Exposure I Chapter 21
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
traditional x-ray machine
Phosphor storage imaging plates (PSP or IP)
CR reader
What components are necessary for CR?
Phosphor layer
The active layer of the PSP
contains europium activated barium fluorohalide
Valency band
In the image acquisition in CR, where are the electrons normally located?
It gives energy to the electrons → moves to the conduction band → becomes trapped in color center
When x-ray photons interact with the phosphor layer what happens to the energy of electrons and where do they move?
Latent image
In CR technology, electrons are trapped in color centers
until they are stimulated by a laser to release their energy as light.
raster pattern
A patter that reads:
top to bottom
left to right
Photostimulated luminescence (PSL)
When electrons move from higher energy level conduction band to lower energy level valency band, what is the energy difference?
Pixel size
spatial resolution is controlled by:
Sampling frequency
Each time the laser shines light it gets signal from the IP and creates a pixel.
pixels/mm
How is sampling frequency measured?
Increased spatial frequency = smaller pixel size = greater spatial resolution = smaller pixel pitch
With an increased spatial frequency (pixel/mm), what happens to pixel size and spatial resolution?
pixel pitch
measures the size of the pixel
accounts for dead space that the laser light didn’t shine on (laser light doesn’t overlap).
smaller pixel pitch = greater spatial resolution
With a smaller pixel pitch, what happens to the spatial resolution?
50%
If exposure is greater than _____ below optimal = underexposed = quantum mottle
200%
If exposure is greater than _____ above optimal = overexposed = low contrast
smallest
_______ IP gives the best resolution = decreases pixel size
Photomultiplier tube (photodetector)
Detects PSL in CR
absorbs light and emits electrons
What components are necessary for CR?
Traditional X-Ray Machine
Phosphor Storage Imaging Plates (PSP / IP)
CR Reader
What are other terms for Phosphor Storage Imaging Plate(s)?
Imaging Plate
PSP
IP
What is the active layer of the imaging plate?
Phosphor Layer
2nd Layer
What substance does the phosphor layer contain?
Europium Activated Barium Fluorohalide
Where are electrons located?
Within the barium fluorohalide phosphor
In the Valency Band
How is the image acquired in CR?
When an x-ray photon interacts with the phosphor.
The electrons are given energy and they move from the valency band to the conduction band.
Where they become trapped in color centers.
What is the latent image in CR technology?
Electrons trapped in color centers
How many steps are there in the CR Image Reading Process?
7 Steps
What is the first 4 Steps of the CR Image Reading Process?
The cassette is placed in the CR Reader.
The CR Reader opens the cassette and removes the IP.
The laser scans the IP in a raster pattern.
The laser gives energy to the electrons trapped in color centers. With this energy, they escape the conduction band and fall back down to the valency band.
What is the last 3 Steps of the CR Image Reading Process?
As the electrons move from a higher energy level to lower energy level, the energy difference is emitted as PSL.
This light (PSL) is detected by a photodetector device:
Photomultiplier
Charged Coupled Device
Which absorbs light and emits electrons (electrical signal).
The signal is then amplified and then sent to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
What is the Raster Pattern?
Left to right, top to bottom (how be read).
What type of laser was used in early technology (1st CR Laser / old laser light)?
Helium Neon Laser
What eventually replaced helium neon lasers (considered as new laser light)?
Solid State Laser Diode
Match Description To Term:
This technology reads the image point by point (laser shines light, moves a little, shines light again and continues in a raster pattern)
Point Scan Reader
Match Description To Term:
This technology uses several laser sources and lens for shaping the beam to scan the IP line by line.
A linear array of CCD detectors are used to capture the light.
Much faster than a PS (Point Scan) CR Reader.
Line Scan Reader
Match Description To Term:
This technology reading uses two photo detectors (one on each side).
Move signal is obtained and a thicker phosphor layer can be used to absorb the x-ray photons better.
(Most recent advancement)
Dual Sided Reading
Match Description To Term:
This refers to the time it takes the latent image to disappear if the IP is not processed.
Fading (Image Fading)
PSL decreases by how much in a period of time? To avoid this from occurring what must be done?
PSL decreases by 25% in 8 hours.
Due to electrons that leak out of the color centers.
To avoid this, IPs must be read as soon as possible.
How is pixel pitch measured?
From the center of one pixel to the center of the next pixel.
This is to account for the empty space between pixels.
What is sampling frequency and how is it measured?
How many pixels does it create per mm.
(Measured in: Pixels/mm)
What determines pixel pitch / distance between pixels?
The movement and spacing of the laser as it scans the IP.
How are pixel pitch, scanning frequency, pixel size, and spatial resolution related?
The more the signal is sampled, the higher the sampling frequency.
The higher the sampling frequency, the smaller the pixel size, which in turn decreases pixel pitch.
As pixel pitch decreases, spatial resolution increases.
How is erasure accomplished with CR?
What are the 2 methods of accomplishing erasure?
What is the process?
Laser scans the image again.
IP is flooded with a bright fluorescent light.
In either case, light is giving energy to electrons that are still trapped in color centers that enable them to return to the valency band.
As this occurs, they are giving off PSL
BUT the light is NOT detected
What is Preprocessing Operations?
These are things the computer does on it’s own.
What are the 4 preprocessing operations?
Exposure Field Recognition
Rescaling (Histogram Analysis)
Grayscale Analysis (Look-Up-Table)
Exposure Indicator (EI)
How does the computer identity the area of interest on an imaging plate?
What is the process called?
What is the process?
Exposure Field Recognition
The computer looks to the center of the imaging plate and then outward to find collimated edges.
The shades of gray within these collimated edges are then used to create the histogram.
What type of a response does a digital detector have to exposure?
Linear Response
Each amount of exposure is recorded and assigned a distinct shade of gray.
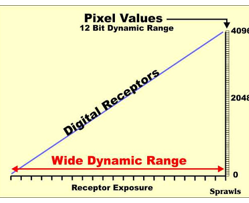
What is exposure latitude?
Range of exposures that produce a diagnostic image.
Digital imaging has exposure latitude / wide variety of kVp and mAs combinations that will produce a diagnostic image.
What is another term for exposure latitude?
Wide Variety
How does exposure latitude lead to dose creep?
The computer can correct better for overexposure than underexposure, technologists may routinely overexpose patients and rely on the computer for corrections.
mAs controls what?
Exposure
How does the computer correct for over/under exposure?
Rescaling
It displays the image with acceptable brightness
What controls/adjust image contrast?
Look-Up-Table
What controls subject contrast?
kVp
How is the image affected if there is over exposure?
Low Contrast Image
How is the image affected if there is under exposure?
Quantum Mottle
What has happened for saturation to occur?
The image was grossly over exposed (4-5 times optimal exposure)
How will the image appear when saturation occurs?
Pixels on the image will display maximum black
Resulting in loss of information (no difference between shades)
Can the lost information be recovered if saturation occurred?
No
Lost information can not be recovered through adjustments (window width / window level)
A repeat is needed.
What is ghosting?
Refers to the remanence of an image from previous exposure / fog that may appear on subsequent images.
How can we avoid ghosting if saturation occurred?
Imagine Plate must be sent through a second erasure to remove all electrons from color centers.
What causes for undercutting to occur?
Anatomy is not properly centered
Collimation may lead to a great deal of unattenuated photons striking the IR (x-ray photons that strike the IR without striking the patient first).
What results in the image from undercutting?
The visibility of the edges of the anatomy are degraded and can not be corrected through (window level / window width)
If undercutting occurs would it be necessary for a repeat?
Yes
It is necessary to properly center the anatomy to the IR and eliminate the unattenuated photons.
What causes a histogram analysis error?
This can occur if:
Part (anatomy) is not properly centered to the detector
Improper collimation
Very tight collimation
Extremely dense material (metal / contrast)
What results from a histogram analysis error?
Unimportant shades of gray being included in the histogram.
What do the shades of black in a histogram analysis error represent?
Unattenuated Photons
What do the shades of light gray in a histogram analysis error represent?
Scatter outside the collimated edges
What do the shades of white in a histogram analysis error represent?
Metal / Contrast (Dense material)
Match Description To Term:
An error has occurred where the computer incorrectly interprets the histogram as being over / under exposed.
Image will display improper brightness, contrast, and exposure indicator.
Histogram Analysis Error
What are the 4 types of Fuji Exposure Mode?
Automatic
Semi-Automatic
Semi-X
Fixed
Match Description To Term: Exposure Mode
What the computer automatically does.
Normal exposure field recognition
Rescaling and Look-Up-Table used
Automatic
Match Description To Term: Exposure Mode
Used for tightly collimated anatomy
Odontoid (Open Mouth)
L5-S1
The computer looks to the center of the IR and then uses a preprogrammed field size based on anatomy imaged.
This eliminates scatter outside the collimated edges from being included in the histogram.
Semi-Automatic
Match Description To Term: Exposure Mode
Used when the part can’t be centered to the IR.
The technologist chooses a quadrant containing the area of interest.
Semi-X
Match Description To Term: Exposure Mode
No computer adjustments are made.
Brightness and contrast controlled by mas and kVp
REX mode in our DR system.
Fixed
How does the size of the imaging plate affect pixel size and resolution?
The smaller the pixel size, the greater the resolution.
Smallest imaging plate should be chosen for the anatomy.
What is the formula to calculate pixel size?
Pixel Size = FOV/Matrix Size