Cell Cycle, Signaling, Photosynthesis & Respiration – Master Vocabulary
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the lecture on cell division, cell signaling, photosynthesis, and cellular respiration. Use them to reinforce definitions and conceptual understanding before your exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Genome
The complete genetic information of a cell or organism.
Chromosome
DNA wrapped around proteins; the visible ‘package’ for genetic material during mitosis.
Somatic Cell
Any body cell other than a reproductive (gamete) cell.
Gamete
A reproductive cell (sperm or egg) containing half the organism’s chromosomes.
Chromatin
DNA-protein complex that forms chromosomes; diffuse in interphase.
Nucleosome
DNA wound around an octet of histones; basic unit of chromatin packing.
Prokaryotic DNA
Single, circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and archaea.
Histone
Positively charged protein that helps package eukaryotic DNA.
Scaffolding Protein
Non-histone protein maintaining overall chromosome structure.
Centrosome
Microtubule-organizing center and origin of the mitotic spindle.
Centriole
Triplet-microtubule cylinder inside animal centrosomes (absent in plants).
Aster
Radial array of short microtubules extending from each centrosome during mitosis.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a duplicated chromosome joined at the centromere.
Centromere
Specialized DNA sequence where sister chromatids are most closely attached.
Interphase
G1, S, and G2 phases; cell growth, DNA replication, preparation for mitosis.
G1 Phase
First gap; major cell growth and normal metabolism.
S Phase
DNA synthesis phase where chromosomes are duplicated.
G2 Phase
Second gap; cell prepares for mitosis, builds spindle components.
Mitosis
Nuclear division producing two genetically identical nuclei.
Prophase
Chromatin condenses; nucleolus disappears; spindle begins to form.
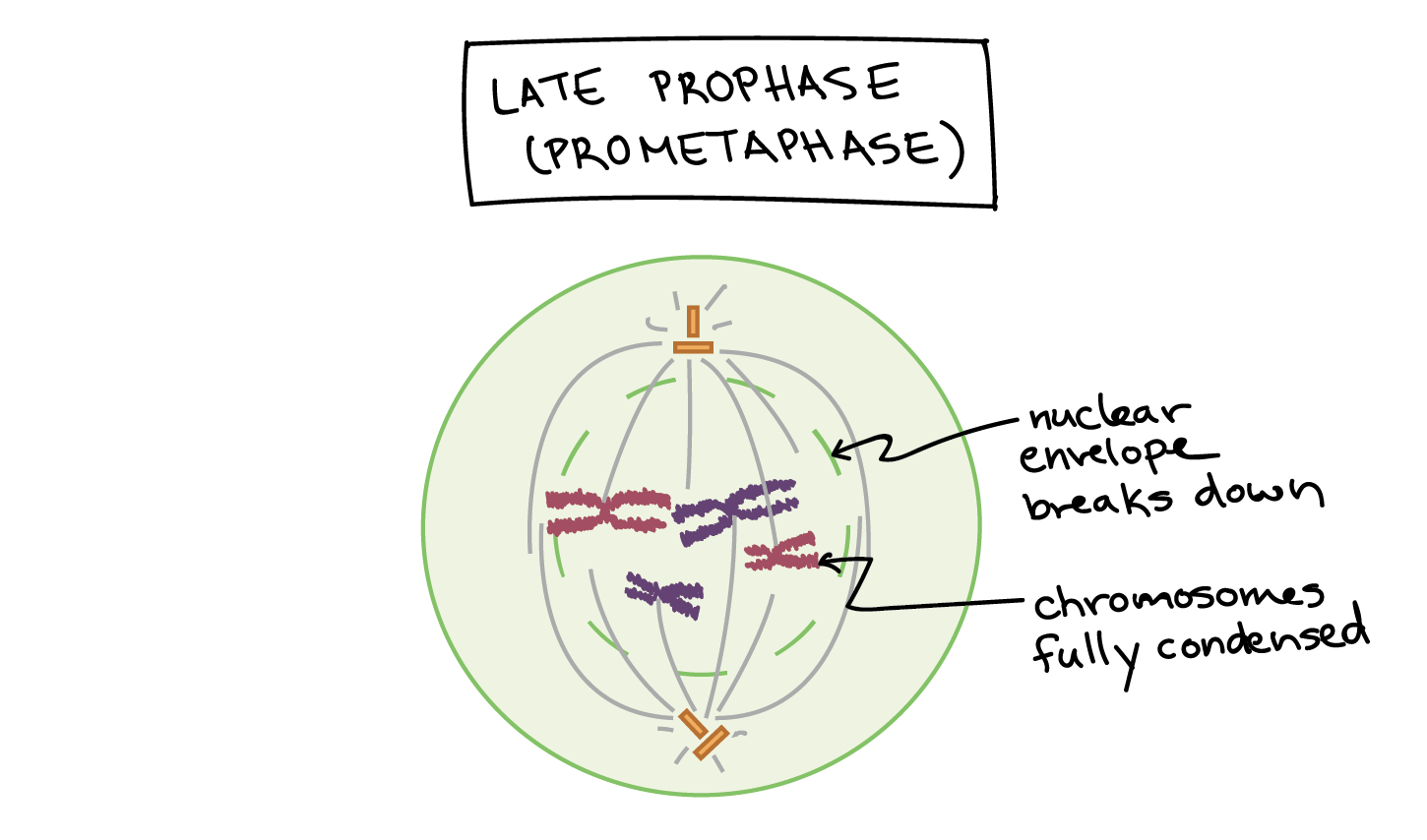
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope fragments; spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores.
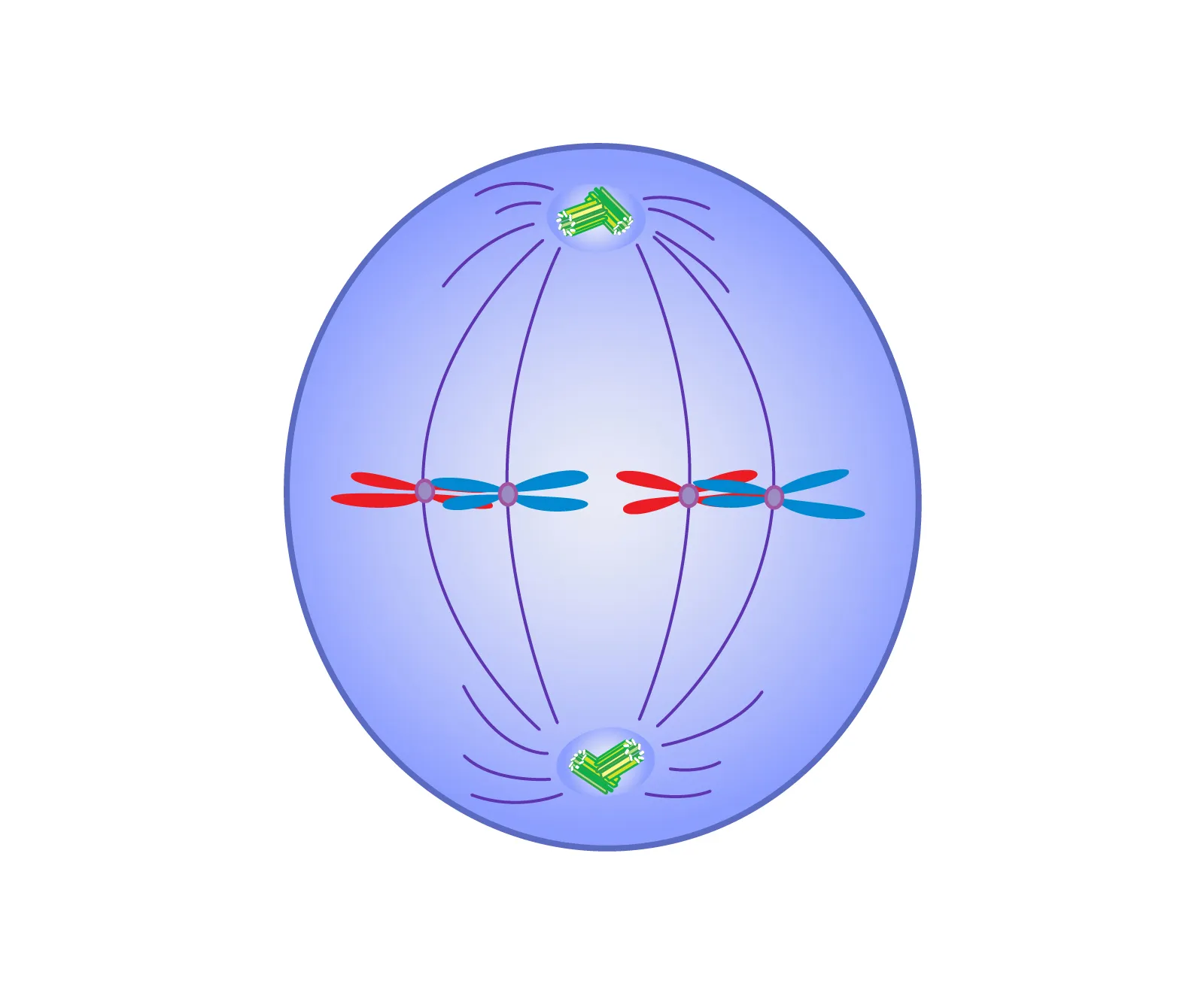
Metaphase
Chromosomes align on the cell’s equatorial (metaphase) plate.
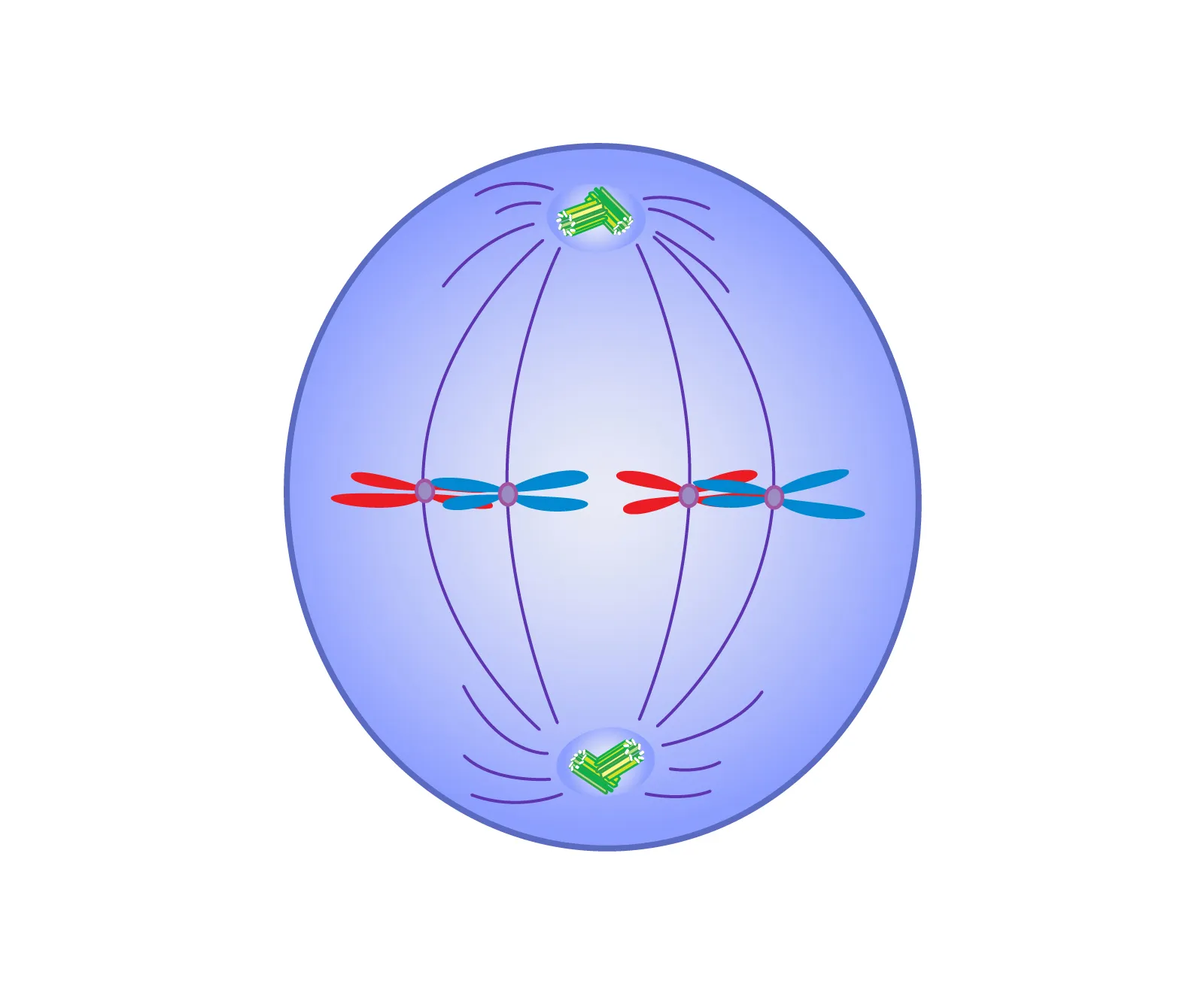
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles.
Telophase
Chromosomes de-condense; nuclear envelopes reform; spindle disassembles.
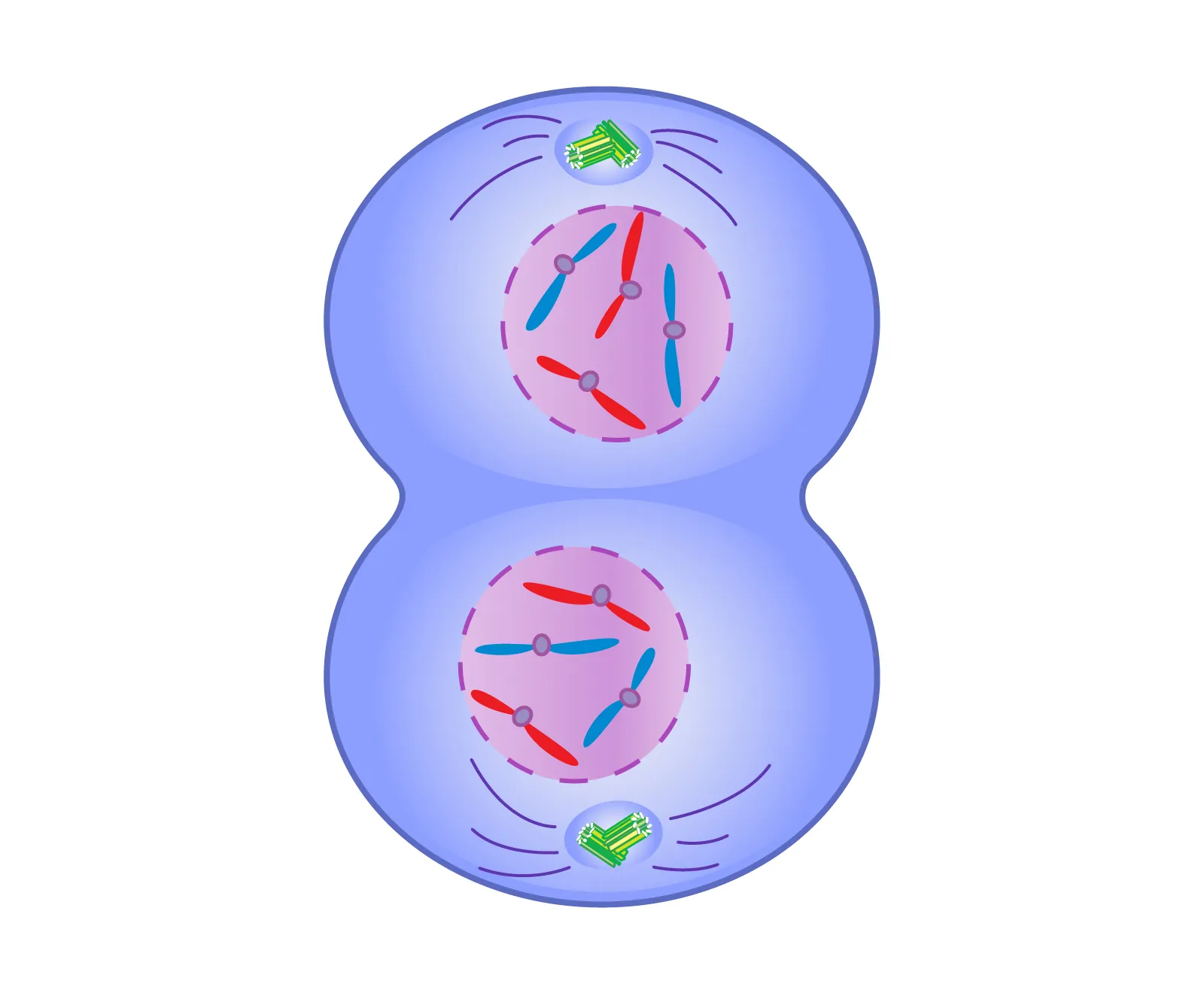
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm; cleaves animal cells via cleavage furrow, plants via cell plate.
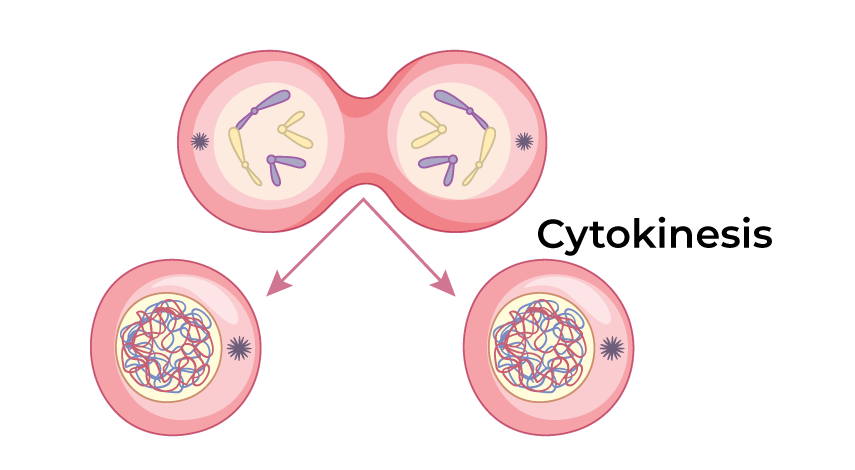
Cleavage Furrow
Contractile actin-myosin ring pinching animal cells in cytokinesis.
Cell Plate
Vesicle-derived partition that forms new wall between daughter plant cells.
Protein Kinase
Enzyme that activates or deactivates proteins by adding phosphate groups.
Cyclin
Regulatory protein whose levels fluctuate and activate Cdks.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (Cdk)
Kinase active only when bound to a cyclin; drives cell-cycle events.
MPF
Maturation-promoting factor; Cdk-cyclin complex triggering mitosis at G2 checkpoint.
Density-Dependent Inhibition
Phenomenon where crowded cells stop dividing.
Anchorage Dependence
Requirement that cells attach to a surface before they divide.
Benign Tumor
Mass of abnormal cells that remains at original site.
Malignant Tumor
Cancerous growth that invades and impairs organ function.
Metastasis
Spread of cancer cells to distant sites via blood or lymph.
Signal Transduction
Series of molecular events converting a signal on a cell’s surface to a specific response.
Reception
Stage where a signaling molecule (ligand) binds to a receptor protein.
Transduction
Relay of signal via cascade of molecular interactions in the cell.
Response
Cellular activity (e.g., gene expression, enzyme activation) triggered by a signal.
Ligand
Molecule that specifically binds to a receptor.
G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
Seven-pass membrane receptor that activates a G protein upon ligand binding.
G Protein
Molecular switch using GDP/GTP to relay signals from GPCRs.
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK)
Dimers that autophosphorylate tyrosines and activate multiple pathways.
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
Membrane receptor that opens/closes ion channel upon ligand binding.
Second Messenger
Small, diffusible molecule or ion relaying signals inside cells (e.g., cAMP, Ca2+).
cAMP
Cyclic AMP; widely used second messenger made from ATP by adenylyl cyclase.
Adenylyl Cyclase
Membrane enzyme converting ATP to cAMP after G-protein activation.
Protein Kinase A
cAMP-activated kinase that phosphorylates many target proteins.
Phosphodiesterase
Enzyme that degrades cAMP to AMP, terminating the signal.
Inositol Triphosphate (IP3)
Second messenger that releases Ca2+ from ER stores.
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Lipid second messenger produced with IP3 by phospholipase C.
Calcium Ion (Ca2+)
Versatile second messenger whose cytosolic levels are tightly regulated.
Protein Phosphatase
Enzyme removing phosphate groups, turning off signaling proteins.
Signal Amplification
Process where one ligand binding event leads to large cellular output.
Cross-Talk
Interaction between different signaling pathways enhancing coordination.
Scaffolding Protein
Large relay protein holding multiple kinases to speed signaling efficiency.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death involving DNA fragmentation and cell blebbing.
Caspase
Main protease family executing apoptosis by cleaving proteins.
Ced-9
C. elegans protein that inhibits apoptotic pathway when active.
Ced-4
C. elegans protein activating Ced-3 to start apoptosis.
Ced-3
C. elegans caspase responsible for apoptotic proteolysis.
Chloroplast
Double-membraned organelle where photosynthesis occurs in plants/algae.
Thylakoid
Flattened membrane sac inside chloroplast; site of light reactions.
Granum
Stack of thylakoids within a chloroplast.
Stroma
Fluid interior of chloroplast surrounding thylakoid stacks; Calvin cycle site.
Thylakoid Lumen
Internal space of a thylakoid where proton gradient builds.
Chlorophyll a
Main photosynthetic pigment absorbing blue-violet & red light.
Chlorophyll b
Accessory pigment broadening the spectrum of light available for photosynthesis.
Carotenoid
Accessory pigment (orange/yellow) absorbing blue/green light; protects chlorophyll.
Xanthophyll
Oxygen-containing carotenoid pigment (yellow/brown).
Phycobilin
Red/blue accessory pigment in cyanobacteria & red algae.
Anthocyanin
Flavonoid pigments giving flowers red-purple hues.
Photosystem I (PS I)
Light-capturing complex with P700 reaction center; generates NADPH.
Photosystem II (PS II)
Light-capturing complex with P680 reaction center; splits water, begins electron flow.
P700
Chlorophyll a reaction-center pair of PS I absorbing at 700 nm.
P680
Chlorophyll a reaction-center pair of PS II absorbing at 680 nm.
Noncyclic Electron Flow
Photosynthetic pathway producing ATP, NADPH, and O2 by linear electron transport.
Cyclic Electron Flow
PS I-dependent pathway producing extra ATP without NADPH or O2.
Photolysis
Light-driven splitting of water into electrons, protons, and oxygen in PS II.
Chemiosmosis
Use of a proton gradient across a membrane to drive ATP synthesis.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme complex coupling proton flow to phosphorylation of ADP.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Thylakoid reactions converting light energy to ATP and NADPH.
Calvin Cycle
Stroma reactions fixing CO2 into carbohydrate using ATP & NADPH.
Carbon Fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules, first step of Calvin cycle.
RuBP
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate; 5-carbon CO2 acceptor in Calvin cycle.
PGA (3-PGA)
3-phosphoglycerate; first stable 3-carbon Calvin cycle product.
G3P (PGAL)
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 3-carbon sugar output of Calvin cycle.
Rubisco
Calvin cycle enzyme catalyzing CO2 (or O2) fixation to RuBP.
C3 Pathway
Standard Calvin cycle where first product is a 3-carbon molecule (PGA).
Photorespiration
Wasteful process where Rubisco adds O2 to RuBP, reducing photosynthetic output.
C4 Pathway
CO2-concentrating mechanism fixing carbon twice in mesophyll & bundle-sheath cells.
Oxaloacetate
Four-carbon first product of C4 carbon fixation.
Bundle-Sheath Cell
Inner leaf cell where C4 plants run the Calvin cycle.
Mesophyll Cell
Photosynthetic leaf cell that performs initial CO2 fixation in C4 plants.
CAM Pathway
Temporal CO2-concentrating strategy fixing CO2 at night, Calvin cycle by day.
Aerobic Respiration
Oxygen-requiring pathway breaking glucose to CO2 & H2O, yielding ~30-32 ATP.
Anaerobic Respiration
Energy pathway without O2, including fermentation; yields far less ATP.
Glycolysis
Cytoplasmic breakdown of glucose to two pyruvate, net 2 ATP & 2 NADH.
Pyruvate
Three-carbon end product of glycolysis.