Cellular Respiration and Energy Production in Biology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is the primary role of ATP in cells?
ATP drives most cellular work.
How is chemical energy from food converted into ATP?
Chemical energy stored in food is used in cellular respiration to generate ATP.
What is the process called that converts food energy into ATP?
Cellular respiration.
What molecule is generated as a result of converting food energy?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What is the primary function of mitochondria in cells?
Mitochondria break down organic molecules by cellular respiration to produce ATP.
What is the main chemical energy currency produced during cellular respiration?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
What are the waste products of cellular respiration?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
What is the role of catabolic pathways in cellular respiration?
Catabolic pathways release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules.
What is fermentation?
Fermentation is the partial degradation of sugars that occurs without oxygen.
What distinguishes aerobic respiration from anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and oxygen, while anaerobic respiration uses compounds other than oxygen.
What is the overall equation for cellular respiration using glucose?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
What is the significance of redox reactions in cellular respiration?
Redox reactions transfer electrons, releasing energy stored in organic molecules, which is used to synthesize ATP.
What is oxidation in the context of redox reactions?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons from a substance.
What is reduction in the context of redox reactions?
Reduction is the addition of electrons to a substance.
What is the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
NAD+ acts as an electron carrier and oxidizing agent during cellular respiration.
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a series of molecules in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons and release energy.
What are the three main stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
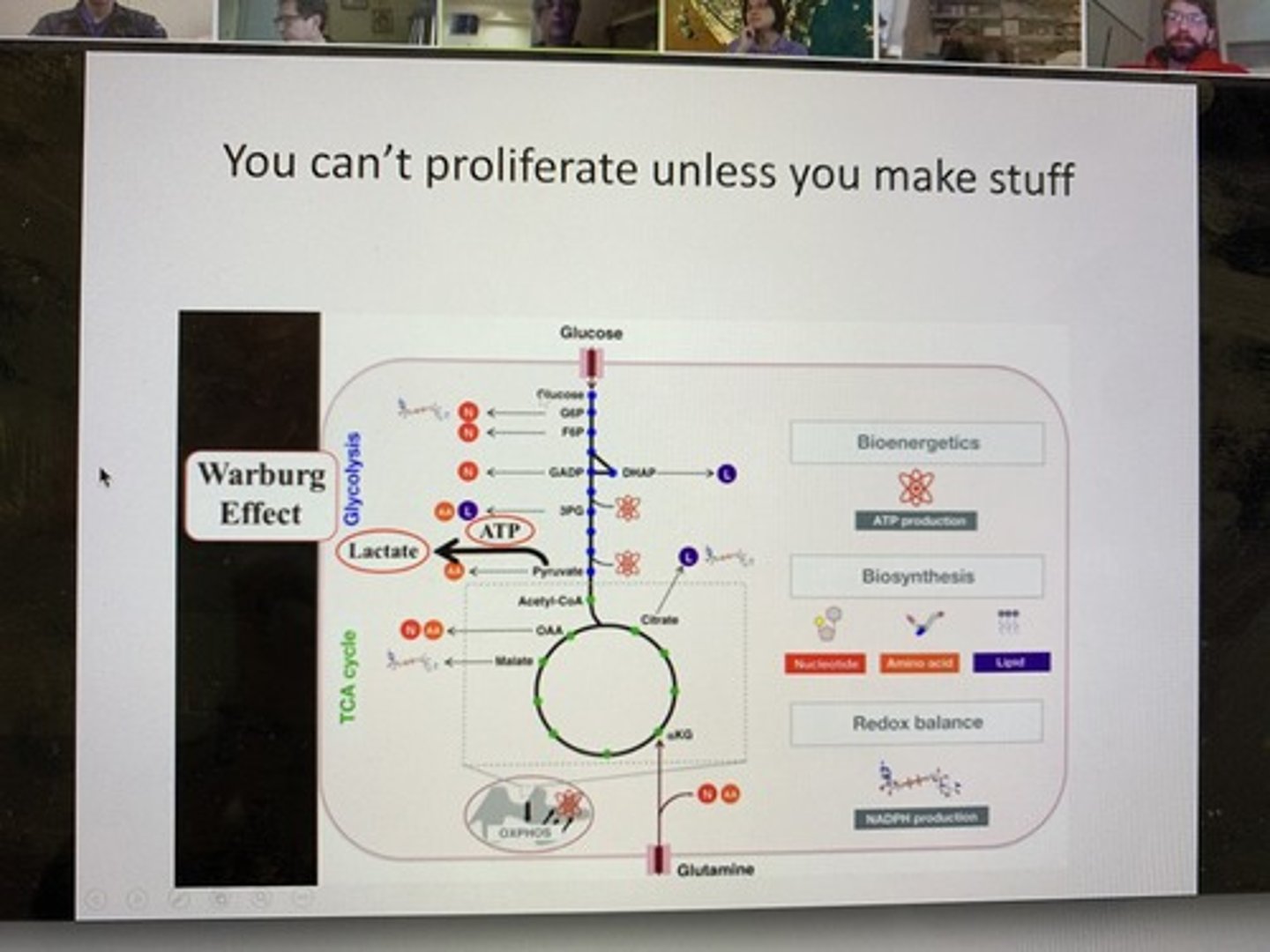
What occurs during glycolysis?
Glycolysis breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a net gain of 2 ATP.
What is the citric acid cycle also known as?
The citric acid cycle is also called the Krebs cycle.
What happens to pyruvate before entering the citric acid cycle?
Pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA, releasing CO2 and reducing NAD+ to NADH.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process that generates most of the ATP during cellular respiration, powered by redox reactions.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs when an enzyme transfers a phosphate group directly from a substrate to ADP to form ATP.
How much ATP can be produced from one molecule of glucose during cellular respiration?
Up to 32 molecules of ATP can be produced from one molecule of glucose.
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm.
What is the energy investment phase of glycolysis?
The energy investment phase uses 2 ATP to split glucose into two three-carbon sugar molecules.
What is the energy payoff phase of glycolysis?
The energy payoff phase produces 4 ATP and reduces 2 NAD+ to NADH, forming 2 pyruvate.
What is the significance of the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration?
The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain?
Oxygen (O2) is the final electron acceptor, forming water (H2O).
What happens to the electrons as they move through the electron transport chain?
Electrons drop in free energy and are ultimately passed to oxygen.
What is the role of chemiosmosis in ATP synthesis?
Chemiosmosis couples the flow of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix to ATP synthesis.
What role do NADH and FADH2 play in cellular respiration?
They transfer electrons to the electron transport chain.
What is the function of the electron transport chain?
It passes electrons through proteins to O2, generating no ATP directly but releasing energy in manageable amounts.
What process uses the energy from the electron transport chain to pump H+ ions?
Chemiosmosis.
How does ATP synthase produce ATP?
H+ ions move through ATP synthase, causing it to spin and catalyze the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
What is the proton-motive force?
The H+ gradient that drives cellular work, including ATP synthesis.
What is the overall energy flow during cellular respiration?
Glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → proton-motive force → ATP.
What percentage of energy from glucose is converted to ATP during cellular respiration?
About 34%.
Why is the exact number of ATP produced during cellular respiration not known?
Because the coupling of redox reactions and photophosphorylation is not direct, and ATP yield varies based on electron carriers.
What happens to cellular respiration in the absence of oxygen?
Glycolysis couples with anaerobic respiration or fermentation to produce ATP.
What are the two common types of fermentation?
Alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
What is produced during lactic acid fermentation?
Lactate and NAD+.
How does fermentation differ from aerobic respiration?
Fermentation uses an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor, while aerobic respiration uses the electron transport chain.
What are obligate anaerobes?
Organisms that carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2.
What are facultative anaerobes?
Organisms that can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration.
What is glycolysis?
A metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to produce ATP and is used in both cellular respiration and fermentation.
What types of molecules can be catabolized in cellular respiration?
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What is beta oxidation?
The process by which fatty acids are broken down to yield acetyl CoA, NADH, and FADH2.
How do small molecules from food contribute to macromolecule synthesis?
They are used to build macromolecules like proteins from amino acids.
What is feedback inhibition in cellular respiration?
A mechanism that prevents wasteful production by regulating enzyme activity based on ATP concentration.