N251 exam 4: lecture 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
virus
Genetic material + protein coat
Either DNA or RNA, never BOTH
They can be in Plants, animals and bacteria
host range
range of animal spp and tissue cells that virus can infect (can be broad or limited). Plant, animal or Bacteria
capsomeres
morphological subunits from which the virus capsid is built
-building blocks of capsid
legos of virus
capsid
protein coat surrounding a virus
-protects genetic material
envelope
lipid-containing membrane that surrounds some viruses
-picked up form host cell when they are Leaving
Nucelocapsid
capsid + nucleic acid
virus
RNA or DNA + Protein
tail
helps get a virus into a cell
virion
Virus that has infected a cell and is ready to go infect other cells
incomplete virion
virion without nucleic acid (empty capsid)
car going through assembly line and forgetting to put engine in
Pseudovirions
When the virus engulfs the host’s nucleic acid, rather than the viral DNA.
It does not replicate
provirus
Viral DNA that inserts into a host genome.
-wont form virus but keep getting replicated with the host dna because it is a part of th chromosome.
General Characteristics
Virions are very small (200-300) compared to E.coli with 1000nm.
They contain very few genes 4-200 vs 3000 for Ecoli genes.
either DNA or RNA
DNA or RNA is either single or double stranded, but most DNA have theur genetic material is a single linear molecule; however, the RNA could have either linear or segmented genomes with different RNA in their capsid.
They have no cellular component, so they have to hijack other cells for energy.
The only enzymes they have will help them to replicate and enter other cells.
genectic informaion is used for
Info to move in and out of the cell
Replicate
Make their capsid
Why is segmented RNA a problem
It is harder to create vaccines for them
a lot of research is with
bacteriophage
-easy to study
Viral Architecture
shape of virus is determined by shape of capsid (Helical or spherical)
-each capsid is composed of many identical units (capsomeres)
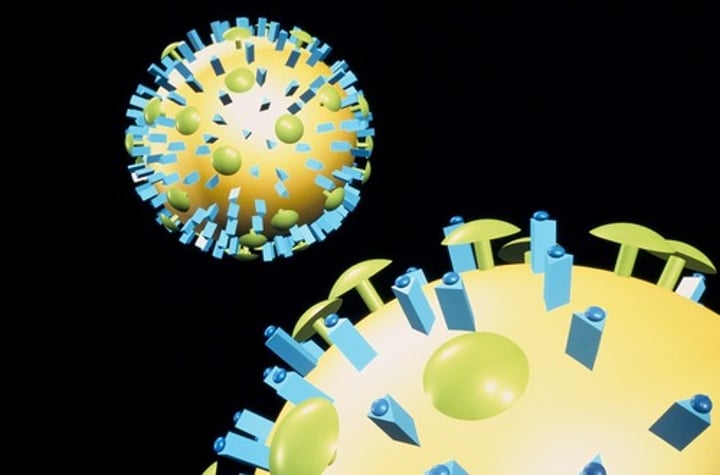
Some viruses have an additional lipid membrane (envelope)
-usually acquired from cytoplasmic membrane of infected cell- structure is similar, double layer of lipids
-just inside the lipid envelope is protein matrix(capsid)
-spikes project from the envelope and attach the virion to host cell- protein, glycoprotein
poxiviridae
Large, enveloped, DNA, small pox
Parvoviridae
Naked, DNA, gastroenteritis outbreak after eating shellfish
Papovaviridae
Naked, circular DNA, Human Papillomavirus.
helical
cigar shaped
-more column like
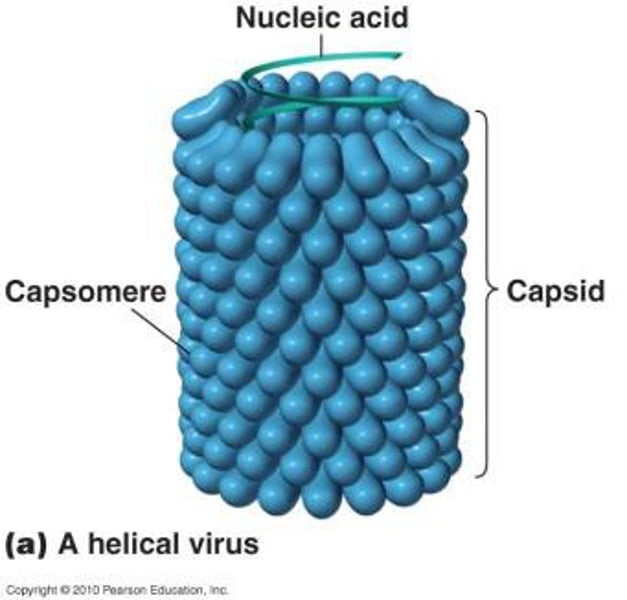
spherical/isometric
Triangle shaped
tobacco moasic virus
-very dangerous virus to tomato plants especially peppers
-in all tobacco
-tobacco plant is like mild common cold
-but its relatives like tomatoes and peppers do not have resistance will weaken tomato plants and kill pepper plants
very large virus and very frequently studied
viruses can be
naked:
-nucleocapsid
enveloped:
-capsid
-enclosed in envelop containing lipids and spikes to protect virus
-PICKED UP FROM HOST AS VIRUS EXITS HOST CELL AFTER REPLICATION
hantavirus
associated with rodents
-left behind in urine and feces
-can lay for a while and be dangerous to humans
zika virus
single stranded RNA virus
-single stranded
-transmitted by mosquitos
-shown link to producing microcephaly in babies: if mother is bitten while pregnant and infected
if bitten and infected at an earlier age, immune system will be able to fight infection
-see increases when zika moves into a new area, people do not have immunity against= hypothesis by professor
rna virus
-rna inside
-capsid surrounding it
-membraneous envelope
-glycoproteins on the envelop
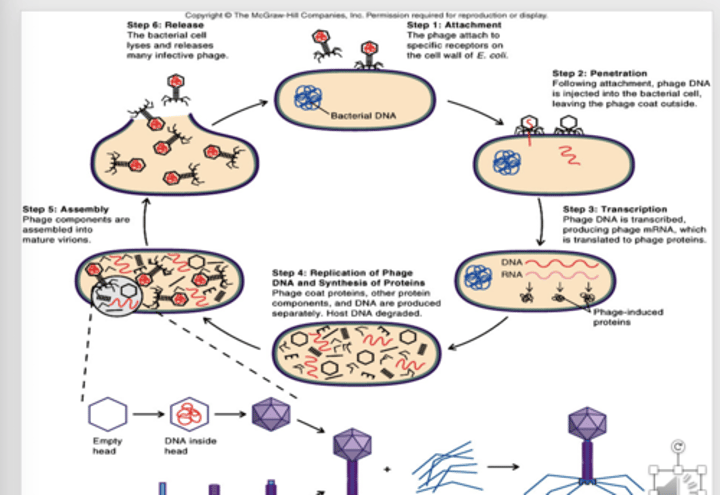
Viral Replication: DNA
1. Attachment: phages attach to host cell receptors
2. Penetration:
-viral nucleic acid enters the host cell
-lysozyme located on tip of the tail, lyses the cell wall
-tip of tail opens and linear DNA in the head passes through the channel and is injected through the cell wall into the interior of the cell
-only the nucleic acid not the entire viron enters
3. Transcription/Translation:
-phage DNA is transcribed leading to production of specific proteins
-part of DNA is transcribed into mRNA
-mRNA is translated into proteins that are specific for infecting cell (phage induced proteins)
-one such protein is a nuclease that degrades DNA of host cell
-host DNA is not transcribed, only phage DNA
4. Replication
-phage DNA copies itself and structural proteins are synthesized
5. Assembly
-phage DNA and protein assemble to form mature virions
-some steps involve a self assembly process
6. Release
-virions are released from the host cell
-lysozyme is coded by phage DNA: lysozyme is digest host cell wall from within, cell lysis and release of phage virions (up to 200)
what can happen when a virus infects a host cell
three options
1. Genetic alteration of host cell and LATENT state of virus
-provirus
-nucleic acid become part of the host cell
-will get replicated, cell itself is not destroyed
-has viral DNA and own DNA
-every-time it divides will produce more copies
-may become active at some point or could stay latent for a while
2. productive infection: more viral particles are produced
-sometimes dont kill: make small hole, viral particles will leak out
3. -can kill host and do true lysis of host cell
laboratory diagnosis
-cell culture: living cells (chick embryos)
-serological techniques: detecting antigen and antibodies
-direct detection of antigen from specimen: polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
-molecular methods: live or dead viruses
viral specimens
-upper respitaroy: n/p swabs, nasal, throat
-lower respiratory: endo trach asp, bronch was, bronchial biopsies
-eye swabs
-stools/rectal swabs
-body fluids: csf, bone marrow, serum, blood, saliva
Specimens: collection and storage
-try and collect between first few days of illness
-want a lot of viral particles
-specimens should not be held at ambient temp: deliver to lab on ice
-do not store for more than 1-3 days
-test rapidly
-freezing at -70c or below will preserve indefintely
temperature recyclying
loss of infectivity from refrig-freezer back and forth