liquid crystals (copy) 5
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what is the fourth state of matter
liquid and crystal
liquid properties (4)
isotropic
optically transparent
1 refractive index
flow
crystal properties (4)
anisotropic
direction dependent
3 refractive indicies
doesnt flow
when something is mesogenic what is it
a liquid crystal
what is a mesophase
a liqud crystal phase
what is isotrophy
uniformity in all directions
what is isotropic in?
liquid phase
what is anisotropy?
directionally dependent
when something is thermotropic what is it
behaviour as a function of temperature
what is lyotropic
solutions of compounds that have liquid crystal behaviour
where are lyotropic crystals formed?
In surfactant solutions
what is birefringence, and what does this mean
the ability to rotate plane polarised light
types of thermotropic liquid crystal (3)
nematic
smectic
cholesteric
organic thermotropic liquid crystal properties (4)
organic
elongated
flat
rigid
easily polarisable
contain dipoles
nematic
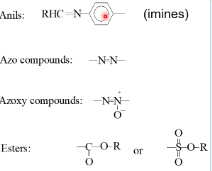
what functional groups do organic thermotropic liquid crystals have
esters
anils
azo compounds
azoxy compounds
how do liquid crystal displays come about (LCD)
weak electrical signals emit an optical response
What doesn’t LCD emit?
Light
How do LCDs modify light?(2)
Scattering
Change in optical density or colour
What do LCDs use?
Low voltages
What is low in LCDs?
Power consumption
Heat produced
What LCDs give?
Good contrast in strong light
Why can’t molecules be parallel?
Due to chiral interaction there is a slight angle between them
Where are cholesteric LC’s used? (4)
Sensors
Thermometers
Fabrics
Display devices
When do cholesterics refract light?
With a wavelength equal to the pitch
What does the cholesteric pitch depend on? (3)
Temp
Press
Electric & Magnetic fields
How are tumours different to surrounding tissues?
Temperature
What are the essential structural features of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals (LLC)
–Amphiphiic
•Polar – head group
•Non-polar – alkyl chain
What is the structure of a potassium stearate surfactant molecule?
non-polar tail
Polar head
Amphiphilic
What happens to the soluble part of potassium stearate(polar head)?
ut’s attracted to the water and is solvated
What happens to the non-soluble part of potassium stearate(non-polar tail)?
hates water and is shielded from the solvent(water)
What happens you add a potassium stearate with a solvent?
Spontaneous formation of aggregates
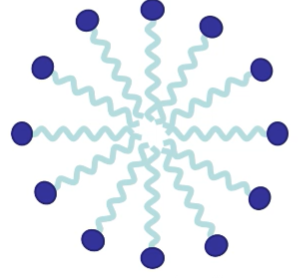
what is formed in an aqueous solvent?
micelle
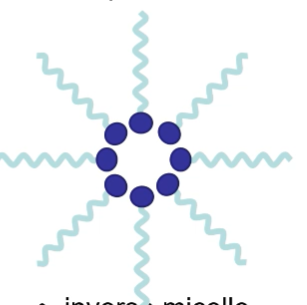
what is formed in a non-polar solvent?
inverse micelle
What happens when we have a very low surfactant concentration?
a monomeric solution is formed
What happens at the Critical micelle concentration (CMC)?
where we have enough micelles added they start to form spheric aggregates(micelles)
What do you get once you keep increasing surfactant concentration
micellar solution
What does a micellar solution do? (3)
Increase number of micelles
Increase size of micelles
Change shape of micelles- rods or discs
What does the hexagonal phase consist of?
close packed rod-like micelles separated by continuous water region.
Describe cell membranes? (2)
Amphiphilic molecules- Phospholipids
Regularly stacked layers
How does matter leave and enter cells?
Lipid bilayer
Proteins
What is the role of lipid bilayers
Fluid and let water in n out
What is the role of proteins?
Act as gates and switches in membranes
What materials can behave as liquid crystals(5)?
Cells
Lipids
Protein n polypeptide solution
DNA n RNA
Polysaccharides