Living Environment Regents
1/266
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
267 Terms
Homeostasis
maintaining a stable internal environment of an organism
cell
Smallest unit of structure in living things that show the characteristics of life. most basic unit of life
Nutrition
The life process where an organism takes in food.
transport
The life process that moves substances through an organism
Reproduction
The life process where organisms generate others of the same kind
Synthesis
Life process where similar substances are joined to make larger ones
Regulation
the life process that helps control homeostasis in an organism
Growth
Life process of an organism increasing in size or cell number
Excretion
removal of cellular waste in an organism
metabloism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Organelle
tiny structures that carry out life functions, similar to what organs do for the body
organ system
A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions in a multicellular organism.
dynamic equilibrium
a state of balance between continuing life processes
Species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
2n
full set of chromosomes (diploid)
n
half set of chromosomes (haploid)
cancer
uncontrolled cell division
Carcinogen
A cancer-causing substance
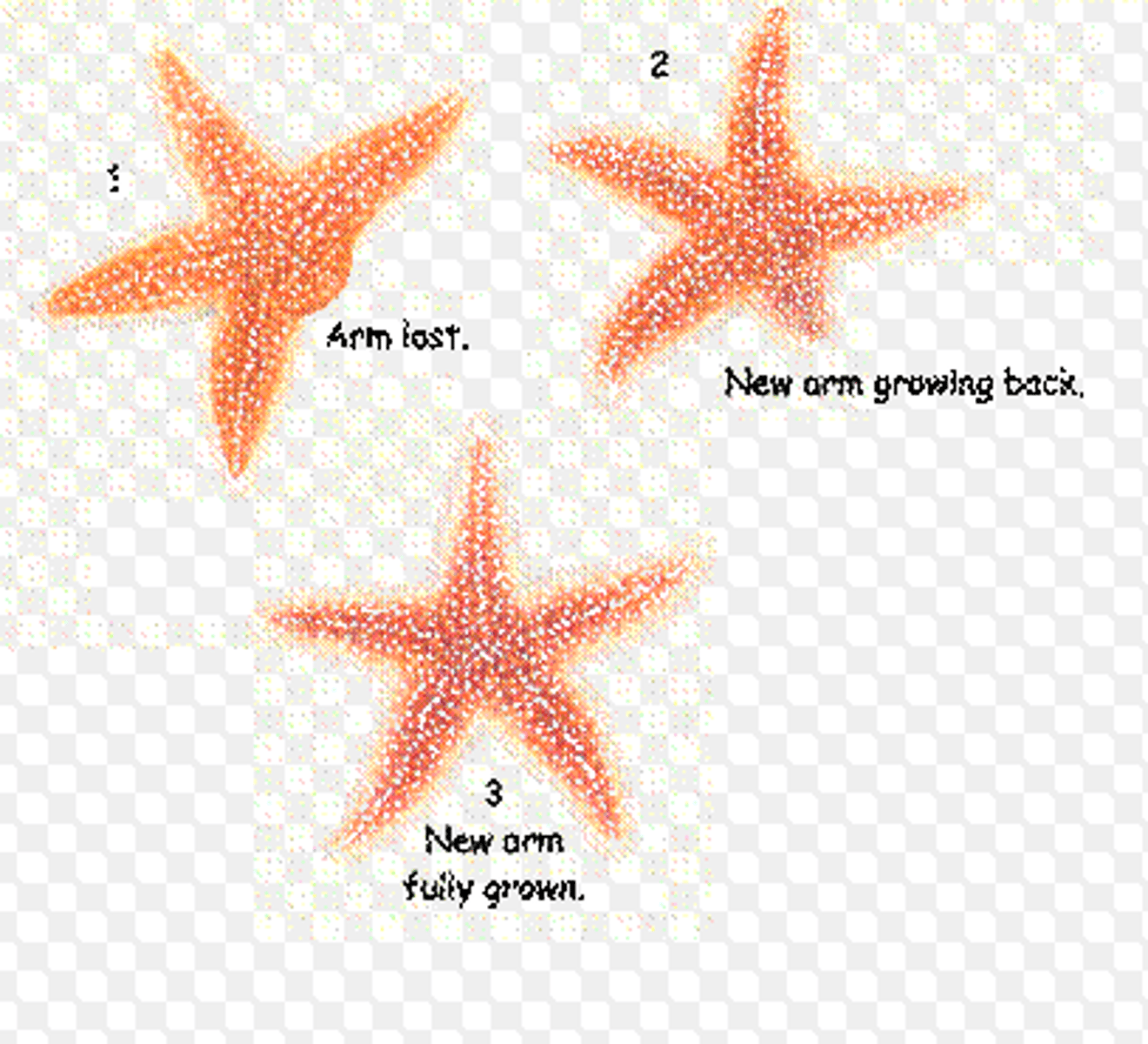
Regeneration
Refers to the replacement or regrowth of lost or damaged tissue/body parts.
Nucleotide
made up of a phosphate, sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Chromosome
contains hereditary information and is made up of DNA
acid
Any substance that releases hydrogen (H+) ions in a solution, causing a pH of less than 7.
active site
The part of an enzyme where the substrate attaches.
amino acids
building blocks of proteins and enzymes.
Base
Any substance that produces hydrogen (H-) ions in a solution causing the pH to be more than 7.
Carbohydrates
made of sugars, they have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio.
biological catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up.
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid - the hereditary material found in the cells of an organism.
enzyme
A biological protein catalyst necessary for most reactions in a cell.
Fats/Lipids
Compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen including fats, oils, and waxes.
Glucose
The most common sugar used by living organisms. It is needed for cellular respiration to occur.
inorganic compounds
compounds that do not contain both carbon and hydrogen
organic compounds
Compounds containing both carbon and hydrogen.
pH scale
Scale measuring how acidic or basic a substance is.
products
new substances made through chemical reactions.
starch
A large carbohydrate compound of simple sugars involved in storing energy in an organism.
Substrate
the substance on which an enzyme acts
stomach
large muscular sac that stores food and continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
Pepsin
Enzyme that breaks down proteins in the stomach
large intestine
Absorbs water from from partially digested food.
anus
The exit point for waste after exiting the small intestine.
ATP
useable energy form for organisms.
digestive system
Converts food into glucose that can be used by cells of the body to make ATP, repair damaged tissue, build muscle, etc.
digestion
the process of breaking down food by mechanical and enzymatic action in the alimentary canal into substances that can be used by the body.
diffusion
the movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration. also referred to as passive transport. does not require ATP
mouth
where digestion begins
Monomer/Subunit
the building block of a molecule
Elements of life
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Building blocks of fats
1 glycerol and 2 fatty acids; CHO
Building blocks of carbohydrates
simple sugars; CHO
Monosccharides
simple sugars
Polysaccharides
complex molecules made up of many sugars
Building blocks of protein
Amino Acids; CHON
Building blocks of nucleic acid
nucleotides; CHOPN
Biomolecules
Molecules that are necessary for our body to carry out our daily life functions; carbohydrates, fats/lipids, proteins, nucleic acid.
-ASE
ending of most enzymes
Denaturation
When enzymes/proteins change shape due to environmental factors such as temperature or pH. Shape determines an enzyme's function.
nucleic acids
- Provides the genetic instructions that code for all proteins found in all living things -this includes our physical traits -Found in all forms of life
DNA pairings
{Adenine (A) and Thymine (T)} + {Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C)}
RNA Pairings
{Adenine (A) and Uracil (U)} + {Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C)}. THERE IS NO T!!!!
cell membrane
semi permeable. it only allows certain substances into and out of the cell based on their size
cell wall
outermost layer of plant cells and gives them their rigid structure. PLANT CELLS ONLY
chloroplast
the site of photosynthesis. is only found in plants
Cytoplasm
jello like watery material inside the cell where all the chemical reactions take place
cell theory
1. All living things have cells
2. All cells come from pre-existing cells
3. The cell is the most basic unit of life
Vacuole
the "storage closet" of the cell because it stores food, water, and waste
Mitochondria
known as the powerhouse of the cell. creates energy, or ATP for the organism
Ribosome
site of protein synthesis
Lyosomes
breakdown of materials inside the cell contains enzymes. Help with digestion. ONLY IN ANIMAL CELLS
Chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
Unicellular Organisms
Living things made up of only one cell
Multi-cellular organisms
Organism made up of more than 1 cell
Exceptions to the cell theory
1. Where did the first cell come from?
2.Viruses
3. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts divide on their own
active transport
Molecules moving from an area of low concentration to high concentration. REQUIRES Energy/ATP.
cell receptors
Molecules on the outside of the cell membrane that accept chemical messengers and cause a change inside the cell.
Reactants of respiration
glucose, oxygen, and water
products of respiration
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
cellular respiration
The life process that produces ATP (energy) for an organism.
Aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen, makes 36 ATP molecules
anaerobic respiration (fermentation)
does not require oxygen, produces 2 ATP molecules, produces lactic acid
lactic acid
product of fermentation (in most organisms), causes muscles to burn.
alcoholic fermentation
the anaerobic process by which yeasts and other microorganisms break down sugars to ATP, CO2, and alcohol.
Biosphere
the portion of the earth (including the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere) where like exists
Biome
a large group of ecosystems that share the same climate and have similar types of communities.
Ecosystem
one or more communities (biotic factors) interacting with each other and their nonliving environment (abiotic factors)
community
Two or more populations interacting which each other
Population
a group of organism which belong to the same species.
Organism
fully functional form of a living being that can survive in a particular environment.
Autotrophs/Producers
organisms that capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and convert it into forms living cells can use.
Primary Producers
the first producers of energy-rich compounds that are later used by other organisms
Heterotrophs/Consumers
cannot make their own food; acquire energy by ingesting other organisms.
Carnivore
kill and eat other animals
Scavengers
consume the carcasses of other animals
Decomposers
chemically break down organic matter. Ex: bacteria, fungi, etc....; are not shown in the energy pyramid. Recycle energy from every level.
Herbivores
Consumers that eat only plants
Omnivores
Consumers that eat both plants and animals.
Food Chain
shows how living organisms get their food. Starts with a producer and ends with the largest consumer.
Food web
shows the flow of energy between organisms and the community as a whole. More stable.
Trophic level
each step in a food chain or food web
energy pyramid
show relative amount of energy available at each trophic level 90% of energy is lost to heat and 10% is transferred to the next organism.