9. Physical and Cognitive Development in Middle Childhood
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Boys → physically active games
Girls → games w verbal expression or counting aloud
Contrast boys’ and girls’ recess-time activities
Peaks sa middle childhood
Hones skeletal and muscle development
Offers safe practice for hunting and fighting skills
Channels aggression and competition
By age 11, it often becomes a way to establish dominance within the peer group
Explain the signifcance of rough-and-tumble play
principle of identity
principle of reversibility
decentering
3 principles that help children understand conservation
neurological development
experience in adapting to the environment
According to Piaget, the switch to logical thinking in older children is dependent on:
F; baliktad
(T/F)
Immature moral judgments → intent
Mature moral judgments → degree of offense
Rigid obedience to authority (2-7 yrs)
Increasing flexibility (7/8-10/11)
Equity (11-12)
formal reasoning
Piaget’s 3 stages of moral development
executive function
Conscious control of thoughts, emotions, and actions to accomplish goals or solve problems
selective attention
hinges on inhibitory control (the voluntary suppression of unwanted responses)
due to neurological maturation
working memory
metamemory
the understanding of processes of memory
mnemonics
external memory aids
Mnemonic strategies using something outside the person
rehearsal
organization
elaboration
making mental associations
Identify four ways in which information processing improves during middle childhood
SA
WM
MM
M
WISC-IV
ages 6-16
Otis-Lennon School Ability Test (OLSAT8)
Group intelligence test for kindergarten through 12th grade
Name and describe two traditional intelligence tests for schoolchildren
Sternberg
triarchic theory of intelligence
Gardner
theory of multiple intelligences
assessed through observation of products
Compare Sternberg’s and Gardner’s theories of intelligence
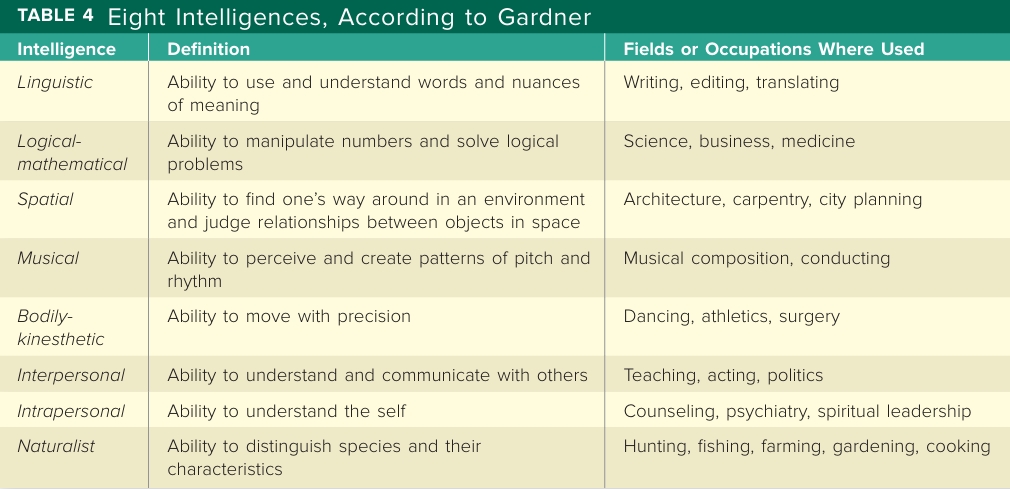
Gardner’s 8 intelligences
(BIILLMNS)
componential element (analytical)
analytic aspect of intelligence
experiential element (experiential)
insightful or creative aspect of intelligence
contextual element (contextual)
practical aspect of intelligence
Elements of Sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence
tacit knowledge
Sternberg’s term for information that is not formally taught or openly expressed but is necessary to get ahead.
Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children (K-ABC-II)
Nontraditional individual intelligence test designed to provide fair assessments of minority children and children with disabilities.
syntax
the deep underlying structure of language that organizes words into understandable phrases and sentences
pragmatics
The major area of linguistic growth during the school years
decoding
Process of phonetic analysis by which a printed word is converted to spoken form before retrieval from long-term memory
phonetic (code-emphasis approach)
emphasizes decoding of unfamiliar words
whole-language approach
emphasizes visual retrieval and use of contextual clues
Children can learn to identify a printed word in two contrasting ways:
visually based retrieval
Process of retrieving the sound of a printed word when seeing the word as a whole.
enrichment programs
Programs for educating the gifted that broaden and deepen knowledge and skills through extra activities, projects, field trips, or mentoring
acceleration programs
Programs for educating the gifted that move them through the curriculum at an unusually rapid pace.
130 or higher
IQ ng gifted
learning disability
most common form of special educ