random last min chem info u should remember
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
WHY DO WE NEED CRACKING
- Cracking converts long chain hydrocarbons into short chain hydrocarbons.
- Long-chain alkanes are broken down into alkanes and alkenes of shorter length.
- Crude oil contains a surplus long chains.
- Shorter chain hydrocarbons are in greater demand, e.g. petrol.
- Cracking also produces alkenes which are used in making polymers and ethanol.
CONDITIONS FOR CRACKING
silica catalyst adn 600-700 degrees
long chain alkAnes -->
shorter alkenes + alkanes
do alkanes have positional isomers??
NO! Only alkEnEs
alkane substitution
halogen and UV light required
test for alkenes
bromine water orange to colourless
dibromoalkanes
bromine water + alkene --> dibromoalkAne (NO UV LIGHT)
substitution example
Halogen + alkane
addition example
dibromoalkanes
substitution vs addition
alkene + bromine ---> (NO UV LIGHT) dibromoalkane (double bond broken)
alkane + halogen --> (ADD UV LIGHT) halgenoalekane thingie
aluminium uses and properties
aircrafts, cans, power cables, pots and pans
low density, resists corrosion, ductile, conducts electriity
copper uses and properties
electrical wires, potspans, water pipes
unreactive, ductile, good conductor of electricity, amllaeable
iron uses and properties
Buildings - Strong
Saucepans - Conducts heat / high melting point / malleable
types of steel and uses
mild steel - nails, car bodys, ship buildings
High-carbon steel--0.6%-1.2% carbon ---cutting tools, masonry nails
Stainless steel--Chromium (and nickel)---cutlery, cooking utensils, kitchen sinks
properties of all steels
Mild steel is a strong material that can easily be hammered into various shapes (malleable). It rusts easily.
High-carbon steel is harder than mild steel but more brittle (not as malleable).
Stainless steel forms a strong, protective oxide layer so is very resistant to corrosion.
phenolpthalein
acid: colourless
alkali : pink
ui
acid: red
alkli: dark blue
methyl orange
acid: dark red
alkali: light orange/yellow
low ph
acidic
high ph
alkali
acids in aq solutions
source of hydrogen ions
alkalis in aq solutions
hydroxides source
acid is a proton
donor
base is a proton
acceptor
bases in reactions
metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia
alkalis are bases that are ___ in water
soluble
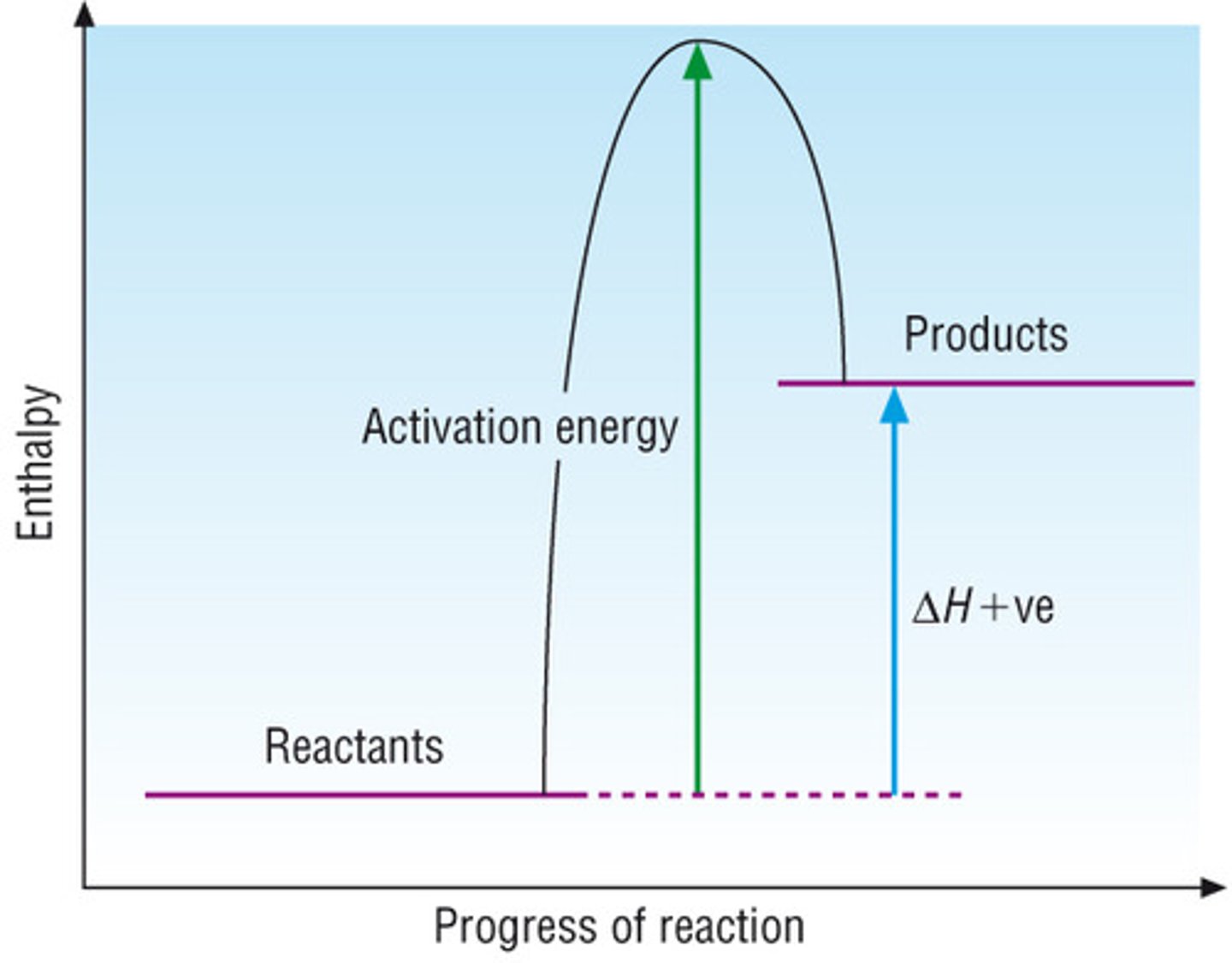
bond breaking is
endothermic
bond making is
exothermic
exothermic reaction profile
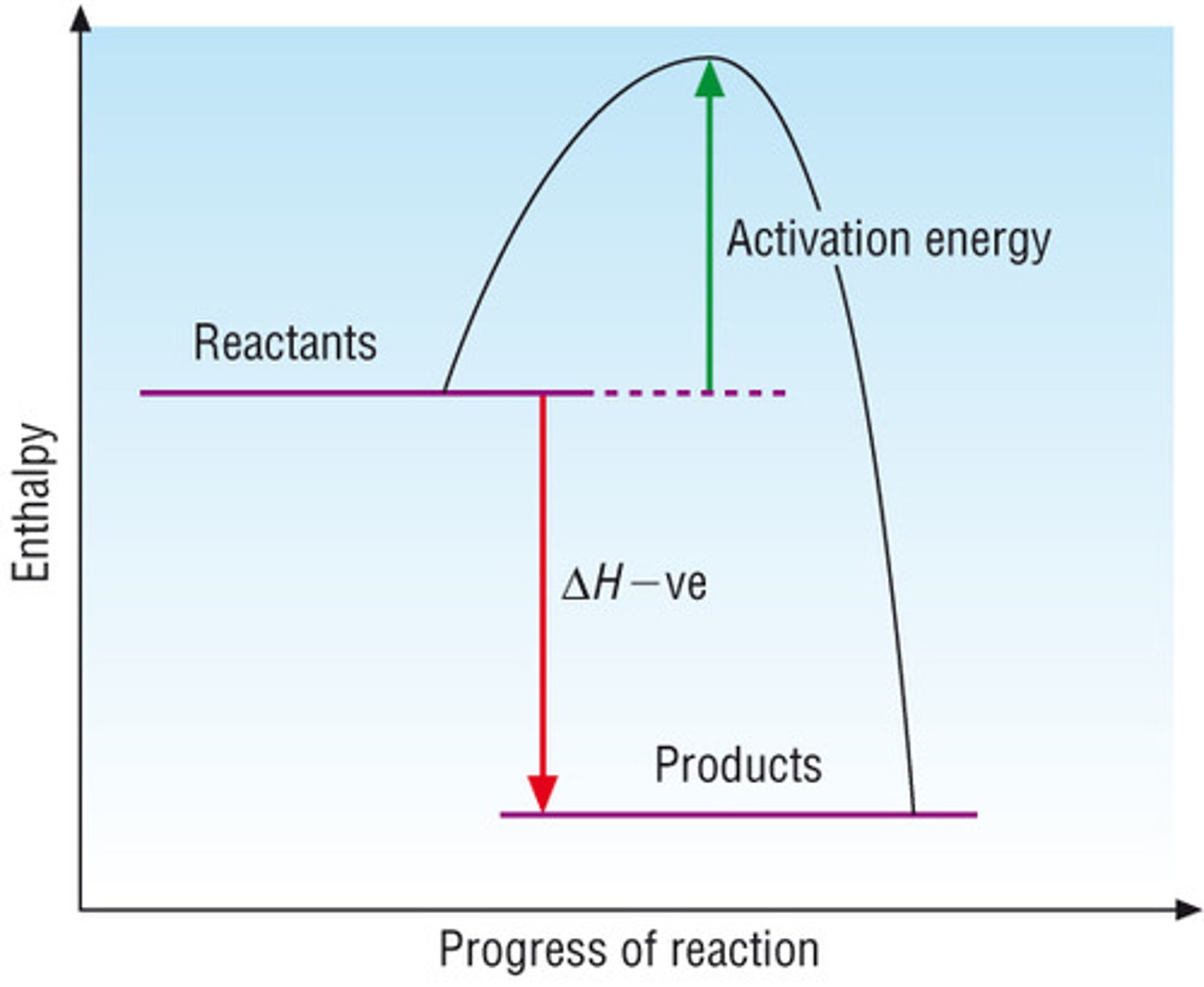
endothermic reaction profile
enthalpy change from bond energy
ΔΗ°=ΣΒΕ(reactants)-ΣΒΕ(products)
neutral ph
7
acidic ph
less than 7
alkaline ph
more than 7
how does decreasing concentration affect the rate of a reaction (3)
1. fewer particles in same volume
2. fewer frequent successful collisions PER UNIT TIME
3. so decreased rate of reaction
why are alkanes saturated compounds (2)
1. All single bonds/no double bonds
2. No other atoms can be added/no addition reactions
magnesium -> magnesium oxide colour
white powder
what color are most ionic compounds
white solids
alcohol + oxygen -->
carbon dioxide + water (ALWAYS. just balance them out)
metal + acid -->
salt + hydrogen
what pH will an alcohol's solution have?
neutral, as they aren't acidic or alkaline.
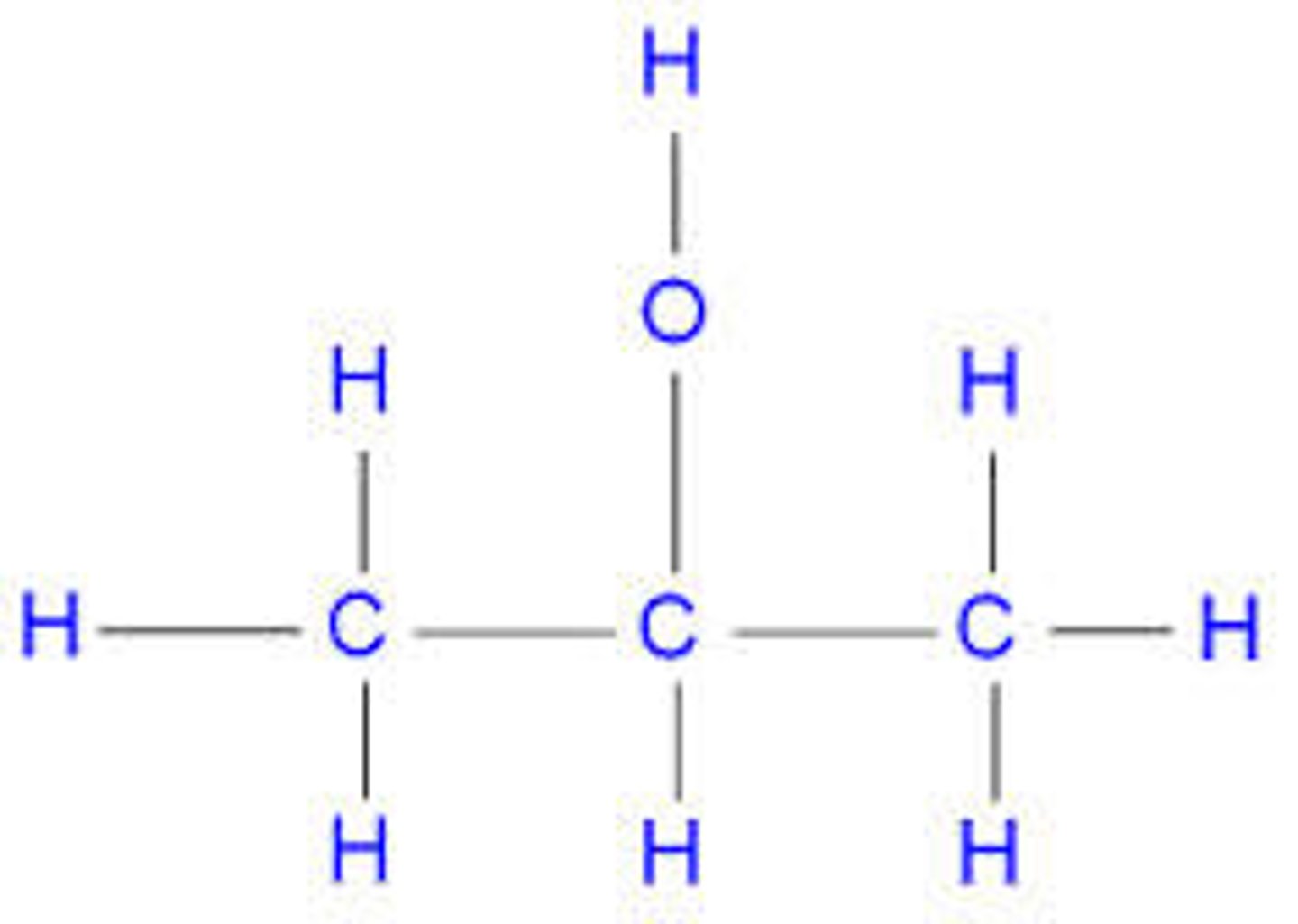
3 properties of alcohols:
1. flammable - can be used as fuels
2. soluble in water - dissolve things like lipids, hydrocarbons
3. become oxidised - then form carboxylic acid.
acid + base --->
(neutralisation) salt + water
Any reaction that has hydrogen and oxygen in it ends up producing ________ EXCEPT for the metal + _______ reaction
water, base (which produces hydrogen)
acid + metal carbonate
→ salt + CO₂ + water
what does it mean to say that ethanoic acid is WEAKLY IONISING?
- it means that it does not ionise a lot, just a little:
-----> to ionise means that it splits up into ions.
- When ethanoic acid is added to water, it splits up into ethanoate and hydrogen
------> why is the hydrogen lost and made into an ion? This is because acids are H+ DONORS, whereas alkalis are OH- DONORS.
Why don't you need to measure the mass of the {reactant/solute} in {this experiment}
Because it is in excess
Why are carboxylic acids weak? (3)
- They are weakly ionising/only partially ionise when dissolved in water.
- This means that only a few H+ ions are released into the water, and as pH is a measure of H+ ion concentration...
- It means they have a high pH = low acidity.
Safety with the solubility practical
- Heat the evaporating basin gently to avoid spitting
what is pH a measure of
the concentration of H+ ions in a solution
Carboxylic acid + metal →
salt + hydrogen
CH₃COOH + H₂O ⇌
CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
Carboxylic acid + metal hydrogen carbonate →
salt + CO₂ + water
carboxylic acid + alcohol -->
ester + water
Conditions for chromatography
- Don't use a pen because the ink could be soluble and move up the chromatography paper.
- The paper should be put in just below the pencil line - this is so the inks and mixtures don't dissolve in the solvent.
- To avoid evaporation of the solutes from the surface of the paper you can put a watch glass on top of the beaker.
What is the RF value?
distance moved by substance/distance moved by solvent
- ALWAYS below 1
- tells you how soluble the solute is
- allows you to compare the solubility to a standard set of comparisons to find out what the component of the ink/mixture is
ethanoic acid + ethanol ⇌
(sulfuric acid catalyst) ethyl ethanoate + water
what catalyst is needed in creating an ester?
sulfuric acid.
draw diagram of propan-1-ol
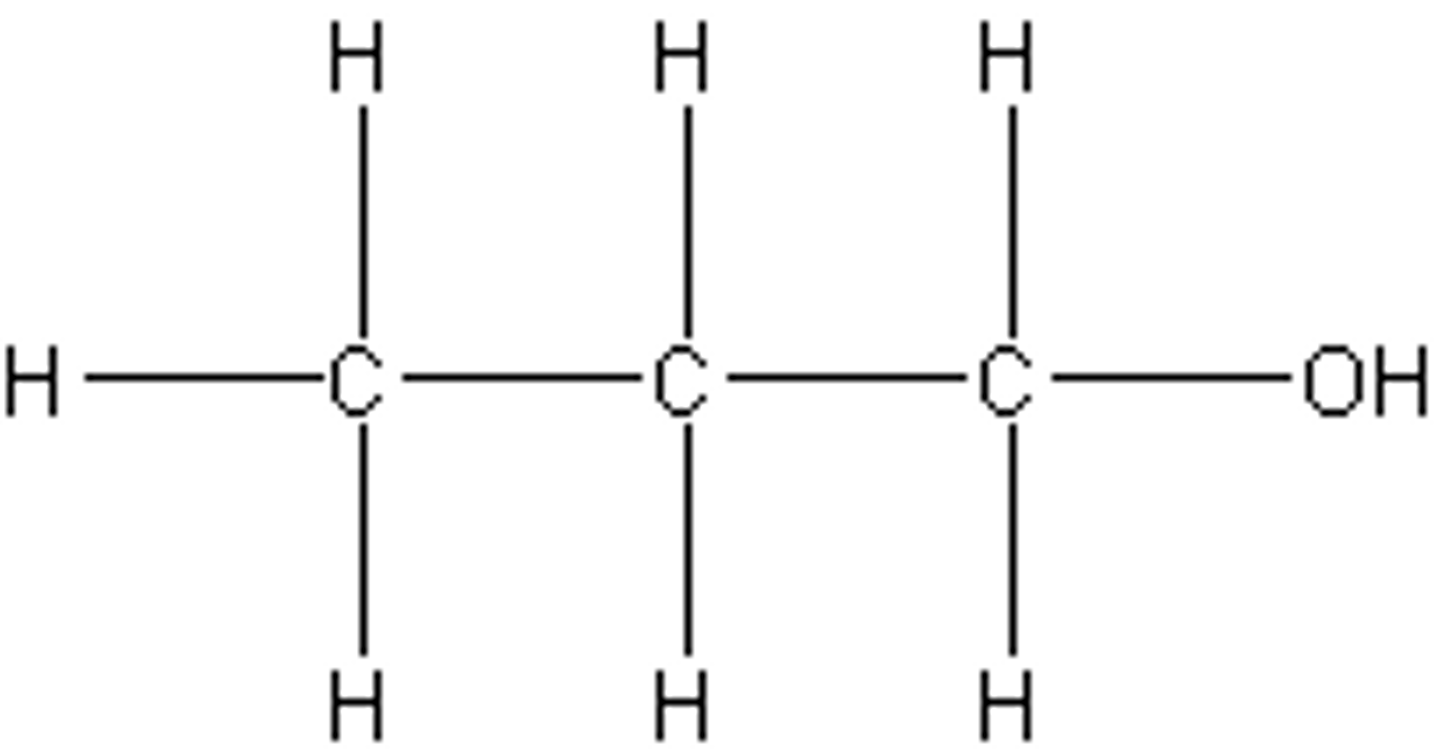
draw diagram of propan-2-ol