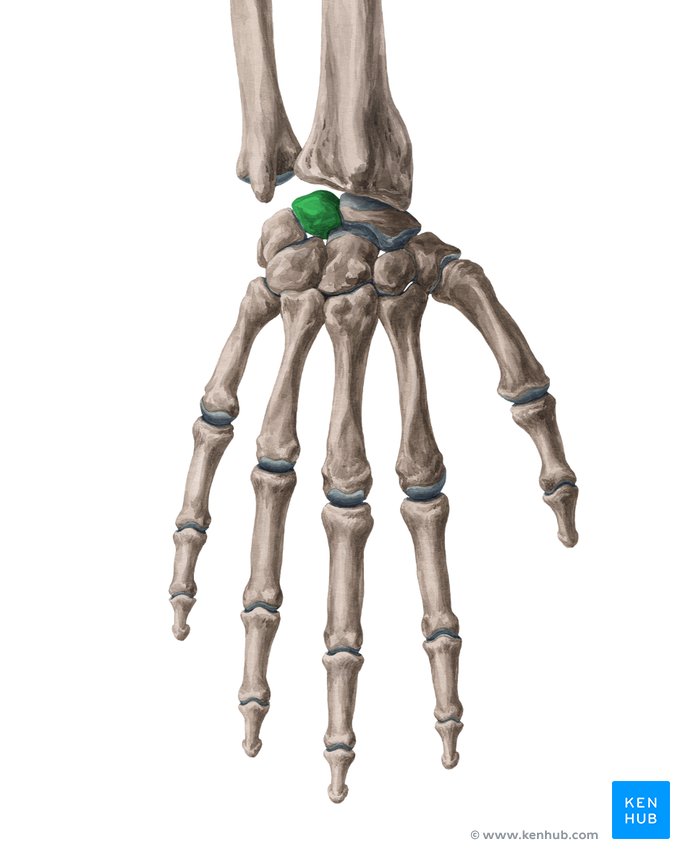
Lunate
Scaphoid
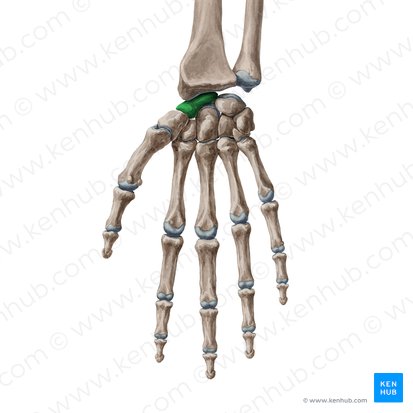
Trapezium
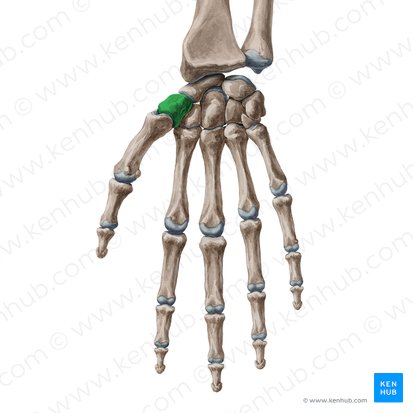
Triquetrum
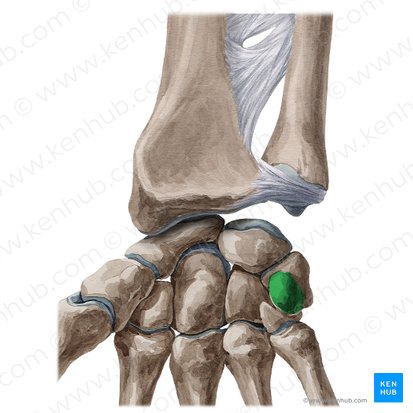
Hamate
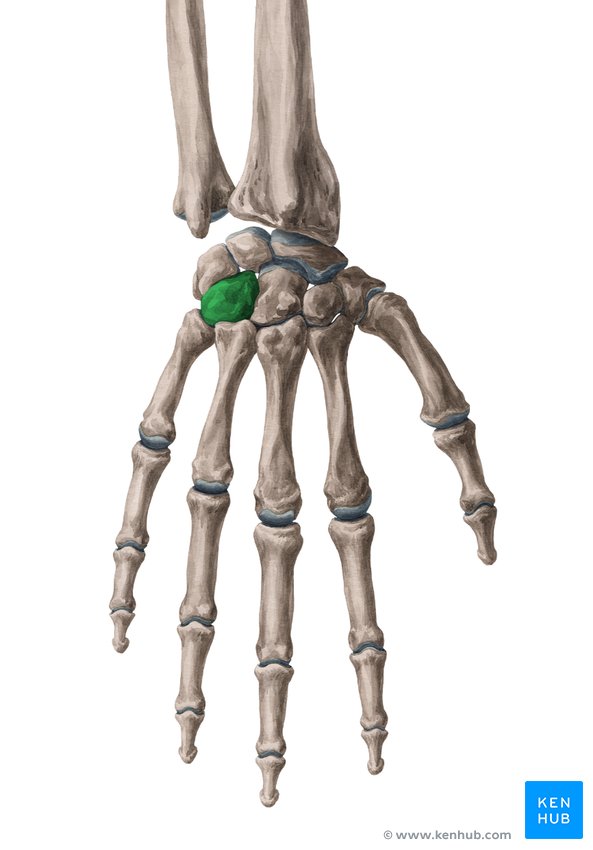
Pisiform
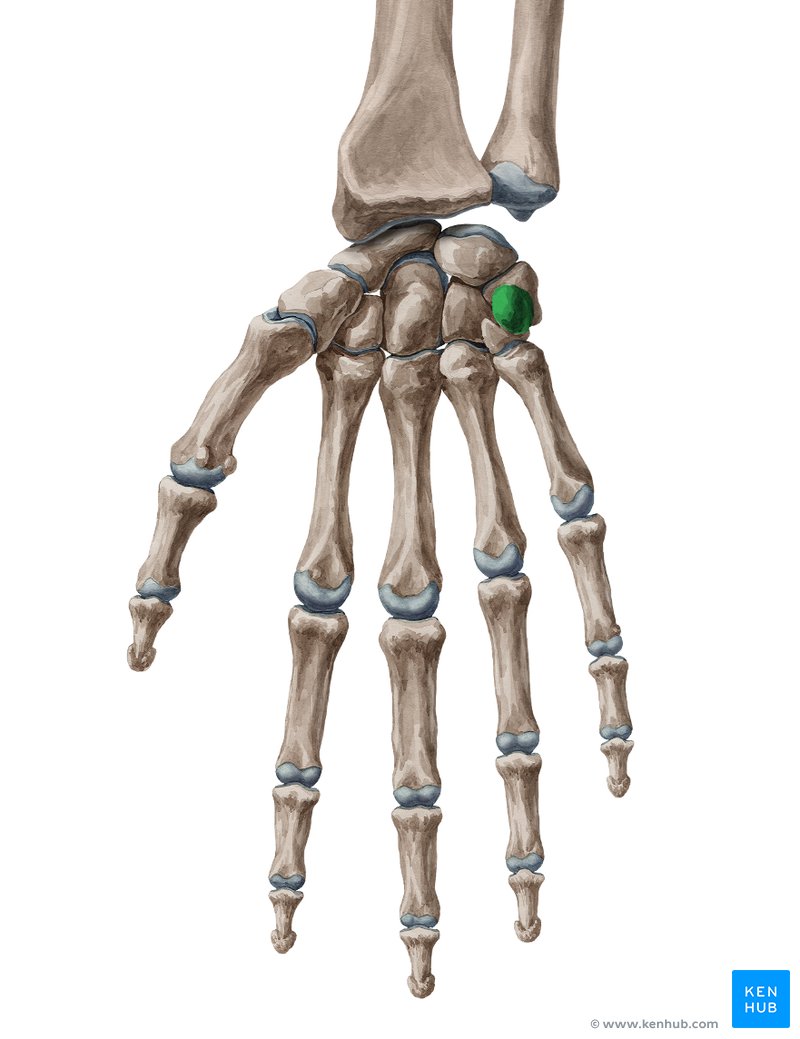
Capitate
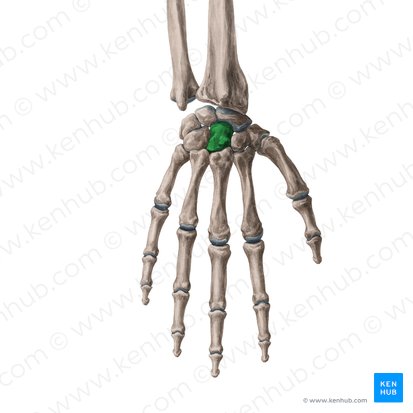
Trapezoid
Sesamoid bones of thumb
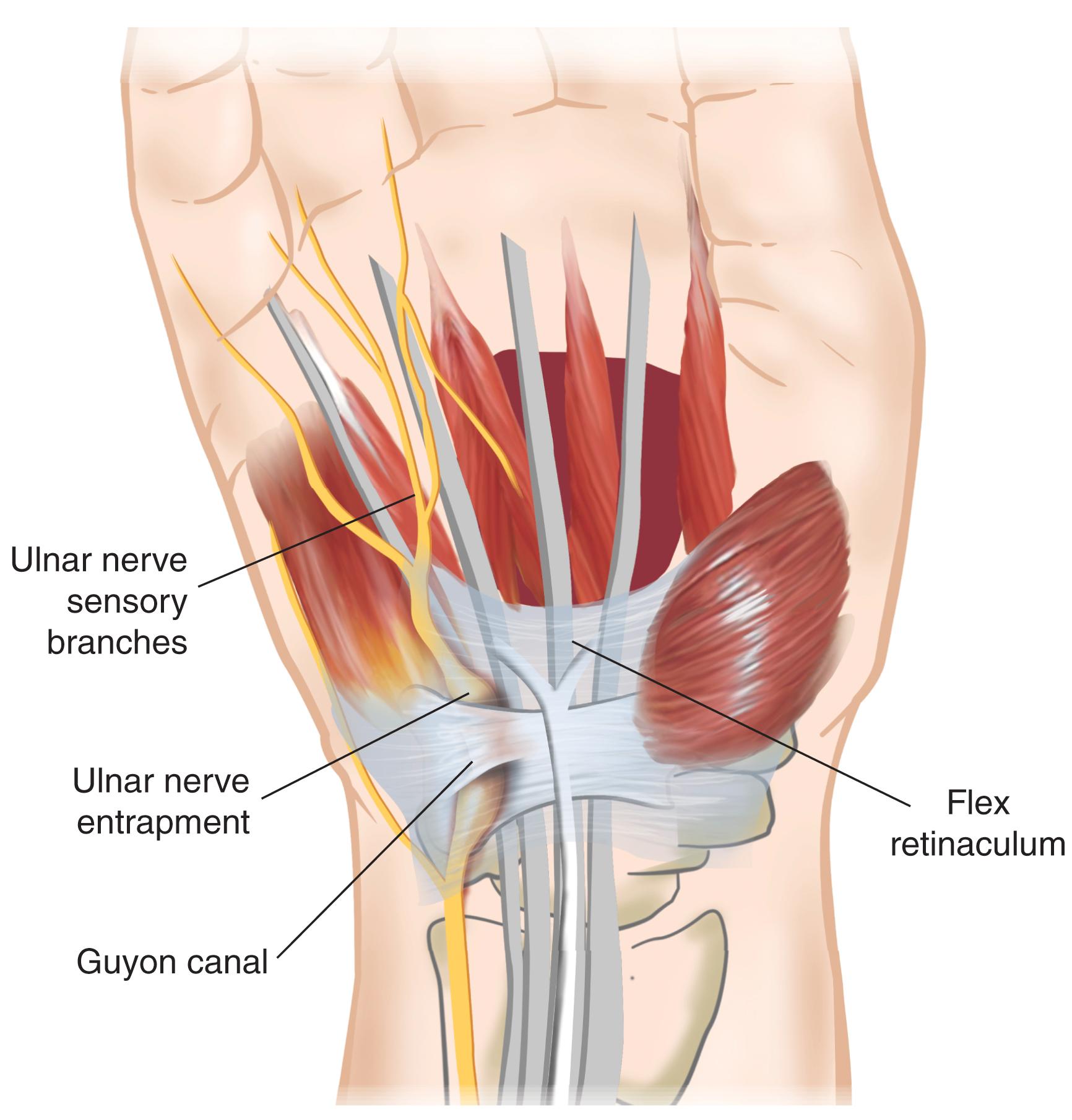
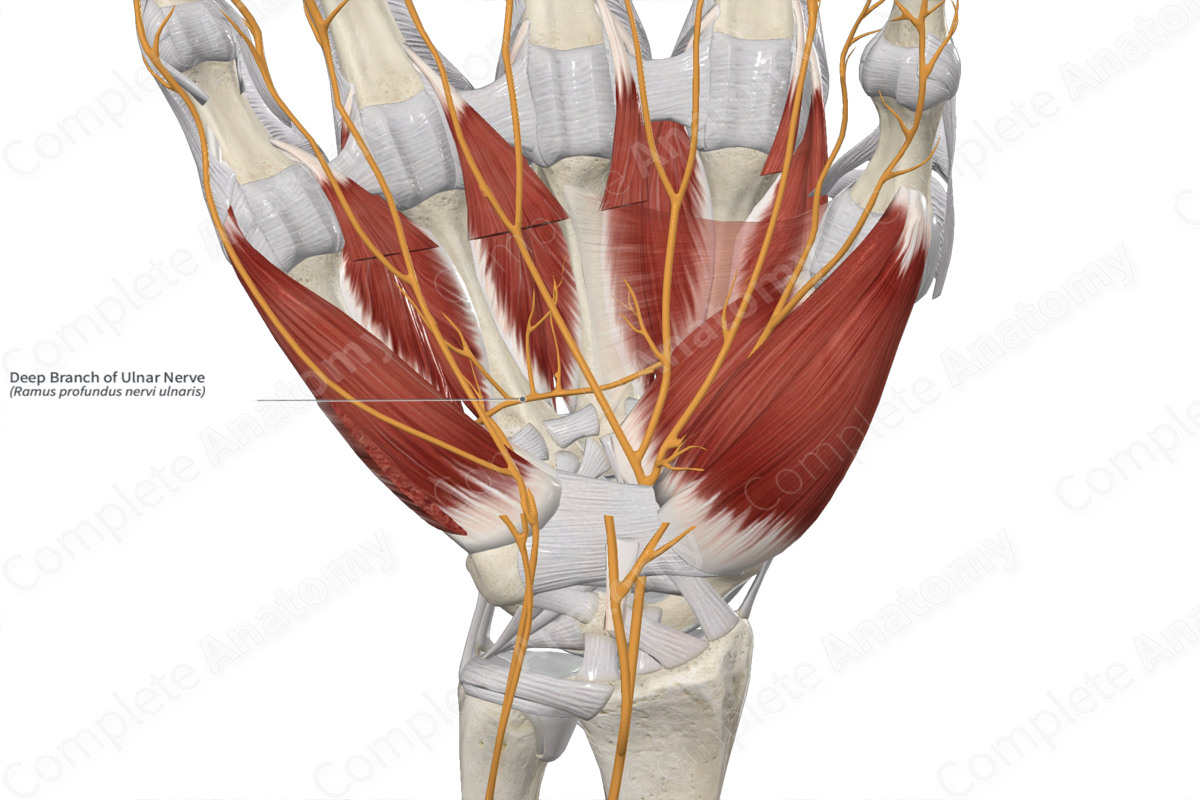
Guyon canal
A fibro-osseous passageway in the wrist that houses the ulnar nerve and artery as they enter the hand
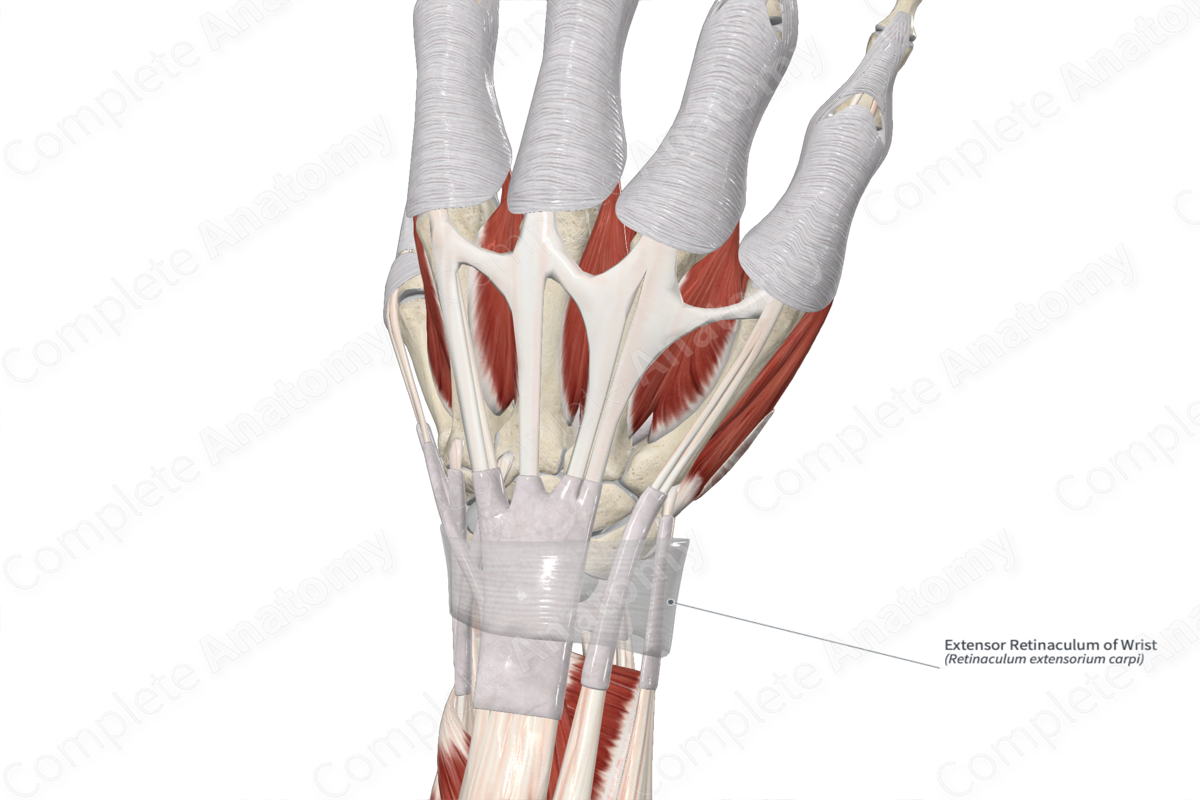
Extensor retinaculum
Keep tendons in place when bending fingers
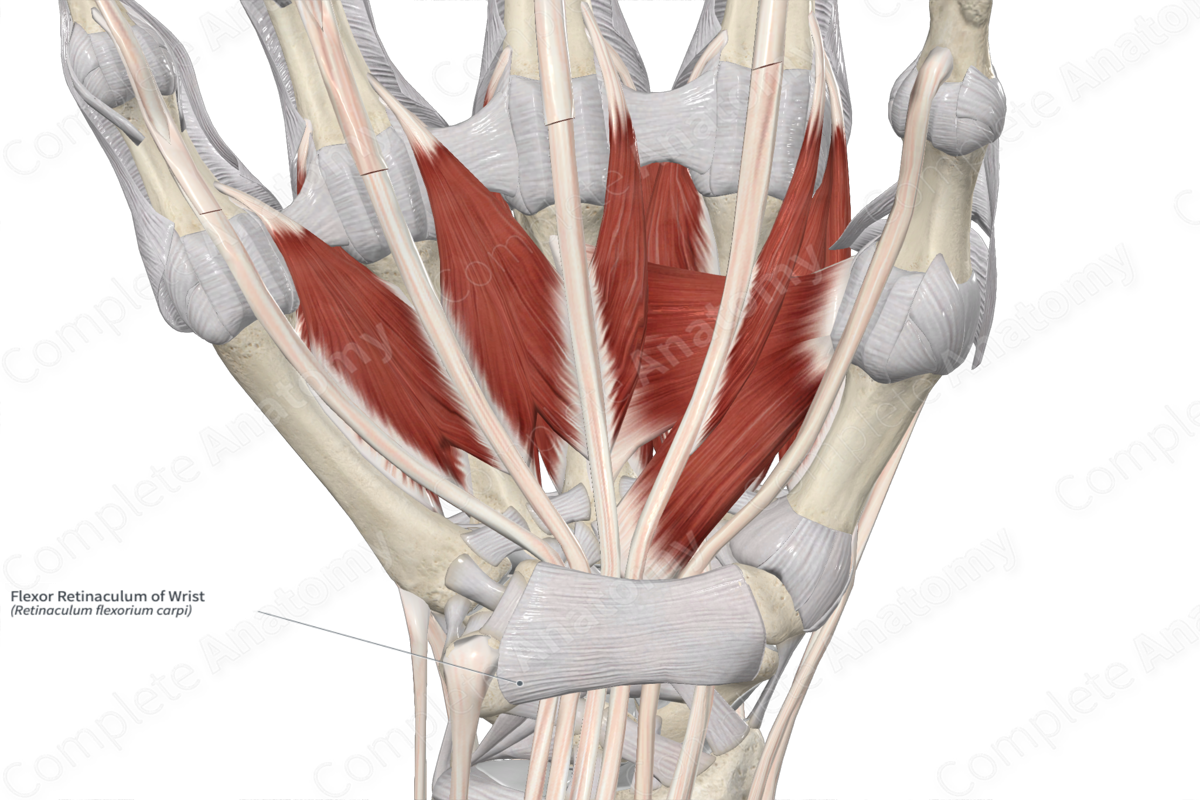
Flexor retinaculum
Acts as a pulley, preventing the tendons of the flexor muscles from bowing outward during wrist flexion
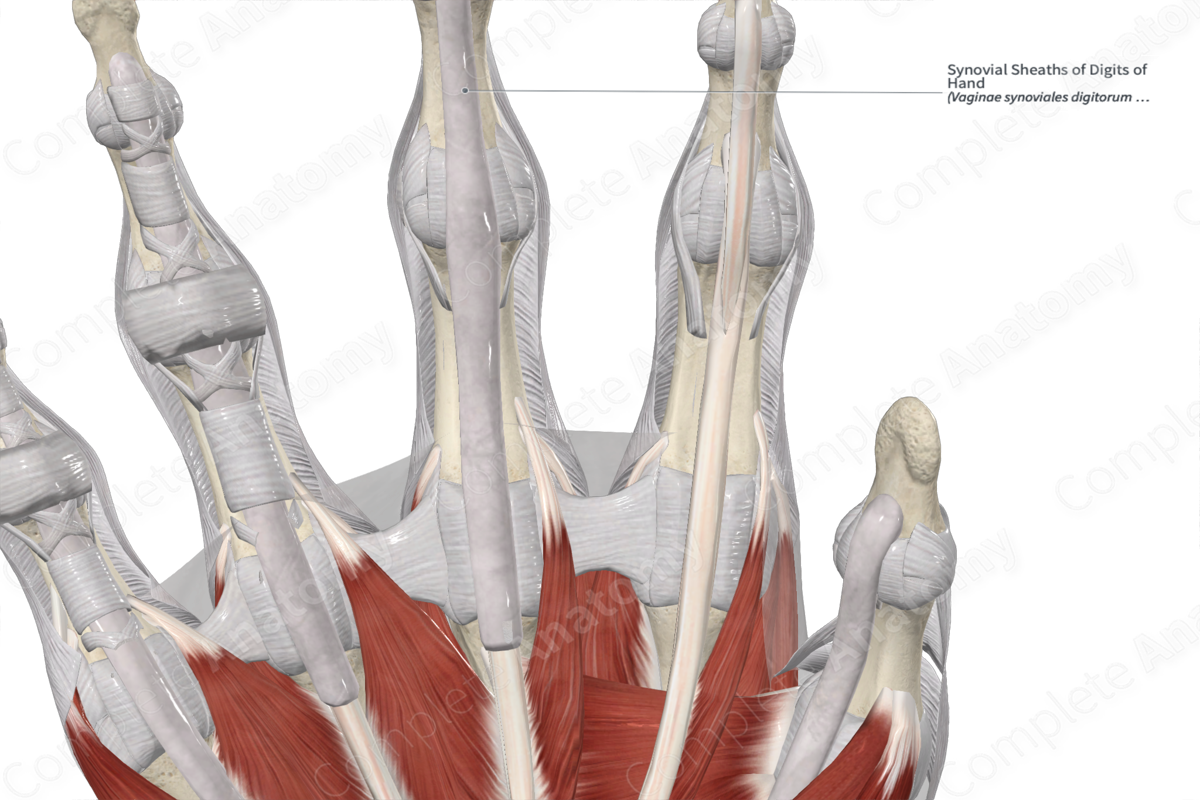
Synovial sheaths
Specialized, fluid-filled sacs that surround tendons, reducing friction and enabling smooth movement of the wrist and hand
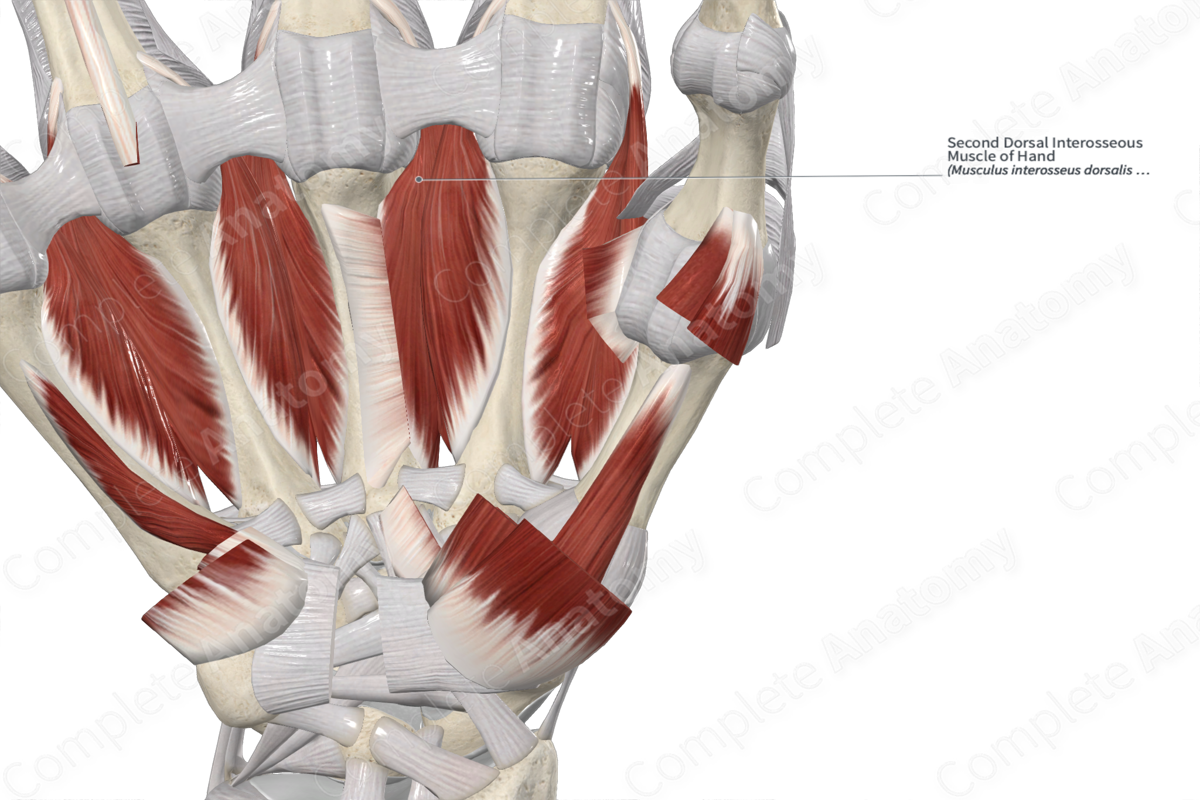
2nd dorsal interosseous
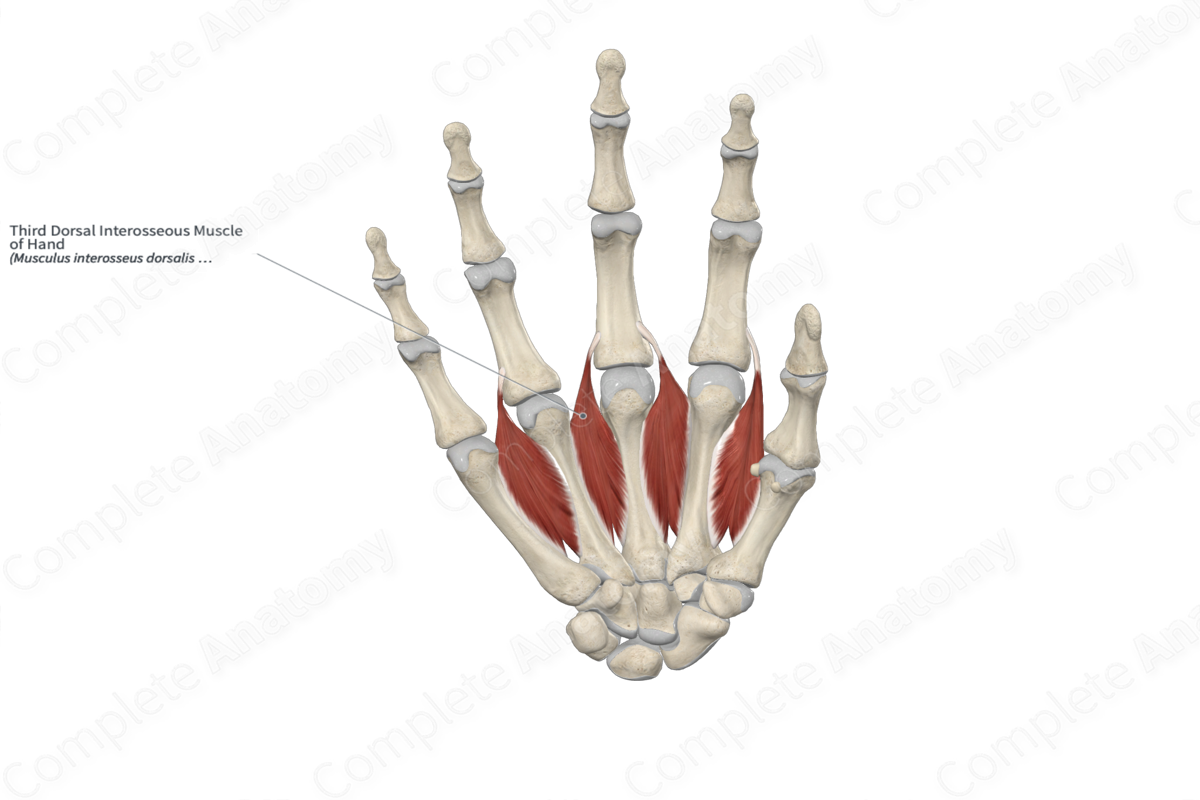
3rd dorsal interosseous
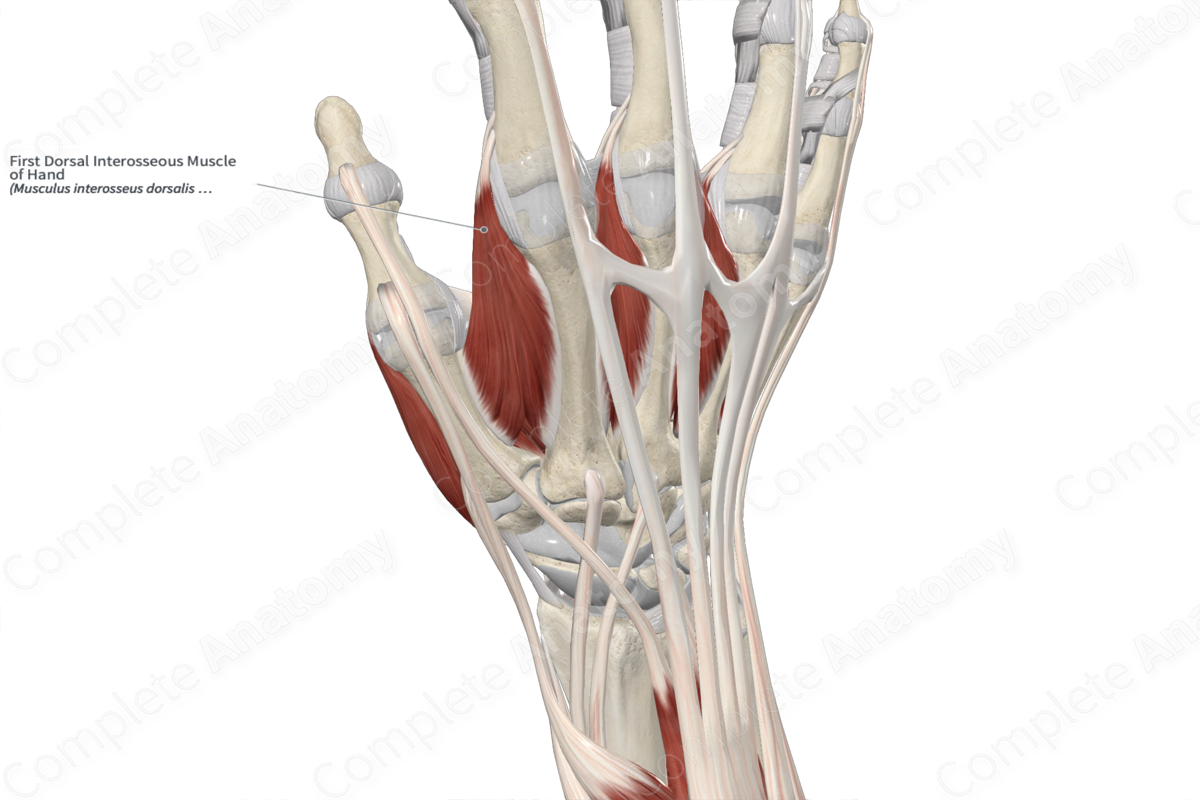
1st dorsal interosseous
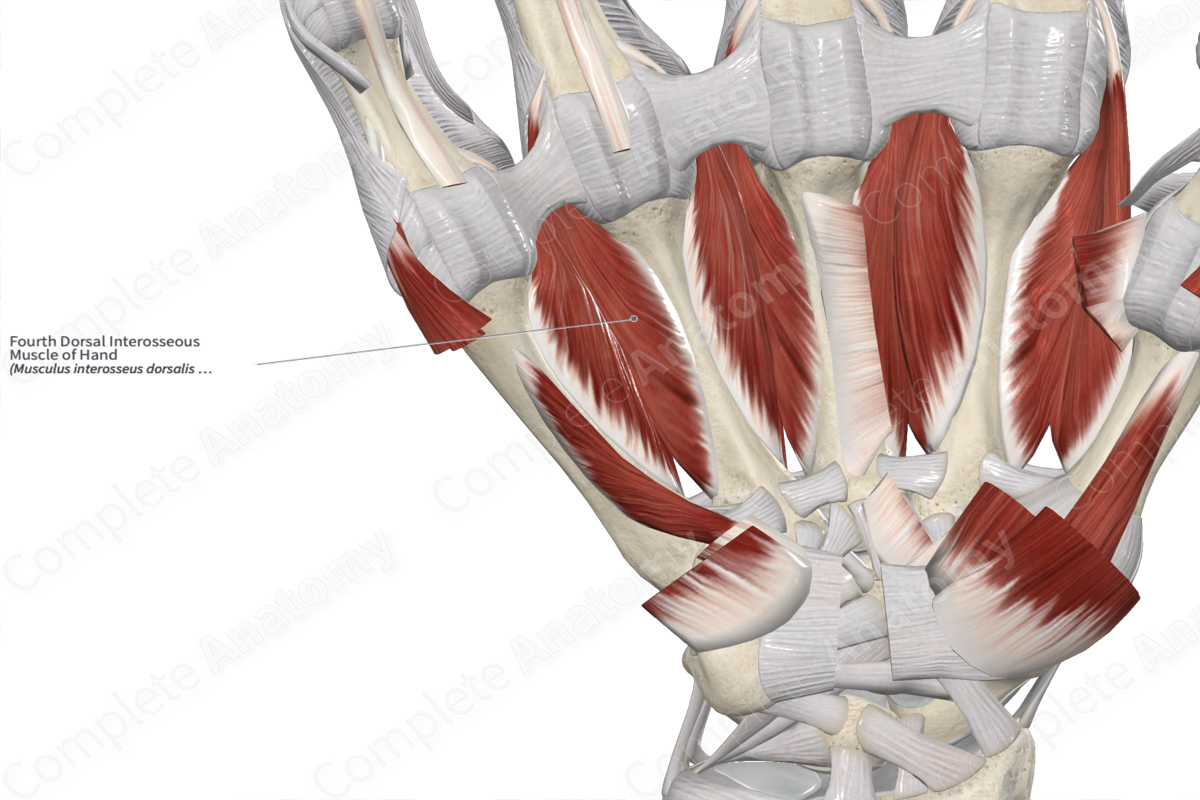
4th dorsal interosseous
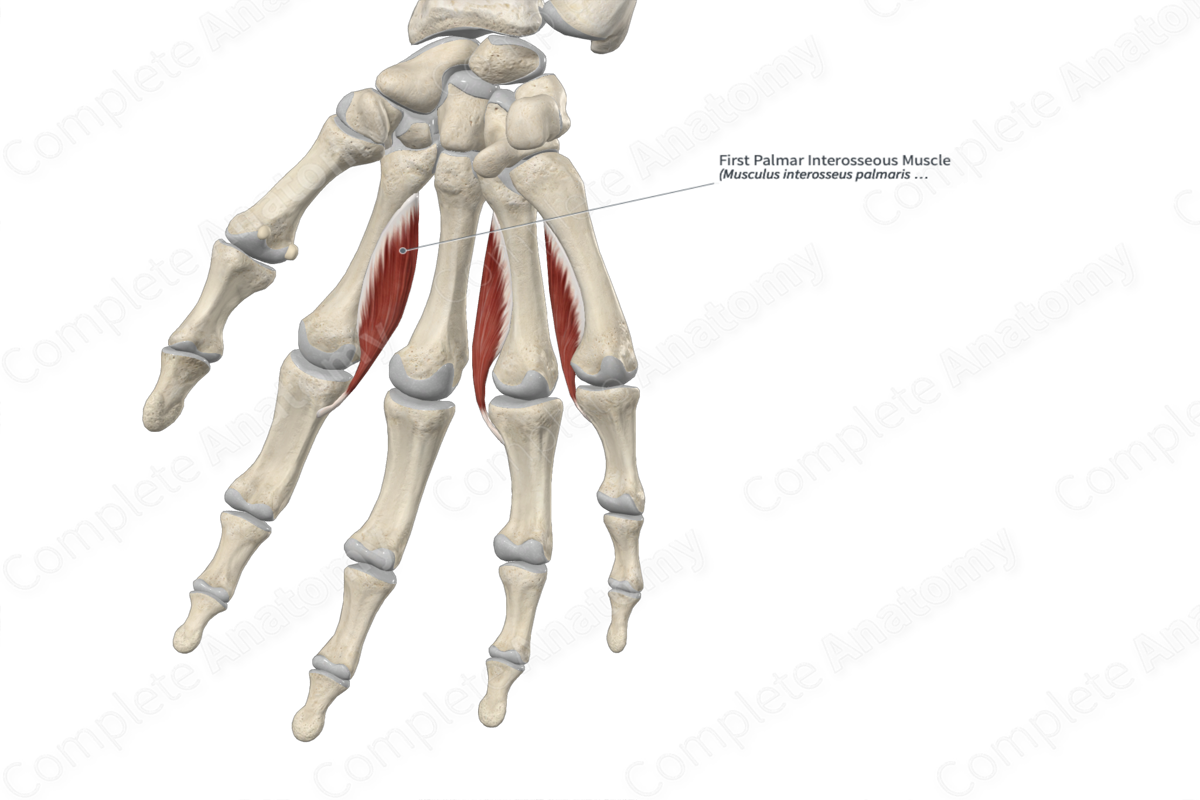
1st palmar interosseous
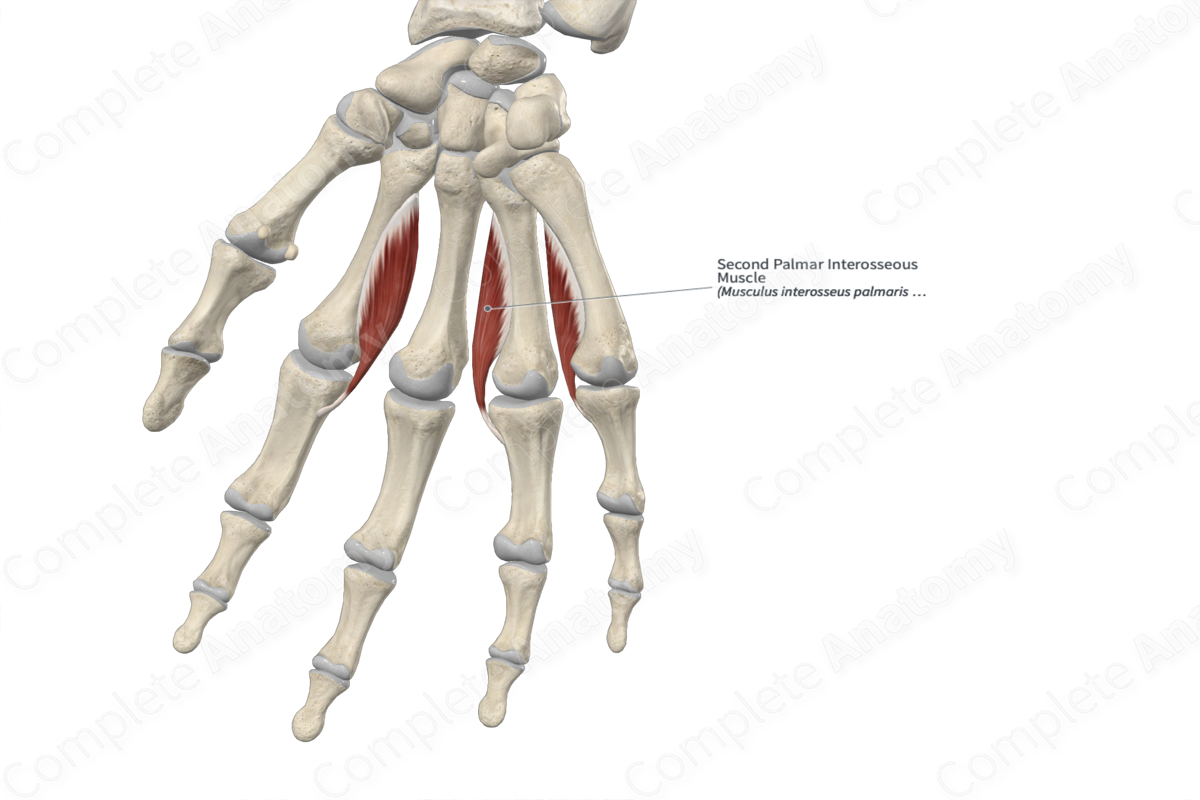
2nd palmar interosseous
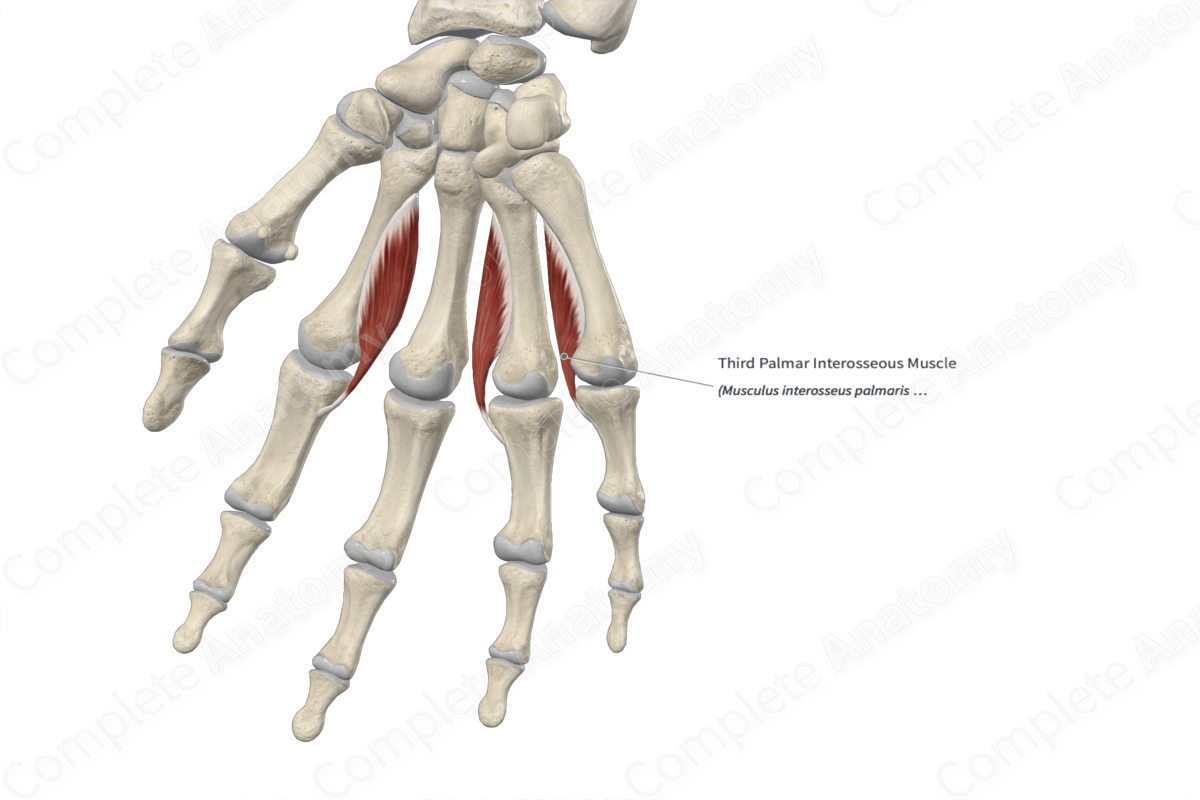
3rd palmar interosseous
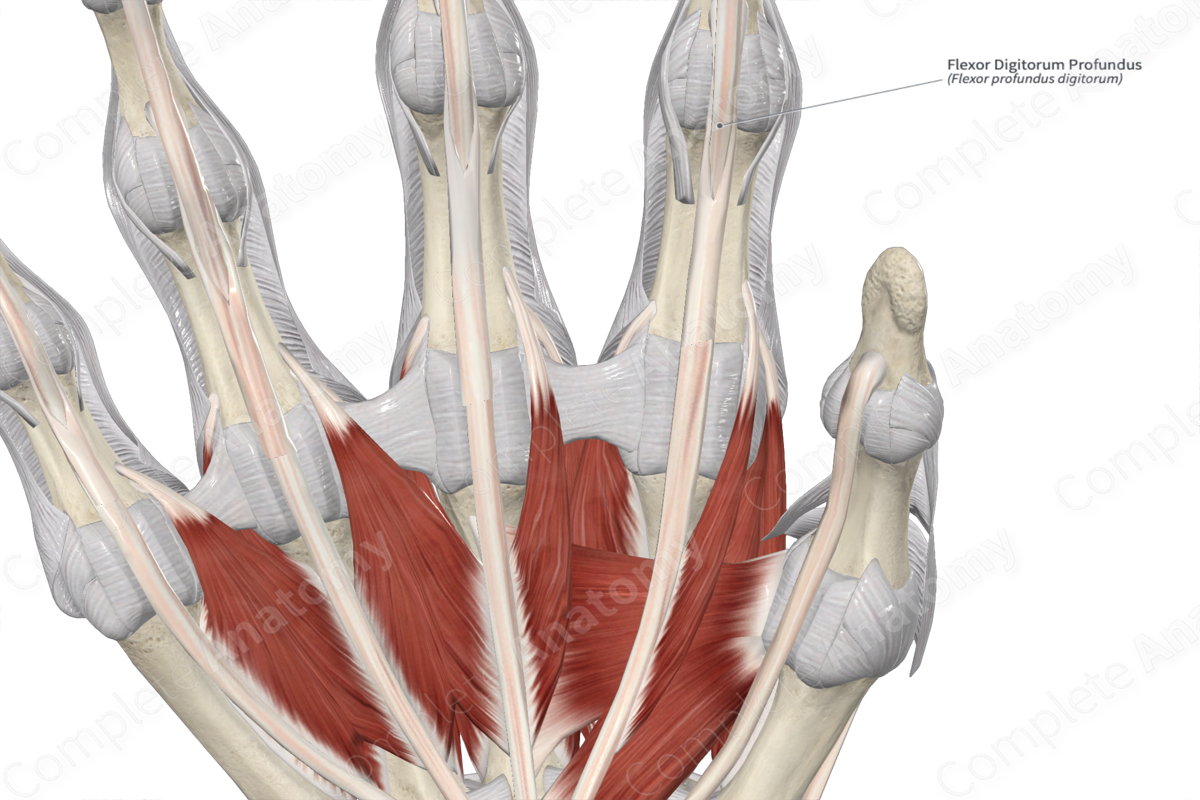
Flexor digitorum profundus tendon
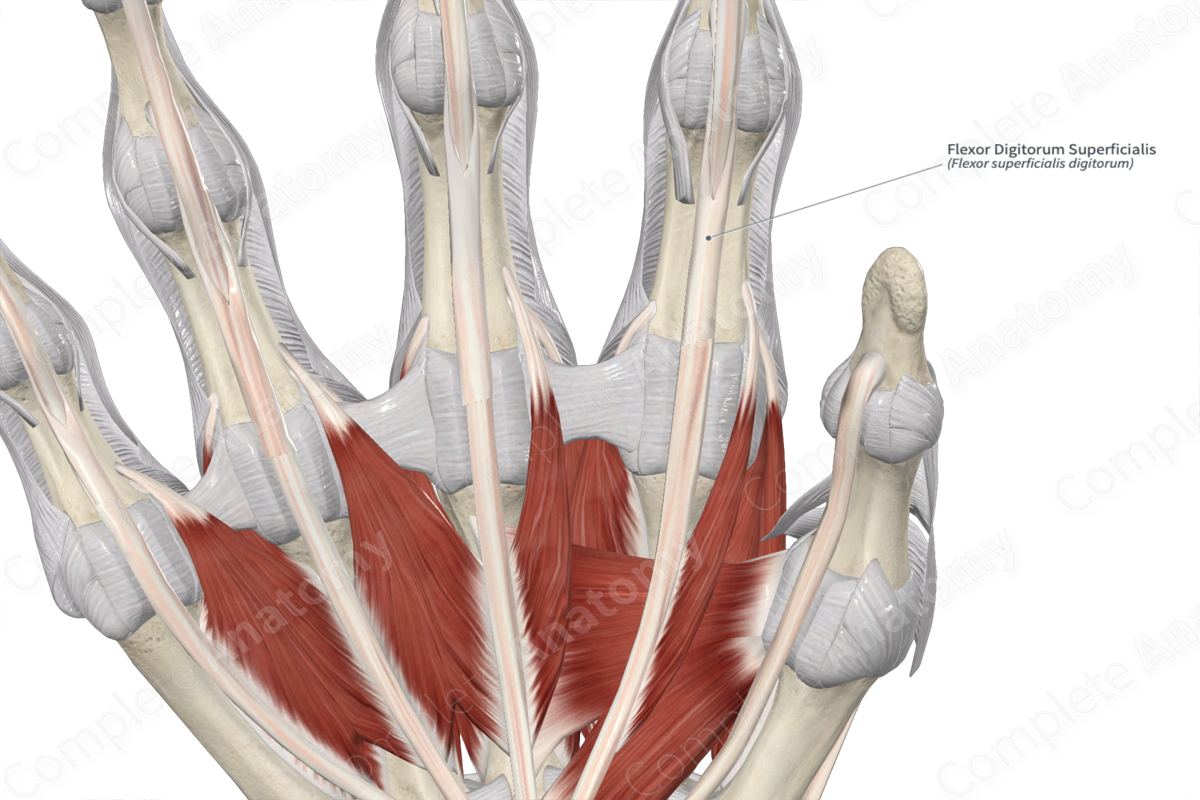
Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
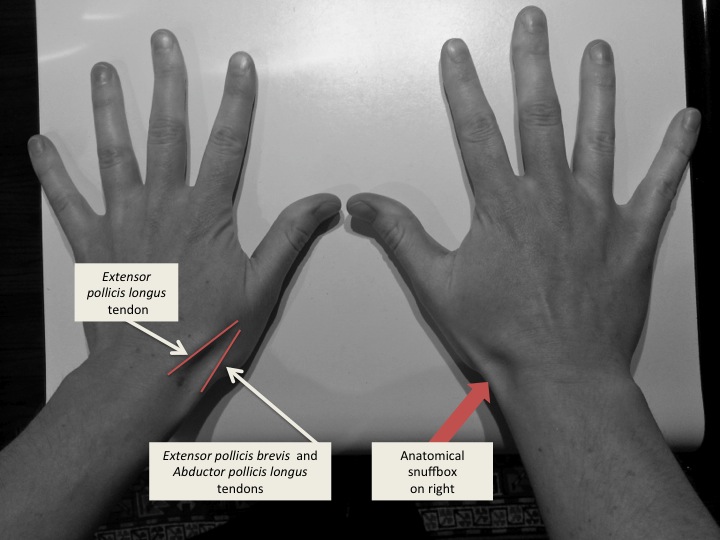
Anatomical snuff box
A triangular depression on the back of the hand, at the base of the thumb
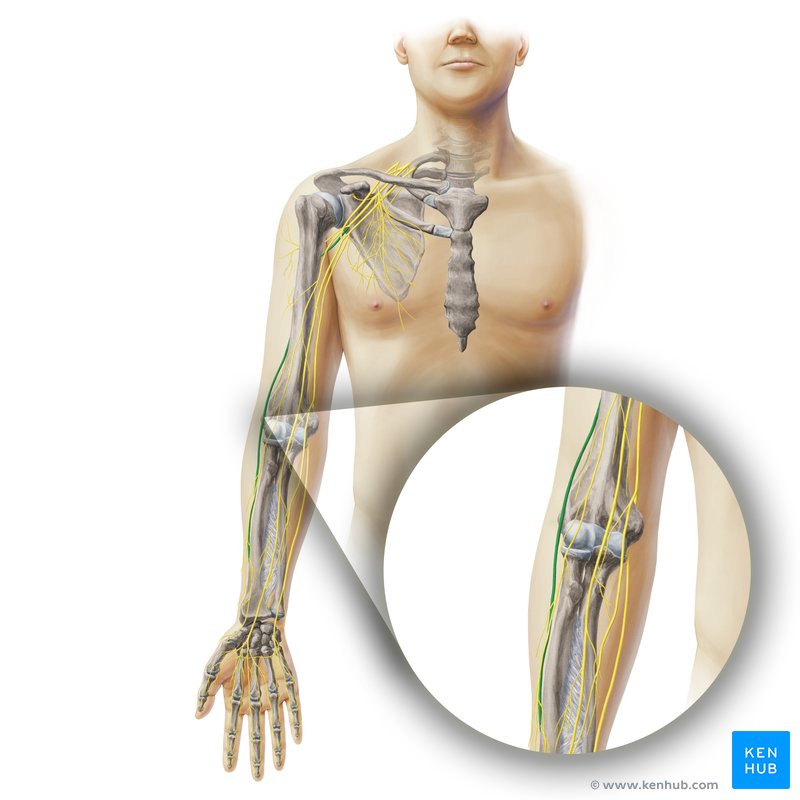
Radial nerve
Ulnar nerve
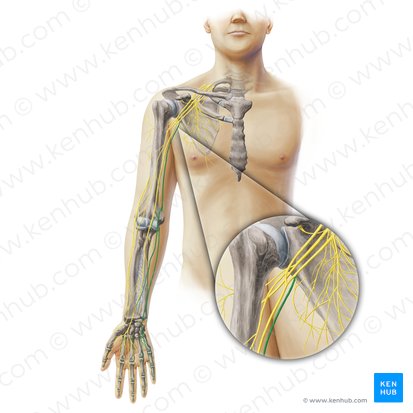
Median nerve
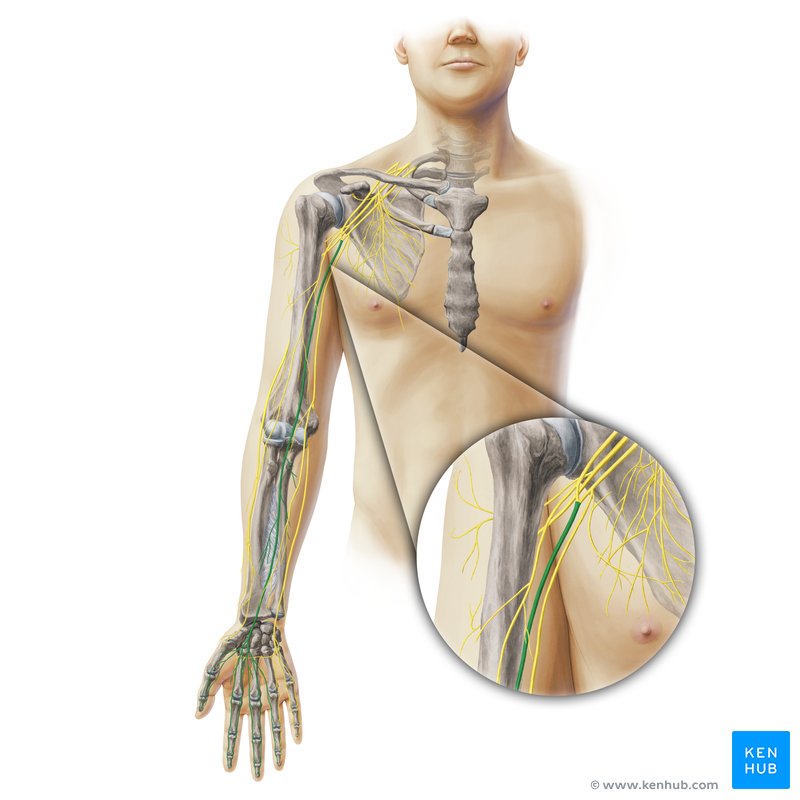
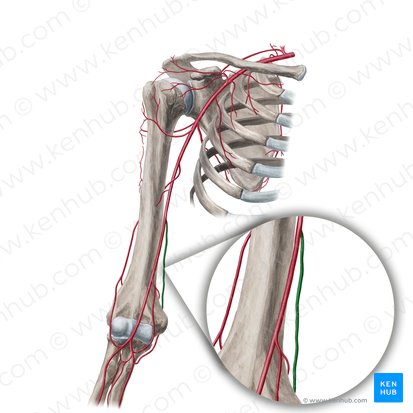
Brachial artery
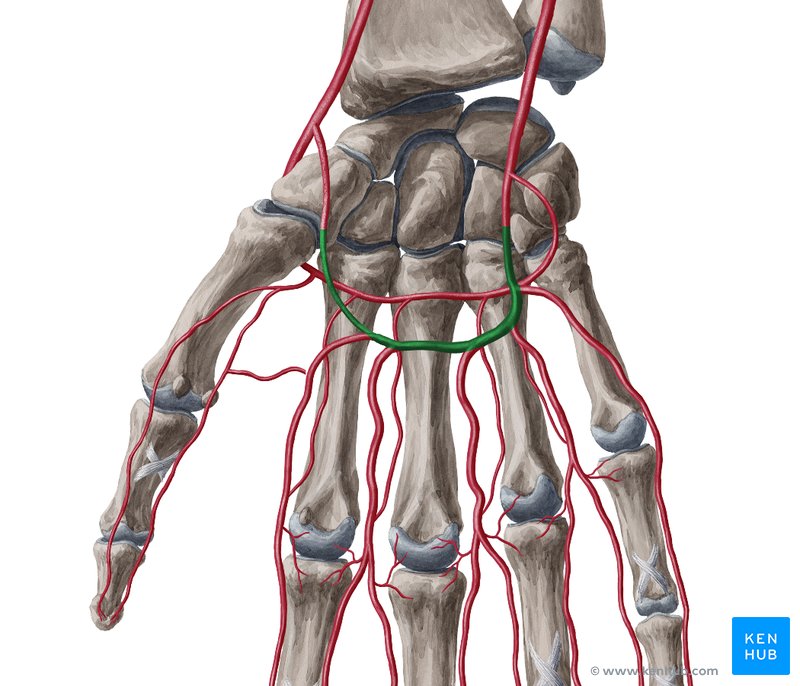
Superficial palmar arch
Ulnar artery
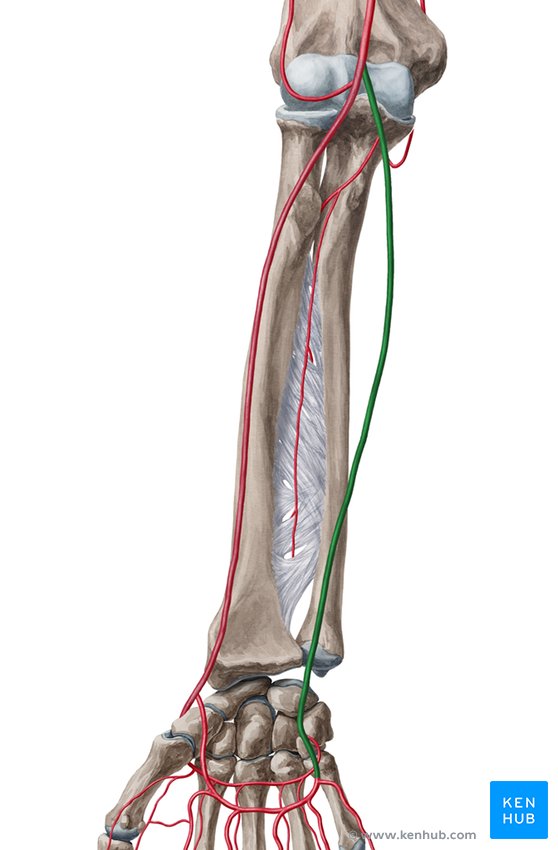
Radial artery
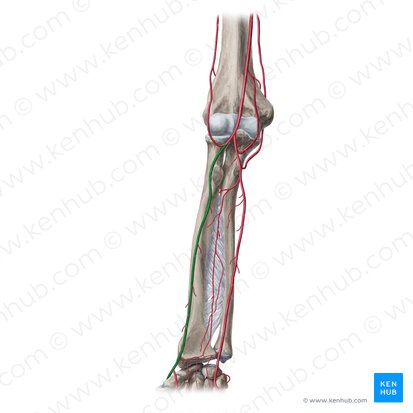
Deep palmar arch
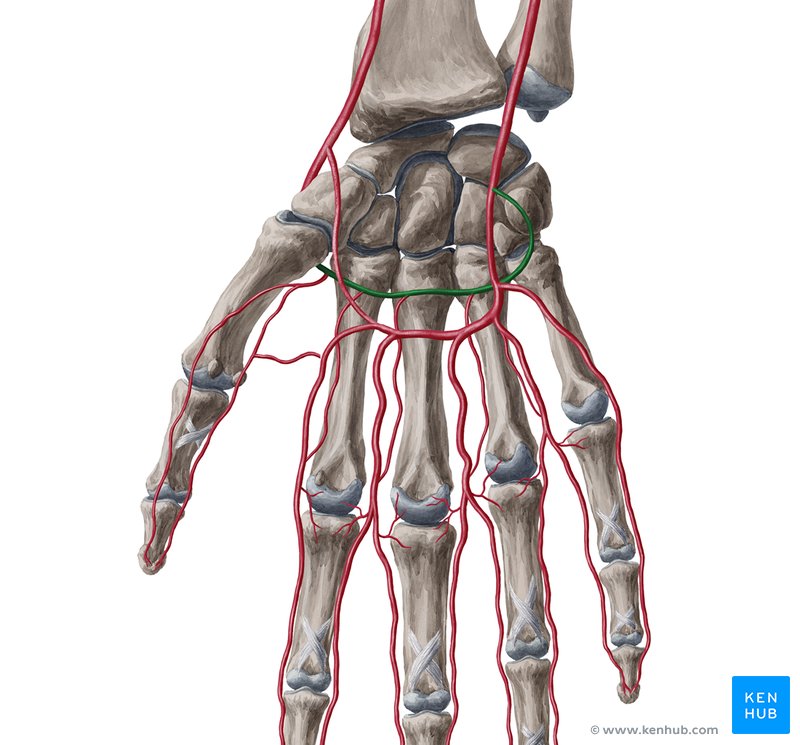
Radiocarpal joint
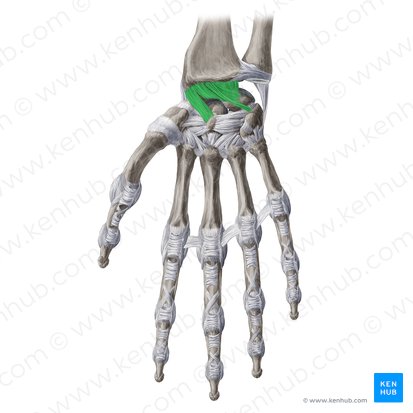
Recurrent branch of median nerve
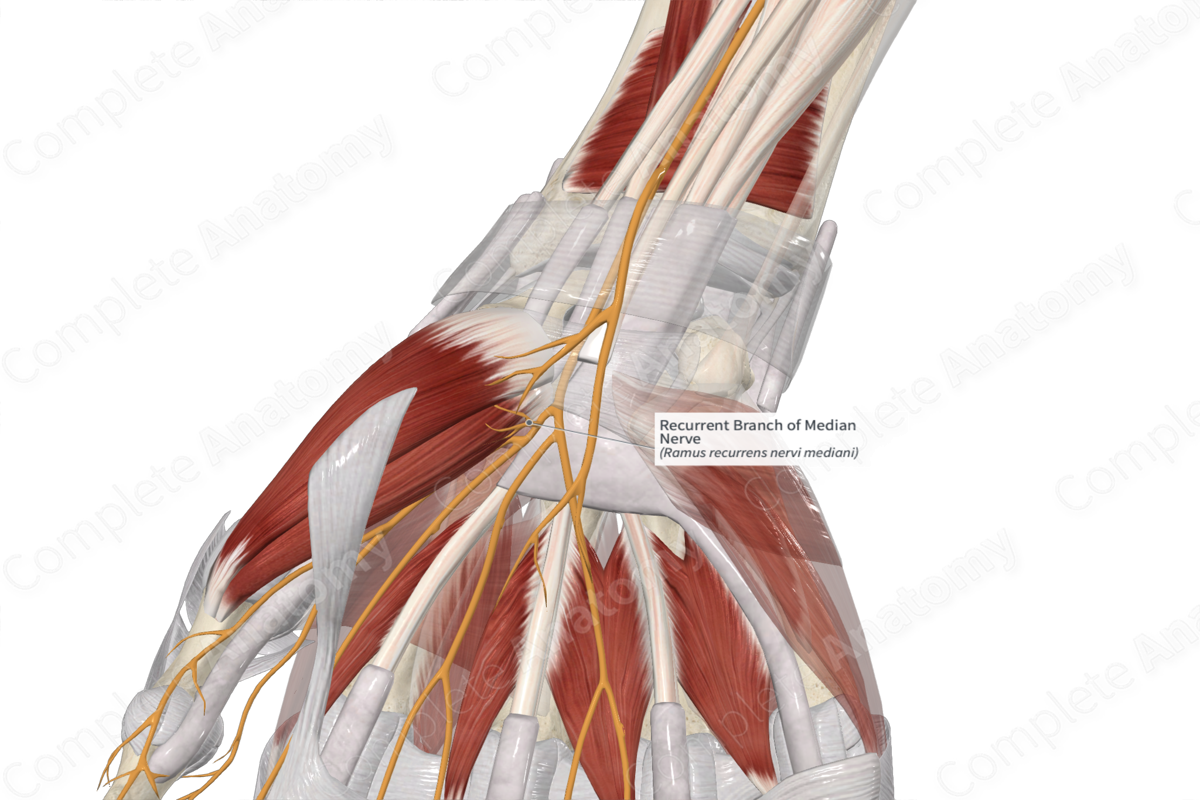
Deep branch of ulnar nerve
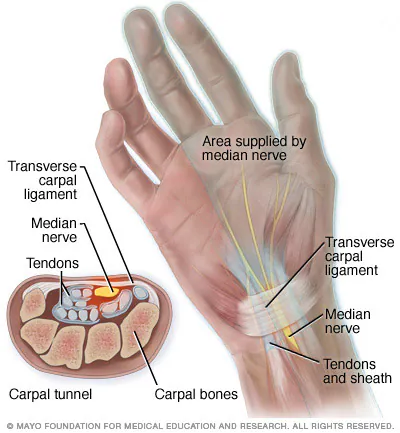
Carpal tunnel
superiorly
laterally
medially
laterally
The cubital fossa is bounded _____ by an imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus, _____ by the brachioradialis, medially by the pronator teres; with the floor consisting of the brachialis _____ and the supinator _____ and the roof being cubital fascia
3, 2
Anterior
Posterior
There are 5 muscles in the two arm compartments
___ in the anterior compartment and ___ in the posterior compartment
_____ compartment
1. Biceps brachii
2. Coracobrachialis
3. Brachialis
_____ compartment
1. Triceps brachii
2. Anconeus
4 tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis
4 tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus
Median nerve
Flexor pollicis longus
Which structures run through the carpal tunnel?
Ulnar nerve
Cubital tunnel syndrome involves which of the following structures?
Median nerve
Radial nerve
Ulnar nerve
Ulnar artery
Ulnar nerve
A patient hits their medial elbow and feels numbness and tingling into their fifth digit and the medial part of their fourth digit. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Radial nerve
Median nerve
Superficial branch of median nerve
Ulnar nerve
FOOSH
What is a common mechanism of injury for a scaphoid fracture?
Profundus brachii, Radial, & Ulnar
The brachial artery splits into which arteries?
Acromioclavicular
A “step down” deformity is the result of a separation of which joint?
Sternoclavicular
Costoclavicular
Acromioclavicular
Glenohumeral
True
T/F the superior portion of the glenoid labrum blends with the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii.
Medial pectoral nerves
Which of the following is NOT part of the nerve supply to the glenohumeral joint?
Suprascapular nerve
Axillary nerve
Lateral pectoral nerves
Medial pectoral nerves
Triangular fibrocartilaginous complex
Which structure is a fibrocartilaginous articular disc which binds the radius and ulna?
Annular ligament
Radial collateral ligament
Triangular fibrocartilaginous complex
Ulnar collateral ligament
Iliac tubercles & L5 vertebrae
The transtubercular plane passes through which of the following two structures?
10th costal cartilage
Iliac tubercles
Mid-inguinal point
L5 vertebra
Inguinal vein
Which of the following is NOT one of the contents of the inguinal canal?
Spermatic cord in males
Round ligament of uterus in females
Inguinal vein
Lymphatic vessels
False
T/F the femoral artery/vein pass through the inguinal canal
fore
hind
mid
The celiac trunk runs to the _____gut,
the inferior mesenteric a to the _____gut,
and the superior mesenteric a to the _____gut